Abstract
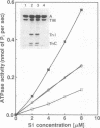
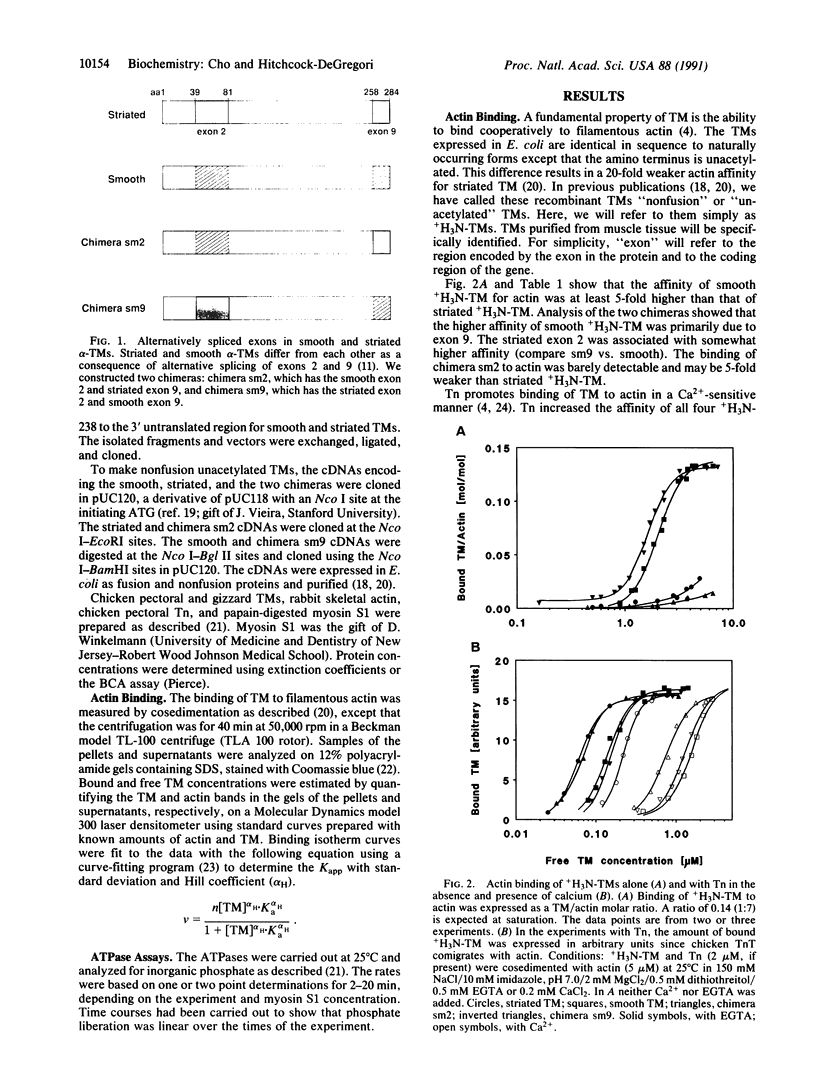
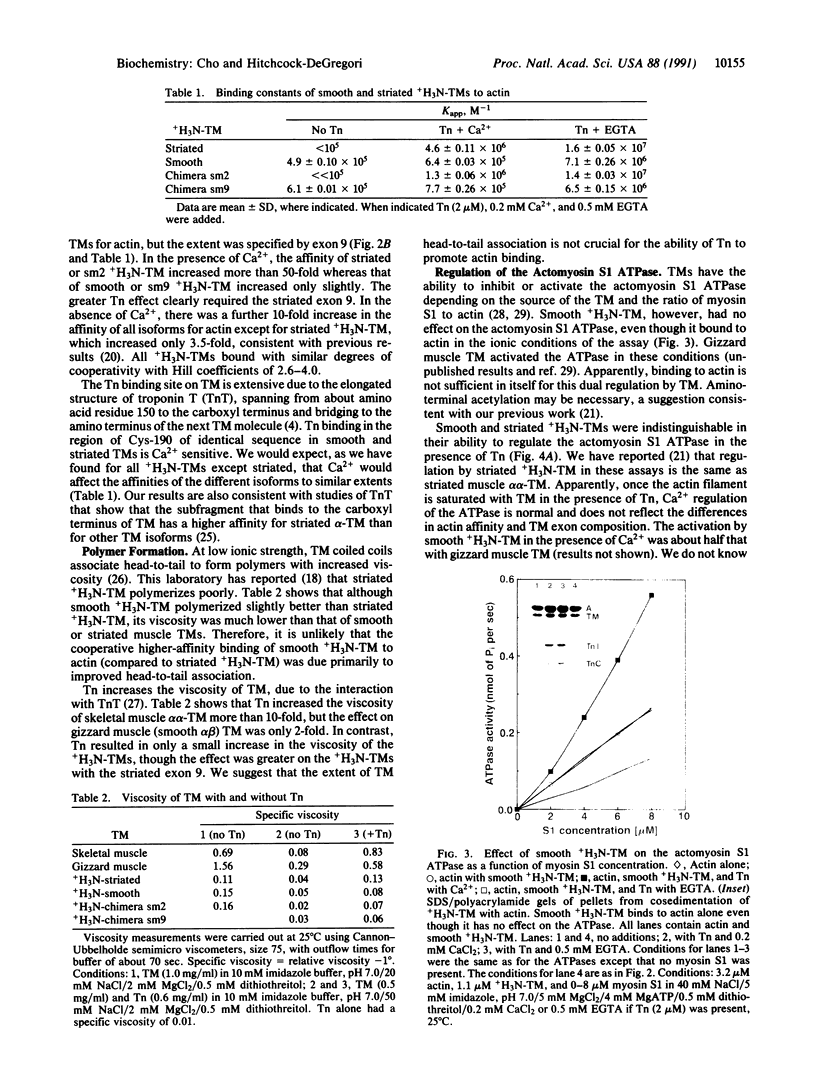
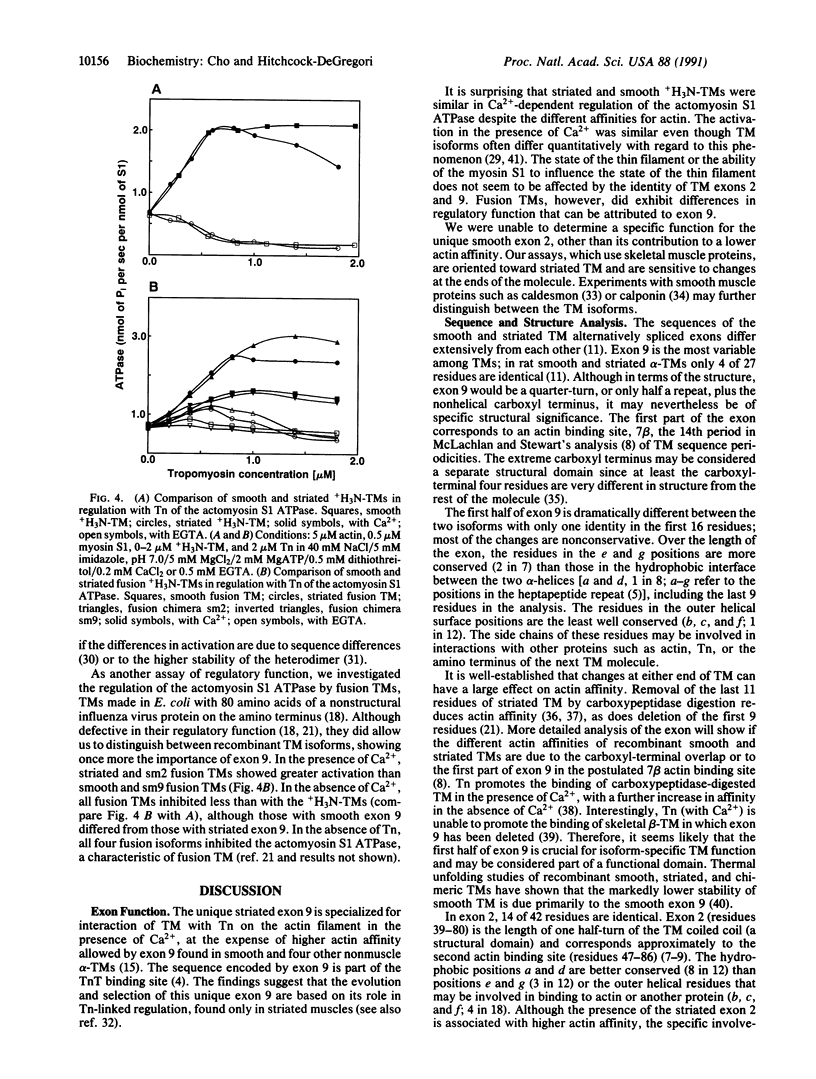
Smooth and striated muscle alpha-tropomyosins differ as a consequence of alternative splicing of exons 2 and 9 encoding amino acid residues 39-80 and 258-284, respectively [Ruiz-Opazo, N., Weinberger, J. & Nadal-Ginard, B. (1985) Nature (London) 315, 67-70]. To understand the relationship between alternatively spliced exons and functional domains in tropomyosin, recombinant unacetylated striated muscle, smooth muscle, and chimeric rat alpha-tropomyosins (+H3N-tropomyosins) expressed in and purified from Escherichia coli were analyzed. The functional differences between the isoforms can be primarily ascribed to exon 9. +H3N-Tropomyosins with the smooth muscle exon 9 bound to skeletal muscle filamentous actin with at least a 5-fold higher affinity than +H3N-tropomyosins with the striated muscle exon 9. On the other hand, in the presence of Ca2+, troponin increased the affinity of +H3N-tropomyosins with the striated muscle exon 9 at least 50-fold, whereas it had little effect on +H3N-tropomyosins with the smooth muscle exon 9. The unique striated muscle alpha-tropomyosin exon 9 seems to be specialized for Ca(2+)-insensitive interaction with troponin on the thin filament. The unique smooth muscle alpha-tropomyosin exon 2 was associated with a slightly lower actin affinity than the striated muscle exon 2. Although the regions encoded by exons 2 and 9 correspond to functional domains, they are not recognizable as independent units or structural domains in the extended coiled-coil structure of this fibrous actin binding protein.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartegi A., Ferraz C., Fattoum A., Sri Widada J., Heitz F., Kassab R., Liautard J. P. Construction, expression and unexpected regulatory properties of a tropomyosin mutant with a 31-residue deletion at the C-terminus (exon 9). Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):845–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M. Caldesmon and thin-filament regulation of muscle contraction. Cell Biophys. 1988 Jan-Jun;12:73–85. doi: 10.1007/BF02918351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho Y. J., Liu J., Hitchcock-DeGregori S. E. The amino terminus of muscle tropomyosin is a major determinant for function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):538–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colote S., Widada J. S., Ferraz C., Bonhomme F., Marti J., Liautard J. P. Evolution of tropomyosin functional domains: differential splicing and genomic constraints. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(3):228–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02100079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Sprang S., Fletterick R., Rutter W. J. Intron-exon splice junctions map at protein surfaces. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):180–182. doi: 10.1038/299180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Nowak E., Drabikowski W. Some functional properties of nonpolymerizable and polymerizable tropomyosin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):143–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00712027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Genes-in-pieces revisited. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):823–824. doi: 10.1126/science.4001923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald R. W., Hitchcock-DeGregori S. E. The structure of the amino terminus of tropomyosin is critical for binding to actin in the absence and presence of troponin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5254–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeley D. H., Golosinska K., Smillie L. B. The effects of troponin T fragments T1 and T2 on the binding of nonpolymerizable tropomyosin to F-actin in the presence and absence of troponin I and troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):9971–9978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock-DeGregori S. E., Heald R. W. Altered actin and troponin binding of amino-terminal variants of chicken striated muscle alpha-tropomyosin expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9730–9735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock-DeGregori S. E., Varnell T. A. Tropomyosin has discrete actin-binding sites with sevenfold and fourteenfold periodicities. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):885–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90343-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn M. C., Menten L. E., Garfinkel D. A convenient computer program for fitting enzymatic rate laws to steady-state data. Comput Biomed Res. 1979 Oct;12(5):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(79)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau S. Y., Sanders C., Smillie L. B. Amino acid sequence of chicken gizzard gamma-tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7257–7263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees-Miller J. P., Goodwin L. O., Helfman D. M. Three novel brain tropomyosin isoforms are expressed from the rat alpha-tropomyosin gene through the use of alternative promoters and alternative RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1729–1742. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. S., Morris E. P. Comparison of the effects of smooth and skeletal tropomyosin on skeletal actomyosin subfragment 1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2070–2072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. S., Morris E. P. Dual effects of tropomyosin and troponin-tropomyosin on actomyosin subfragment 1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8073–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. S., Qian Y. Unfolding/refolding studies of smooth muscle tropomyosin. Evidence for a chain exchange mechanism in the preferential assembly of the native heterodimer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1134–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak A. S., Golosinska K., Smillie L. B. Induction of nonpolymerizable tropomyosin binding to F-actin by troponin and its components. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14330–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M., Smillie L. B. Sequence repeats in alpha-tropomyosin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M. The 14-fold periodicity in alpha-tropomyosin and the interaction with actin. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):271–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M. Tropomyosin coiled-coil interactions: evidence for an unstaggered structure. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A. Analysis of the primary sequence of alpha-tropomyosin from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):519–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B. Binding of troponin-T fragments to several types of tropomyosin. Sensitivity to Ca2+ in the presence of troponin-C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10587–10592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Fillers J. P., Cohen C. Tropomyosin crystal structure and muscle regulation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):111–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pont M. J., Woods E. F. Denaturation of tropomyosin by guanidine hydrochloride. Int J Protein Res. 1971;3(4):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1971.tb01710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potekhin S. A., Privalov P. L. Co-operative blocks in tropomyosin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):519–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Opazo N., Nadal-Ginard B. Alpha-tropomyosin gene organization. Alternative splicing of duplicated isotype-specific exons accounts for the production of smooth and striated muscle isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4755–4765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Roberts G. C. Nuclear magnetic resonance evidence for a flexible region at the C-terminus of alpha-tropomyosin. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSAO T. C., BAILEY K., ADAIR G. S. The size, shape and aggregation of tropomyosin particles. Biochem J. 1951 Jun;49(1):27–36. doi: 10.1042/bj0490027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Hiwada K., Kokubu T. Vascular smooth muscle calponin. A novel troponin T-like protein. Hypertension. 1988 Jun;11(6 Pt 2):620–626. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.11.6.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner A., Walsh T. P. Interaction of tropomyosin-troponin with actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 15;20(19):5633–5642. doi: 10.1021/bi00522a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Ver A., Carlos A., Seidel J. C. Modulation of the actin-activated adenosinetriphosphatase activity of myosin by tropomyosin from vascular and gizzard smooth muscles. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 14;23(4):774–779. doi: 10.1021/bi00299a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. F., Desselberger U., Palese P., Ferguson B., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Efficient expression of influenza virus NS1 nonstructural proteins in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6105–6109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zot A. S., Potter J. D. Structural aspects of troponin-tropomyosin regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:535–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]