Abstract
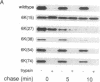
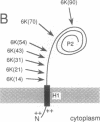
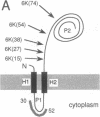
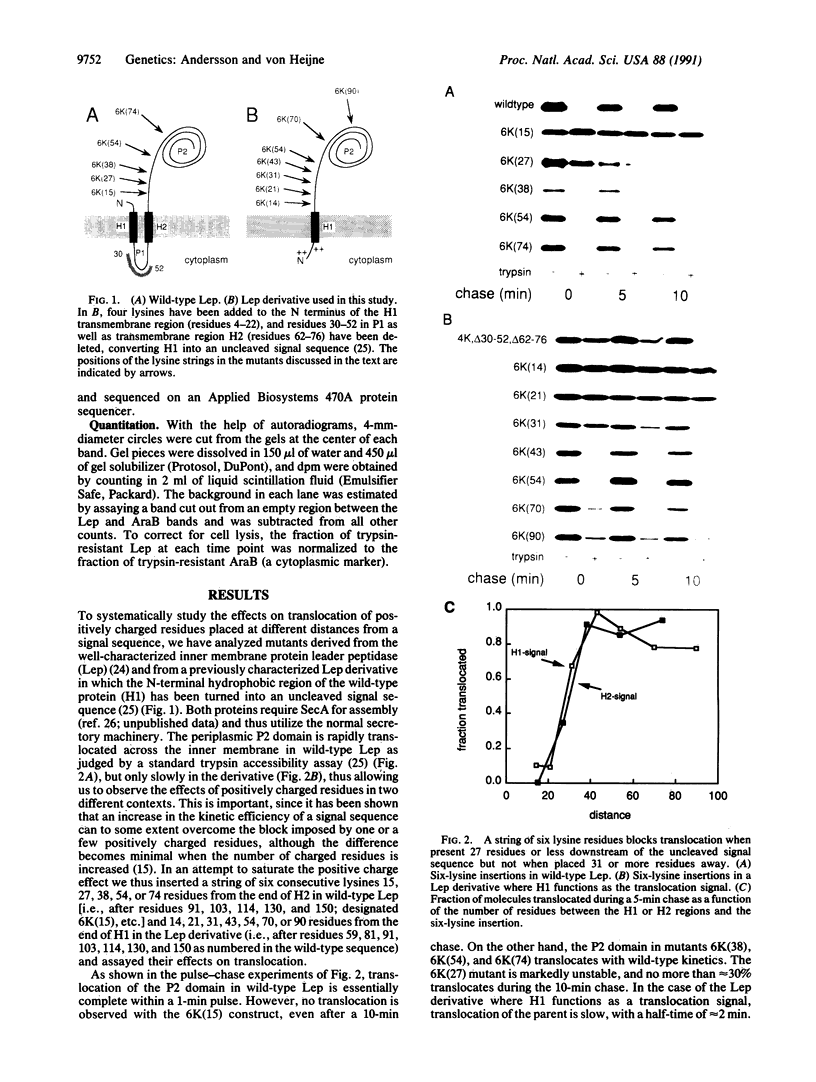
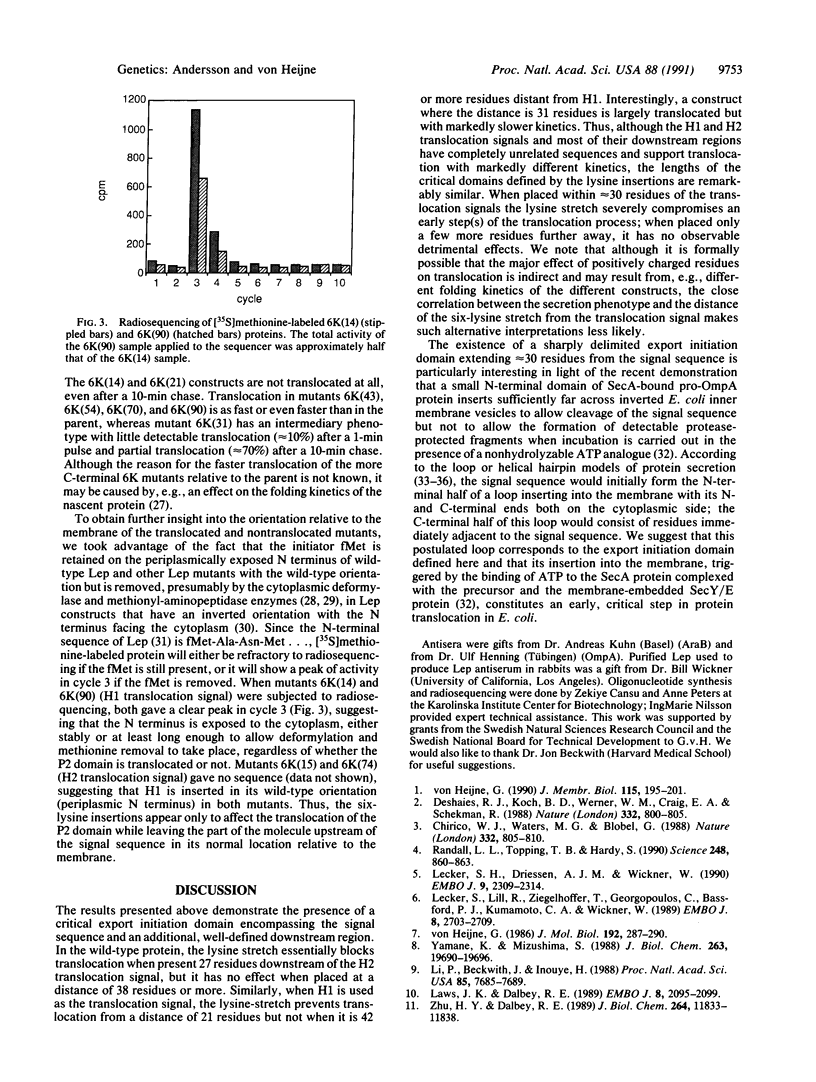
Signal sequences serve to target proteins to the secretory pathway in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, although necessary, the presence of a signal sequence is not always sufficient to ensure efficient membrane translocation. One feature of the nascent chain that adversely affects secretion, at least in Escherichia coli, is the presence of positively charged amino acids immediately downstream of the signal sequence. We have exploited this sensitivity to positively charged residues to demonstrate the presence of a sharply delimited "export initiation domain" that comprises the signal sequence and its approximately 30 downstream residues. A string of six consecutive lysines completely blocks translocation when placed inside this domain but not when placed only a few residues further away.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. Positively charged amino acid residues can act as topogenic determinants in membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9446–9450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. The role of charged amino acids in the localization of secreted and membrane proteins. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90378-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Wickner W. Leader peptidase of Escherichia coli: critical role of a small domain in membrane assembly. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):783–787. doi: 10.1126/science.3544218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Wickner W. The role of the polar, carboxyl-terminal domain of Escherichia coli leader peptidase in its translocation across the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13844–13849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flinta C., Persson B., Jörnvall H., von Heijne G. Sequence determinants of cytosolic N-terminal protein processing. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 2;154(1):193–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., MacIntyre S., Degen M., Henning U. Cell surface exposure of the outer membrane protein OmpA of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):491–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. J., Randall L. L. A kinetic partitioning model of selective binding of nonnative proteins by the bacterial chaperone SecB. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):439–443. doi: 10.1126/science.1989077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirel P. H., Schmitter M. J., Dessen P., Fayat G., Blanquet S. Extent of N-terminal methionine excision from Escherichia coli proteins is governed by the side-chain length of the penultimate amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8247–8251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S., Lee J. H., Ray D. S. High-level expression of M13 gene II protein from an inducible polycistronic messenger RNA. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A. Bacteriophage M13 procoat protein inserts into the plasma membrane as a loop structure. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1413–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.3317833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laws J. K., Dalbey R. E. Positive charges in the cytoplasmic domain of Escherichia coli leader peptidase prevent an apolar domain from functioning as a signal. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2095–2099. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S. H., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. ProOmpA contains secondary and tertiary structure prior to translocation and is shielded from aggregation by association with SecB protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2309–2314. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S., Lill R., Ziegelhoffer T., Georgopoulos C., Bassford P. J., Jr, Kumamoto C. A., Wickner W. Three pure chaperone proteins of Escherichia coli--SecB, trigger factor and GroEL--form soluble complexes with precursor proteins in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2703–2709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Beckwith J., Inouye H. Alteration of the amino terminus of the mature sequence of a periplasmic protein can severely affect protein export in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7685–7689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Eschbach M. L., Mutschler B. Export incompatibility of N-terminal basic residues in a mature polypeptide of Escherichia coli can be alleviated by optimising the signal peptide. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 May;221(3):466–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00259413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Topping T. B., Hardy S. J. No specific recognition of leader peptide by SecB, a chaperone involved in protein export. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):860–863. doi: 10.1126/science.2188362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U., Wickner W. Delta mu H+ and ATP function at different steps of the catalytic cycle of preprotein translocase. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):927–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90317-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. G., Harris C. R., Knowles J. R. A conservative amino acid substitution, arginine for lysine, abolishes export of a hybrid protein in Escherichia coli. Implications for the mechanism of protein secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20082–20088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. Mechanisms of membrane assembly: general lessons from the study of M13 coat protein and Escherichia coli leader peptidase. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1081–1086. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Silver P., Wickner W. The isolation of homogeneous leader peptidase from a strain of Escherichia coli which overproduces the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7898–7902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Wickner W. Bacterial leader peptidase, a membrane protein without a leader peptide, uses the same export pathway as pre-secretory proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Wickner W., Goodman J. M. Sequence of the leader peptidase gene of Escherichia coli and the orientation of leader peptidase in the bacterial envelope. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12073–12080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H. Y., Dalbey R. E. Both a short hydrophobic domain and a carboxyl-terminal hydrophilic region are important for signal function in the Escherichia coli leader peptidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11833–11838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Blomberg C. Trans-membrane translocation of proteins. The direct transfer model. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):175–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Control of topology and mode of assembly of a polytopic membrane protein by positively charged residues. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):456–458. doi: 10.1038/341456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Net N-C charge imbalance may be important for signal sequence function in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. The signal peptide. J Membr Biol. 1990 May;115(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01868635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Wickner W., Dalbey R. E. The cytoplasmic domain of Escherichia coli leader peptidase is a "translocation poison" sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3363–3366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]