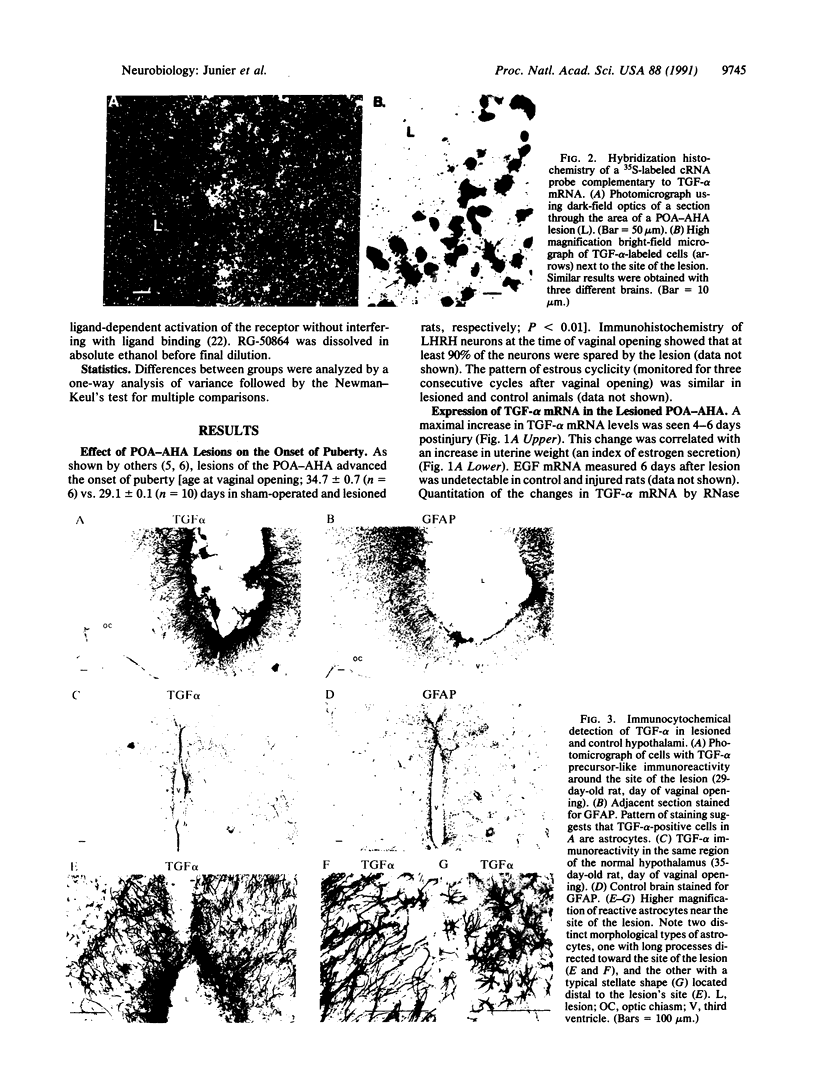
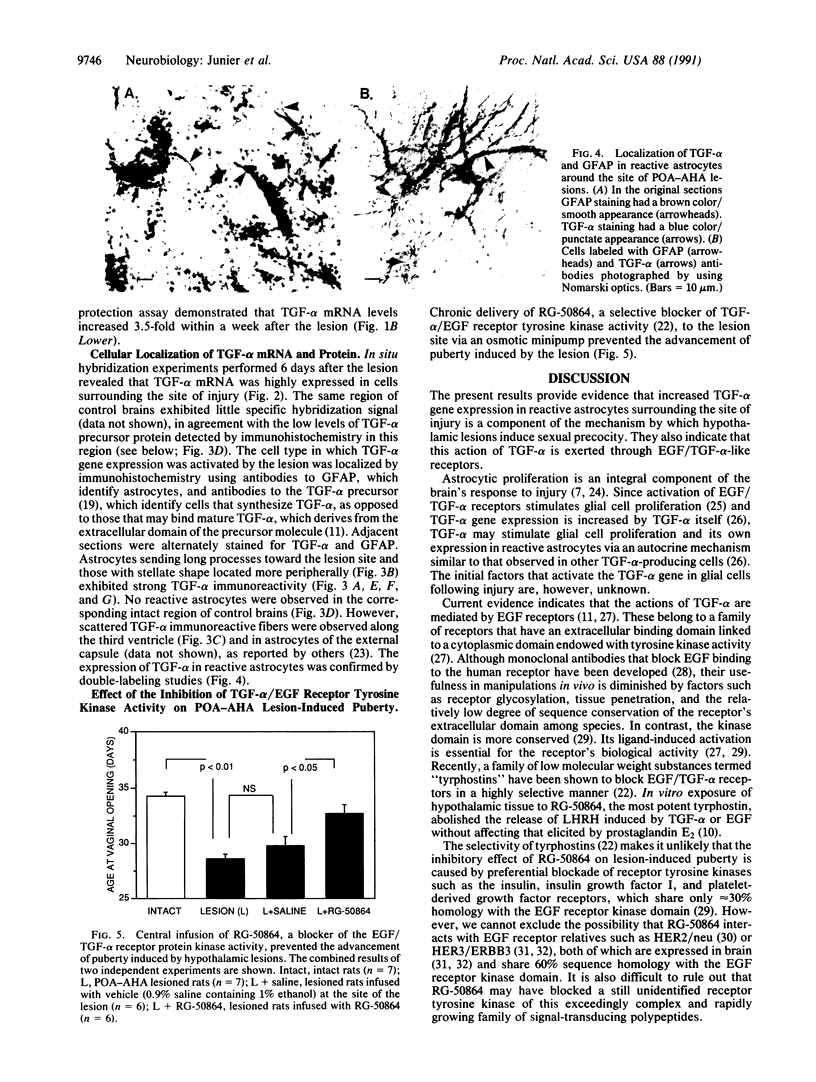
Abstract
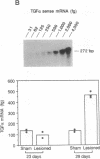
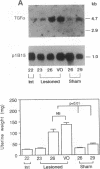
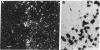
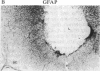
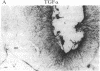
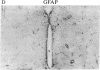
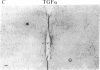
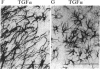
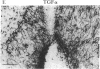
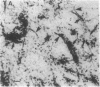
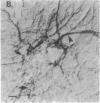
It has long been known that lesions of the hypothalamus lead to female sexual precocity. While an increased production of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH), the neurohormone that controls sexual development, appears to mediate the advancement of puberty induced by these lesions, little is known about the mechanism(s) by which hypothalamic injury activates LHRH secretion. Since brain lesions result in accumulation of neurotrophic/mitogenic activities in the injured area, we tested the hypothesis that transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha), a mitogenic polypeptide recently shown to stimulate LHRH release, is produced in response to hypothalamic injury and mediates the effect of the lesion on puberty. Radiofrequency lesions of the preoptic area-anterior hypothalamic area (POA-AHA) of 22-day-old female rats resulted in precocious puberty within 7 days after the operation. RNA blot hybridization revealed that lesion-induced puberty was preceded by an increase in TGF-alpha mRNA levels in the POA-AHA. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) mRNA was undetectable in both intact and lesioned hypothalami. TGF-alpha mRNA levels, quantitated by RNase protection assays, were 3.5-fold greater in lesioned animals approaching puberty than in age-matched controls. Immunohistochemical studies, utilizing single- and double-staining procedures, demonstrated the presence of TGF-alpha precursor-like immunoreactivity in reactive astrocytes surrounding the lesion site. Hybridization histochemistry showed increased TGF-alpha mRNA expression in cells of the same area, further implicating reactive astrocytes as a site of TGF-alpha synthesis. The actions of TGF-alpha are mediated by its interaction with EGF receptors. Continuous infusion of RG-50864, an inhibitor of EGF receptor kinase activity, at the site of injury prevented the advancement of puberty induced by the lesion. These results suggest that TGF-alpha acting via EGF-like receptors contributes to the acceleration of puberty induced by anterior hypothalamic lesions. They also indicate that activation of TGF-alpha gene expression in glial cells is a component of the hypothalamic response to injury.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advis J. P., Ramirez V. D. Plasma levels of LH and FSH in female rats with precocious puberty induced by hypothalamic lesions. Biol Reprod. 1977 Oct;17(3):313–320. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod17.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacciari E., Fréjaville E., Cicognani A., Pirazzoli P., Frank G., Balsamo A., Tassinari D., Zappulla F., Bergamaschi R., Cristi G. F. How many cases of true precocious puberty in girls are idiopathic? J Pediatr. 1983 Mar;102(3):357–360. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80648-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7709–7712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Derynck R., Wilcox J. N., Bringman T. S., Goustin A. S., Moses H. L., Pittelkow M. R. Production and auto-induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in human keratinocytes. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):817–820. doi: 10.1038/328817a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOVAN B. T., VAN DER WERFF TEN BOSCH J. J. Precocious puberty in rats with hypothalamic lesions. Nature. 1956 Oct 6;178(4536):745–745. doi: 10.1038/178745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R. Transforming growth factor alpha. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon J. H., Annis C. M., Gentry L. E., Twardzik D. R., Loughlin S. E. Localization of cells containing transforming growth factor-alpha precursor immunoreactivity in the basal ganglia of the adult rat brain. Growth Factors. 1990;2(2-3):241–250. doi: 10.3109/08977199009071510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Twardzik D. R., Lim G. J., Ranchalis J. E., Lee D. C. Expression and characterization of transforming growth factor alpha precursor protein in transfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1585–1591. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Kawamoto T., Cochet C., Le A., Sato J. D., Masui H., McLeod C., Mendelsohn J. Monoclonal anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies which are inhibitors of epidermal growth factor binding and antagonists of epidermal growth factor binding and antagonists of epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7755–7760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman G. E., Lee W. S., Attardi B., Yann V., Fitzsimmons M. D. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone neurons express c-fos antigen after steroid activation. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1736–1741. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Issing W., Miki T., Popescu N. C., Aaronson S. A. Isolation and characterization of ERBB3, a third member of the ERBB/epidermal growth factor receptor family: evidence for overexpression in a subset of human mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakos S., Basbaum A. I. Benzidine dihydrochloride as a chromogen for single- and double-label light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical studies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Aug;34(8):1047–1056. doi: 10.1177/34.8.2426333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lara H. E., Hill D. F., Katz K. H., Ojeda S. R. The gene encoding nerve growth factor is expressed in the immature rat ovary: effect of denervation and hormonal treatment. Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):357–363. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rose T. M., Webb N. R., Todaro G. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for rat transforming growth factor-alpha. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):489–491. doi: 10.1038/313489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Smith M. S., Hoffman G. E. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone neurons express Fos protein during the proestrous surge of luteinizing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5163–5167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Schachner M. Epidermal growth factor stimulates DNA-synthesis of astrocytes in primary cerebellar cultures. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;220(2):393–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00210517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. S., Kornblum H. I., Leslie F. M., Bradshaw R. A. Trophic stimulation of cultured neurons from neonatal rat brain by epidermal growth factor. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.3498986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Hill D. F., Katz K. H. The genes encoding nerve growth factor and its receptor are expressed in the developing female rat hypothalamus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jan;9(1-2):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90129-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R. The mystery of mammalian puberty: how much more do we know? Perspect Biol Med. 1991 Spring;34(3):365–383. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1991.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Urbanski H. F., Costa M. E., Hill D. F., Moholt-Siebert M. Involvement of transforming growth factor alpha in the release of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone from the developing female hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9698–9702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Whitney G. S., Neubauer M. G., Green J. M., McDonald V. L., Todaro G. J., Shoyab M. Molecular cloning and expression of an additional epidermal growth factor receptor-related gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4905–4909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. L., Morrison R., de Vellis J., Herschman H. R. Epidermal growth factor binding and mitogenic activity on purified populations of cells from the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasawa E., Noonan J. J., Nass T. E., Loose M. D. Posterior hypothalamic lesions advance the onset of puberty in the female rhesus monkey. Endocrinology. 1984 Dec;115(6):2241–2250. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-6-2241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaish P., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Blocking of EGF-dependent cell proliferation by EGF receptor kinase inhibitors. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):933–935. doi: 10.1126/science.3263702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]