Abstract
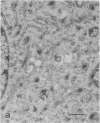
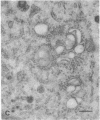
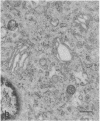
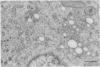
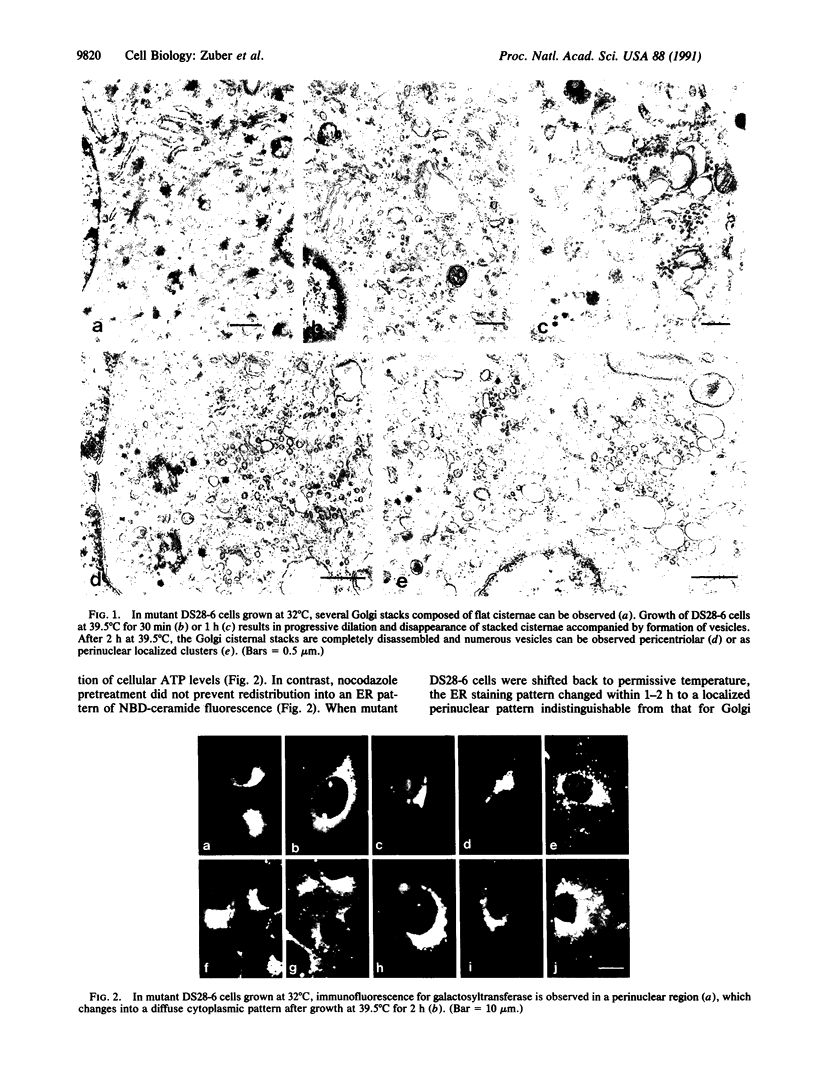
The temperature-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell mutant DS28-6 has been previously shown to be pleiotropically defective in protein secretion. We have examined the mutant cells to determine the intracellular site of the block in secretion. By transmission electron microscopy a time-dependent disassembly of the Golgi apparatus was found under nonpermissive temperature, which resulted in the loss of the cisternal stack. Complete reorganization of the Golgi apparatus occurred after shift to permissive temperature. Under nonpermissive temperature, a microtubule- and energy-dependent redistribution of Golgi mannosidase II and galactosyltransferase into a pattern characteristic of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) was observed. Inhibition of protein synthesis by cycloheximide had no influence on Golgi mannosidase II redistribution. Evidence for Golgi apparatus-associated processing of oligosaccharides in the ER was obtained by lectin-gold cytochemistry revealing the presence of the galactose (beta 1----4)N-acetylglucosamine sequence and sialic acid residues. Furthermore, 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl-tagged ceramide, a lipidic trans-Golgi apparatus marker in CHO cells, exhibited an energy-dependent redistribution into the ER. These effects were fully reversible upon shift to permissive temperature. Thus, mutant DS28-6 cells exhibit key features of the brefeldin A phenotype, which suggests that the observed brefeldin A effects result from interference with a normally occurring cellular process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess T. L., Kelly R. B. Constitutive and regulated secretion of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:243–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Russ G., Yewdell J. W. Brefeldin A redistributes resident and itinerant Golgi proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):61–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egea G., Goldstein I. J., Roth J. Light and electron microscopic detection of (3 Gal beta 1,4 GlcNAc beta 1) sequences in asparagine-linked oligosaccharides with the Datura stramonium lectin. Histochemistry. 1989;92(6):515–522. doi: 10.1007/BF00524763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Oda K., Ikehara Y. Dynamic distribution of the Golgi marker thiamine pyrophosphatase is modulated by brefeldin A in rat hepatoma cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1989 Oct;14(5):605–616. doi: 10.1247/csf.14.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Oda K., Yokota S., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18545–18552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Pfeiffer S., Simons K., Matlin K. Exit of newly synthesized membrane proteins from the trans cisterna of the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):949–964. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. IV. Metabolic requirements. J Cell Biol. 1968 Dec;39(3):589–603. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D. Sorting and traffic in the central vacuolar system. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):703–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90783-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. U., Roth J., Paulson J. C. Alteration of terminal glycosylation sequences on N-linked oligosaccharides of Chinese hamster ovary cells by expression of beta-galactoside alpha 2,6-sialyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13848–13855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Misumi Y., Miki K., Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Ikehara Y. Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moremen K. W., Touster O. Biosynthesis and modification of Golgi mannosidase II in HeLa and 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6654–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano A., Nishijima M., Maeda M., Akamatsu Y. A temperature-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant pleiotropically defective in protein export. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 30;845(3):324–332. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Fujiwara T., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A arrests the intracellular transport of viral envelope proteins in primary cultured rat hepatocytes and HepG2 cells. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):161–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2650161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Hirose S., Takami N., Misumi Y., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A arrests the intracellular transport of a precursor of complement C3 before its conversion site in rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Sepanski M. A., Martin O. C. Molecular trapping of a fluorescent ceramide analogue at the Golgi apparatus of fixed cells: interaction with endogenous lipids provides a trans-Golgi marker for both light and electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2067–2079. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkel V. S., Liu A. Y., Miura Y., Magner J. A. The effects of brefeldin-A on the high mannose oligosaccharides of mouse thyrotropin, free alpha-subunits, and total glycoproteins. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):310–318. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Application of lectin--gold complexes for electron microscopic localization of glycoconjugates on thin sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Aug;31(8):987–999. doi: 10.1177/31.8.6190857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Lucocq J. M., Charest P. M. Light and electron microscopic demonstration of sialic acid residues with the lectin from Limax flavus: a cytochemical affinity technique with the use of fetuin-gold complexes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Nov;32(11):1167–1176. doi: 10.1177/32.11.6208237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Postembedding labeling on Lowicryl K4M tissue sections: detection and modification of cellular components. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:513–551. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61625-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Taatjes D. J., Lucocq J. M., Weinstein J., Paulson J. C. Demonstration of an extensive trans-tubular network continuous with the Golgi apparatus stack that may function in glycosylation. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Kuismanen E. Pre- and post-Golgi vacuoles operate in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Palade G. E., Farquhar M. G. Temperature-sensitive steps in the transport of secretory proteins through the Golgi complex in exocrine pancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6425–6429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schekman R. Protein localization and membrane traffic in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:115–143. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Stenbeck G., Brecht A., Lottspeich F., Orci L., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. A coat subunit of Golgi-derived non-clathrin-coated vesicles with homology to the clathrin-coated vesicle coat protein beta-adaptin. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):215–220. doi: 10.1038/349215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper N. L., Mann P. L., Shaper J. H. Cell surface galactosyltransferase: immunochemical localization. J Cell Biochem. 1985;28(3):229–239. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240280305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shite S., Seguchi T., Mizoguchi H., Ono M., Kuwano M. Differential effects of brefeldin A on sialylation of N- and O-linked oligosaccharides in low density lipoprotein receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17385–17388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taatjes D. J., Roth J., Weinstein J., Paulson J. C., Shaper N. L., Shaper J. H. Codistribution of galactosyl- and sialyltransferase: reorganization of trans Golgi apparatus elements in hepatocytes in intact liver and cell culture. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;44(2):187–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Temperature and energy dependence of secretory protein transport in the exocrine pancreas. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1477–1482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki M. Fluorescent labeling of endoplasmic reticulum. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;29:125–135. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer J. B., Palade G. E. Effects of Brefeldin A on the Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum and viral envelope glycoproteins in murine erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;54(1):38–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer J. B., Palade G. E. Targeting and processing of glycophorins in murine erythroleukemia cells: use of brefeldin A as a perturbant of intracellular traffic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6992–6996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. W., Jr, Lutz M. S., Mills S. E., Lechler-Osborn S. Use of brefeldin A to define sites of glycosphingolipid synthesis: GA2/GM2/GD2 synthase is trans to the brefeldin A block. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6838–6842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Echten G., Iber H., Stotz H., Takatsuki A., Sandhoff K. Uncoupling of ganglioside biosynthesis by Brefeldin A. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;51(1):135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]