Abstract
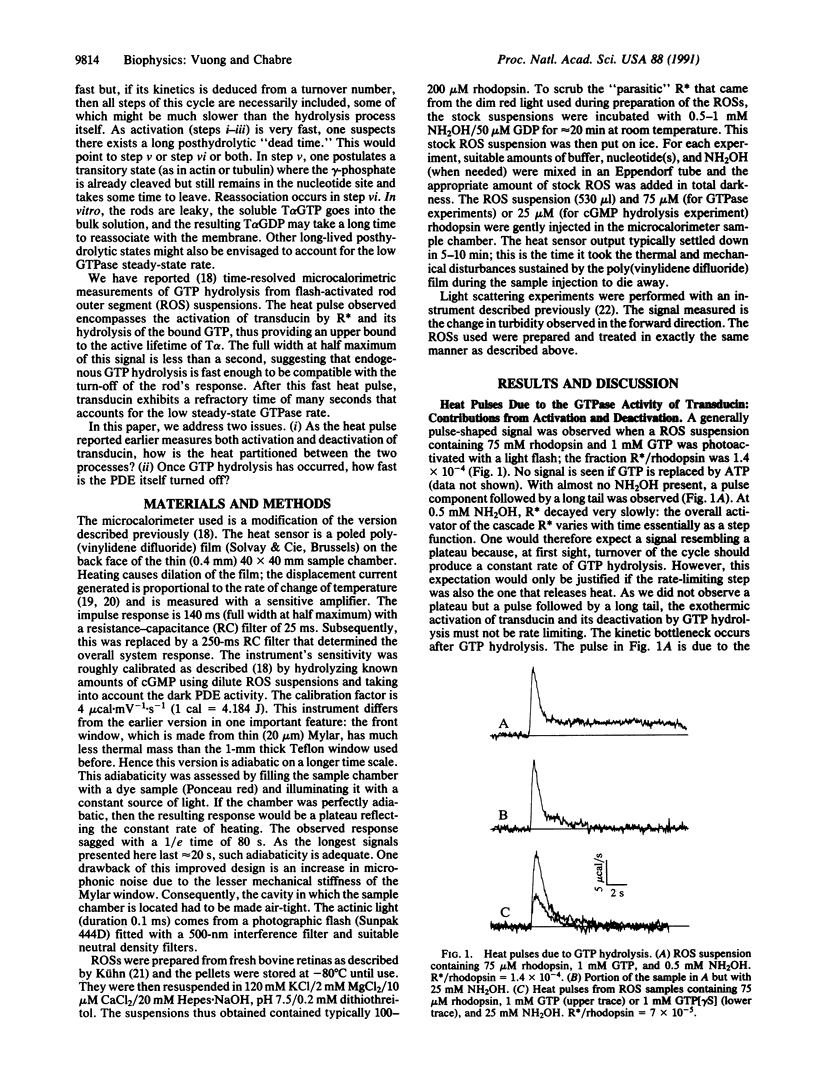
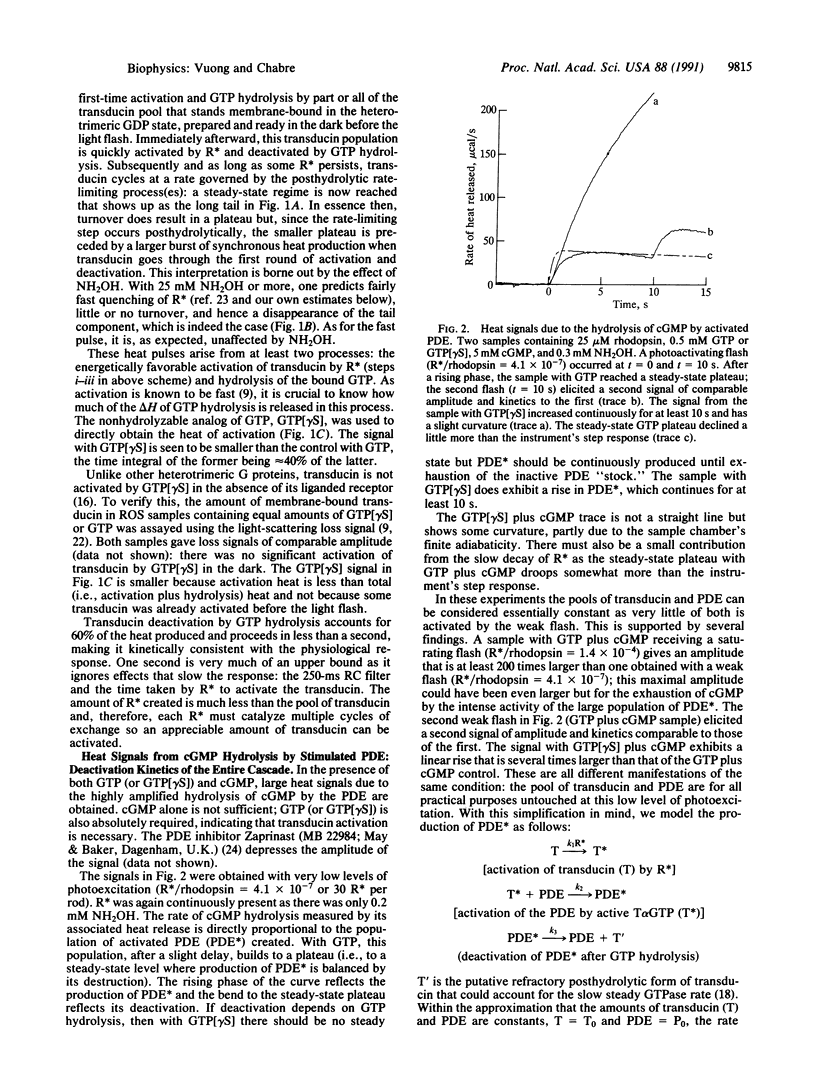
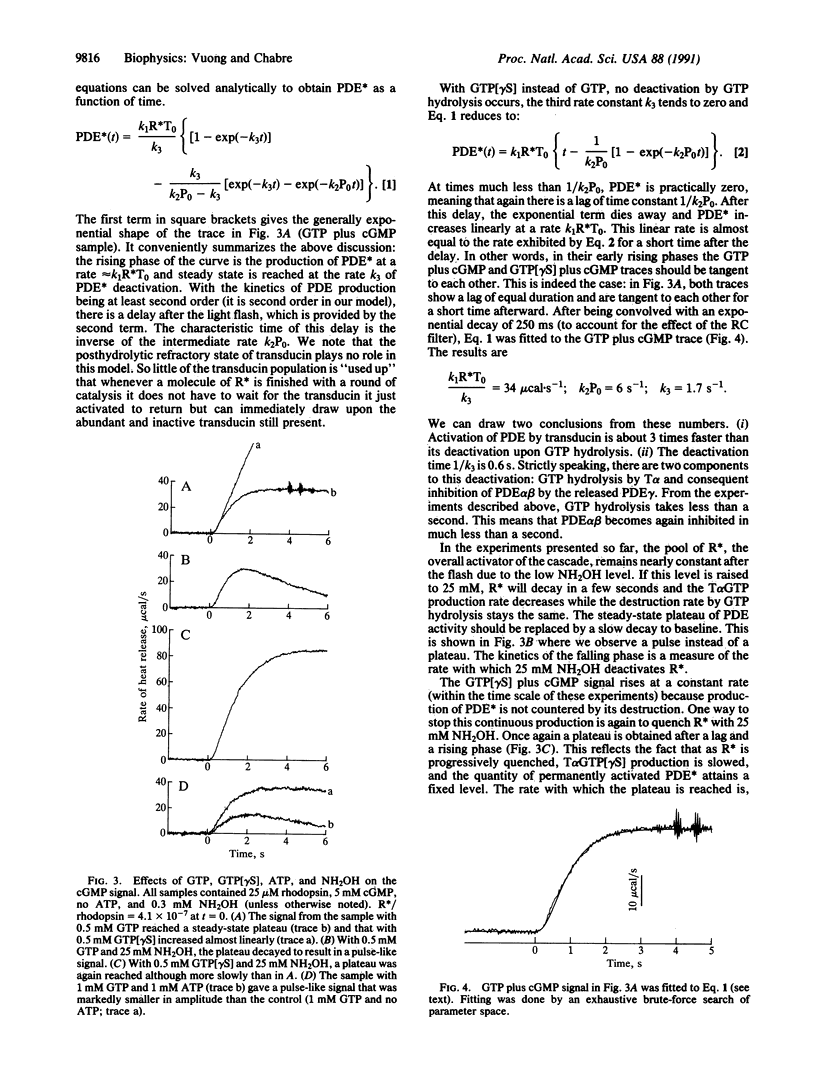
The response of the retinal rod cell to a dim flash lasts less than a second. This phototransduction is mediated by a guanine nucleotide-binding (G) protein cascade in which rhodopsin is the receptor, transducin is the G-protein, and the cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE) is the effector. Photoexcited rhodopsin activates transducin which in turn activates PDE. For this underlying biochemistry to be kinetically compatible with the photoresponse, both transducin and PDE must be deactivated in subsecond times. We report here direct measurements of their deactivation kinetics. The rate of heat release when transducin and PDE hydrolyze, respectively, GTP and cGMP was measured using time-resolved microcalorimetry. With only GTP present, the heat pulse comes from the activation of transducin and its subsequent deactivation by endogenous GTP hydrolysis. The nonhydrolyzable analog guanine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate was used to distinguish between these two processes: about 40% of the total heat is due to activation. From the time course of the deactivation heat, the active lifetime of transducin is less than 1 s at 22 degrees C. With both GTP and cGMP present, the highly amplified hydrolytic activity of the PDE is responsible for most of the heat produced; its rate of release is directly proportional to the amount of activated PDE. Measurements of this rate at low photoexcitation levels (e.g., 30 molecules of photoexcited rhodopsin per rod) provide much kinetic information about the cascade. Notably, deactivation of the PDE takes 0.6 s (at 23 degrees C) and absolutely requires GTP hydrolysis. This concurs with the subsecond lifetime of active transducin and means that, once GTP hydrolysis has occurred, the hitherto active PDE is quickly inhibited.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arshavsky VYu, Antoch M. P., Philippov P. P. On the role of transducin GTPase in the quenching of a phosphodiesterase cascade of vision. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nunn B. J., Schnapf J. L. The photocurrent, noise and spectral sensitivity of rods of the monkey Macaca fascicularis. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:575–607. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Reifsnyder D. H. Primary sequence of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes and the design of selective inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90066-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckert F., Vuong T. M., Chabre M. Light and GTP dependence of transducin solubility in retinal rods. Further analysis by near infra-red light scattering. Eur Biophys J. 1988;16(4):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00261263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deterre P., Bigay J., Forquet F., Robert M., Chabre M. cGMP phosphodiesterase of retinal rods is regulated by two inhibitory subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizhoor A. M., Ray S., Kumar S., Niemi G., Spencer M., Brolley D., Walsh K. A., Philipov P. P., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Recoverin: a calcium sensitive activator of retinal rod guanylate cyclase. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):915–918. doi: 10.1126/science.1672047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. I. Separation and reconstitution of the subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10495–10502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Ross P. D., Tate R. L., Yoshikami S. Transduction heats in retinal rods: tests of the role of cGMP by pyroelectric calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K. P., Emeis D., Schnetkamp P. P. Interplay between hydroxylamine, metarhodopsin II and GTP-binding protein in bovine photoreceptor membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 31;725(1):60–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(83)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Purification and characterization of the gamma regulatory subunit of the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase from retinal rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11094–11099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W., Stryer L. Highly cooperative feedback control of retinal rod guanylate cyclase by calcium ions. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):64–66. doi: 10.1038/334064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., Matthews H. R. Incorporation of analogues of GTP and GDP into rod photoreceptors isolated from the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:463–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Pugh E. N., Jr ATP mediates rapid reversal of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase activation in visual receptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):734–736. doi: 10.1038/287734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton P. A. Light response of vertebrate photoreceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):847–883. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. J., Cerione R. A. The intrinsic fluorescence of the alpha subunit of transducin. Measurement of receptor-dependent guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15498–15505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather W. A., Detwiler P. B. Intracellular biochemical manipulation of phototransduction in detached rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9290–9294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher A., Kühn H., Hofmann K. P. Kinetics, binding constant, and activation energy of the 48-kDa protein-rhodopsin complex by extra-metarhodopsin II. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1770–1775. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitaramayya A., Casadevall C., Bennett N., Hakki S. I. Contribution of the guanosinetriphosphatase activity of G-protein to termination of light-activated guanosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate hydrolysis in retinal rod outer segments. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4880–4887. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki I., Nakaye T. Heat produced by the dark-adapted bullfrog retina in response to light pulses. Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83462-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuong T. M., Chabre M., Stryer L. Millisecond activation of transducin in the cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):659–661. doi: 10.1038/311659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuong T. M., Chabre M. Subsecond deactivation of transducin by endogenous GTP hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):71–74. doi: 10.1038/346071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Hall S. W., Kühn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka G., Eckstein F., Stryer L. Stereochemistry of the guanyl nucleotide binding site of transducin probed by phosphorothioate analogues of GTP and GDP. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8094–8101. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



