Abstract
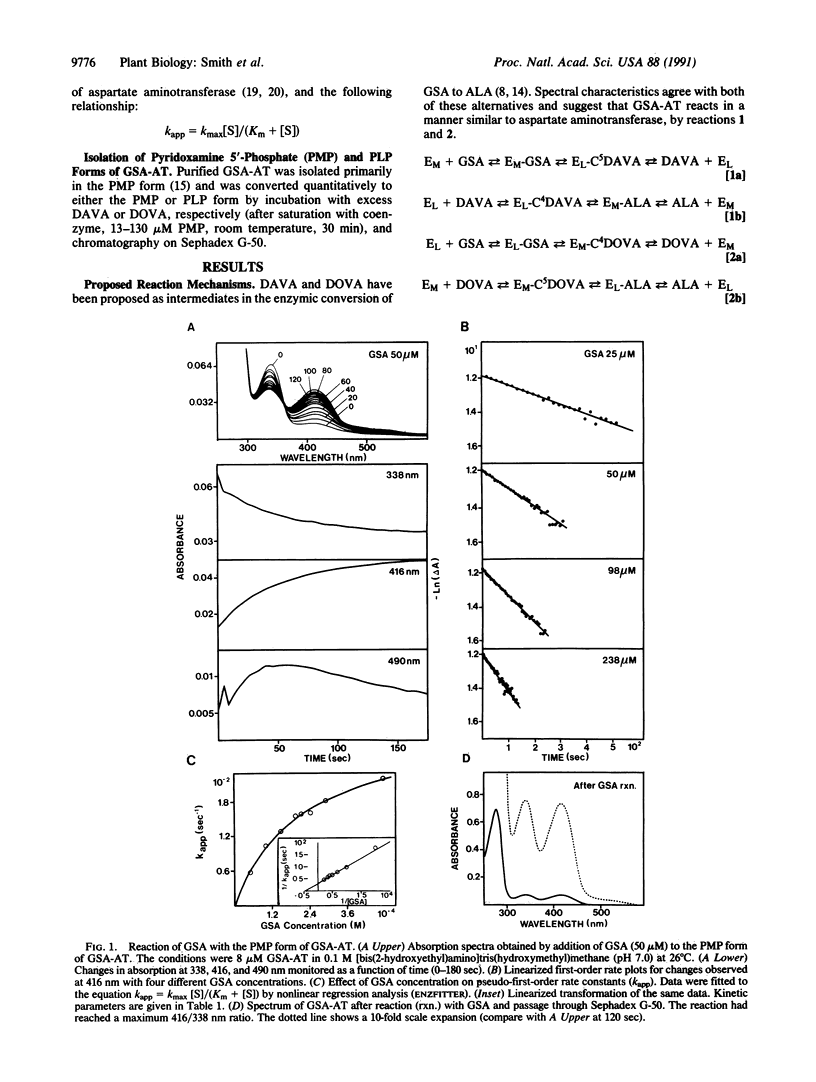
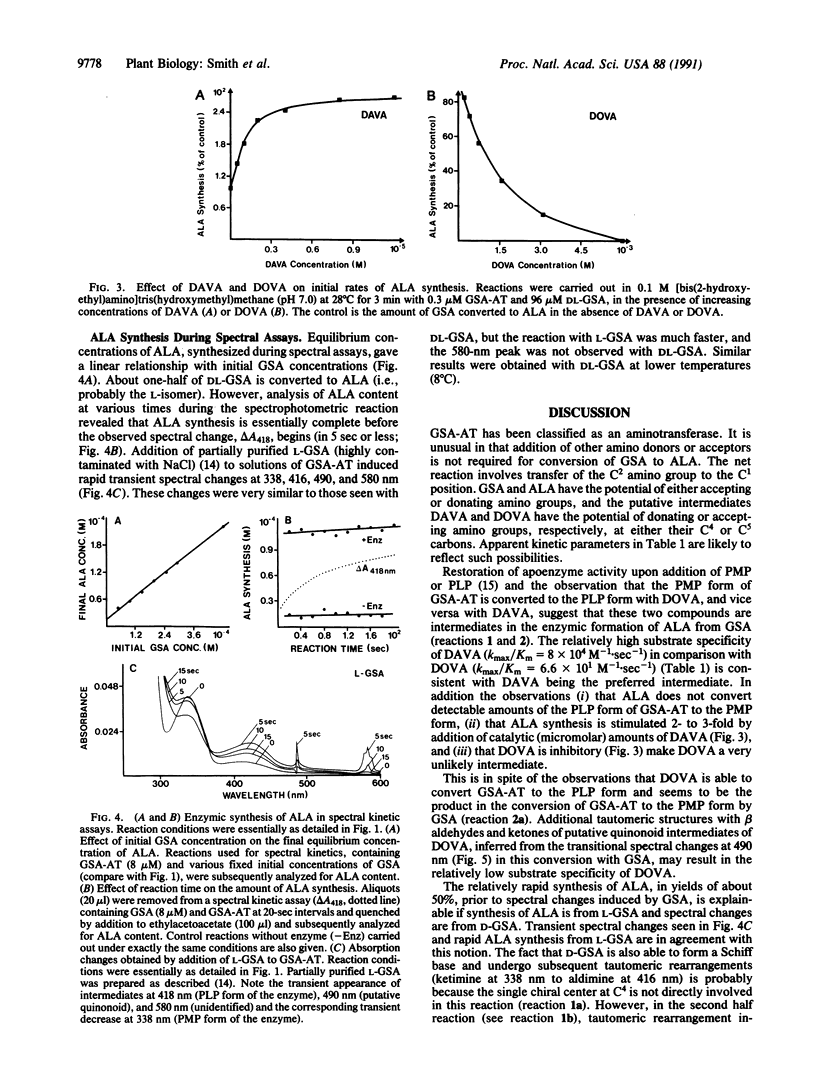
Purified Synechococcus glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminotransferase (GSA-AT; EC 5.4.3.8) has absorption maxima characteristic of vitamin B6-containing enzymes and can be converted to the pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate or pyridoxal 5'-phosphate form by reaction with diaminovalerate or dioxovalerate, respectively, suggesting that these two analogues are intermediates in the conversion of glutamate 1-semialdehyde (GSA) to 5-aminolevulinate (ALA). Values for Km and kmax were calculated for GSA, diaminovalerate, ALA, and gabaculine from absorption change rates during conversion of one coenzyme form of GSA-AT to the other, upon addition of one of these compounds. The substrate specificity (kmax/Km) of diaminovalerate is about 3 orders of magnitude larger than that of dioxovalerate, making the latter an unlikely intermediate in the enzymic conversion of GSA to ALA. GSA reacts with both coenzyme forms, whereas ALA only reacts with the pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate form of the enzyme. However, ALA does form a complex with the pyridoxal 5'-phosphate form of GSA-AT and inhibits reactions between gabaculine and GSA-AT. This relatively stable complex (Ki = 8 M) may have significance in enzyme inhibition. Both L and D enantiomers of GSA react with GSA-AT. Spectral changes observed upon addition of DL-GSA are apparently due to reaction with the less reactive D-isomer. L-GSA is converted to ALA prior to major spectral changes induced by the racemic mixture.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breu V., Dörnemann D. Formation of 5-aminolevulinate via glutamate-1-semialdehyde and 4,5-dioxovalerate with participation of an RNA component in Scenedesmus obliquus mutant C-2A'. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 17;967(2):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(88)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumm P. J., Thomas G. A., Friedmann H. C. The role of 4,5-dioxovaleric acid in porphyrin and vitamin B12 formation by clostridia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):814–822. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90710-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronin C. N., Kirsch J. F. Role of arginine-292 in the substrate specificity of aspartate aminotransferase as examined by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4572–4579. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Avissar Y. J., Rhie G. E., Beale S. I. Cloning and sequence of the Salmonella typhimurium hemL gene and identification of the missing enzyme in hemL mutants as glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7071–7084. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7071-7084.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm B., Bull A., Breu V. Structural genes of glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase for porphyrin synthesis in a cyanobacterium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00282635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm B., Bull A., Welinder K. G., Gough S. P., Kannangara C. G. Purification and partial amino acid sequence of the glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase of barley and synechococcus. Carlsberg Res Commun. 1989;54(2):67–79. doi: 10.1007/BF02907586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm B. Primary structure of a key enzyme in plant tetrapyrrole synthesis: glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm B., Smith A. J., Kannangara C. G., Smith M. Gabaculine-resistant glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase of Synechococcus. Deletion of a tripeptide close to the NH2 terminus and internal amino acid substitution. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12495–12501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Rutberg L., Schröder I., Hederstedt L. The Bacillus subtilis hemAXCDBL gene cluster, which encodes enzymes of the biosynthetic pathway from glutamate to uroporphyrinogen III. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2590–2599. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2590-2599.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Kahn A., Ash D. E., Gough S., Kannangara C. G. Biosynthesis of delta-aminolevulinate in greening barley leaves. IX. Structure of the substrate, mode of gabaculine inhibition, and the catalytic mechanism of glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. Carlsberg Res Commun. 1988;53(1):11–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02908411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilag L. L., Jahn D., Eggertsson G., Söll D. The Escherichia coli hemL gene encodes glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3408–3413. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3408-3413.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Kuramitsu S., Inoue K., Kagamiyama H., Hiromi K., Tanase S., Morino Y. Substitution of a lysyl residue for arginine 386 of Escherichia coli aspartate aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9673–9681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn D., Chen M. W., Söll D. Purification and functional characterization of glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminotransferase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):161–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannangara C. G., Gough S. P., Bruyant P., Hoober J. K., Kahn A., von Wettstein D. tRNA(Glu) as a cofactor in delta-aminolevulinate biosynthesis: steps that regulate chlorophyll synthesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Apr;13(4):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soper T. S., Manning J. M. Inactivation of pyridoxal phosphate enzymes by gabaculine. Correlation with enzymic exchange of beta-protons. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13930–13936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



