Abstract
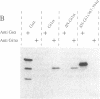
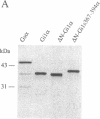
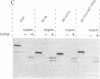
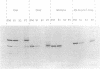
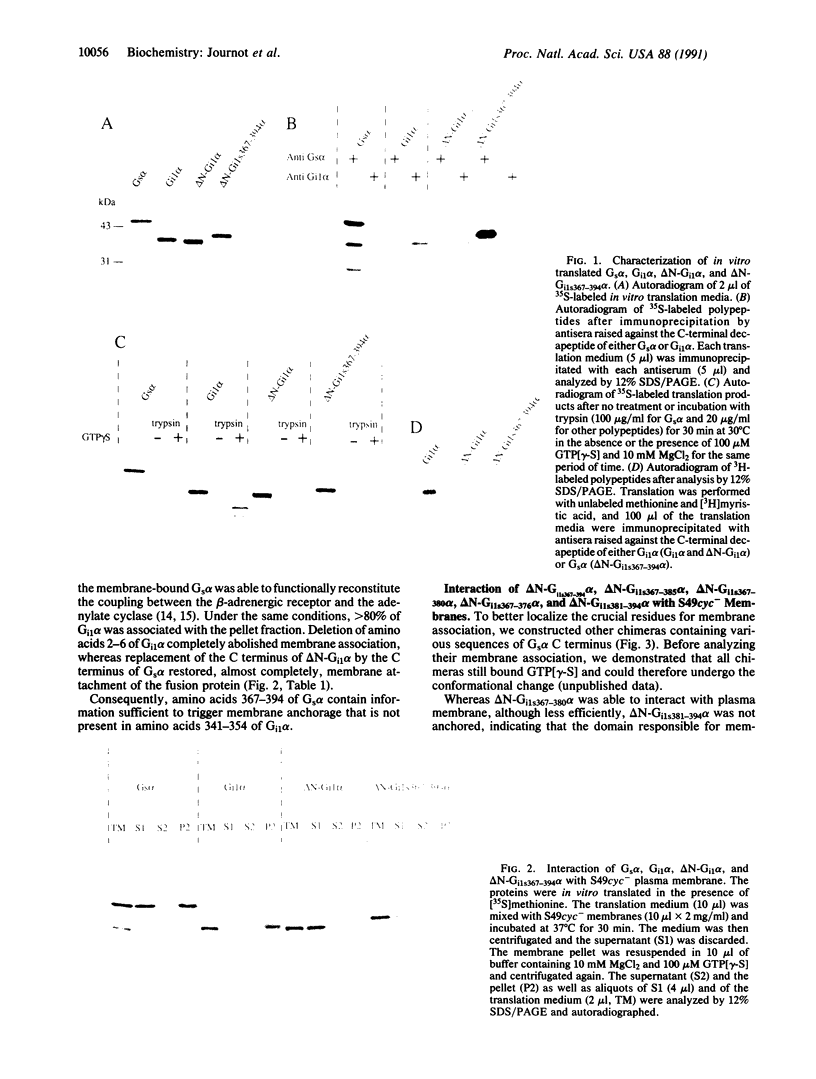
Signal transduction GTP-binding proteins are tightly associated with plasma membrane. In the resting state, the anchorage of the alpha subunit could be indirect by means of the other beta gamma subunits or polydisperse multimers. In the activated state, although the alpha subunit is dissociated from other subunits, it is not released from the membrane and therefore is likely to contain information necessary to remain associated with the plasma membrane. Previous proteolytic experiments suggested that, in contrast to other G proteins alpha subunits, the C-terminal domain of Gs alpha (the G protein involved in adenylate cyclase stimulation) is essential for membrane association of the activated form. To better define the crucial residues involved in membrane attachment, we constructed chimeras between a soluble core and various parts of the Gs alpha C-terminal domain. We first deleted codons 2-6 of Gi1 alpha (the inhibitory G protein of the i1 subtype) to generate a soluble GTP-binding protein, delta N-Gi1 alpha. We then replaced the last 14 C-terminal codons of delta N-Gi1 alpha by different domains of the Gs alpha C terminus and looked for the membrane association of chimeric proteins after in vitro transcription, in vitro translation, and interaction with S49 cyc- membranes (obtained from a mutant cell line that does not express Gs alpha). Our results showed that addition of amino acids 367-376 of Gs alpha is sufficient to promote membrane association of the soluble N-terminal deleted Gi1 alpha.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audigier Y., Journot L., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J. The carboxy-terminal domain of Gs alpha is necessary for anchorage of the activated form in the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Masters S. B., Miller R. T., Sullivan K. A., Heideman W. Mutations probe structure and function of G-protein alpha chains. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):221–228. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Sefton B. M. Myristoylated alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7493–7497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deichaite I., Casson L. P., Ling H. P., Resh M. D. In vitro synthesis of pp60v-src: myristylation in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4295–4301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide B., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Mullaney I., Unson C., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. GTP-binding proteins in brain and neutrophil are tethered to the plasma membrane via their amino termini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1398–1405. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Nash C. R. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. II. Evidence for distinct binding sites and conformational changes revealed by limited proteolysis with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10503–10510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrion J., Brabet P., Nguyen Than Dao B., Homburger V., Dumuis A., Sebben M., Rouot B., Bockaert J. Ultrastructural localization of the GTP-binding protein Go in neurons. Cell Signal. 1989;1(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. Expression of cDNAs for G proteins in Escherichia coli. Two forms of Gs alpha stimulate adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11375–11381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K., Ishibashi S. Specific binding of tubulin to a guanine nucleotide-binding inhibitory regulatory protein in adenylate cyclase system, Ni. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 15;132(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. L., Simonds W. F., Merendino J. J., Jr, Brann M. R., Spiegel A. M. Myristoylation of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein alpha subunit is essential for its membrane attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):568–572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journot L., Bockaert J., Audigier Y. Reconstitution of cyc- S49 membranes by in vitro translated Gs alpha. Membrane anchorage and functional implications. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81460-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journot L., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Audigier Y. Deletion within the amino-terminal region of Gs alpha impairs its ability to interact with beta gamma subunits and to activate adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9009–9015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattera R., Graziano M. P., Yatani A., Zhou Z., Graf R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Gilman A. G., Brown A. M. Splice variants of the alpha subunit of the G protein Gs activate both adenylyl cyclase and calcium channels. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.2536957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. T., Masters S. B., Sullivan K. A., Beiderman B., Bourne H. R. A mutation that prevents GTP-dependent activation of the alpha chain of Gs. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):712–715. doi: 10.1038/334712a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Heukeroth R. O., Gordon J. I., Gilman A. G. G-protein alpha-subunit expression, myristoylation, and membrane association in COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):728–732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Rodbell M. Octyl glucoside extracts GTP-binding regulatory proteins from rat brain "synaptoneurosomes" as large, polydisperse structures devoid of beta gamma complexes and sensitive to disaggregation by guanine nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6413–6417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon S. E., Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. Participation of the amino-terminal region of T alpha in subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15746–15751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Pulsifer L., Wolf L. G. The amino terminus of G protein alpha subunits is required for interaction with beta gamma. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8996–8970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olate J., Mattera R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Reticulocyte lysates synthesize an active alpha subunit of the stimulatory G protein Gs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10394–10400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Yan K., Rasenick M. M. Tubulin binds specifically to the signal-transducing proteins, Gs alpha and Gi alpha 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1239–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow J. W., Van Amsterdam J. R., Neer E. J. Conformations of the alpha 39, alpha 41, and beta.gamma components of brain guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Analysis by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7571–7579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woon C. W., Soparkar S., Heasley L., Johnson G. L. Expression of a G alpha s/G alpha i chimera that constitutively activates cyclic AMP synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5687–5693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane H. K., Farnsworth C. C., Xie H. Y., Howald W., Fung B. K., Clarke S., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Brain G protein gamma subunits contain an all-trans-geranylgeranylcysteine methyl ester at their carboxyl termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5868–5872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]