Abstract
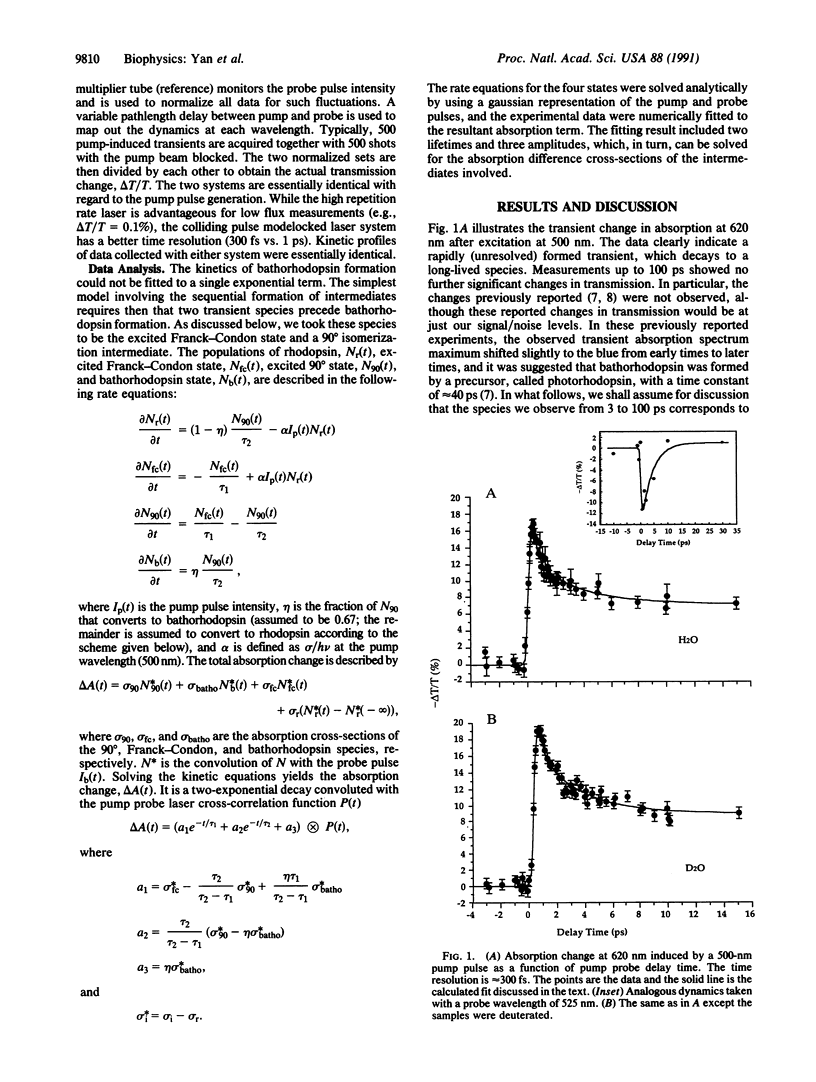
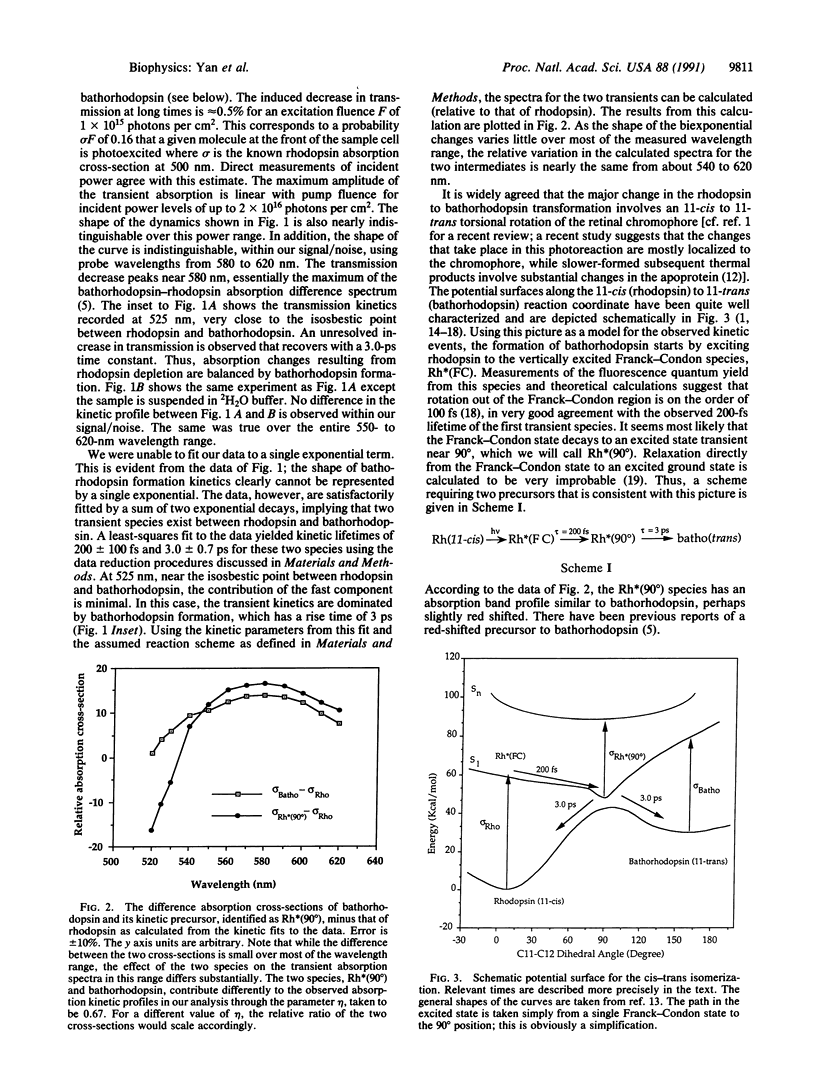
We report on time-resolved absorption studies of the bovine visual pigment rhodopsin with subpicosecond resolution at room temperature. Our data show that bathorhodopsin, rhodopsin's early photoproduct, is photochemically formed in 3.0 +/- 0.7 ps. The data suggest that bathorhodopsin formation is kinetically preceded by two species along the rhodopsin-to-bathorhodopsin reaction coordinate. The first is identified with the vertically excited Franck-Condon state. This decays with an approximately 200-fs lifetime to an intermediate, which then decays to bathorhodopsin in 3.0 ps. We assign this intermediate to be an excited state transient near 90 degrees along the 11-12 torsional coordinate of rhodopsin's chromophore. Exchange of rhodopsin's exchangeable protons for deuterons does not affect the observed dynamics. These observations are both qualitatively and quantitatively consistent with molecular dynamics calculations, which model the rhodopsin to bathorhodopsin phototransition as a cis-trans isomerization along the 11-12 torsional coordinate of rhodopsin's chromophore.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applebury M. L. Dynamic processes of visual transduction. Vision Res. 1984;24(11):1445–1454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(84)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. R., Einterz C. M., Knapp H. M., Murray L. P. The nature of the primary photochemical events in rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1988 Mar;53(3):367–385. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83114-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. R., Hubbard L. M. Molecular dynamics of trans-cis isomerization in bathorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):517–534. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84865-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. R. Nature of the primary photochemical events in rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 26;1016(3):293–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. R. Photophysics and molecular electronic applications of the rhodopsins. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1990;41:683–733. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.41.100190.003343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch G. E., Applebury M. L., Lamola A. A., Rentzepis P. M. Formation and decay of prelumirhodopsin at room temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2802–2806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender R. H., Doukas A., Crouch R., Nakanishi K. Molecular flow resonance Raman effect from retinal and rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1621–1629. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. Energy uptake in the first step of visual excitation. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):531–533. doi: 10.1038/282531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doukas A. G., Junnarkar M. R., Alfano R. R., Callender R. H., Kakitani T., Honig B. Fluorescence quantum yield of visual pigments: evidence for subpicosecond isomerization rates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4790–4794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. H., Monger T. G., Alfano R. R., Aton B., Callender R. H. Cis-trans isomerisation in rhodopsin occurs in picoseconds. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):179–180. doi: 10.1038/269179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Ebrey T., Callender R. H., Dinur U., Ottolenghi M. Photoisomerization, energy storage, and charge separation: a model for light energy transduction in visual pigments and bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2503–2507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandori H., Matuoka S., Shichida Y., Yoshizawa T. Dependency of photon density on primary process of cattle rhodopsin. Photochem Photobiol. 1989 Feb;49(2):181–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1989.tb04094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder S. J., Kliger D. S. A new approach to understanding the initial step in visual transduction. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):567–570. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83667-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monger T. G., Alfano R. R., Callender R. H. Photochemistry of rhodopsin and isorhodopsin investigated on a picosecond time scale. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85205-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff A. R., Callender R. H. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of rhodopsin in retinal disk membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4243–4248. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Applebury M. L., Rentzepis P. M. Primary photochemical event in vision: proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3119–3123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick G. A., Cooper T. M., Holloway R. A., Murray L. P., Birge R. R. Energy storage in the primary photochemical events of rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2556–2562. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



