Figure 5.
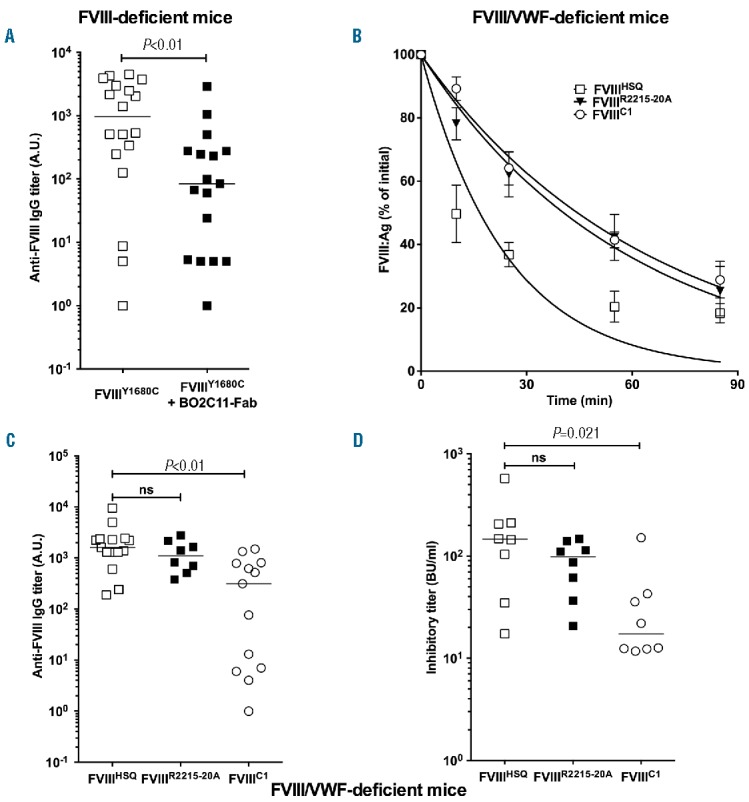
Contribution of the C1 and C2 domains of FVIII to FVIII immunogenicity in the absence of binding to VWF. Panel A. FVIII-deficient mice were administered with B domain-deleted FVIIIY1680C (0.4 μg, open squares) or FVIIIY1680C pre-incubated with a 2-fold molar excess of BO2C11 Fab (closed squares) intravenously once a week for 4 weeks. One week after the last injection, blood samples were collected. Anti-FVIII IgG titers are defined as arbitrary units based on standard curves generated using mAb6. The graph depicts a pool of two independent experiments. Panel B. B domain-deleted FVIIIHSQ, FVIIIC1 or FVIIIR2215-20A (10 nM in 100 μl) were administered to FVIII-deficient mice and the residual FVIII levels were measured at different time points (n=3 mice per time point) by ELISA. The data are plotted as a percentage of the initial FVIII levels (measured 5 minutes after administration) versus time (mean±SEM) and are representative of 2 independent experiments. Experimental data were fitted using a one-phase decay curve to determine the in vivo half-lives. Panels C and D. Double FVIII/VWF-deficient mice were injected intravenously once a week for 4 weeks with 0.5 μg of FVIIIHSQ, FVIIIC1 or FVIIIR2215-20A. One week after the last injection, blood samples were collected. Anti-FVIII IgG titers were measured as described above (C). Inhibitory titers towards FVIII were assessed using a modified Bethesda assay (D). Horizontal bars depict medians. Statistical significances were assessed using the two-tailed non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. ns: not significant: FVIII: factor VIII; IgG: immunoglobulin G; A.U.: arbitrary unit; Fab: fragment antigen binding; VWF: von Willebrand factor; Ag: antigen.
