Abstract
For the purpose of improving recombinant protein production from mammalian cells, an unbiased, high-throughput whole-genome RNA interference screen was conducted using human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK 293) cells expressing firefly luciferase. 21,585 human genes were individually silenced with three different siRNAs for each gene. The screen identified 56 genes that led to the greatest improvement in luciferase expression. These genes were found to be included in several pathways involved in spliceosome formation and mRNA processing, transcription, metabolic processes, transport and protein folding. The 10 genes that most enhanced protein expression when down regulated, were further confirmed by measuring the effect of their silencing on the expression of three additional recombinant proteins.
Among the confirmed genes, OAZ1- the gene encoding the ornithine decarboxylase antizyme1- was selected for detailed investigation, since its silencing improved the reporter protein production without affecting cell viability. Silencing OAZ1 caused an increase of the ornithine decarboxylase enzyme and the cellular levels of putrescine and spermidine; an indication that increased cellular polyamines enhances luciferase expression without affecting its transcription. The study shows that OAZ1 is a novel target for improving expression of recombinant proteins. The genome-scale screening performed in this work can establish the foundation for targeted design of an efficient mammalian cell platform for various biotechnological applications.
Keywords: siRNA, HEK 293, OAZ1, Luciferase, protein production
Introduction
RNA interference (RNAi), first discovered as a natural biological process of eukaryotic cells for protecting the genome against foreign nucleic acids (Napoli et al., 1990; van der Krol et al., 1990), has been developed and utilized as a revolutionary tool in deducing gene functions and in combating genetic defects, viral diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancers (Aagaard and Rossi, 2007). siRNAs are 21–25 nucleotide double-strand RNA fragments with symmetric 2-nucleotides 3’-end overhangs (Hamilton and Baulcombe, 1999). The guide strand of siRNA can be incorporated into RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which brings about sequence-specific degradation of the homologous single stranded mRNAs (Jinek and Doudna, 2009). In recent years, large-scale genetic screens have been made possible by the availability of genome-wide siRNA libraries, as well as the development of sophisticated new instrumentation and bioinformatics approaches for data analysis (Conrad and Gerlich, 2010; Huang et al., 2009). They have been used to investigate the biological functions of specific genes and pathways in various diseases (Seyhan and Rya, 2010) and important biological processes, including signal transduction, cell aging or death, cell or organelle organization, protein localization and responses of host cells to pathogens (Bard et al., 2006;.Brognard and Hunter, 2011; Cherry, 2008; Ni and Lee, 2010;Orvedahl et al., 2011). However, there has been limited use of a genome-wide siRNA screen for improving heterologous protein production (Bard et al., 2006; Simpson et al., 2012), an important process intensively investigated by the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry.
In the current work, we performed a genome-wide siRNA screen to identify genes that may influence recombinant protein production, using Photinus pyralis (firefly) luciferase as a reporter protein. With a high-throughput format, 21,585 genes were individually silenced with three different siRNAs, in HEK-CMV-Luc2-Hygro cells constitutively expressing firefly luciferase. The viable cell number and the luciferase activity were measured following the screening and the results were incorporated into genome-wide loss-of-function data. Statistical data analyses were conducted, followed by a validation screen where ten target genes (leading to greatest improvement of luciferase production) were confirmed. Among these selected genes, OAZ1 the gene that encodes antizyme 1, an inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase (Pegg, 2006),was chosen for more detailed studies, since its silencing caused minimal effect on cell viability.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
HEK-CMV-Luc2-Hygro cell line constitutively expressing P. pyralis luciferase (Progema) and HEK- GPC3-hFc cell line constitutively secreting glypican-3 hFc-fusion protein (GPC3-hFc)(Feng et al., 2013) (a gift from Dr. Mitchell Ho, NCI, National Institutes of Health) were maintained in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). The inducible T-Rex-SERT-GFP cell line (Abdul-Hussein et al. 2013)and T-Rex-NTSR1-GFP cell line (Xiao et al. 2015) were maintained as an adherent culture in DMEM containing 10% certified FBS, 5µg/mL blasticidin and 200µg/mL zeocin (Invitrogen). All cells were maintained in a humidified incubator set at 37°C and 5% CO2.
High-throughput genome-wide screen for luciferase expression
The Silencer® Select Human genome siRNA library (Ambion), which targets 21,585 human genes with 3 siRNAs per gene, was used for screening. Each siRNA is arrayed in an individual well (Corning 3570, 384 well, white, solid bottom plates). The transfection was done in duplicates: 0.8 pmol of each siRNA was spotted to a well of a 384-well plate (Corning) and 20 µL of serum-free DMEM containing 0.07 µL of Lipofectamine RNAiMax (Life Technologies) was then added to each well. This lipid-siRNA mixture was incubated at ambient temperature for 30 minutes prior to addition of 4000 cells in 20 µL of DMEM containing 20% FBS (Gibco). After incubating the transfected cells at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 72 hours, 20 µL of ONE-Glo™ Reagent (Promega) was added to one set of replicates for ‘overall luciferase yield’ quantification and 20 µL of Cell Titer-Glo™ Reagent (Promega) was added to the second set of replicates for ‘viable cell density’ measurement. All plates were incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes to stabilize the luminescent signal and the signal was then measured with PerkinElmer Envision 2104 Multilabel plate reader. All plates had a full column (16 wells) of Silencer Select Negative Control #2 (Life Technologies) for data normalization and a full column of siPLK1 (Ambion Silencer Select, cat# s448) was also used as on-plate reference for transfection efficiency. Both controls were also used in all validation transfections.
The 56 genes which got targeted by at least two independent siRNAs (out of three) resulting in enhanced luciferase production with MAD-based z-score>3 from the primary screen were subjected to validation screen using 3 additional Silencer® siRNAs (Ambion) with different sequences from those used in the primary screen. Ten gene candidates were selected based on the criteria that 3 out of 6 siRNAs displayed a MAD-based z-score>3. The transfection and assay processes were the same as in the primary genome-wide screen. Data visualization was performed in R computational environment (https://www.R-project.org/) by using ‘hexbin’ and ‘ggplot2’ packages (R Core Team, 2015; Carr, 2015; Wickham, 2009).
Statistical analysis of primary screen data
The screen generated end-point data for ‘overall luciferase yield’ and ‘viable cell density’ in each well. For each plate, the median value of the negative control wells was set as 100% and was used to normalize corresponding sample wells. The ‘overall luciferase yield’ and ‘viable cell density’ were exported as % of negative control and the median absolute deviation (MAD) - based z-score was calculated for each sample (Chung et al., 2008).
Gene ontology (GO) analysis
In order to get the maximum coverage of GO annotation data for 119 selected siRNA’s targeting 56 genes, PANTHER classification system (http://www.pantherdb.org/) and AmiGO 2 GO browser were used (Mi et al., 2013; Carbon et al., 2009). The construction of a heat map was accomplished using Partek® Genomics Suite® software, version 6.6 Copyright ©; 2015, Partek Inc., St. Louis, MO, USA.
Validation transfection
Ten targeted genes were selected and tested in four HEK 293 cell lines expressing different reporter proteins, glycan-3 hFc-fusion protein (GPC3-hFc), neurotensin receptor type 1-GFP (NTSR1-GFP) and serotonin transporter-GFP (SERT-GFP), using 1 representative siRNA for each gene. Transfection was performed in 12-well plate format. 500µL of serum-free DMEM media containing siRNA and Lipofectamine RNAiMax was incubated in each well for 20 min at ambient temperature and 500µL DMEM containing 20% FBS and cells was then added for transfection. The final siRNA concentration in each well was 40nM. Lipofectamine RNAiMax volumne and cell seeding number in each well have been optimized for each cell line (Table S1).
ELISA for determination of GPC3-hFc production
5 days after transfection, clarified cell culture supernatant was used for determination of GPC3-hFc concentration by ELISA and cells were detached and counted by trypan blue exclusion using a CEDEX cell quantification system (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). AffiniPure F(ab’)2 Fragment Goat Anti-Human IgG (min X Bov, Ms, RbSrProt, Cat. 109-006-170, Jackson Immunology,5µg/mL in PBS) was used to coat a 96-well plate (50 µL per well) at 4°C overnight. After blocking the plate with 2% BSA in PBS, 50µl of pre-diluted cell culture supernatant was added, and the plate was incubated at room temperature for 1 h to allow binding to occur. After the plate was washed twice with PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20, Peroxidase-conjugated AffiniPure Goat-anti-human IgG (Cat. 109-035-098, Jackson Immunology) was added at 1:4000 dilution (50µL/well). Following incubation at room temperature for 1 hour, the plate was washed 4 times and signals were detected with Peroxidase Substrate System (KPL).
Flow cytometry analysis for determination of NTSR1-GFP and SERT-GFP production
3 days after transfection, cells were induced with 1µg/mL tetracycline. 24 hours later, cells from each well were detached with non-enzymatic cell dissociation buffer (Gibco, Cat. No. 13150-016) and washed twice with cold PBS. Cell densities were adjusted to 0.5 million cells/mL with PBS and then subjected to flow cytometry analysis. Green fluorescence was measured with Guava Easycyte 5HT and Incyte software (Millipore). The green fluorescence signal and cell gating were adjusted using uninduced T-REx-293-NTSR1-GFP cells, with more than 99.5% of the cells in low fluorescence range (<100). The setting was kept the same for all cell samples.
OAZ1 silencing studies
HEK-CMV-Luc2-Hygro cells in 6 well plates were transfected with Silencer siRNA for oaz1 gene (Catalog number: AM51331, assay ID: 46078). The transfection was done in 6-well plate format: 0.12 nmol of each siRNA and 1.5mL of serum-free DMEM containing 11.25 µL of Lipofectamine RNAiMax (Life Technologies) was then added to each well. This lipid-siRNA mixture was incubated at ambient temperature for 30 min prior to adding 2×105 cells in 1.5mL of DMEM containing 20% FBS (Gibco). The transfected cells were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 and were harvested after 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours. Luciferase activity was determined using ONE-Glo™ Reagent (Promega) and aliquots of transfected cells.
Isolation of RNA and real-time qRT-PCR
Cells were trypsinized from 6-well plates, washed twice with cold PBS and cell pellets were flash frozen on dry ice and stored at −80°C until extraction. RNA was extracted using the RNeasy kit (Qiagen) and then treated with DNase using TURBO DNA-free™ Kit (Life Technologies). cDNA was generated from the RNA using the Maxima Frist Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit for qRT-PCR (Thermo Scientific). The real-time qPCR was performed using Fast SYBR® Green Master Mix (Life Technologies) in 7900 HT Fast Real Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems).The 2−ΔΔCt method was used for relative expression analysis(Livak and Schmittgen, 2001) with GAPDH as the reference gene. Cells transfected with negative control siRNA and harvested after 24hours were set as calibrator. Primers used for each gene are: luc (Promega), 5’-TCACGAAGGTGTACATGCTTTGG-3’ and 5’-GATCCTCAACGTGCAAAAGAAGC-3’; ODC1, 5’-TAAAGGAACAGACGGGCTCT-3’ and 5’- CCATAGACGCCATCATTCAC-3’; OAZ1: 5’- GGAACCGTAGACTCGCTCAT-3’ and 5’-TCGGAGTGAGCGTTTATTTG-3’; GAPDH: 5’- CATCAATGGAAATCCCATCA-3’ and 5’- TTCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGAC-3’.
Western blotting
Transfected cells were lysed in buffer containing 50 mMTris-HCl, pH 7.4, 5 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40, and protease inhibitor mixture. Proteins (~20 µg) were separated by SDS-PAGE (4–12% gel) in MES buffer and transferred to 0.2-µm nitrocellulose membrane for immunodetection using mouse anti-ODC (Sigma, catalog number O1136) and mouse anti-β-actin (BD biosciences, catalogue number 612657) primary antibodies and HRP conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibodies (abCAM, catalog number ab20043). Signals were detected with an ECL Plus chemiluminescence reagent.
Measurement of cellular polyamine concentration
Cells in six-well plates were washed twice with PBS, harvested, and precipitated with 0.1mL cold 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA). A total of 50µL of the TCA supernatant was used for polyamine analysis by an ion exchange chromatographic system (Biochrom). TCA precipitates were dissolved in 0.1 N NaOH and aliquots were used for protein determination by the Bradford method. Polyamine contents were estimated as nmol/mg protein.
Results
1. Identification of genes whose silencing leads to enhanced luciferase expression
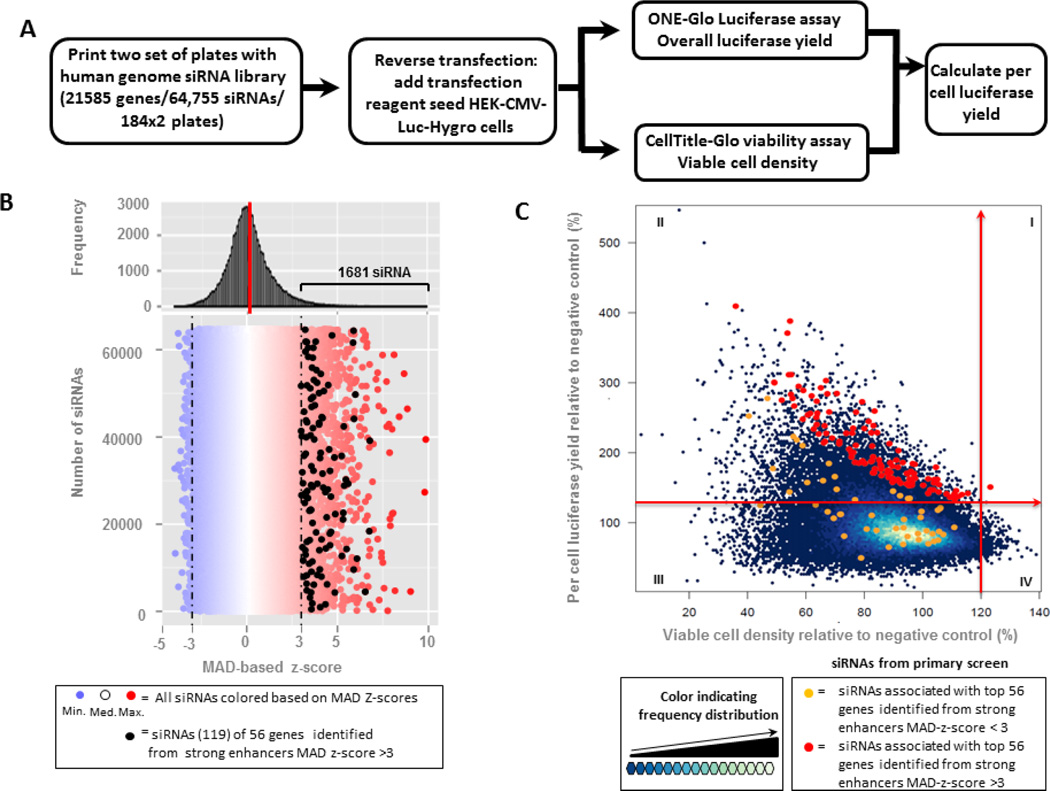
A human genome-wide siRNA screen was conducted in HEK-CMV-Luc2-Hygrocells by using siRNA library targeting 21,585 human genes, with 3 independent arrayed siRNAs per gene. The transfection was done in duplicate: one set of plates was used for measuring the overall luciferase yield and the second set was used for the determination of viable cell density, from which the per cell luciferase yield was calculated (Figure 1A). The distribution of siRNA activity based on the overall luciferase yield is illustrated in the histogram shown in Figure 1B, where the red and blue colour circle indicates up and down regulation of luciferase expression, respectively. Out of the 64,755 siRNA’s tested 1,681 significantly enhanced luciferase expressions (MAD-based z-score > 3, or 40% to 178% higher than negative control). From these 1,681 siRNAs, 56 genes with at least 2 siRNAs scoring > 3 MAD were selected and subjected to follow up evaluation with additional siRNAs.11,207 (17.3%) of the siRNAs tested, listed in Table S3, improved per cell luciferase expression by more than 20% (Fig. 1C quadrant I&II), while only 254(0.4%) of the siRNAs tested, listed in Table S2, achieved more than 20% enhancement in viable cell density (Fig. 1C quadrant I&IV). The 168 siRNAs associated with the 56 selected genes are indicated by red or orange circles, in which red was used as the colour for siRNAs with > 3 MAD score,
Fig. 1. Genome-wide human siRNA library screen with HEK-CMV-luc2-Hygro cell line.
(A) Workflow of the primary screen; (B) Distribution of siRNA effect on improved overall luciferase expression, The 119 siRNAs corresponding to 56 identified genes with strong enhancer MAD z-score (>3) are indicated as black circles. (C)Relative per cell luciferase yield as a function of the relative cell viability for each sRNA tested. The 20% increase cut-offs are highlighted and divide the entire population into quadrants (I, II, III and IV). siRNAs associated with top 56 genes with a MAD-z score>3 are indicated as red circles and those with MAD-z-score < 3 as orange circles.
2. Identification of pathways affecting viable cell density and recombinant protein productivity
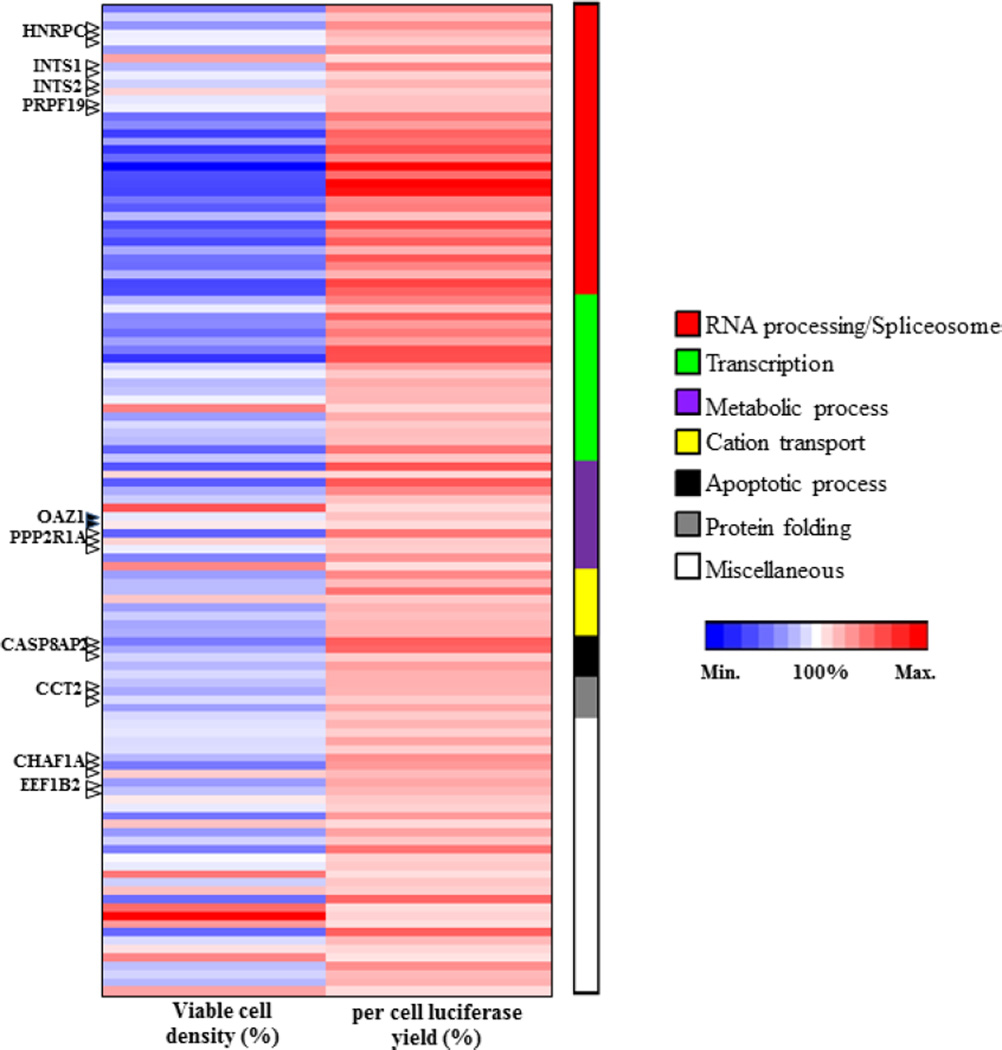
To identify pathways that affect the reporter protein production, functional ontology analyses were carried out using the 119 siRNAs (Table 3) against the 56 genes that significantly improved the specific luciferase yield, using the PANTHER (http://www.pantherdb.org/) (Mi et al., 2013) and AmiGO 2 GO browser (Carbon et al., 2009). The heat map (Figure 2) shows that all the siRNAs enhanced per cell luciferase yield (pink to red spectrum), but the majority negatively affected the cell viability (blue shades) which is undesirable in recombinant protein production. The enhancer siRNAs were found to be enriched in the following specific pathways: mRNA processing/spliceosome, transcription, metabolic process, cation transport and protein folding.
Table 3.
List of the 119 SiRNA targeting the selected 56 genes
| No. | Symbol | Viable cell density (%) |
per cell luciferase yield (%) |
Gene_ID | siRNA sequence | Biological process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | APOBEC3H | 66.938 | 227.583 | 164668 | AGAGGCUACUUUGAAAACAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 2 | APOBEC3H | 88.955 | 171.805 | 164668 | CAAGUCACCUGUUACCUCAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 3 | HNRNPC | 73.809 | 227.741 | 3183 | ACACUCUUGUGGUCAAGAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 4 | HNRNPC | 96.599 | 184.201 | 3183 | GAUGAAGAAUGAUAAGUCAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 5 | HNRNPC | 97.392 | 163.496 | 3183 | CAACGGGACUAUUAUGAUAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 6 | HNRPDL | 75.879 | 227.884 | 9987 | CCCGGAUACUUCUGAAGAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 7 | HNRPDL | 108.214 | 140.868 | 9987 | GAACGAGUACAGCAAUAUAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 8 | INTS1 | 83.129 | 238.606 | 26173 | GUUCAUCCAUAAGUACAUUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 9 | INTS1 | 96.256 | 153.438 | 26173 | AGAUCUUUGUCAAGGUGUAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 10 | INTS2 | 88.908 | 185.522 | 57508 | GACAUUGGAUCAUACUAAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 11 | INTS2 | 103.888 | 156.977 | 57508 | GGCGAAUGCUCCUGACUAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 12 | PRPF19 | 94.579 | 170.349 | 27339 | GCGCAAGCUUAAGAACUUUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 13 | PRPF19 | 97.007 | 170.088 | 27339 | GCUCAUCGACAUCAAAGUUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 14 | RBM22 | 63.879 | 256.443 | 55696 | CCAUAUAUCCGAAUGACCAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 15 | RBM22 | 71.395 | 212.652 | 55696 | CGGAAUCAAUGAUCCUGUAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 16 | SART1 | 51.696 | 275.068 | 9092 | GCAUCGAGGAGACUAACAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 17 | SART1 | 77.169 | 257.929 | 9092 | CAAUGAUUCUUACCCUCAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 18 | SF3B3 | 49.133 | 300.611 | 23450 | CAACCUUAUUAUCAUUGAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 19 | SF3B3 | 62.659 | 233.649 | 23450 | GUUUCAUCUGGGUUCGCUAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 20 | SF3B4 | 35.915 | 409.361 | 10262 | GCAUCAGCUCACAACAAAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 21 | SF3B4 | 55.962 | 266.627 | 10262 | GUCCUAUCACCGUAUCUUAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 22 | SNRPB | 54.559 | 388.072 | 6628 | AGAUACUGGUAUUGCUCGAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 23 | SNRPB | 53.645 | 370.824 | 6628 | UGGUCUCAAUGACAGUAGAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 24 | SNRPB | 66.394 | 238.463 | 6628 | GGCUGUACAUAGUCCUUUUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 25 | SNRPD2 | 58.901 | 247.842 | 6633 | UGUGGACUGAGGUACCCAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 26 | SNRPD2 | 82.950 | 171.198 | 6633 | CUGCCGCAACAAUAAGAAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 27 | SNRPE | 54.945 | 311.516 | 6635 | GGAUCAUGCUAAAAGGAGAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 28 | SNRPE | 64.385 | 226.659 | 6635 | CAUUGGUUUUGAUGAGUAUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 29 | SNRPF | 54.854 | 283.281 | 6636 | AGGGCUAUCUGGUAUCUGUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 30 | SNRPF | 79.386 | 188.094 | 6636 | GGUGUAAUAAUGUCCUUUAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 31 | U2AF1 | 65.083 | 292.710 | 7307 | GAAUAACCGUUGGUUUAAUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 32 | U2AF1 | 63.672 | 240.287 | 7307 | GGAACACUAUGAUGAGUUUtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 33 | U2AF1 | 82.333 | 187.362 | 7307 | GGUGCUCUCGGUUGCACAAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 34 | U2AF2 | 54.133 | 311.348 | 11338 | CCAACUACCUGAACGAUGAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 35 | U2AF2 | 55.405 | 277.511 | 11338 | CAGCAAACCUUUGACCAGAtt | RNA processing/Spliceosome |
| 36 | CNOT1 | 81.492 | 244.722 | 23019 | GCUAUUUCCAGCGAAUAUAtt | Transcription |
| 37 | CNOT1 | 96.002 | 173.284 | 23019 | GGAGGAAUCUCGAAUGCGAtt | Transcription |
| 38 | KAT5 | 70.586 | 284.565 | 10524 | GGAGAAAGAAUCAACGGAAtt | Transcription |
| 39 | KAT5 | 71.473 | 216.209 | 10524 | GGACGGAAGCGAAAAUCGAtt | Transcription |
| 40 | L3MBTL4 | 63.577 | 250.367 | 91133 | GAACUUCAAUGGAAAACAUtt | Transcription |
| 41 | L3MBTL4 | 77.107 | 210.336 | 91133 | GAUCGUUUGAGAGAACAAAtt | Transcription |
| 42 | MZF1 | 66.872 | 302.994 | 7593 | CAGGUAGUGUAAGCCCUCAtt | Transcription |
| 43 | MZF1 | 49.189 | 299.886 | 7593 | AGGUUACAGAGGACUCAGAtt | Transcription |
| 44 | NKX3-2 | 88.616 | 212.905 | 579 | GAACCGUCGCUACAAGACAtt | Transcription |
| 45 | NKX3-2 | 96.869 | 162.999 | 579 | CCCUCCUACUAUUACCCGUtt | Transcription |
| 46 | POU5F1 | 83.011 | 194.043 | 5460 | GGAGAUAUGCAAAGCAGAAtt | Transcription |
| 47 | POU5F1 | 85.820 | 180.401 | 5460 | GUCCGAGUGUGGUUCUGUAtt | Transcription |
| 48 | RDBP | 97.298 | 183.386 | 7936 | AGAGGACCCAGAUUGUCUAtt | Transcription |
| 49 | RDBP | 111.487 | 145.707 | 7936 | AAGUCAACAUAGCCCGAAAtt | Transcription |
| 50 | TBX1 | 75.599 | 193.846 | 6899 | GCAAAGAUAGCGAGAAAUAtt | Transcription |
| 51 | TBX1 | 91.538 | 161.634 | 6899 | GGAUCACGCAGCUCAAGAUtt | Transcription |
| 52 | ZBTB41 | 85.750 | 176.019 | 360023 | CCAGUUCGACCUGAACAAAtt | Transcription |
| 53 | ZBTB41 | 83.351 | 171.308 | 360023 | GACCUAUACUCAUUCUGCAtt | Transcription |
| 54 | ZNF358 | 61.490 | 256.085 | 140467 | GUUUCGACCUCGAUCCAGAtt | Transcription |
| 55 | ZNF358 | 85.866 | 167.413 | 140467 | CAGCCUCACCAAGCACAAAtt | Transcription |
| 56 | ABCB8 | 57.472 | 294.800 | 11194 | CGACCAUCAUGGAAAACAUtt | Metabolic process |
| 57 | ABCB8 | 103.662 | 146.993 | 11194 | CGCUUUAACUGGAAGCUCUtt | Metabolic process |
| 58 | ACSF2 | 59.084 | 288.857 | 80221 | GAAACUGCAUGAGAAGACAtt | Metabolic process |
| 59 | ACSF2 | 80.013 | 234.608 | 80221 | CGAUGUUCGUGGACAUUCUtt | Metabolic process |
| 60 | ALDH3A2 | 87.831 | 171.072 | 224 | CACUUUCCUGGGUAUUGUAtt | Metabolic process |
| 61 | ALDH3A2 | 115.513 | 141.760 | 224 | CAACAGUACUUACCGAUGUtt | Metabolic process |
| 62 | OAZ1 | 94.839 | 169.972 | 4946 | GCCUUGCUCCGAACCUUCAtt | Metabolic process |
| 63 | OAZ1 | 101.904 | 141.842 | 4946 | GAUUAUCCUUGUACUUUGAtt | Metabolic process |
| 64 | PPP2R1A | 60.645 | 254.007 | 5518 | GAACAGCUGGGAACCUUCAtt | Metabolic process |
| 65 | PPP2R1A | 104.020 | 161.613 | 5518 | CUUCGACAGUACUUCCGGAtt | Metabolic process |
| 66 | PPP2R1A | 96.357 | 157.243 | 5518 | GGAGUUCUUUGAUGAGAAAtt | Metabolic process |
| 67 | 4-Sep | 68.989 | 220.902 | 5414 | GGACCAAGCCCUAAAGGAAtt | Metabolic process |
| 68 | 4-Sep | 110.815 | 140.658 | 5414 | GCAGUGGACAUAGAAGAGAtt | Metabolic process |
| 69 | DENND5B | 76.131 | 235.013 | 160518 | CGAUAUGCUUUUCUACGUUtt | Cation transport |
| 70 | DENND5B | 83.636 | 176.821 | 160518 | CCAGCGAUACAACUCCUAUtt | Cation transport |
| 71 | KCNJ10 | 83.512 | 259.478 | 3766 | GCAGGCACAUGGUUCCUCUtt | Cation transport |
| 72 | KCNJ10 | 105.029 | 161.785 | 3766 | AGGUCAAUGUGACUUUCCAtt | Cation transport |
| 73 | KCTD15 | 76.798 | 186.195 | 79047 | CCAAGUCCAAUGCACCUGUtt | Cation transport |
| 74 | KCTD15 | 88.009 | 174.946 | 79047 | CCUGGACAGUUUGAAGCAAtt | Cation transport |
| 75 | SLC12A8 | 78.156 | 185.175 | 84561 | GCUUCCUCUUGGACCUCAAtt | Cation transport |
| 76 | SLC12A8 | 80.173 | 184.608 | 84561 | GCGGAAAAGGUAUCCCUCAtt | Cation transport |
| 77 | CASP8AP2 | 67.320 | 284.062 | 9994 | CCAACAAGGAAGACGAAAAtt | Apoptotic process |
| 78 | CASP8AP2 | 79.253 | 272.683 | 9994 | CCCUGUUCAUUAUAAGUCUtt | Apoptotic process |
| 79 | CASP8AP2 | 89.677 | 157.868 | 9994 | GGAUAUUGGAGGCUAGUCAtt | Apoptotic process |
| 80 | CDCA7 | 82.689 | 209.398 | 83879 | GACUAUUGAUACCAAAACAtt | Apoptotic process |
| 81 | CDCA7 | 90.976 | 189.252 | 83879 | GCAAUGCUUGCAAAACUCAtt | Apoptotic process |
| 82 | CCT2 | 85.046 | 189.850 | 10576 | CAUUGGUGUUGACAAUCCAtt | Protein folding |
| 83 | CCT2 | 79.093 | 186.786 | 10576 | GUUGCAAACUUAUCGAGGAtt | Protein folding |
| 84 | CCT2 | 91.558 | 160.246 | 10576 | CUCUUAUGGUAACCAAUGAtt | Protein folding |
| 85 | CCT7 | 76.280 | 200.322 | 10574 | AAAUGCAACCCAAAAAGUAtt | Protein folding |
| 86 | CCT7 | 90.987 | 160.687 | 10574 | GUACCUGCGGGAUUACUCAtt | Protein folding |
| 87 | C22orf26 | 93.181 | 185.763 | 55267 | CCACCCUACUAUGUACUGUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 88 | C22orf26 | 94.537 | 155.385 | 55267 | GCUAAGUCUUUUCCACAGUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 89 | C3orf19 | 91.714 | 202.960 | 51244 | CAGUUACUUUCAAAACUCUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 90 | C3orf19 | 92.429 | 156.418 | 51244 | CAACAGAUCAGAGAACAAAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 91 | CHAF1A | 82.390 | 228.483 | 10036 | GCCUGAAUCUUGUCCCAAAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 92 | CHAF1A | 66.511 | 215.853 | 10036 | GAAGAAGACUCUGUACUCAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 93 | CHAF1A | 104.553 | 179.207 | 10036 | CGAAACUUGUCAACGGGAAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 94 | EEF1B2 | 75.570 | 200.070 | 1933 | AGAAAGCUUUGGGCAAAUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 95 | EEF1B2 | 85.471 | 183.071 | 1933 | GGAAGAACGUCUUGCACAAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 96 | EEFSEC | 101.897 | 162.677 | 60678 | GAACAAAAUAGACCUCUUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 97 | EEFSEC | 95.368 | 152.850 | 60678 | CUGUGGAAAAGAUACCGUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 98 | FAM102A | 66.121 | 214.156 | 399665 | GCCCACUAUUCUCAGCUCAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 99 | FAM102A | 105.514 | 143.889 | 399665 | GCAUCUGUCCGAUCGCUCUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 100 | FRZB | 74.811 | 205.132 | 2487 | GGGACACUGUCAACCUCUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 101 | FRZB | 89.583 | 163.431 | 2487 | CAUCAAGCCCUGUAAGUCUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 102 | ICA1L | 67.947 | 258.104 | 130026 | UGAAGAUAAUCGAGAAAUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 103 | ICA1L | 100.201 | 153.426 | 130026 | ACAGGUCUUUAUCAAAGCAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 104 | MARK2 | 95.471 | 162.372 | 2011 | GACUCAGAGUAACAACGCAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 105 | MARK2 | 112.248 | 137.554 | 2011 | GCCUAGGAGUUAUCCUCUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 106 | MFRP | 88.359 | 164.639 | 83552 | CUAACUACCCAGACCCUUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 107 | MFRP | 105.583 | 154.286 | 83552 | GCAACAGAAUCGAGCAAGAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 108 | MGRN1 | 63.690 | 273.535 | 23295 | CCCUGAAGGUUACCUCUUUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 109 | MGRN1 | 113.437 | 140.103 | 23295 | GGAUGACGAGCUGAACUUUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 110 | OCRL | 123.199 | 150.843 | 4952 | GAUUACUUCUUGACUAUCAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 111 | OCRL | 109.377 | 136.174 | 4952 | CUCCCGCAGUUGAACAUCAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 112 | OR10P1 | 61.943 | 281.113 | 121130 | CUCUGAUUGUCACCUCUUAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 113 | OR10P1 | 91.526 | 179.268 | 121130 | GCUCCUCUGUUACCACAGAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 114 | PRR15 | 102.629 | 146.756 | 222171 | CGCUCACCAACAGCAGAAAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 115 | PRR15 | 110.986 | 133.601 | 222171 | CUUUUAAUGUUAAACUACAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 116 | RAB31 | 84.418 | 228.634 | 11031 | GAACUUCACAAGUUCCUCAtt | Miscellaneous |
| 117 | RAB31 | 89.607 | 180.764 | 11031 | CAAUGGAACAAUCAAAGUUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 118 | TACC2 | 82.634 | 188.258 | 10579 | GGAUUACAGAAACUCCUAUtt | Miscellaneous |
| 119 | TACC2 | 108.211 | 141.104 | 10579 | GAGCAGAGAUCAUAACCAAtt | Miscellaneous |
Fig. 2. Functional categorization of strong enhancer siRNA-associated genes.
Heat map was generated based on percent viable cell density and per cell luciferase yield for each of the 119 siRNAs that significantly enhanced luciferase production. The values are indicated by range of red (maximum) and blue (minimum) intensities. The functional categories are indicated by bars of different colours and the numbers of siRNAs in each group indicated by the bar lengths.
3. Selection of ten genes whose silencing leads to enhanced luciferase expression
For selecting gene candidates for further work, three additional siRNAs were tested for each of the 56 target genes identified from the primary screen. From the combined data of the primary and the validation screen of the 56 genes, ten genes were selected, based on the criteria that at least 3 out of the 6 siRNAs tested displayed a MAD-based z-scores higher than 3.0 (Table 1). The viable cell number was also taken into consideration to remove candidates with significant toxicity. The median value of the overall luciferase yield for each selected gene calculated from the 6 siRNAs was improved by 24% to 72% compared with negative control, and the median of MAD-based z-scores ranged from 2.13 to 4.55.
Table 1.
Confirmed top 10 genes with 3 or more siRNAs yielding > 50% increase in luciferase activity. A 50% increase is biologically relevant and also corresponds to high statistical significance (>3 MAD-based z-scores).
| Gene | Description | Overall luciferase yield (%)*,† |
MAD-based z-score* |
Viable cell density (%)*,† |
MAD-based z-score* |
Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INTS1 | Integrator Complex Subunit 1 |
172 | 4.55 | 96 | 0.46 | 3’- end processing of small nuclear RNAs U1 and U2 |
| INTS2 | Integrator Complex Subunit 2 |
165 | 4.17 | 89 | −0.11 | 3’- end processing of small nuclear RNAs U1 and U2 |
| HNRNPC | Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein |
163 | 4.10 | 97 | 0.48 | Influencing pre-mRNA processing and other aspects of mRNA metabolism and transport |
| CASP8AP2 | Caspase 8 Associated Protein 2 |
156 | 3.70 | 79 | −0.86 | Activation and regulation of CASP8 in FAS-mediated apoptosis |
| OAZ1 | Ornithine Decarboxylase Antizyme |
153 | 3.57 | 115 | 0.36 | Inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase and inactivating the polyamine uptake transporter |
| PPP2R1A | Protein Phosphatase 2, Regulatory Subunit A, Alpha |
153 | 3.56 | 96 | 0.46 | Serving as a scaffold for Protein Phosphatase 2 assembly, essential for signal transduction pathways |
| PRPF19 | Pre-mRNA Processing Factor 19 |
147 | 3.27 | 96 | 0.41 | Spliceosome assembly and activating pre-mRNA splicing |
| CHAF1A | Chromatin Assembly Factor 1, Subunit A |
138 | 2.80 | 82 | −0.62 | mediating chromatin assembly in DNA replication and DNA repair |
| CCT2 | Chaperonin Containing TCP1, Subunit 2 (Beta) |
126 | 2.23 | 85 | −0.41 | Chaperonin-mediated protein folding of actin, tubulin and other proteins |
| EEF1B2 | Eukaryotic Translation Elongation Factor 1 Beta 2 |
124 | 2.13 | 85 | −0.38 | exchanging GDP bound to EF-1-α to GTP during the transfer of aminoacylated tRNAs to the ribosome |
All values are medians of result from 6 siRNAs (3 siRNAs in primary screen and 3 siRNAs in validation screen) targeting a top gene.
Values are normalized to negative control siN.C. transfected cells (set as 100%).
Four out of the ten target genes, INTS1, INTS2, HNRNPC, and PRPF19, are involved in mRNA splicing process; they encode important proteins for spliceosome formation, such as integrator complex, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein and pre-mRNA processing factor 19. The remainder of the identified genes encodes proteins involved in a wide span of biological functions, including cell growth and division, signal transduction, apoptosis, regulation of cellular polyamine concentration and protein translation and folding.
4. Effects of silencing the ten target genes on secreted and membrane protein production
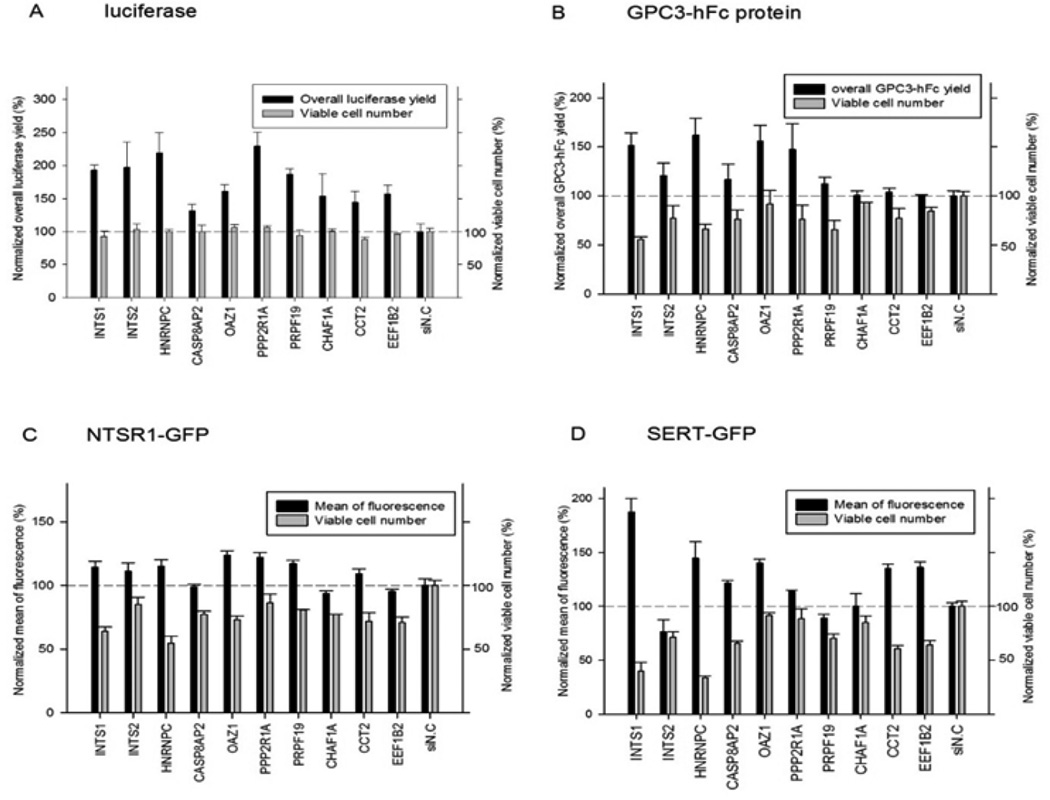
To examine the silencing effect of the 10 selected genes on the expression of other recombinant proteins from HEK293 cells, three additional cell lines were tested: 1) HEK-GPC3-hFc cell line, which constitutively secretes glypican −3 hFc-fusion protein (GPC3-hFc) (Feng et al., 2013) as a representative of antibody secreting cell lines, 2) T-REx-293-NTSR1-GFP cell line constructed previously for the production of functional neurotensin receptor type I (NTSR1)(Xiao et al., 2015) and 3) T-REx-293-SERT-GFP cell line (Abdul-Hussein et al., 2013), an inducible cell line for high level expression of serotonin transporter (SERT), a “hard-to-express” 12 transmembrane domain protein. Both NTRS1 and SERT were fused with GFP at the C-terminus, allowing proximal protein quantification by flow cytometry. As shown in Figure 3, the siRNAs against the ten selected genes exhibited varying effects on the expression of the secreted and the membrane proteins. The silencing of INTS1, HNRHPC, OAZ1 and PPP2R1A consistently improved the expression of all reporter proteins tested. However, the silencing of INTS1 and HNRNPC led to a significantly reduced viable cell number, an indication that these genes may be essential for cell survival or cell growth. Silencing of the OAZ1 and PPP2R1A genes showed minimal negative effects on the viable cell number.
Fig. 3. Effects of the 10 selected enhancer siRNAs on four HEK cell lines expressing different recombinant proteins.
(A) Luciferase, (B) GPC3-hFc, (C) NTSR1-GFP, (D) SERT-GFP; Protein expression and cell viability were normalized against cells transfected with the negative control siRNA (si N.C.). The experiment was performed twice with different passages of cells. For each biological sample, the measurement was done in duplicates. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM).
5. Effect of silencing OAZ1 on luciferase expression
Among the selected genes, the antizyme 1 (OAZ1) was chosen for follow-up studies since its silencing consistently improved cytosolic, secreted and membrane protein expression and caused minimal growth disadvantage in the four cell lines tested (Figure 3). Five of the six OAZ1siRNAs tested (Table 2) enhanced luciferase production (luciferase activity (%)) by 28–74%, and OAZ1 siRNA5 was chosen for the rest of the study. Unlike OAZ1 siRNAs, the siRNAs against antizyme isoforms OAZ2 (a minor isoform) and OAZ3 (a testis specific form) caused no significant enhancement of luciferase production (Table 2).
Table 2.
The list of siRNAs targeting the polyamine pathway genes, OAZ1, OAZ2, OAZ3, ODC and AZIN1 and their effects on luciferase activity, cell viability and per cell luciferase yield. The data are from the primary siRNA screen, except for the last three additional siRNAs against OAZ1
| Gene Symbol | siRNA sequence | Luciferase activity (%) |
Viable cell number (%) |
Per cell luciferase yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OAZ1 | GCCUUGCUCCGAACCUUCAtt | 161.1 | 94.8 | 169.9 |
| GAUUAUCCUUGUACUUUGAtt | 144.5 | 101.9 | 141.8 | |
| GGCUGAAUGUAACAGAGGAtt | 127.6 | 94.9 | 134.5 | |
| CCGUAGACUCGCUCAUCUCtt | 174.4 | 85.4 | 204.2 | |
| GCUAACUUAUUCUACUCCGtt | 171.1 | 110.6 | 154.7 | |
| GGGAAUAGUCAGAGGGAUCtt | 92.8 | 102.7 | 90.4 | |
| OAZ2 | ACAUCGUCCACUUCCAGUAtt | 97.4 | 96.3 | 101.1 |
| GGACCUCCCUGUGAAUGAUtt | 95.4 | 86.0 | 110.9 | |
| CAGAUGGAUUAUUAGCUGAtt | 94.9 | 105.4 | 90.0 | |
| OAZ3 | CCGGGAAAGUUUGACUGCAtt | 101.5 | 75.8 | 133.9 |
| CCACGACCAGCUUAAAGAAtt | 90.5 | 95.76 | 94.5 | |
| GACUUUCACUUCCGCCUUAtt | 74.3 | 87.7 | 84.7 | |
| ODC1 | GAUGACUUUUGAUAGUGAAtt | 18.0 | 56.1 | 32.1 |
| GCAUGUAUCUGCUUGAUAUtt | 20.0 | 50.7 | 39.4 | |
| GCUUGCAGUUAAUAUCAUUtt | 28.4 | 60.8 | 46.7 | |
| AZIN1 | CACUCGCAGUUAAUAUCAUtt | 25.2 | 64.6 | 39.0 |
| CGAUGAACAUGUUAGACAUtt | 30.4 | 72.1 | 42.2 | |
| GCCCUCUGUUGGAUAUCUAtt | 45.6 | 72.1 | 63.2 |
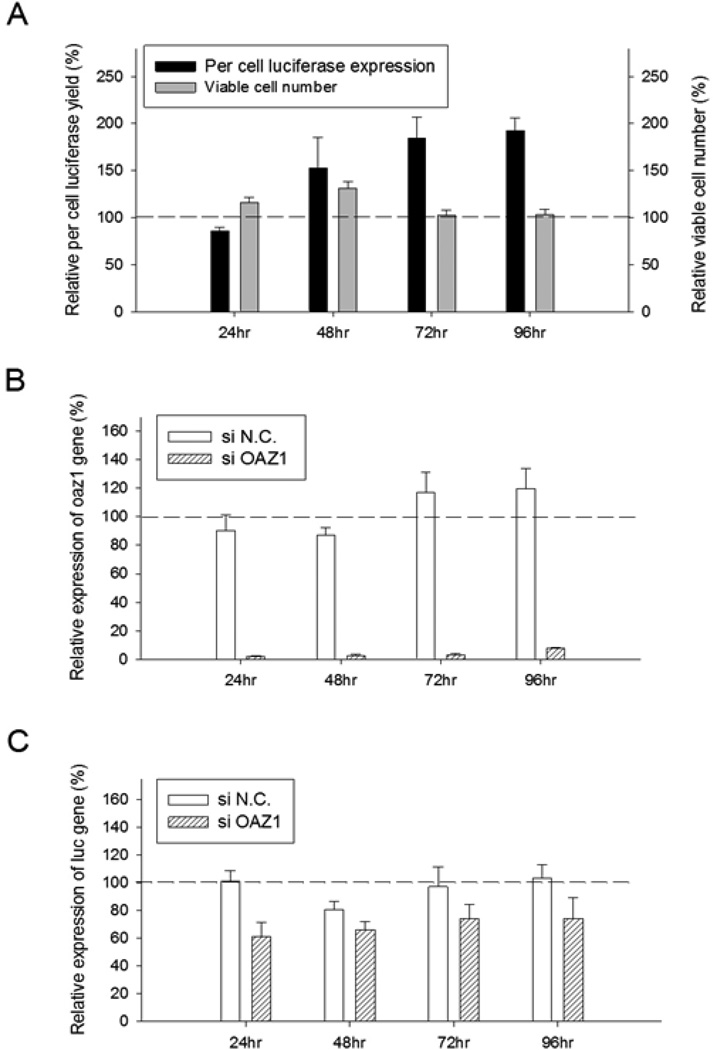
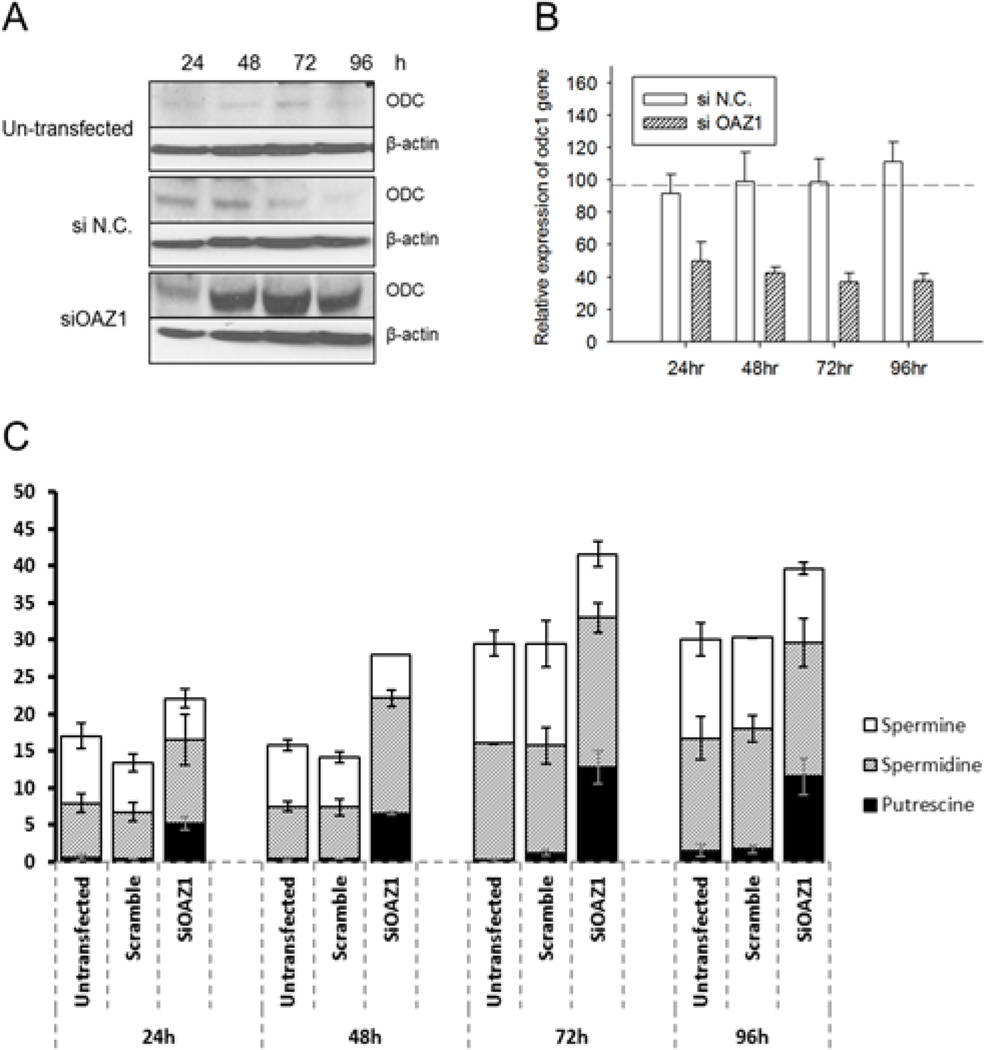
As cells transfected with siOAZ1 showed significantly higher luciferase production for an extended period of time (Figure 4A), the efficacies of silencing antizyme 1 was evaluated with qRT-PCR (Figure 4B). The expression of OAZ1 mRNA in the 24–72 hour period following the transfection of siRNA, was less than 3% compared with negative control siRNA-transfected cells, confirming the silencing by the siRNA. Throughout the 96 hour period luciferasem RNA levels did not increase and remained somewhat lower than those of negative control cells (Figure 4C), an indication that the enhanced luciferase production is the result of an increased translation.
Fig. 4. Effects of OAZ1 siRNA transfection on cell viability, luciferase yield, mRNA levels of OAZ1 and mRNA levels of luciferase.
(A) Cell viability and luciferase protein expression; (B) Relative expression of OAZ1-mRNA; (C) Relative expression of luciferase mRNA. The relative levels of luciferase yield and cell viability in the OAZ1 siRNA-transfected cells were compared to those of cells transfected with negative control siRNA (siN.C.) Transfection was done with two different passages of cells and each biological sample was measured in triplicates. Error bars represent SEM.
6. Effect of silencing OAZ1 on ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and cellular polyamines
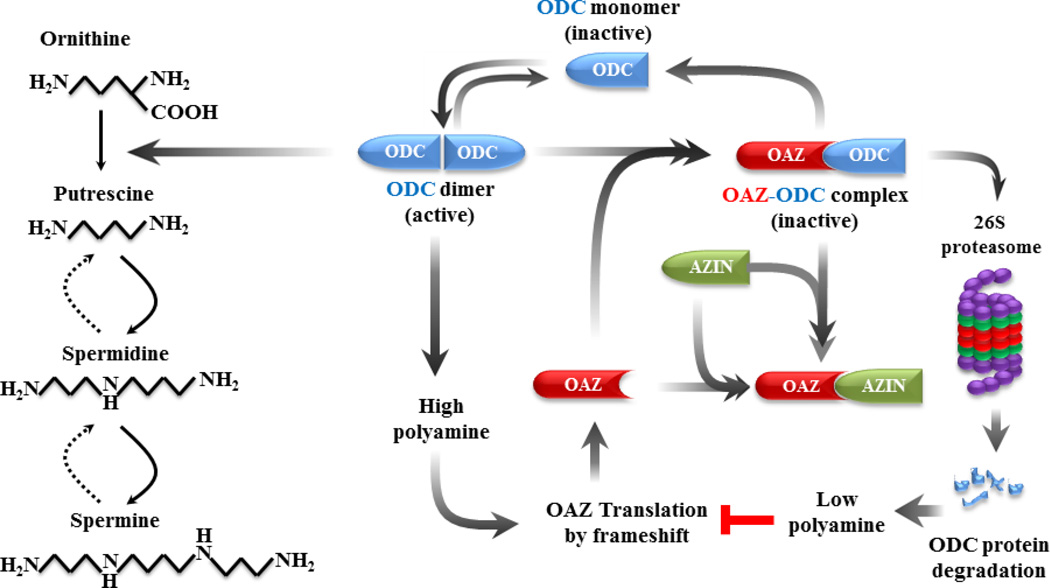
OAZ1 is a negative regulator of the ODC, a rate-limiting enzyme in the polyamine biosynthesis (Coffino, 2001; Kahana, 2009; Pegg, 2006). OAZ1 inactivates ODC by forming heterodimers with the ODC monomer and by directing the protein to degradation by the 26S proteasome (Miyazaki et al., 1992; Murakami et al., 1992). OAZ1 itself is regulated by antizyme inhibitor (AZIN), an ODC-like protein that increase the ODC concentration as a result of reducing OAZ (Scheme 1). As seen in Figure 5A, the silencing of OAZ1 with siRNA increased significantly the ODC level from 24 to 96 hours, as was expected from the known inhibitory effect of OAZ1 on ODC. But at the same time little or no change in the ODC level was observed in the un-transfected and in the negative controlled transfected cells. The elevated ODC is obviously not the result of enhanced ODC transcription, since qRT-PCR analysis shown consistent reduction of ODC mRNA levels after OAZ1 silencing (Figure 5B). As seen in Figure 5C, silencing OAZ1 caused changes in cellular polyamine levels; the putrescine concentration was 10 fold higher compared with the negative control cells. Spermidine concentration was increased to a lesser extent, whereas spermine was either unchanged or reduced.
Scheme 1. Schematic diagram of polyamine pathway and regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) by antizyme (OAZ) and antizyme inhibitor (AZIN).
Simplified pathway of polyamine synthesis from ornithine is indicated by solid arrows and polyamine catabolism by broken arrows. ODC is regulated by OAZ whose translation is turned on by +1 ribosomal frame shifting at a high concentration of polyamines. OAZ is in turn regulated by AZIN, which is an ODC-like protein, but devoid of the enzyme activity.
Fig. 5. Effects of silencing OAZ1 on the ODC protein levels, on ODC mRNA and on cellular polyamines.
(A) Western blot of ODC, (B) ODC mRNA level, (C) Cellular polyamines concentration. Polyamine concentrations were normalized against total protein and presented as nmol/mg total protein. Transfection was done with two different passages of cells and each biological sample was measured in triplicates. Error bars represent SEM. si N.C. indicates control scramble siRNA.
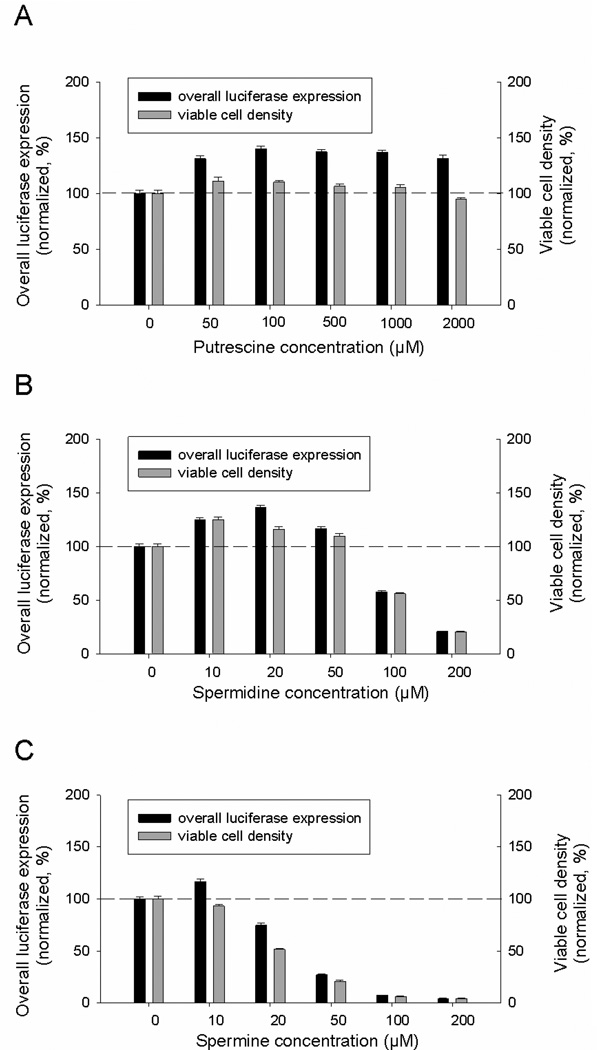
7. Effects of exogenous polyamines on luciferase protein expression
Increased cellular polyamines in OAZ1-silenced cells are most likely responsible for the enhanced cellular production of the reporter proteins. To further verify this, the impacts of exogenously added polyamines on luciferase expression level and viable cell number were determined. As can be seen in Figure 6A, up to 40% increase of luciferase expression was observed when putrescine was added to medium at 100 µM and 10% enhanced growth was observed with putrescine addition at 50 µM. Higher concentrations did not lead to further enhancement of luciferase production. The spermidine effect is seen in Figure 6B; 36% increase in luciferase expression was observed at 20 µM, and 24% increase in cell growth was achieved at 10 µM. In case of spermine addition, only 16% increase in luciferase expression was observed at 10 µM and higher concentrations caused reduction in both luciferase expression and viable cell(Figure 6C). The inhibitory effects of spermidine (>100 µM) and spermine (>20 µM) are probably due to generation of the toxic oxidation products by ruminant serum oxidases present in the culture medium (Pegg, 2013).
Fig. 6. Effect of exogenous polyamines on luciferase expression and cell growth.
Two different passages of cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of polyamines and each biological sample was measured in triplicates. Error bars represent SEM.
Discussion
Cultured mammalian cells are the dominant vehicle for production of recombinant proteins for bio-therapeutics and structural studies. As a result, continuous effort has been directed toward improving cellular production capabilities. Previous work (Xiao et al., 2014) demonstrated the ability to improve recombinant protein expression based primarily on knowledge of specific genes and pathways, yet there is a need for discovering novel genes and pathways for further improvement of production. Genome-wide screening using SiRNA has emerged as a powerful tool for probing gene functions and for target discovery in various diseases (Bard et al., 2006; Brognard and Hunter, 2011; Cherry, 2008; Ni and Lee, 2010; Orvedahl et al., 2011). However, it has rarely been used to identify targets for enhanced recombinant protein production (Bard et al., 2006; Simpson et al., 2012).The purpose of the present study was is to discover new candidates suitable for improving recombinant protein production from HEK 293 cells, by performing high throughput RNA interference screen.
An HEK293 cell line expressing the luciferase reporter was subjected to interference with 64,755 siRNAs targeting 21,585 human genes. 1,681 siRNAs (2.6% of the library) improved the luciferase expression with an MAD-based z-score >3. To eliminate the introduction of ‘false positives’ due to off-target effects, gene hits were considered ‘true positives’ only if more than two single siRNAs targeting the gene passed the MAD-based z-score >3. As a result, fifty six genes were selected and validated with 3 additional siRNAs for each gene. From the data generated by the six siRNAs for each of the 56 genes, ten genes were selected for further analysis. These genes showed an increase in luciferase yield of 3 MAD-based z-scores by 3 or more siRNAs, corresponding to a 40% increase in luciferase activity.
The effects of the siRNAs targeting the ten identified genes on recombinant protein expression from the HEK cells were assessed further by measuring the expression of three additional recombinant proteins: a secreted protein (GPC3-hFc) and two “hard-to-express” membrane proteins (neurotensin receptor type I and serotonin transporter). Silencing of the INTS1, HNRHPC, OAZ1, and PPP2R1A genes consistently improved production of all the tested proteins. Of these four genes, silencing INTS1 or HNRHPC affected cell viability of the other two genes that only slightly affected the cell, OAZ1 was chosen for follow-up studies.
The identification of OAZ1 as a gene whose silencing can enhance recombinant protein production is an indication that this gene normally suppresses protein synthesis. This is compatible with the known function of theOAZ1 as a negative regulator of polyamine homeostasis, cell proliferation and transformation (Bercovich et al., 2011; Coffino, 2001; Kahana, 2009; Pegg, 2006). OAZ1 is a negative regulator of ODC, a rate-limiting enzyme in polyamine biosynthesis. OAZ1 itself is known to be regulated by AZIN, an ODC-like protein that increases the ODC concentration as a result of reducing OAZ1 concentration (Scheme 1). Silencing of OAZ1 was also associated with increased cellular levels of putrescine and spermidine, and addition of external putercine and spermidine caused increased protein expression in the control cells. The observation that increasing the concentration of cellular putrescine and spermidine increases the biosynthesis of reporter proteins without increasing their transcription provides new insights into the primary function of polyamines in the regulation of translation. Consistent with this observation is published information (Mandal et al., 2013) that depleting cellular spermidine and spermine by over-expressing spermidine/spermine N1 -acetyltransferase 1(SSAT1) led to suppression of protein biosynthesis without inhibiting DNA and RNA biosynthesis. We believe that this report is the first to identify polyamine pathways as promising targets for improved recombinant protein production.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr E. C. Wolff (NIDCR, NIH) and Mrs. D Livnat for critical reading of the manuscript and editorial assistance, Dr R Grisshammer (NINDS/NIH) for providing NTSR1 construct, Dr C.G. Tate (MRC Cambridge, UK) for the T-Rex-SERT-GFP cell line, Dr M Ho (NCI/NIH) for HEK-GPC3-hFc cell line.
Funding
The research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK/NIH), National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS/NIH) and the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR/NIH)
Footnotes
This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as doi: [10.1002/bit.26017]
Additional Supporting Information may be found in the online version of this article.
References
- Aagaard L, Rossi JJ. RNAi therapeutics: principles, prospects and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007;59(2–3):75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-Hussein S, Andrell J, Tate CG. Thermostabilisation of the serotonin transporter in a cocaine-bound conformation. J Mol Biol. 2013;425(12):2198–2207. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.03.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bard F, Casano L, Mallabiabarrena A, Wallace E, Saito K, Kitayama H, Guizzunti G, Hu Y, Wendler F, DasGupta R, Perrimon N, Malhotra V. Functional genomics reveals genes involved in protein secretion and Golgi organization. Nature. 2006;439(7076):604–607. doi: 10.1038/nature04377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovich Z, Snapir Z, Keren-Paz A, Kahana C. Antizyme affects cell proliferation and viability solely through regulating cellular polyamines. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(39):33778–33783. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.270637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brognard J, Hunter T. Protein kinase signaling networks in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011;21(1):4–11. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.10.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon S, Ireland A, Mungall CJ, Shu SQ, Marshall B, Lewis S. AmiGO: online access to ontology and annotation data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(2):288–289. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. hexbin:Hexagonal Binning Routines R package version 1.27.1. 2015 http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=hexbin.
- Cherry S. Genomic RNAi screening in Drosophila S2 cells: what have we learned about host-pathogen interactions? Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008;11(3):262–270. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung N, Zhang XD, Kreamer A, Locco L, Kuan PF, Bartz S, Linsley PS, Ferrer M, Strulovici B. Median absolute deviation to improve hit selection for genome-scale RNAi screens. J Biomol Screen. 2008;13(2):149–158. doi: 10.1177/1087057107312035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P. Regulation of cellular polyamines by antizyme. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2(3):188–194. doi: 10.1038/35056508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad C, Gerlich DW. Automated microscopy for high-content RNAi screening. J Cell Biol. 2010;188(4):453–461. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200910105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng M, Gao W, Wang R, Chen W, Man YG, Figg WD, Wang XW, Dimitrov DS, Ho M. Therapeutically targeting glypican-3 via a conformation-specific single-domain antibody in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(12):E1083–E1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217868110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286(5441):950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5441.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinek M, Doudna JA. A three-dimensional view of the molecular machinery of RNA interference. Nature. 2009;457(7228):405–412. doi: 10.1038/nature07755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana C. Antizyme and antizyme inhibitor, a regulatory tango. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(15):2479–2488. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0033-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal S, Mandal A, Johansson HE, Orjalo AV, Park MH. Depletion of cellular polyamines, spermidine and spermine, causes a total arrest in translation and growth in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(6):2169–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219002110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mi H, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT, Thomas PD. Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system. Nat Protoc. 2013;8(8):1551–1566. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki Y, Matsufuji S, Hayashi S. Cloning and characterization of a rat gene encoding ornithine decarboxylase antizyme. Gene. 1992;113(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y, Matsufuji S, Kameji T, Hayashi S, Igarashi K, Tamura T, Tanaka K, Ichihara A. Ornithine decarboxylase is degraded by the 26S proteasome without ubiquitination. Nature. 1992;360(6404):597–599. doi: 10.1038/360597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli C, Lemieux C, Jorgensen R. Introduction of a chimeric chalcone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible co-suppression of homologous genes in trans . Plant Cell. 1990;2(4):279–289. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni Z, Lee SS. RNAi screens to identify components of gene networks that modulate aging in Caenorhabditis elegans . Brief Funct Genomics. 2010;9(1):53–64. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elp051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvedahl A, Sumpter R, Jr, Xiao G, Ng A, Zou Z, Tang Y, Narimatsu M, Gilpin C, Sun Q, Roth M, Forst CV, Wrana JL, Zhang YE, Luby-Phelps K, Xavier RJ, Xie Y, Levine B. Image-based genome-wide siRNA screen identifies selective autophagy factors. Nature. 2011;480(7375):113–117. doi: 10.1038/nature10546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg AE. Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(21):14529–14532. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R500031200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg AE. Toxicity of polyamines and their metabolic products. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013;26(12):1782–1800. doi: 10.1021/tx400316s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. A language and environment for statistical computing. 2015 www.R-project.org.
- Seyhan AA, Rya TE. RNAi screening for the discovery of novel modulators of human disease. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010;11(7):735–756. doi: 10.2174/138920110792927766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson JC, Joggerst B, Laketa V, Verissimo F, Cetin C, Erfle H, Bexiga MG, Singan VR, Hériché JK, Neumann B, Mateos A, Blake J, Bechtel S, Benes V, Wiemann S, Ellenberg J, Pepperkok R. Genome-wide RNAi screening identifies human proteins with a regulatory function in the early secretory pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(7):764–774. doi: 10.1038/ncb2510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Krol AR, Mur LA, Beld M, Mol JN, Stuitje AR. Flavonoid genes in petunia: addition of a limited number of gene copies may lead to a suppression of gene expression. Plant Cell. 1990;2(4):291–299. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham H. ggplot2:elegant graphics for data analysis. New York: Springer; 2009. p. 213p. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao S, Shiloach J, Betenbaugh MJ. Engineering cells to improve protein expression. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2014;26:32–38. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2014.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao S, Chen YC, Betenbaugh MJ, Martin SE, Shiloach J. MiRNA mimic screen for improved expression of functional neurotensin receptor from HEK293 cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015;112(8):1632–1643. doi: 10.1002/bit.25567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.