Abstract
Background
Cancer stem cells (CSCs), which have been isolated from various malignancies, were closely correlated with the occurrence, progression, metastasis and recurrence of the malignant cancer. Little is known about the tumor stem-like cells (TSLCs) isolated from benign tumors. Here we want to explore the global expression profile of RNA of tumor stem-like cells isolated from MMQ rat prolactinoma cells.
Methods
In this study, total RNA was extracted from MMQ cells and MMQ tumor stem-like cells. RNA expression profiles were determined by Agilent Rat 8 × 60 K Microarray. Then we used the qRT-PCR to test the result of Microarray, and found VEGFA had a distinct pattern of expression in MMQ tumor stem-like cells. Then WB and ELISA were used to confirm the VEGFA protein level of tumor sphere cultured from both MMQ cell and human prolactinoma cell. Finally, CCK-8 was used to evaluate the reaction of MMQ tumor stem-like cells to small interfering RNAs intervention and bevacizumab treatment.
Result
The results of Microarray showed that 566 known RNA were over-expressed and 532 known RNA were low-expressed in the MMQ tumor stem-like cells. These genes were mainly involved in 15 different signaling pathways. In pathway in cancer and cell cycle, Bcl2, VEGFA, PTEN, Jun, Fos, APC2 were up-regulated and Ccna2, Cdc25a, Mcm3, Mcm6, Ccnb2, Mcm5, Cdk1, Gadd45a, Myc were down-regulated in the MMQ tumor stem-like cells. The expression of VEGFA were high in tumor spheres cultured from both MMQ cell and human prolactinomas. Down-regulation of VEGFA by small interfering RNAs partially decreased cell viability of MMQ tumor stem-like cells in vitro. Bevacizumab partially suppressed the proliferation of MMQ tumor stem-like cells.
Conclusions
Our findings characterize the pattern of RNA expression of tumor stem-like cells isolated from MMQ cells. VEGFA may act as a potential therapeutic target for tumor stem-like cells of prolactinomas.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12935-017-0390-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Tumor stem-like cell, MMQ cell, Prolactinoma, VEGFA, Microarray
Background
Prolactinomas are the most common subtype of pituitary adenomas with the proportion ranging from 40 to 66%, and occur with the population prevalence of 6–10 per 100,000 per year [1–3]. Since the mid–1980s, dopamine agonists (DA) have become the first-line therapy for the patients with prolactinomas [2, 4, 5]. However, it is not known how prolactinomas develop and tumor recurrence after withdrawal of DA treatment.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are defined as the unique subpopulation in the tumor, which possess the ability to initiate tumor growth and sustain self-renewal as well as metastatic potential [6, 7]. The further research discovered that cancer stem cells, which had been isolated from leucocythemia and other various malignancies, were closely correlated with the occurrence, progression, metastasis and recurrence of the malignant cancer [8–10]. However, little is known about the tumor stem-like cells (TSLCs) isolated from benign tumors. Xu [11] had proved for first time that tumor stem-like cells can be isolated from pituitary adenoma. Recently, Chen [12] and Mertens [13] had further demonstrated that the tumor stem-like cells were existed and identificated in pituitary adenoma. However, the global expression profile of RNA in tumor stem-like cells (TSLCs) isolated from prolactinoma kept unknown. Medical treatment is the first choice for prolactinoma [2, 4, 5], which results in limited tumor specimen source, moreover, there are small number of cells available from human prolactinoma postsurgical samples for in vitro experiments. Human pituitary adenomas cells grow very slowly in vitro [13], then it is difficult to get enough tumor cells to evaluate the molecular characteristic of TSLCs from human prolactinoma. MMQ rat prolactinoma cells are traditionally used as a substitutes for human prolactin-secreting pituitary adenoma cells in laboratory experiments, mainly because stably express prolactin (PRL) and have similar biological characteristics [14]. Therefore, research on characterizing RNAs expression of MMQ tumor stem-like cells will help to lay the foundation for human prolactinoma.
In this study, total RNA was extracted from three classical cultured MMQ cells and three MMQ tumor stem-like cells cultured in serum-free suspension medium containing growth factor. Then, their RNA expression profiles were determined by Agilent Rat 8 × 60 K Microarray. We validated these differentially expressed RNA by qRT-PCR and analyzed their potential function. Furthermore, the expression of VEGFA which over-expressed in the MMQ tumor stem-like cells was detected in tumor spheres isolated from human prolactinomas. Finally, we evaluated the cell viability after down-regulation of VEGFA by small interfering RNAs and the reaction to bevacizumab in MMQ tumor stem-like cells.
Methods
MMQ cell culture and reagents
MMQ rat prolactinoma cell line was used in this study, which was purchased from the Cell Bank of the Shanghai Branch of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and cultured in F12 medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) supplemented with 2.5% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco), 15% horse serum (Gibco) and 100 U/ml penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco). Cells were maintained in humidified atmosphere with 37 °C and 5% CO2.
MMQ tumor stem-like cell culture and reagents
To obtain MMQ tumor stem-like cells, as described in our previous report [15], in brief, MMQ cells were cultured in DMEM/F12 medium (Gibco) supplemented with B27 (1×, Gibco), EGF (20 ng/ml, Preprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA), bFGF (20 ng/ml, Preprotech) and 100 U/ml penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco). After been cultured for 2–3 weeks, MMQ tumor spheres can grow and form in serum-free suspension medium. Then, the MMQ tumor spheres were identified by immunofluorescence examination of stem cell markers and transplantation assay (see Additional file 1: Figure S1). Finally, the MMQ tumor spheres were resuspended and incubated with Rabbit anti-CD133 (1:50, MyBioSource, USA) for 30 min at 4 °C. After washing with PBS, cells were incubated with FITC-conjugated Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (1:50, Santa Cruz, USA) for 30 min at 4 °C. Subsequently, FACS Calibur Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences) was used to isolate and collect the CD133 positive tumor stem-like cells from the MMQ tumor spheres.
Patients and tissue samples
Tumor specimens were obtained from pituitary prolactinomas resected via the transsphenoidal approaches in Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University from March 2012 to December 2015. Research was approved by Clinical Medicine ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (permission: 2012–2013). Five pituitary adenomas samples (n = 5; 3 men and 2 women) were classified as prolactinomas according to the 2004 edition of the World Health Organization classification of pituitary tumors [16], which were ranged in age from 27 to 54 years. All had increased prolactin serum levels from 112.1 to >2000 ng/ml and the tumor volumes varied from 365 to 7800 mm3. Tumor tissues were immersed in DMEM medium (Gibco) for cell culture development.
Human prolactinoma cell culture
Tissue samples were disaggregated with scalpel, washed in DMEM and fractured further by pipetting. Tumor cells were released from the tissues by enzymatic treatment with trypsase (Gibco) and grown in DMEM with 15% Fetal Bovine Serum (Gibco) until reaching confluency. Then tumor cells were collected and cultured in serum-free suspension medium which similar to MMQ tumor stem-like cells. Tumor spheres can grow and form in serum-free suspension medium after 2 to 3 weeks. Then, the human prolactinoma spheres were identified by immunofluorescence examination of stem cell markers (see Additional file 2: Figure S2).
RNA extraction and evaluation
MMQ cells and CD133 positive tumor stem-like cells were homogenized in TRIzol reagent and total RNA was isolated according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Invitrogen, CA). The concentration and purity of total RNA were determined by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer at 260 and 280 nm.
Microarrays and gene expression analysis
An Agilent gene expression array (KangChen Bio-tech Inc.) was used to investigate the global expression profile of MMQ tumor stem-like cells; the array represented more than 41,000 transcripts (http://www.kangchen.com.cn). The microarray datasets were normalized in Gene Spring GX using the Agilent FE one-color scenario (mainly quantile normalization). Differentially expressed genes were identified through fold-change screening (fold change ≥2.0). The gene ontology (GO) biological process and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis were performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery 6.7, (DAVID; http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) and were ranked by P values [17, 18].
Verification of the RNA expression by qRT-PCR
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to verify RNA expression identified by Agilent Rat 8 × 60 K Microarray. The primers for the identified RNA were designed using Premier 5.0. Mixtures of 1 µg of total RNAs, 50 nM reverse primer, 5 units of M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Toyobo), 2 units of the RNAase inhibitor (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan) and 0.5 µM dNTP were incubated for 30 min at 16 °C, 30 min at 42 °C and 15 min at 70 °C. The reaction mixes were used as the templates for qRT-PCR using SYBR® Green Real-time PCR Master Mix-Plus (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan) on the Applied Biosystems 7500 detection system. The PCR mixture including 1 µl RT product of total RNA, 10 µl SYBR-Green Real-time PCR Master Mix-plus, 2 µl plus solution, 2 µl each specific forward and reverse primers, and 3 µl DEPC water was made up the final volume to 20 µl. The reaction was performed at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles at 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. Each sample was ran in triplicate and actin was used as internal control. Melting curves were used for verifying the specificity of each PCR reaction. The cycle threshold (Ct) was the mean value of three Ct values. The relative expression level of RNA was analyzed by the 2−∆∆Ct method.
PCR primers used were as follows
Bcl2 (Rat-Forward): 5′-cgggacgcgaagtgctattg-3′;
Bcl2 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-cggttgctctcaggctggaa-3′;
VEGFA (Rat-Forward): 5′-gagttaaacgaacgtacttgcaga-3′;
VEGFA (Rat-Reverse): 5′-tctagttcccgaaaccctga-3′;
VEGFA (Human-Forward): 5′-ttgctgctctacctccaccat-3′;
VEGFA (Human-Reverse): 5′-ggtgatgttggactcctcagtg-3′;
PTEN (Rat-Forward): 5′-ggcacaagaggccctggatt-3′;
PTEN (Rat-Reverse): 5′-tgcaagttccgccactgaaca-3′;
Jun (Rat-Forward): 5′-ccgtgagtgaccgcgacttt-3′;
Jun (Rat-Reverse): 5′-ctgggctgtgcgcagaagtt-3′;
Fos (Rat-Forward): 5′-accagagcgccccatcctta-3′;
Fos (Rat-Reverse): 5′-ctcctccgattccggcactt-3′;
APC2 (Rat-Forward): 5′-atcccaaggccacctggcta-3′;
APC2 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-tccccacaccgtcaccaagt-3′;
Ccna2 (Rat-Forward): 5′-ttgctggagctgccttccac-3′;
Ccna2 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-ctgttgggcatgctgtggtg-3′;
Cdc25a (Rat-Forward): 5′-ccttgccgatcgatgtggac-3′;
Cdc25a (Rat-Reverse): 5′-cgttggctccggaacatctg-3′;
Mcm3 (Rat-Forward): 5′-catccaggagatgccggaga-3′;
Mcm3 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-acgttgcaggcgatcaggac-3′;
Mcm6 (Rat-Forward): 5′-tgcaccaaccaacccacgat-3′;
Mcm6 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-gaacgccaccgaacagcatc-3′;
Ccnb2 (Rat-Forward): 5′-gctgggccaaggaaaatgga-3′;
Ccnb2 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-tgcctagggtctgcccatca-3′;
Mcm5 (Rat-Forward): 5′-tggcacagccaagtcacagc-3′;
Mcm5 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-cacggtcatcttcccgcatc-3′;
Cdk1 (Rat-Forward): 5′-cagatttcggccttgccaga-3′;
Cdk1 (Rat-Reverse): 5′-ttcttggtcgccagctctgc-3′;
Gadd45a (Rat-Forward): 5′-tgctcagcaaggctcggagt-3′;
Gadd45a (Rat-Reverse): 5′-gttgctgacccgcaggatgt-3′;
Myc (Rat-Forward): 5′-tcggctcccctgaaaagagc-3′;
Myc (Rat-Reverse): 5′-tcgctctgctgttgctggtg-3′;
Actin (Rat-Forward): 5′-cctctatgccaacacagtgc-3′;
Actin (Rat-Reverse): 5′-gtactcctgcttgctgatcc-3′
Actin (Human -Forward): 5′-gggacctgactgactacctc-3′;
Actin (Human -Reverse): 5′-tcatactcctgcttgctgat-3′
Western Blot
Proteins were separated on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA). The membrane was blocked with 5% non-fat milk and incubated with Rabbit anti-VEGFA mAb (epitomics) or rabbit anti-Actin mAb (cell signaling). After being washed extensively, a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Massachusetts, USA) was added to the system. The proteins were detected using ECL reagents (Pierce).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs)
The level of VEGFA of supernatant from culture medium was measured using a commercially available ELISA kit, according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Excell biology, Shanghai, China). The minimal detectable concentration was 4 pg/mL for VEGFA. The inter-assay and intra-assay coefficients of variation were less than 10%.
Gene silencing assay
MMQ tumor stem-like cells and MMQ cells grown in 6-well plates to ~50% confluency were serum-starved overnight and transfected with 100 pmol Silencer® Select Negative Control #1 siRNA (Cat. No. 4390843, Ambion, USA) and Silencer® Select Pre-Designed VEGFA siRNA (Cat. No. 4390771; ID: s236285, Ambion, USA) for 24 h using Lipofectamine™ 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After an additional 8 h incubation (serum-free medium), samples were collected at indicated times for further study.
Cell proliferation assay
Cell proliferation was measured using the CCK-8 assay kit (Dojindo, Japan). 10,000 cells, treated with bevacizumab (Roche, 4 mg/μl) or DMSO for 72 h, were plated into each well of a 96-well plate. On the day of harvest, 10 μl CCK-8 was added to 90 μl of culture medium. The cells were subsequently incubated for 4 h at 37 °C and the optical density was measured at 450 nm. Three independent experiments were performed.
Statistical analysis
Data were described as mean ± SEM. The T test statistic was applied to evaluate the difference between MMQ cells with tumor stem-like cells. P < 0.05 was considered as a significant difference. The calculations were performed with the software SPSS 17.0.
Results
Overview of gene expression array
Microarray systems were broadly used to investigate gene expression patterns and functional classification in stem cell [19]. In this paper, to evaluate the gene differences between MMQ cells and tumor stem-like cells, we extracted RNA from three classical cultured MMQ cells and three MMQ tumor stem-like cells cultured in serum-free suspension medium containing growth factor, and hybridized in Agilent Rat 8 × 60 K microarrays. The resulting data were analyzed by the GABRIEL (Genetic Analysis by Rules Incorporating Expert Logic) system, a knowledge based system of computer algorithms. As shown in Fig. 1a, the distributive differences of all detection gene probe (excluding controlled probe and flagged probe) in Agilent Rat 8 × 60 K microarrays tended to normal distribution, which was accurate and practical value. The expression levels of RNAs in the two libraries were normalized. The volcano plots of RNAs in classical MMQ cells and MMQ tumor stem-like cells was shown in Fig. 1b, the inclusion criteria of alternative gene: the expression of the gene was changed more than 2.0 folds and the P value was less than 0.05. After trimming sequences with contaminants, the results of Microarray showed that 566 known RNA were over-expressed (the blue spots on the right), and 532 known RNA were specially low-expressed in the MMQ tumor stem-like cells (the blue spots on the left).
Fig. 1.
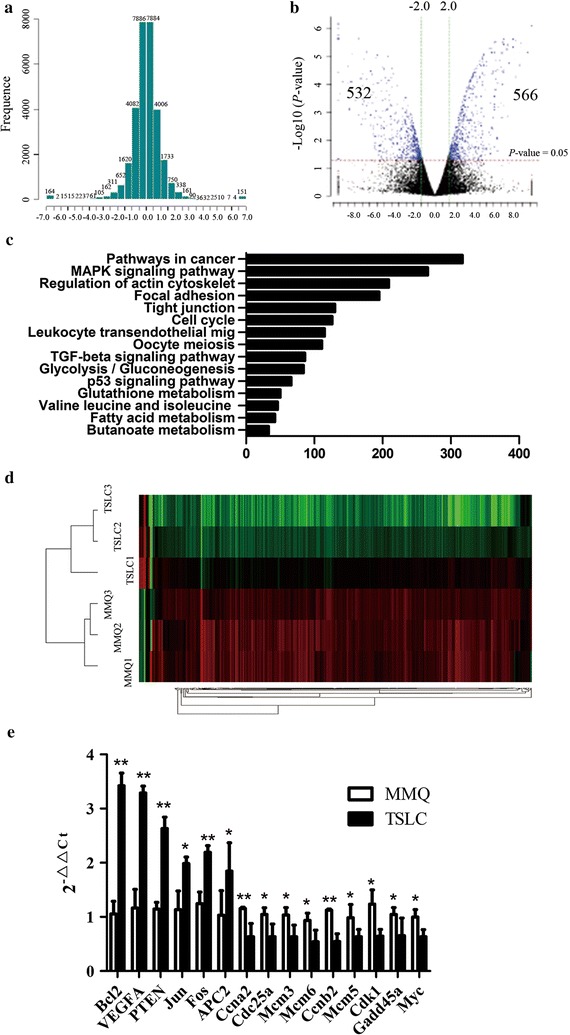
Overview of gene expression array. a Normal distribution of RNAs in classical MMQ cells and MMQ TSLCs. The Log2 absciss are presented the differences existing between the 2 group. The vertical axis showed the number of probe. In general, the figure become approximately normally distribution, which showed the up-regulated RNA should be roughly the same as the down-regulated RNA. b Volcano Plots of RNAs in classical MMQ cells and MMQ TSLCs. The Log2 absciss are presented the differences existing between the 2 group. The vertical axis showed the P value, which represented the significance of the difference. The red line mean the P = 0.05. The inclusion criteria of alternative gene: the expression of the gene was changed more than 2.0 folds (the green line) and the P value was less than 0.05 (the red line). Microarray showed that 566 known RNA were over-expressed and 532 known RNA were low-expressed in the MMQ TSLCs. c Biological processes analysis of the gene expression profiles. 15 pathway were shown to be significantly regulated with more than 500 genes differential expression in two group. d The cluster analysis of classical MMQ cells and MMQ TSLCs. Further study in pathway in cancer and cell cycle between MMQ cells and TSLCs were taken into consideration. According to the clustering analysis of three times independent microarray experiments, 82 candidate genes were selected. E. To verify the 82 candidate genes, MMQ cells and MMQ TSLCs were used to perform qRT-PCR for the identified RNAs. 15 differential expressed genes existed steady difference. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. TSLC tumor stem-like cell
Biological processes analysis of the gene expression profiles
GO analysis is a functional analysis associating differentially expressed genes with GO categories. The GO categories are derived from Gene Ontology (http://www.geneontology.org), which comprises three structured networks of defined terms to describe gene product attributes. This functional analysis was used to predict significant differences between MMQ cells and tumor stem-like cells. As shown in Table 1, pathway in cancer, MAPK signaling pathway, regulation of actin cytoskeleton, focal adhesion, tight junction, cell cycle, leukocyte transendothelial migration, oocyte meiosis, TGF-beta signaling pathway, gluconeogenesis, P53 signaling pathway, glutathione metabolism, valine leucine and isoleucine degradation, fatty acid metabolism, butanoate metabolism were shown to be significantly regulated with more than 500 genes differential expression in two group (Fig. 1c; P value < 0.01).
Table 1.
Biological processes analysis of the gene expression profiles
| Geneset name | Genes in geneset | Description | Genes in overlap (k) | k/K | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway in cancer | 317 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno05200:pathways in cancer | 25 | 0.07886 | 0.0159 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 266 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04010:MAPK signaling pathway | 21 | 0.07895 | 0.0281 |
| Regulation of action cytoskeleton | 209 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04810:regulation of action cytoskeleton | 19 | 0.09091 | 0.0106 |
| Focal adhesion | 195 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04510:focal adhesion | 20 | 0.10256 | 0.0023 |
| Tight junction | 130 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04530:tight junction | 17 | 0.13077 | 0.0004 |
| Cell cycle | 126 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04110:cell cycle | 18 | 0.14286 | 8.7916E−05 |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | 115 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04670:leukocyte transendothelial migration | 14 | 0.12174 | 0.0031 |
| Oocyt meiosis | 111 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04114:oocyt meiosis | 12 | 0.10811 | 0.0163 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | 86 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04350:TGF-beta signaling pathway | 11 | 0.12791 | 0.0075 |
| Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis | 84 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno00010:glycolysis/gluconeogenesis | 10 | 0.11905 | 0.018 |
| p53 signaling pathway | 66 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno04115:p53 signaling pathway | 11 | 0.16667 | 0.001 |
| Glutathione metabolism | 50 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno00480:glutathione metabolism | 7 | 0.14 | 0.0306 |
| Valine leucine and isoleucine degradation | 46 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno00280:valine leucine and isoleucine degradation | 7 | 0.15217 | 0.0211 |
| Fatty acid metabolism | 42 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno00071:fatty acid metabolism | 6 | 0.14286 | 0.0481 |
| Butanoate metabolism | 33 | Genes annotated by the KEGG rno00650:butanoate metabolism | 7 | 0.21212 | 0.0042 |
Differential expression of RNAs between two groups in pathway in cancer and cell cycle
Earlier studies [20] had shown that cancer stem cells played a key role in neurogenic tumor regeneration, metastasis and recurrence. Cancer stem cells was resistant to conventional chemo- and radio-therapy, which was a important factor in drug resistance and recurrence [21–23]. Given that conventional therapies preferentially targeted cycling cells, quiescence was thought to render cancer stem cells resistant to such treatment [24, 25]. Based on the above, further study in pathway in cancer and cell cycle between MMQ cells and tumor stem-like cells were taken into consideration. According to the clustering analysis of three times independent microarray experiments (Fig. 1d). We rearranged the gene involved in these two cell signal pathway, stably changed more than 3.0-folds were chosen to in-depth study. As shown in Additional file 3: Table S1, 82 candidate genes were selected.
Evaluation of gene expression changes by qRT-PCR
To verify the Microarray analysis results, ten classical cultured MMQ cells and ten MMQ tumor stem-like cells were used to perform qRT-PCR for the identified RNAs. 15 differential expressed genes existed steady difference, Bcl2, VEGFA, PTEN, Jun, Fos, APC2 were up-regulated and Ccna2, Cdc25a, Mcm3, Mcm6, Ccnb2, Mcm5, Cdk1, Gadd45a, Myc were down-regulated in MMQ tumor stem-like cells group (P < 0.05, Fig. 1e).
Gene ontology (GO) category and pathway analysis
The cell signaling pathway of those 15 RNAs were predicted by KEGG and Database of gene ontology (GO). In pathway in cancer, we found that Bcl2, VEGFA, PTEN, Jun, Fos, APC2 gene expression were up-regulated and the expression of Myc was down-regulated in the MMQ TSLCs. In the pathway in cell cycle, we found that the expression of Ccna2, Cdc25a, Mcm3, Mcm6, Ccnb2, Mcm5, Cdk1, Gadd45a were down-regulated in the MMQ tumor stem-like cells. (see Additional file 4: Figure S3, Additional file 5: Figure S4)
VEGFA expression was up-regulated in MMQ tumor stem-like cells
As previously reported [27], VEGFA was confirmed to associate with promoting cancer stemness, and played an important role in the neovascularization of TSLCs. To further investigate the exact effect of VEGFA in MMQ tumor stem-like cells. As shown in Fig. 2a, VEGFA mRNA expression in MMQ tumor stem-like cells were increased 273.2% compared with MMQ cells (P < 0.01). Morever, we found the level of VEGFA in culture medium supernatant of MMQ tumor sphere cells was 77.9% higher than that in MMQ cells (Fig. 2b, P < 0.01). The protein expression of VEGFA increased 102.3% in MMQ tumor sphere cells compared with MMQ cells (Fig. 2c, P < 0.01).
Fig. 2.
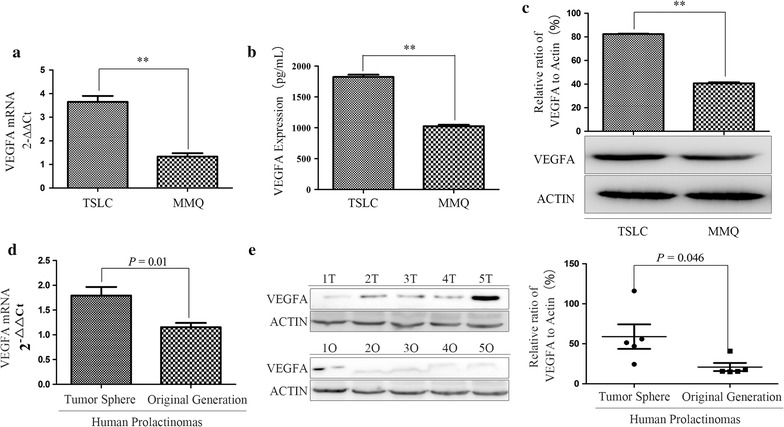
VEGFA expression was up-regulated in MMQ tumor stem-like cells and human prolactinoma tumor sphere cells. a VEGFA mRNA expression in MMQ TSLCs significantly increased compared with that in MMQ cells. b The VEGFA level of culture medium supernatant from MMQ TSLCs was higher than that from MMQ cells. c The protein expression of VEGFA significantly increased in MMQ TSLCs compared with MMQ cells evaluated by WB. d Human prolactinoma tumor spheres cultured in serum-free suspension medium had higher VEGFA mRNA, evaluated by qRT-PCR, compared with the original generation cells. e The expression of VEGFA protein of human prolactinoma tumor spheres was also significantly increased compared with that of the original generation cells. TSLC tumor stem-like cell, T human prolactinoma tumor spheres, O original generation cells of human prolactinoma. **P < 0.01
VEGFA expression was up-regulated in human prolactinoma tumor sphere cells
In next set of experiments, we wanted to further validate the expression of VEGFA in human prolactinoma. Tumor cells from 5 human prolactinomas were collected and cultured in serum-free suspension medium for 2–3 weeks, which were similar to MMQ tumor stem-like cells, human prolactinoma tumor spheres could grow and form (see Additional file 2: Figure S2). Then we found that VEGFA mRNA increased 55.5% in human prolactinoma tumor spheres, and the expression of VEGFA protein was also significantly increased compared with the original generation cells (Fig. 2d, e).
VEGFA silencing suppressed the growth of MMQ tumor stem-like cells in vitro
To address the efficacy of VEGFA on MMQ tumor stem-like cells, we down-regulated the expression of VEGFA in MMQ cells and MMQ tumor stem-like cells by small interfering RNAs. As shown in Fig. 3a, b, MMQ cells and tumor stem-like cells transfected with VEGFA siRNA showed efficient silencing of VEGFA expression, as evaluaed by real-time RT-PCR (Fig. 3a) and immunoblot analysis (Fig. 3b). VEGFA mRNA expression decreased 43.7 and 33.9% in MMQ tumor stem-like cells and MMQ cells by siRNA silencing compared with siControl transfected cells, respectively. The protein expression of VEGFA decreased 32.4 and 26.6% in tumor stem-like cells and MMQ cells by siRNA silencing, respectively. In cell viability assay, tumor stem-like cells showed reduction of cell viability by VEGFA silencing compared with siControl transfected cells (Fig. 3c). At 96 h after transfected siRNA, cell viability reduced 16.5%. The cell viability has no difference between transfected with VEGFA siRNA and transfected with SiControl in MMQ cells (data not shown). These finding showed that VEGFA may be required for the growth of tumor stem-like cells in vitro.
Fig. 3.
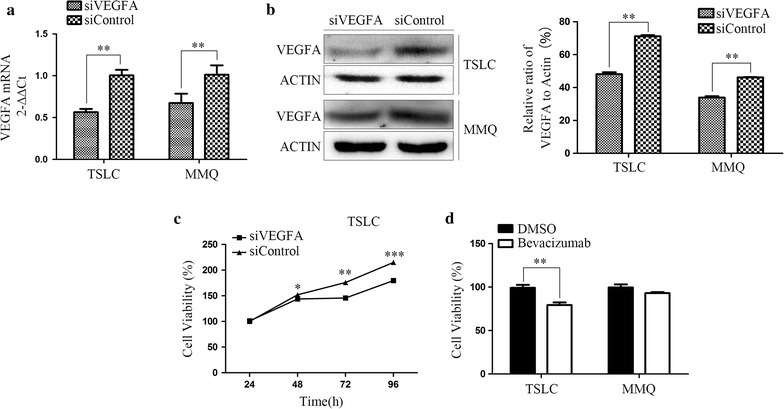
The growth-suppressive effect of VEGFA silencing and bevacizumab on MMQ tumor stem-like cells in vitro. a, b The effect of VEGFA knockdown via siRNA silencing in TSLC and MMQ cells. The cells were transfected with siControl or siVEGFA for 72 h and subjected to quantitative PCR and immunoblot analysis of VEGFA expression. c VEGFA knockdown via siRNA silencing inhibited the proliferation of TSLC. The cells were transfected with siControl or siVEGFA for 24–96 h and subjected to cell proliferation assay by CCK-8. d 10,000 MMQ TSLC, treated with bevacizumab (4 mg/μl) or DMSO for 72 h, were plated into each well of a 96-well plate and subjected to cell proliferation assay by CCK-8. The viability of MMQ TSLC treated with bevacizumab decreased compared with the negative DMSO group. TSLC: tumor stem-like cell. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
Bevacizumab could inhibit the proliferation of MMQ tumor stem-like cells in vitro
Bevacizumab, prevented solid tumor from growing by suppressing the production of VEGF, was the most commonly used anti-angiogenesis chemotherapy. The viability of MMQ tumor stem-like cells treated with bevacizumab decreased 19.7% compared with the DMSO group at 72 h. However, there were no significant difference in MMQ between bevacizumab group and DMSO group (Fig. 3d). These findings demonstrated that bevacizumab partially inhibited the proliferation of MMQ tumor stem-like cells.
Discussion
An increasing body of evidence has indicated that cancer stem cells are the root of tumor metastasis and recurrence [26]. Cancer stem cells do not only reserve the characteristics of stem cells, but also have their own nature. The research of the tumor stem cells will give a new therapeutic approach for targeting tumor [27]. However, no study has been reported which investigated the RNAs expression profile for tumor stem-like cells isolated from pituitary prolactinoma.
The present study reports, to our knowledge for the first time, the RNA expression profile in MMQ tumor stem-like cells in comparison with MMQ cells. Agilent Rat 8 × 60 K Microarray was performed to screen the differential RNAs. The results of Microarray showed that 566 known RNA were over-expressed and 532 known RNA were low-expressed in the MMQ tumor stem-like cells. These genes were mainly involved in 15 different signaling pathways. After validated by qRT-PCR, we found that 15 RNAs were differentially expressed between MMQ tumor stem-like cells and MMQ cells in the pathway in cancer and cell cycle. Bcl2, VEGFA, PTEN, Jun, Fos, APC2 were up-regulated and Ccna2, Cdc25a, Mcm3, Mcm6, Ccnb2, Mcm5, Cdk1, Gadd45a, Myc were down-regulated in MMQ tumor stem-like cells group.
The theory of cancer stem cell proposed that the tumor tissue had its own cancer stem cells in it and regarded cancer stem cell as the key to regeneration, metastasis and recurrence [20]. If its stem cells were eradicated, the rest of a tumour might die off [28]. In order to clarify the differences of gene expression in tumour formation, we put research emphasis on the pathway in cancer. We found that Bcl2, VEGFA, PTEN, Jun, Fos, APC2 gene expression were up-regulated and the expression of Myc was down-regulated in the MMQ TSLCs. These differentially expressed genes were mainly involved in cell apoptosis and differentiation. Studies show that APC was an E3 ligase enzyme [29], which might combine with Bcl2 to protected TSLCs from apoptosis process by increasing the stability of mitochondrial outer membrane, halting the intrinsic apoptotic pathways [30] and possessing the ability to infinite differentiation. Jun and Fos were overexpression in MMQ tumor stem-like cells, they were the important component of AP-1 transcriptional activating complex [31], Which might play a key role in the differentiation of cancer stem cells. AP-1 could promote dopaminergic neuronal differentiation by combining with PTEN [32]. The expression alteration of these gene describe above suggested that MMQ tumor stem-like cells owned more efficient anti-apoptosis ability and were more tolerated than MMQ cells to the changes of cultured condition in vitro, such as medication treatment and nutrient scarcity. Their self-renewal and differentiation are under strict control, if the conditions are suitable, tumor stem-like cells could immediately differentiate into the daughter cells and form tumors rapidly. These results are consistent with previous studies [6, 7, 25, 33].
Earlier studies had shown that TSLCs maintained in a non-proliferative state (referred to as quiescence, dormancy, or G0 phase) and entered the cell cycle infrequently [33, 34]. Given that conventional therapies preferentially targeted cycling cells, quiescence was thought to render TSLCs resistant to chemo- and radio-therapy [24, 25]. In the pathway in cell cycle, we found that the expression of Ccna2, Cdc25a, Mcm3, Mcm6, Ccnb2, Mcm5, Cdk1, Gadd45a were down-regulated in the MMQ tumor stem-like cells. The expression of Ccna2, Ccnb2, and Cdk1 were low, which could reduce G1/S-phase arrest [35] and the transition from G2 to M phase [36], furthermore enhanced the ability of anti-apoptosis of tumor stem cells [37]. Mcm3, Mcm5, Mcm6 proteins had been identified as important participants of DNA replication [38] and Cdc25a [39] and Gadd45a [40] was essential for DNA repair. The low expression of the gene might contribute to the delay in cell cycle and the decrease of DNA repair, the damaged or mutated DNA might be a key role in tumor stem cells infinite proliferation. Our results might help to explain the mechanism of tumor stem-like cells maintained in a non-proliferative state.
One of the most interesting observations of the current study was that VEGFA had a distinct pattern of expression in MMQ tumor stem-like cells and was further validated in tumor spheres of human prolactinoma.
VEGFA was a central regulator of angiogenesis [41, 42]. VEGFA could created a perivascular niche for TSLCs by stimulating angiogenesis in a paracrine manner, and directly stimulated cancer stemness and renewal [43].
The pituitary contains abundant VEGFA [44], and VEGFA participated in the formation of the vascular network of a new pituitary tumor [45, 46], and increased tumoral VEGFA expression was observed during the development of estrogen-induced prolactinoma in rats [47]. These data indicated that VEGFA might contribute to adequate temporal vascular supply. Furthermore, VEGFA expression was related to invasion of pituitary adenoma [48]. The expression of VEGFA obviously increased in pituitary adenoma with extrasellar growth than that in intrasellar ones, suggesting VEGFA could be markers for poor outcome after tumor resection [49]. Previous studies [50, 51] revealed that VEGFA protein expression was high in the dopamine agonist resistant prolactinomas. Furthermore, the patients with tumor recurrence showed a significant rise in serum concentrations of VEGFA. The antiangiogenic treatments were effective in inhibiting the growth of primary dopamine resistant prolactinomas as well as the transplanted adenomas [52]. In our study, both expression and secretion of VEGFA increased obviously in tumor stem-like cells of prolactinomas. Our results, integrating with the reports mentioned above, indicated that VEGFA secreted by tumor stem-like cells might play a key role in the occurrence and progression of prolactinoma and act as a potential therapeutic target.
There are several limitations in this study. Firstly, the high expression of VEGFA in MMQ tumor stem-like cells is tested in vitro, the in vivo environment is so much more complicated than in cell lines. Secondly, the regulation mechanisms of VEGFA in the tumor stem-like cells is not clear. Here, a further experiment is needed to confirm how the VEGF is involved in human prolactinomas formation and progression in vivo. This may help us to have a much better understanding of the mechanism for the beneficial effect of tumor stem-like cells on prolactinomas formation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our study characterize the pattern of RNA expression of MMQ stem-like cells. This finding may provide potential targets for development of TSLC-based therapies and lay the foundation for the further study in RNA-involved mechanism of MMQ tumor stem-like cells in the future.
Authors’ contributions
SZP and ZYZ were responsible for the design of the experiments. SZP, CL, LJL, WCD, LQ and ZGQC performed the experiments. SZP, LCZ, GSB, LCH and ZYZ analysed the data. SZP and ZYZ wrote the paper. ZYZ supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Research was approved by Clinical Medicine ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (permission: 2012–2013). Written informed consent was obtained from each patient or guardian participants.
Funding
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201687); the Medical Scientific Research foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (WKJ-ZJ-1525), the Research Special Fund for Public Welfare Industry of Health (201402008); the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2014AA020610).
Abbreviations
- Actin
alpha 1, skeletal muscle
- APC2
adenomatosis polyposis coli 2
- Bcl2
B-Cell CLL/lymphoma 2
- bFGF
basic fibroblast growth factor
- CCK-8
cell counting kit-8
- Ccna2
cyclin A2
- Ccnb2
cyclin B2
- Cdc25a
cell division cycle 25A
- Cdk1
cyclin-dependent kinase 1
- CSCs
cancer stem cells
- Ct
cycle threshold
- DA
dopamine agonist
- DAVID
database for annotation, visualization and integrated discovery
- DEPC
diethy pyrocarbonate
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- EGF
epidermal growth factor
- ELISA
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
- Fos
FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog
- Gadd45a
growth arrest and DNA damage inducible alpha
- GO
gene ontology
- Jun
Jun Proto-Oncogene
- KEGG
kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- Mcm3
minichromosome maintenance complex component 3
- Mcm5
minichromosome maintenance complex component 5
- Mcm6
minichromosome maintenance complex component 6
- MMQ
MMQ rat pituitary prolactinoma cell
- Myc
V-Myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog
- PTEN
phosphatase and tensin homolog
- qRT-PCR
quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction
- SEM
standard error of mean
- TSLCs
tumor stem-like cells
- VEGFA
vascular endothelial growth factor A
- WB
western blot
Additional files
Additional file 1: Figure S1. The characteristic identification of MMQ TSLC.
Additional file 2: Figure S2. The characteristic identification of tumor spheres isolated from human prolactinoma.
Additional file 3: Table S1. 82 candidate genes in pathway in cancer and cell cycle between MMQ TSLCs and MMQ cells.
Additional file 4: Figure S3. GO analysis and KEGG pathway analysis of 15 differentially expressed genes for the pathway in cancer.
Additional file 5: Figure S4. GO analysis and KEGG pathway analysis of 15 differentially expressed genes for the pathway in cell cycle.
Contributor Information
Zhipeng Su, Email: drsuzhipeng@163.com.
Lin Cai, Email: cailin1021@sina.cn.
Jianglong Lu, Email: 674686390@qq.com.
Chuzhong Li, Email: lichuzhong@163.com.
Songbai Gui, Email: guisongbai@hotmail.com.
Chunhui Liu, Email: liuchunhui16@163.com.
Chengde Wang, Email: yihe723@126.com.
Qun Li, Email: garylina@126.com.
Qichuan Zhuge, Email: zhugeqichuan@vip.163.com.
Yazhuo Zhang, Phone: 0086-10-67096763, Email: zyz2004520@yeah.net.
References
- 1.Casanueva FF, Molitch ME, Schlechte JA, Abs R, Bonert V, Bronstein MD, et al. Guidelines of the pituitary society for the diagnosis and management of prolactinomas. Clin Endocrinol. 2006;65(2):265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wu ZB, Yu CJ, Su ZP, Zhuge QC, Wu JS, Zheng WM. Bromocriptine treatment of invasive giant prolactinomas involving the cavernous sinus: results of a long-term follow up. J Neurosurg. 2006;104(1):54–61. doi: 10.3171/jns.2006.104.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vroone L, Daly AF, Beckers A. Challenges and controversies in the treatment of prolactinomas. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2014;9(6):593–604. doi: 10.1586/17446651.2014.949239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gillam MP, Molitch ME, Lombardi G, Colao A. Advances in the treatment of prolactinomas. Endocr Rev. 2006;27(5):485–534. doi: 10.1210/er.2005-9998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Melmed S, Casanueva FF, Hoffman AR, Kleinberg DL, Montori VM, Schlechte JA, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of hyperprolactinemia: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clini Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(2):273–288. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ, Jamieson CH, Jones DL, et al. Cancer stem cells–perspectives on current status and future directions: AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(19):9339–9344. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Frank NY, Schatton T, Frank MH. The therapeutic promise of the cancer stem cell concept. J Clini Investig. 2010;120(1):41–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI41004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guan Y, Gerhard B, Hogge DE. Detection, isolation, and stimulation of quiescent primitive leukemic progenitor cells from patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Blood. 2003;101(8):3142–3149. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T, et al. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature. 2004;432(7015):396–401. doi: 10.1038/nature03128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pece S, Tosoni D, Confalonieri S, Mazzarol G, Vecchi M, Ronzoni S, et al. Biological and molecular heterogeneity of breast cancers correlates with their cancer stem cell content. Cell. 2010;140(1):62–73. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xu Q, Yuan X, Tunici P, Liu G, Fan X, Xu M, et al. Isolation of tumour stem-like cells from benign tumours. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(2):303–311. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen L, Ye H, Wang X, Tang X, Mao Y, Zhao Y, et al. Evidence of brain tumor stem progenitor-like cells with low proliferative capacity in human benign pituitary adenoma. Cancer Lett. 2014;349(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.03.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mertens F, Gremeaux L, Chen J, Fu Q, Willems C, Roose H, et al. Pituitary tumors contain a side population with tumor stem cell-associated characteristics. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015;22(4):481–504. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lin SJ, Leng ZG, Guo YH, Cai L, Cai Y, Li N, et al. Suppression of mTOR pathway and induction of autophagy-dependent cell death by cabergoline. Oncotarget. 2015;6(36):39329–39341. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen J, Cai I, Song X, Chen X, Huang K, Lu J, et al. Culture and identification of the tumor stem-like cells isolated from rat prolactinoma MMQ cell lines. Chin J Neurosurg. 2015;31(12):1268–1273. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Delellis RA, Lloyd RV, Heitz PU, Eng C. World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of tumours of endocrine organs. Lyon: IARC; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 17.da Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Feng XL, Liu QT, Cao RB, Zhou B, de Li Y, Zhang YP, et al. Gene expression profiling of hybridoma cells after bursal-derived bioactive factor BP5 treatment. Amino Acids. 2012;43(6):2443–2456. doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pan KH, Lih CJ, Cohen SN. Analysis of DNA microarrays using algorithms that employ rule-based expert knowledge. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99(4):2118–2123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.251687398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, Squire J, et al. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2003;63(18):5821–5828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de Wetering M, Begthel H, van den Born M, et al. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature. 2009;457(7229):608–611. doi: 10.1038/nature07602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Visvader JE. Cells of origin in cancer. Nature. 2011;469(7330):314–322. doi: 10.1038/nature09781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sf S, Szczesna K, Iliou MS, Al-Qahtani M, Mobasheri A, Kobolak J, et al. In vitro models of cancer stem cells and clinical applications. BMC Cancer. 2016;16(Suppl 2):738. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2774-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yoshida GJ, Saya H. Therapeutic strategies targeting cancer stem cells. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(1):5–11. doi: 10.1111/cas.12817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Essers MA, Trumpp A. Targeting leukemic stem cells by breaking their dormancy. Mol Oncol. 2010;4(5):443–450. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Knoepfler P. Journal club. A cell biologist looks at the risk and promise of a new insight into stem cells and cancer. Nature. 2009;457(7228):361. doi: 10.1038/457361e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chambers I, Smith A. Self-renewal of teratocarcinoma and embryonic stem cells. Oncogene. 2004;23(43):7150–7160. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Al-Hajj M, Clarke MF. Self-renewal and solid tumor stem cells. Oncogene. 2004;23(43):7274–7282. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rahimi H, Ahmadzadeh A, Yousef-amoli S, Kokabee L, Shokrgozar MA, Mahdian R, et al. The expression pattern of APC2 and APC7 in various cancer cell lines and AML patients. Adv Med Sci. 2015;60(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2015.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Aref S, Salama O, Al-Tonbary Y, Mansour A. Assessment of bcl-2 expression as modulator of fas mediated apoptosis in acute leukemia. Hematology. 2004;9(2):113–121. doi: 10.1080/1024533042000205496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lee JE, Lim MS, Park JH, Park CH, Koh HC. PTEN promotes dopaminergic neuronal differentiation through regulation of ERK-dependent inhibition of S6 K signaling in human neural stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10):1319–1329. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brown PH, Chen TK, Birrer MJ. Mechanism of action of a dominant-negative mutant of c-Jun. Oncogene. 1994;9(3):791–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kreso A, Dick JE. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14(3):275–291. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Takeishi S, Nakayama KI. To wake up cancer stem cells, or to let them sleep, that is the question. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(7):875–881. doi: 10.1111/cas.12958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Takayama MA, Taira T, Tamai K, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H. ORC1 interacts with c-Myc to inhibit E-box-dependent transcription by abrogating c-Myc-SNF5/INI1 interaction. Genes Cells. 2000;5(6):481–490. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2000.00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pagano M, Pepperkok R, Verde F, Ansorge W, Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ming P, Cai T, Li J, Ning Y, Xie S, Tao T, et al. A novel arylbenzofuran induces cervical cancer cell apoptosis and G1/S arrest through ERK-mediated Cdk2/cyclin-A signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2016;7(27):41843. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jurikova M, Danihel L, Polak S, Varga I. Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: Markers of proliferation in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 2016;118(5):544–552. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2016.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang P, Zou F, Zhang X, Li H, Dulak A, Tomko RJ, Jr, et al. microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69(20):8157–8165. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wingert S, Rieger MA. Terminal differentiation induction as DNA damage response in hematopoietic stem cells by GADD45A. Exp Hematol. 2016;44(7):561–566. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2016.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ferrara N, Keyt B. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic biology and clinical implications. Exs. 1997;79:209–232. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9006-9_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, Shou M, Lee CW, Barr S, et al. Local delivery of marrow-derived stromal cells augments collateral perfusion through paracrine mechanisms. Circulation. 2004;109(12):1543–1549. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000124062.31102.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Beck B, Driessens G, Goossens S, Youssef KK, Kuchnio A, Caauwe A, et al. A vascular niche and a VEGF-Nrp1 loop regulate the initiation and stemness of skin tumours. Nature. 2011;478(7369):399–403. doi: 10.1038/nature10525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ochoa AL, Mitchner NA, Paynter CD, Morris RE, Ben-Jonathan N. Vascular endothelial growth factor in the rat pituitary: differential distribution and regulation by estrogen. J Endocrinol. 2000;165(2):483–492. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1650483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Banerjee SK, Zoubine MN, Tran TM, Weston AP, Campbell DR. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor164 and its co-receptor neuropilin-1 in estrogen-induced rat pituitary tumors and GH3 rat pituitary tumor cells. Int J Oncol. 2000;16(2):253–260. doi: 10.3892/ijo.16.2.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kim K, Yoshida D, Teramoto A. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in pituitary adenomas. Endocr Pathol. 2005;16(2):115–121. doi: 10.1385/EP:16:2:115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Banerjee SK, Sarkar DK, Weston AP, De A, Campbell DR. Over expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor during the development of estrogen-induced rat pituitary tumors may mediate estrogen-initiated tumor angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1997;18(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1093/carcin/18.6.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lloyd RV, Scheithauer BW, Kuroki T, Vidal S, Kovacs K, Stefaneanu L. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in human pituitary adenomas and carcinomas. Endocr Pathol. 1999;10(3):229–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02738884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sanchez-Ortiga R, Sanchez-Tejada L, Moreno-Perez O, Riesgo P, Niveiro M, Pico Alfonso AM. Over-expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in pituitary adenomas is associated with extrasellar growth and recurrence. Pituitary. 2013;16(3):370–377. doi: 10.1007/s11102-012-0434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cristina C, Perez-Millan MI, Luque G, Dulce RA, Sevlever G, Berner SI, et al. VEGF and CD31 association in pituitary adenomas. Endocr Pathol. 2010;21(3):154–160. doi: 10.1007/s12022-010-9119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Luque GM, Perez-Millan MI, Ornstein AM, Cristina C, Becu-Villalobos D. Inhibitory effects of antivascular endothelial growth factor strategies in experimental dopamine-resistant prolactinomas. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;337(3):766–774. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.177790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cristina C, Luque GM, Demarchi G, Lopez Vicchi F, Zubeldia-Brenner L, Perez Millan MI, et al. Angiogenesis in pituitary adenomas: human studies and new mutant mouse models. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:608497. doi: 10.1155/2014/608497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.


