Figure 2. Fractionated radiation-induced Notch signaling promotes EMT in breast cancer cells.
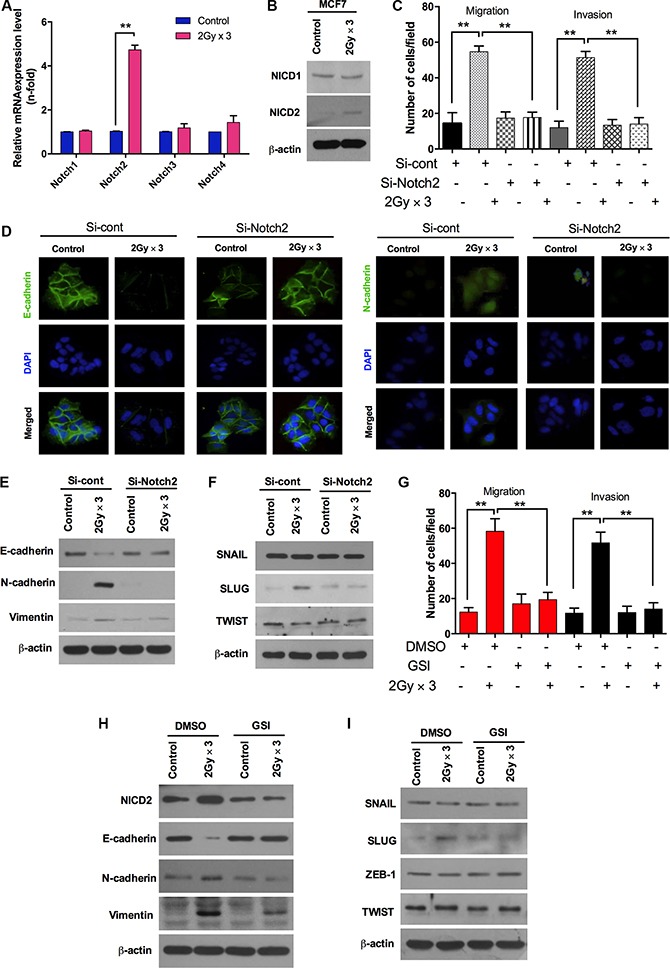
(A) qRT PCR analysis for mRNA levels of Notch family members (Notch1-4) in MCF7 breast cancer cell after fractionated irradiation. (B) Protein expression of Notch family such as Notch1 (NICD1) and Notch2 (NICD2) in MCF7 after fractionated irradiation. (C)) Migration and invasion assay in transwells after irradiation of MCF7 that are transfected with siRNA targeting Notch2. (D) Immunocytochemistry for EMT markers (E-cadherin and N-cadherin) after fractionated irradiation of MCF7 that are treated with siRNA targeting Notch2. (E) Western blot for EMT markers such as E-cadherin, N-cadherin and Vimentin in MCF7 cells that are transfected with siRNA targeting Notch2 prior to irradiation. (F) Western blots for EMT transcription factors such as SNAIL, SLUG and TWIST in MCF7 cells that are transfected with siRNA targeting Notch2 and irradiated afterwards. (G) Migration and invasion assay in transwells after irradiation of MCF7 that are treated with gamma-secretase inhibitor, well known Notch signaling inhibitor (GSI, 20 μM). (H and I) Western blot for EMT markers and regulators after fractionated irradiation in MCF7 cells that are treated with pretreated with GSI. β-actin was used as a loading control. Error bars represent mean ± S.D. of triplicate samples. *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01.
