Abstract
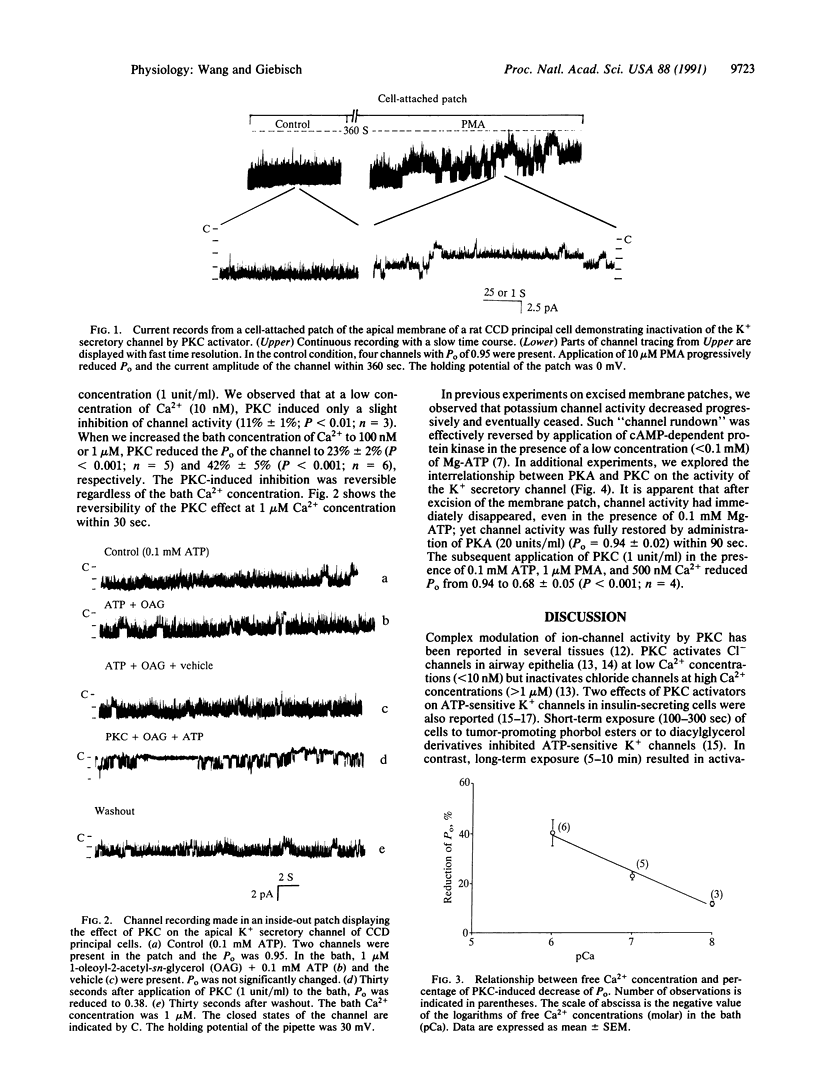
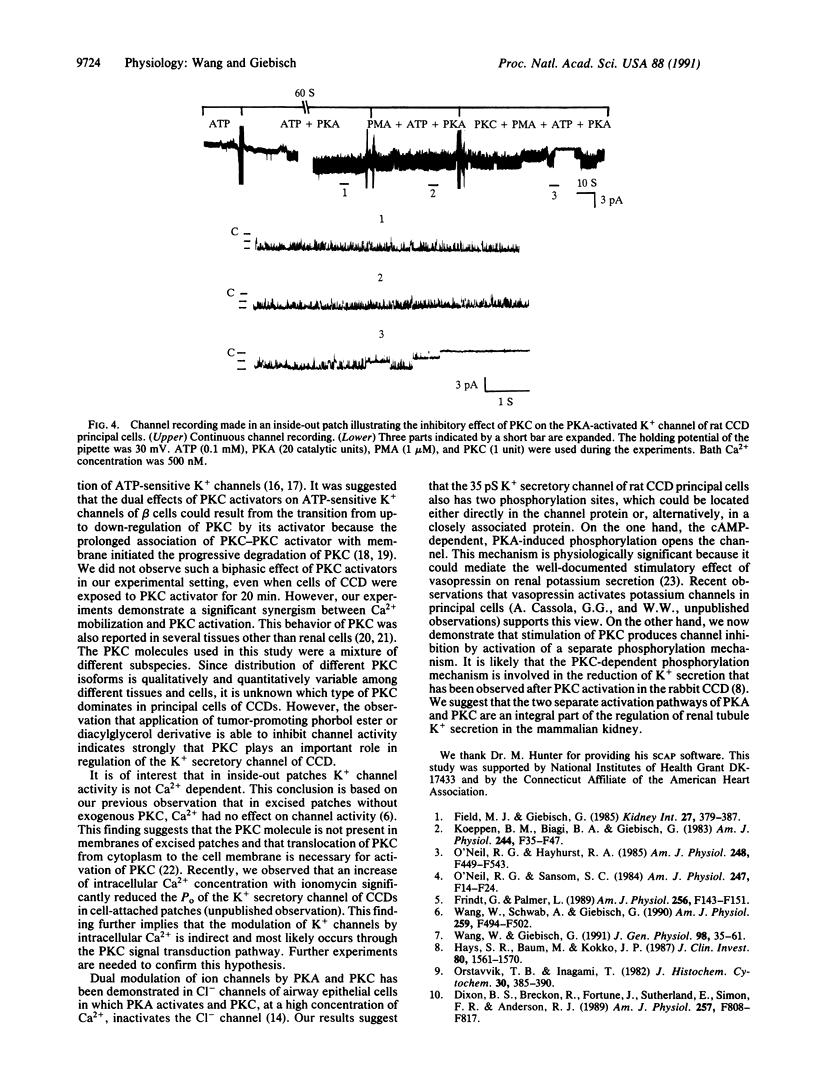
A small-conductance K+ channel in the apical membrane of rat cortical collecting duct (CCD) cells controls K+ secretion in the kidney. Previously, we observed that the activity of the channel is stimulated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)-induced channel phosphorylation. We now have applied the patch-clamp technique to study the effects of protein kinase C (PKC) on the secretory K+ channel of rat CCD. In cell-attached patches, application of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate progressively reduced the open probability and current amplitude of the K+ channel. In inside-out patches, administration of PKC reversibly decreased the channel open probability (Po) without changing the channel conductance. The PKC-induced inhibition of channel activity was Ca2+ dependent: Po decreased 42%, 23%, and 11% in the presence of 1000 nM, 100 nM, and 10 nM free Ca2+, respectively. We also demonstrate that PKC antagonizes the stimulatory effect of PKA on the apical K+ secretory channel of rat CCD. These results suggest regulation of K(+)-channel activity by two separate sites of phosphorylation with distinct and opposite effects on channel activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dixon B. S., Breckon R., Fortune J., Sutherland E., Simon F. R., Anderson R. J. Bradykinin activates protein kinase C in cultured cortical collecting tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F808–F817. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. J., Giebisch G. J. Hormonal control of renal potassium excretion. Kidney Int. 1985 Feb;27(2):379–387. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Palmer L. G. Low-conductance K channels in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F143–F151. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. R., Baum M., Kokko J. P. Effects of protein kinase C activation on sodium, potassium, chloride, and total CO2 transport in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1561–1570. doi: 10.1172/JCI113242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang T. C., Lu L., Zeitlin P. L., Gruenert D. C., Huganir R., Guggino W. B. Cl- channels in CF: lack of activation by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1351–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.2472005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano T., Go M., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Assay and purification of protein kinase C. Methods Enzymol. 1986;124:349–352. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)24026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Biagi B. A., Giebisch G. H. Intracellular microelectrode characterization of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F35–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., McCann J. D., Anderson M. P., Clancy J. P., Liedtke C. M., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Welsch M. J. Regulation of chloride channels by protein kinase C in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1353–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.2472006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jr, Sahyoun N., Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P. Role of intracellular calcium mobilization in the regulation of protein kinase C-mediated membrane processes. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):549–551. doi: 10.1038/317549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Hayhurst R. A. Functional differentiation of cell types of cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 2):F449–F453. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.3.F449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Sansom S. C. Characterization of apical cell membrane Na+ and K+ conductances of cortical collecting duct using microelectrode techniques. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F14–F24. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavvik T. B., Inagami T. Localization of kallikrein in the rat kidney and its anatomical relationship to renin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Apr;30(4):385–390. doi: 10.1177/30.4.7037945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Eddlestone G. T., Ciani S. Metabolic regulation of the K(ATP) and a maxi-K(V) channel in the insulin-secreting RINm5F cell. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):219–237. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer J. A., Troutman S. L. Effect of ADH on rubidium transport in isolated perfused rat cortical collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):F1063–F1072. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.6.F1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman M. S., Sekiguchi K., Nishizuka Y. Modulation of ion channel activity: a key function of the protein kinase C enzyme family. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):211–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., Schwab A., Giebisch G. Regulation of small-conductance K+ channel in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):F494–F502. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.3.F494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Giebisch G. Dual effect of adenosine triphosphate on the apical small conductance K+ channel of the rat cortical collecting duct. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Jul;98(1):35–61. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Dunne M. J., Peter-Riesch B., Bruzzone R., Pozzan T., Petersen O. H. Activators of protein kinase C depolarize insulin-secreting cells by closing K+ channels. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2443–2449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Parker P. J., Ullrich A., Stabel S. Down-regulation of protein kinase C is due to an increased rate of degradation. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):775–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2440775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J. R., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in insulinoma cells: activation by somatostatin and protein kinase C and the role of cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2971–2975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



