Abstract
Phenomena characterized by power-law probability distributions abound in nature and the applied sciences. We show that many of these power laws are well described by the Student, or t, distribution, and we discuss the origin of this universality based on three examples (Brownian motion, Knudsen diffusion in rough pores, and bubbly multiphase flow). These case studies are representative for a large class of systems with heterogeneous features, examples of which can be found from Earth sciences to astrophysics, and even in the social sciences. We show that common forms of polydispersity, such as polydispersity arising naturally as a result of aggregation–fragmentation phenomena, typically lie at the basis of the observed scaling. We conclude that complicated arguments based on long-range correlations or nonergodicity are often incorrect or misleading in explaining many naturally observed power laws and, in particular, those described by the Student distribution.
Keywords: power-law statistics, polydispersity, Student distribution
The abundance of power-law-tailed probability distributions in nature made them the focus of intense scientific investigation during the last few decades. Significant progress in this area is primarily due to advances in the physics of disordered systems (1, 2), critical phenomena (3), and turbulence (4), which were stimulated by the advent of fractal theory (5) and complex-systems research.
This article focuses on the Student, or t, distribution, which is a frequently occurring probability distribution with power-law tails, as shown below:
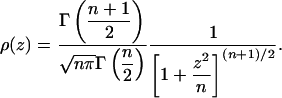 |
Here, ρ(z) denotes the probability density function (PDF) of variable z, and n is the number of “degrees of freedom” (for n → ∞, this PDF converges to a Gaussian). A change of variable, 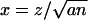 , leads to the following alternative form of the above expression:
, leads to the following alternative form of the above expression:
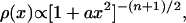 |
[1] |
where a is a real parameter. Student's distribution (Fig. 1) is well known in statistics, where it quantifies deviations from the mean in samples for which the standard deviation is unknown. Here, we propose using Student's distribution as a parameterized model for power-law behavior, instead of in its customary statistical role. As such, it has been largely overlooked, with a few exceptions in turbulence (6) and finance (7).
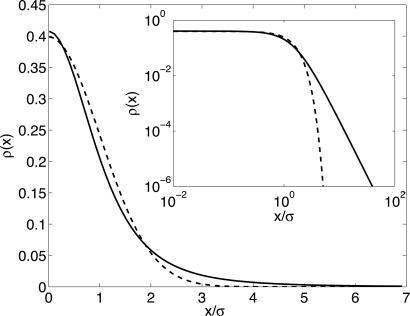
Fig. 1.
Comparison between Gaussian (dashed lines) and anomalous Student statistics (solid lines). For the case n = 3 and a = 1, see Eq. 1.(Inset) The log–log plot of the same curves shows the power-law nature of the tail of Student's distribution. The standard deviation of x is indicated by σ. Both distributions are symmetric with respect to x = 0.
Although the subject has received considerable attention, the origin of power-law statistics is still very much debated. The fact that such distributions can arise both in the presence and absence of long-range spatiotemporal correlations has been known for a long time (2, 8). However, in the recent literature, the tendency is to attribute the observation of power laws mostly to the presence of long-range correlations and even to a thermodynamic theory of nonergodic systems proposed by Tsallis (9), in which the Boltzmann factor has a Student form. The result of this study goes against these trends. We demonstrate that the t distribution provides an accurate representation for power-law statistics seen in various heterogeneous systems that have polydisperse features, that are entirely “classical” in the thermodynamic sense, and in which spatial or temporal correlations do not play a major role.
We do not intend to downplay the importance of long-range correlations or their significant role in scaling phenomena. Rather, we wish to illustrate that more often than not, simple uncorrelated polydispersity is sufficient to explain a great number of phenomena for which an exotic thermodynamic behavior or difficult to interpret long-range correlations are often advanced as the primary cause (Occam's razor).
Polydispersity as a Source of Student's Distributions
The mechanism that we present for the genesis of Student's distributions in uncorrelated systems involves the convolution of a normal distribution with a gamma or power-law distribution reflecting polydispersity. As such, the Student distribution is a member of a larger family known as scale mixtures of normal distributions (10).
Brownian Motion. An elementary example is an ensemble of Brownian particles (i.e., a plume) in a fluid. The system is assumed to be dilute, so the particles do not interact with each other. Being in thermal equilibrium with its environment, every particle undergoes Brownian diffusion, so the probability of finding it at a later time t around position x is Gaussian as follows:
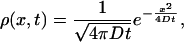 |
[2] |
where the diffusion coefficient is given by Einstein's formula, D = kT/6πμR, with μ being the fluid viscosity (all particles are released at the same point x = 0 at t = 0). At fixed temperature, D is a function of the particle size R only. If the system is polydisperse, with a gamma distribution of particle sizes f(R) ∝ Rτe–λR (λ > 0), the dispersion of the entire plume is apparently “anomalous” because the averaged ρ has power-law tails:
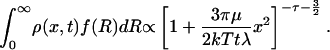 |
[3] |
This distribution is precisely of the Student type (Eq. 1), with n = 2τ + 2(τ >–3/2), and a = 3πμ/2kTtλ. This power-law form of ρ is obviously not the result of long-range correlations (correlations are absent here), Lévy statistics, or departure from thermodynamic equilibrium, but only a reflection of polydispersity. Remarkably, this simple convolution mechanism for producing power-law distributions (Fig. 2) can be very prolific because the required ingredients are abundant in nature. It is hard to overstate the importance and ubiquity of Gaussian distributions. They are a direct manifestation of the central-limit theorem, and the diffusion equation that produces them is one of the most fundamental equations in physics. Brownian motion and random walks lie at the origin of all essential theories and applications of transport. Furthermore, the required form of polydispersity is also ubiquitous. As a result of Smoluchowski aggregation–fragmentation kinetics, many particle distributions in particle technology, atmospheric sciences, and Earth sciences are gamma-like (11), and thus, distribution 3 is likely to be found in a broad range of experiments (e.g., dispersion of aerosol pollutants from industrial smokestacks, dispersion of volcanic clouds, diffusion of dyes and polymers in solution, diffusion of cell aggregates in physiological systems, etc.).†
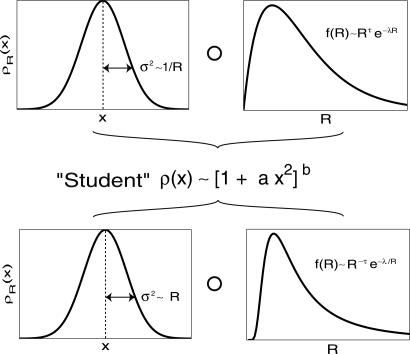
Fig. 2.
The genesis of an apparently anomalous probability distribution in a heterogeneous, polydisperse system. (Left) Normal PDF corresponding to a fixed length scale R. (Right) The polydispersity of the system is reflected in a broad distribution of sizes f(R). Averaging ρR(x) over all length scales, R results in Student's PDF, when the variance σ2 is proportional to 1/R and f(R) ∼ Rτ e–λR (gamma polydispersity) (Upper), or σ2 ∝ R and f(R) ∼ R–τ e–λ/R (truncated power-law polydispersity) (Lower). Both λ and τ are positive parameters. Note that such polydispersity is very common as a result of Smoluchowski-type aggregation–fragmentation kinetics.
From an experimental viewpoint, it is also noteworthy that a measurement of distribution 3 allows the extraction of parameters describing the heterogeneous nature of the plume: the exponent of the Student distribution and the prefactor of x2 give parameters τ and λ of the gamma distribution, respectively.
Knudsen Diffusion in Rough Pores. A second example with broad applicability is that of diffusion in disordered media. One of the most well known approaches to statistical modeling of diffusion in heterogeneous structures is to consider the time scale of Brownian motion as a fluctuating variable. In the continuous-time random-walk model, transport is abstracted as random hopping on a lattice, with the hopping time sampled from a probability distribution (1, 12, 13). Such a description corresponds, for example, to particles being trapped at lattice sites for a variable amount of time tw. The probability density of a hopping event of size x is given as follows:
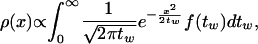 |
[4] |
where f(tw) is the distribution of waiting times at a lattice site. Central to the continuous-time random-walk approach is the assumption that the distribution of waiting times is sampled uniformly by the diffusion process. In other words, this process has no memory and a spatially averaged distribution of trapping times. This assumption is justified whenever spatial correlations in the medium have a finite range. The successful application of the theory to many problems in solid-state physics (NMR spectroscopy, aging of glasses, conduction in amorphous semiconductors, etc., as described in ref. 1 and references therein) is proof that this assumption is valid in many physical systems.
If the trapping times have a broad distribution with a power-law tail, f(tw) 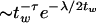 (gamma distribution of hopping frequency 1/tw), then the probability density ρ(x) will again have the Student form as follows:
(gamma distribution of hopping frequency 1/tw), then the probability density ρ(x) will again have the Student form as follows:
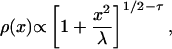 |
[5] |
provided that τ > 1/2.
The background of a power-law distribution of waiting times f(tw) is very general; it can have either a physical or chemical nature, reflecting the heterogeneity of the medium. A concrete example involving a physical trapping mechanism is Knudsen diffusion in rough pores (Fig. 3). Knudsen diffusion is the main transport mechanism in porous media, when motion of diffusing gas molecules is dominated by molecule–wall, rather than intermolecular, collisions. It occurs if the pore diameter is smaller than the mean free path of the molecules, which is frequently the case in nanoporous media used in catalysis and separation processes. In a channel with fractally rough walls, recent dynamic Monte Carlo simulations (14) have shown that Knudsen “flights” are indeed distributed according to an inverse power law, with an exponent related to the fractal dimension of the walls.
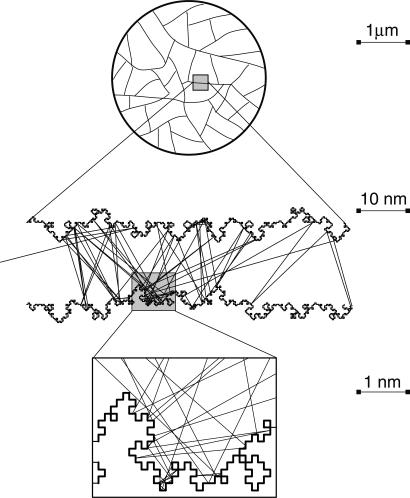
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of a typical amorphous, porous catalyst particle. (Top) The particle crisscrossed by a network of pores. (Middle) Close-up view of an individual pore. The walls are fractally rough on scales smaller than the pore diameter. A typical trajectory of a molecule diffusing inside the pore in the Knudsen regime is shown also (note how the molecule seems to get trapped inside some fjords, occasionally spending a long time bouncing off the walls). (Bottom) Individual large fjord on the pore wall, with detail of the trajectory. These large fjords (fractal cascades of smaller fjords) are considered as lattice sites for the diffusion of molecules along the pore axis.
A consequence of fractal self-similarity is that the walls contain cascades of “fjords” of a power-law distribution of sizes, truncated at the upper and lower cutoff of fractal scaling, just like a natural coastline (15). By projecting the motion onto the pore axis, diffusion along the channel may be modeled as a random walk on a coarse-grained lattice, by considering large fjords as lattice sites. Diffusing particles entering such a fjord are occasionally trapped inside, colliding many times with the walls before finally moving to another large fjord (Fig. 3). The motion between individual lattice sites is completely uncorrelated with the time a molecule spends at any particular site (i.e., in any cascade of fjords). This picture is consistent with a continuous-time random-walk description of pore transport, in which the diffusive motion of molecules between lattice sites is coupled to a random waiting time at every site. On very general grounds, it can be shown that the waiting times have a power-law-tailed distribution, which reflects the fact that the fjords themselves have a power-law distribution of sizes. Following the argument leading to Eq. 5, the continuous-time random-walk approach yields a Student-like PDF ρ(x) (e.g., in a catalyst particle with fractal dimension of pore walls Df = 2.33, simulations yield τ ≈ 1.1).
We stress that the power-law statistics are not generated by spatial correlations associated with fractality: fractally rough porous solids typically have an upper cutoff of wall roughness (comparable with the pore diameter), which is many times smaller than the particle or pore network size (16), so spatial correlations are very limited in extent. The polydispersity of fjords leading to a power-law distribution of trapping times is the sole source of the observed Student-like statistics for displacements x smaller than the largest fjord.
Multiphase Flow. To further illustrate the variety of situations in which polydispersity induces Student statistics, we present a third example in the form of a widely used form of chemical reactor, known as a fluidized bed (17), in which a layer of particles is set in motion by an upward gas stream (Fig. 4). Because of its excellent heat and mass transfer properties, the device is used widely in industry as a catalytic reactor or as a means of heating, cooling, drying, or coating particles. When the gas flow rate exceeds a certain threshold, bubbles are formed, and the bed behaves very much like a boiling liquid.
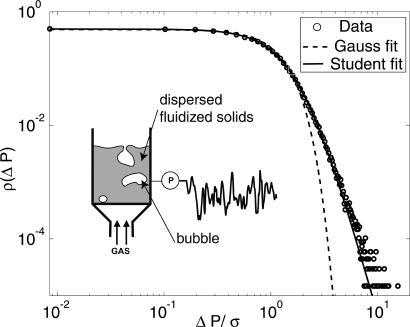
Fig. 4.
Student's (solid) and Gaussian (dashed) fit of the PDF of pressure fluctuations in a gas-fluidized bed of solid particles. Pressure increments ΔP = P(t +Δt) – P(t) over a time interval Δt = 50 ms are normalized to their standard deviation σ. The Student fit yields n ≈ 3. (Inset) Sketch of the pressure measurement (see ref. 18 for complete details).
A measurement of pressure was carried out in such a column in the bubbling fluidization regime, and the statistics of pressure increments ΔP(t, Δt) = P(t +Δt) – P(t) were calculated (see ref. 18 for details of the experiment). For relatively short time delays (Δt ≤ 50 ms), and a wide range of process parameters, the PDF of ΔP is fitted by a Student distribution, Eq. 1, with remarkable accuracy (Fig. 4). As the time delay is increased, the PDF of ΔP changes from power-law-tailed to Gaussian. A very similar phenomenon has been observed for the statistics of velocity increments in single phase turbulence (19, 20), as well as short-time stock returns (21, 22).
A hydrodynamic theory of fluidization (23) can be used to show that every bubble carries along a pressure perturbation, and that the variance of measured pressure increments ΔP(t, Δt) for each bubble is proportional to the bubble radius R. In actual fluidized beds, bubbles have a broad distribution of sizes, a consequence of bubble growth that occurs primarily through coalescence of smaller bubbles. Therefore, the measured distribution of pressure fluctuations is as follows:
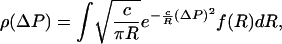 |
[6] |
where c is a positive constant. The bubble-growth mechanism can be modeled by using Smoluchowski aggregation– fragmentation equations (24–26), producing a power-law distribution of sizes, f(R) ∼ R–τe–λ/R (τ, λ > 0), as verified in experiments and computer models (27). Hence,
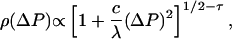 |
[7] |
as long as τ > 1/2 (fits of actual data yield τ ≈ 5/2).
Although the behavior of pressure fluctuations in fluidization closely resembles that of velocity increments in turbulence and that of financial market returns, the former system is significantly different from the latter two. Whereas extended spatial or temporal correlations can be assumed in turbulence and the stock market (8), correlations in a fluidized bed are very limited in extent. Here, power-law statistics seems to be only the reflection of bubble polydispersity.
The experimentalist will also find it very valuable that a simple measurement of the distribution 7 can, in principle, completely quantify heterogeneity; the exponent of the distribution and the prefactor of (ΔP)2 give the parameters of the bubble-size distribution, which are notoriously difficult to measure in multiphase systems.
Polydispersity vs. Anomalous Thermodynamics
In addition to showing that power-law-tailed distributions commonly arise in the absence of long-range correlations, the three examples presented above are also remarkable for a second reason. They display Student-like statistics of the relevant variables instead of the Gaussian expected in normal circumstances (i.e., in the absence of polydispersity).
It is tempting to label this behavior as thermodynamically anomalous and to conclude that normal, conventional thermodynamics does not provide a good description of these systems. In recent years, a rapidly expanding body of literature has associated Student's distributions measured in various systems with a new thermodynamic formalism proposed by Tsallis (9). This theory is a generalization of statistical mechanics, in which the Boltzmann factor e–βε, representing the probability ρ of a microstate of energy ε, is replaced by a power-law form (Fig. 1),
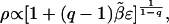 |
[8] |
where q is a positive parameter, whereas 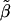 plays a similar role as β = 1/kBT of traditional statistical mechanics (kB and T denote the Boltzmann constant and temperature, respectively). To preserve the structure of conventional statistical mechanics, the Tsallis theory requires that the following new expression for entropy,
plays a similar role as β = 1/kBT of traditional statistical mechanics (kB and T denote the Boltzmann constant and temperature, respectively). To preserve the structure of conventional statistical mechanics, the Tsallis theory requires that the following new expression for entropy,
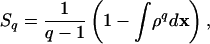 |
[9] |
replace the celebrated Boltzmann–Gibbs logarithmic form S ∼ ∫ ρ log ρ dx (where dx denotes the volume element in phase space). Traditional statistical mechanics is recovered in the limit q → 1. The striking feature of the proposed entropic form is that it is not additive; i.e., the Tsallis entropy of a system is not the sum of the individual entropies of its parts. This property provided the Tsallis theory with the label of “nonextensive thermodynamics and generated controversy (28, 29).
In the literature related to nonextensive thermodynamics, ε is often regarded not as energy but as a generic quadratic form (ε ∼ x2), which makes the Boltzmann factor of Eq. 8 precisely of the Student form. In applications, x has been interpreted as, for example, the velocity of a diffusing cell in a cellular aggregate (30), the logarithm of a NASDAQ stock return (22), the velocity increment of a turbulent field (20), and even the rank of a word in literary text (31).
The “nonextensive” framework was introduced for systems that have a fractal phase space, are nonergodic and far from thermal equilibrium, and do not sample phase space in the dense and uniform way that is required in some formulations of classical thermodynamics. As such, the Tsallis formalism has been proven to be relevant for systems operating at the edge of chaos (32), as well as for many-body systems with long-range interactions (33). Probability distributions of the type given in Eq. 8 were also found to be solutions of a certain class of nonlinear Fokker–Planck equations (34–36).
Clearly, none of the examples discussed in this article fits these categories. All three instances of Student statistics were explained based on elementary statistical ingredients, such as convolution, and within the assumption of thermal equilibrium.‡ The conclusion that Student's distributions often arise from polydispersity casts some doubts on the relevance of the Tsallis formalism for many systems, and on their frequent interpretation as being nonextensive.
Noah vs. Joseph
Mandelbrot (5) illustrates the contrast between uncorrelated polydispersity and long-range correlations, as different sources for power-law behavior, by using the following two citations. Genesis, chapter 6, verses 11 and 12 (story of Noah), reads: “...were all of the fountains of the great deep broken up, and the windows of heaven were opened. And the rain was upon the earth forty days and forty nights,” whereas Genesis, chapter 41, verses 29 and 30 (story of Joseph), reads: “...there came seven years of great plenty throughout the land of Egypt. And there shall arise after them seven years of famine.”
The first citation emphasizes the importance of isolated, uncorrelated extreme events, the statistics of which may be crucial in cases in which rare events carry enormous costs. The occurrence of natural disasters is an obvious example of the “Noah effect,” as Mandelbrot calls it. The second citation refers to the “Joseph effect,” which is the clustering of events, with strong correlations and persistence over a long time or distance. Both classes of phenomena may display power-law statistics, i.e., large events that occur rarely, but not nearly as rarely as would be anticipated from a normal or Gaussian distribution. In fact, the Joseph and Noah effects may even occur together, as in financial time series (8) and diffusion processes (2), but they are essentially unrelated statistical phenomena.
In statistical analysis, great care needs to be taken in the interpretation of power laws. PDFs or Fourier spectra of variables that characterize a process or phenomenon convey only information about the frequency of individual events and not about their spatial or temporal distribution. Clustering, intermittency, and persistence are studied by correlation analysis, either local or global. Despite this clear difference, Noah and Joseph are still often confused. The Noah effect accounts for all power-law distributions discussed in this article.
Conclusion
The three examples analyzed in this article are representative for a common mechanism that produces Student distributions without any assumption of nonergodicity, long-range correlations, or thermodynamic nonequilibrium. Instead, we show that polydispersity can make systems seem anomalous by featuring non-Gaussian statistics, when in fact they are normal in the conventional thermodynamic sense and in local equilibrium.
In many systems, power-law statistics of the Student type arises from the convolution of the normal distribution with either a gamma or a power-law distribution (see Fig. 2). The Gaussian distribution usually appears by the action of the central-limit theorem, and its convolution partner is a manifestation of the polydispersity of the system, seen in a broad sense. An important source of the kind of polydispersity that is required to produce Student statistics is Smoluchowski aggregation–fragmentation kinetics (24–26), which describes a wide variety of systems from particle technology to astrophysics, biology, geophysics, and even sociology. The abundance of such systems may account for the ubiquity of power-law distributions of the Student type throughout the natural world.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Pionier grant and an Open Competition grant from the Dutch National Science Foundation (NWO).
Author contributions: S.G. and M.-O.C. designed research; S.G. and M.-O.C. performed research and analyzed data; and S.G. and M.-O.C. wrote the paper.
Abbreviation: PDF, probability density function.
Footnotes
The assumption that all particles are released at the same position x = 0 at time t = 0isan idealization and, in principle, contradicts the statement that the system is dilute. A more realistic approach considers an initial dispersion Δx0 of the plume, which leads to a slight distortion of the Student distribution near the center. For x >> Δx0, Eq. 3 still holds.
Advocates of nonextensive thermodynamics (37, 20) used a similar convolution argument to model systems in which temperature fluctuates with gamma statistics. Such “exotic” systems are continuously out of thermal equilibrium (they never relax to Boltzmann statistics), so the use of Tsallis thermodynamics in their description may be justified. Here, we argue that a scenario involving polydispersity (i.e., in which features of the system other than the temperature fluctuate with a broad distribution) may often provide a simple alternative explanation for the occurrence of experimentally measured distributions of the type shown in Fig. 1.
References
- 1.Havlin, S. & Ben-Avraham, D. (2002) Adv. Phys. 51, 187–292. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bouchaud, J.-P. & Georges, A. (1990) Phys. Rep. 195, 127–293. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sornette, D. (2000) Critical Phenomena in Natural Sciences (Springer, Berlin).
- 4.Frisch, U. (1995) Turbulence (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York).
- 5.Mandelbrot, B. B. (1983) The Fractal Geometry of Nature (Freeman, New York).
- 6.von Karman, T. (1937) J. Aeronaut. Sci. 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Blattberg, R. & Gonedes, N. (1974) J. Bus. 47, 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mandelbrot, B. B. (1998) Multifractals and 1/f Noise (Springer, New York).
- 9.Tsallis, C. (1988) J. Stat. Phys. 52, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mallows, C. & Andrews, D. (1974) J. R. Stat. Soc. B 36, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hinds, W. C. (1999) Aerosol Technology (Wiley, New York).
- 12.Scher, H. & Montroll, E. (1975) Phys. Rev. B 12, 2455–2477. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shlesinger, M. F., Zaslavsky, G. M. & Klafter, J. (1993) Nature 263, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Malek, K. & Coppens, M.-O. (2003) J. Chem. Phys. 119, 2801–2811. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mandelbrot, B. B. (1967) Science 155, 636–638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Coppens, M.-O. (1999) Catal. Today 53, 225–243. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kunii, D. & Levenspiel, O. (1991) Fluidization Engineering (Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston), 2nd Ed.
- 18.Gheorghiu, S., van Ommen, J. R. & Coppens, M.-O. (2003) Phys. Rev. E 67, 041305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Noullez A., Wallace, G., Lampert, W., Miles, R. B. & Frisch, U. (1997) J. Fluid Mech. 339, 287–307. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Beck, C., Lewis, G. S. & Swinney, H. L. (2001) Phys. Rev. E 63, 035303(R). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ghasghaie, S., Breymann, W., Peinke, J., Talkner, P. & Dodge, Y. (1996) Nature 381, 767–769. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Borland, L. (2002) Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 098701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Davidson, J. F. & Harrison, D. (1963) Fluidised Particles (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, U.K.).
- 24.Chandrasekhar, S. (1943) Rev. Mod. Phys. 15, 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vicsek, T. & Family, F. (1984) Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ernst, M. H. (1985) in Fundamental Problems in Statistical Mechanics VI, ed. Cohen, E. G. D. (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam), pp. 329–364.
- 27.Pannala, S., Daw, C. S. & Halow, J. (2003) Int. J. Chem. Reac. Eng. 1, A20. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cho, A. (2002) Science 297, 1268–1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nauenberg, M. (2003) Phys. Rev. E 67, 036114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Upadhyaya, A., Rieu, J.-P., Glazier, J. A. & Sawada, Y. (2001) Physica A 293, 549–558. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Montemurro, M. A. (2001) Physica A 300, 567–578. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Baldovin, F. & Robledo, A. (2002) Phys. Rev. E 66, 045104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Latora, V., Rapisarda, A. & Tsallis, C. (2001) Phys. Rev. E 64, 056134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Borland, L. (1998) Phys. Rev. E 57, 6634–6642. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tsallis, C. & Bukman, D. J. (1996) Phys. Rev. E 54, R2197–R2200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zanette, D. H. & Alemany, P. A. (1995) Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 366–369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wilk, G. & Wlodarczyk, Z. (2000) Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 2770–2773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]