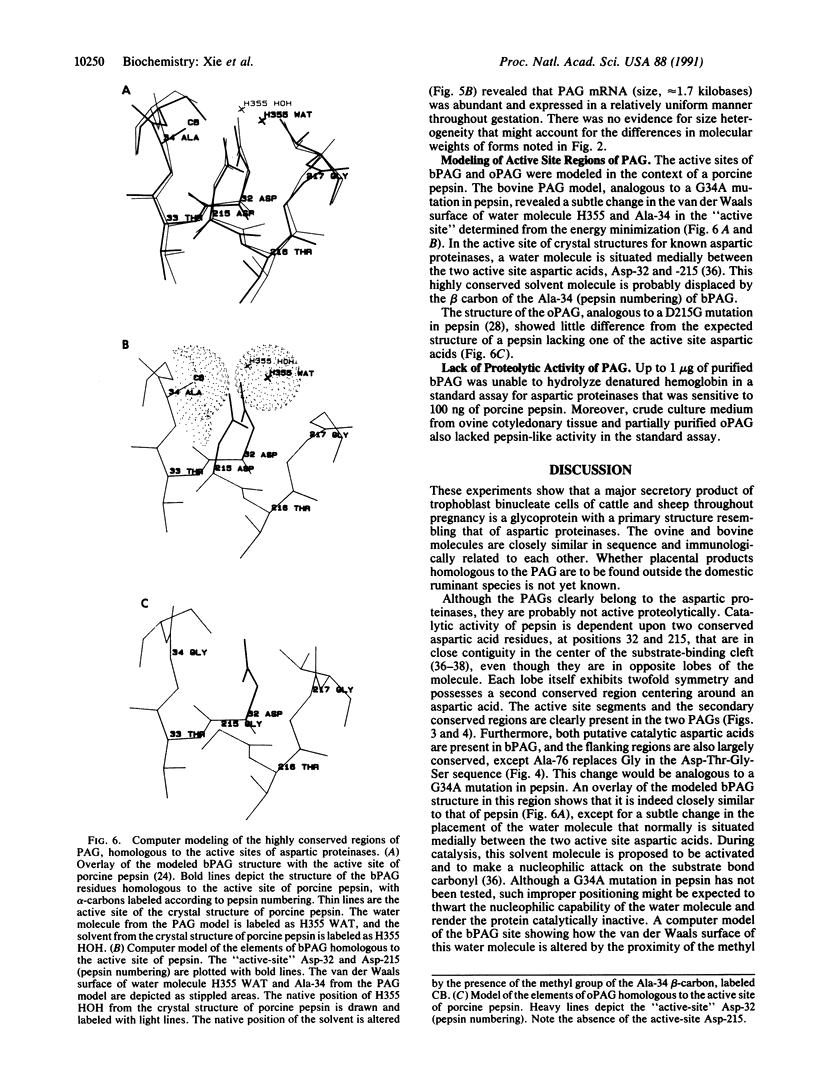
Abstract
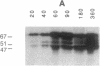
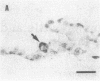
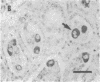
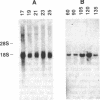
Pregnancy in cattle and sheep can be diagnosed by the presence of a conceptus-derived antigen in maternal serum that is secreted by trophoblast and placental tissue primarily as an acidic component of Mr 67,000. Molecular cloning of its cDNA reveals that the antigen belongs to the aspartic proteinase family and has greater than 50% amino acid sequence identity to pepsin, cathepsin D, and cathepsin E. The inferred sequences of the ovine and bovine polypeptides show approximately 73% identity to each other. Critical amino acid substitutions at the active site regions suggest that both proteins are enzymatically inactive. The antigen is a product of trophoblast binucleate cells that invade maternal endometrium at implantation sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreeva N. S., Zdanov A. S., Gustchina A. E., Fedorov A. A. Structure of ethanol-inhibited porcine pepsin at 2-A resolution and binding of the methyl ester of phenylalanyl-diiodotyrosine to the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11353–11365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma T., Pals G., Mohandas T. K., Couvreur J. M., Taggart R. T. Human gastric cathepsin E. Predicted sequence, localization to chromosome 1, and sequence homology with other aspartic proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16748–16753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshier D. P. A histological and histochemical examination of implantation and early placentome formation in sheep. J Reprod Fertil. 1969 Jun;19(1):51–61. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0190051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E., Hamilton W. C., Sasser R. G., Ruder C. A., Hass G. M., Williams R. J. Detection and partial characterization of two bovine pregnancy-specific proteins. Biol Reprod. 1982 Jun;26(5):925–933. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod26.5.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R. The structure and function of the aspartic proteinases. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:189–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Kornfeld S., Chirgwin J. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godkin J. D., Bazer F. W., Moffatt J., Sessions F., Roberts R. M. Purification and properties of a major, low molecular weight protein released by the trophoblast of sheep blastocysts at day 13-21. J Reprod Fertil. 1982 May;65(1):141–150. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0650141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka M., Sasaki K., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Cloning and structural analysis of the calf prochymosin gene. Gene. 1986;43(3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imakawa K., Anthony R. V., Kazemi M., Marotti K. R., Polites H. G., Roberts R. M. Interferon-like sequence of ovine trophoblast protein secreted by embryonic trophectoderm. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):377–379. doi: 10.1038/330377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imakawa K., Hansen T. R., Malathy P. V., Anthony R. V., Polites H. G., Marotti K. R., Roberts R. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of complementary deoxyribonucleic acids corresponding to bovine trophoblast protein-1: a comparison with ovine trophoblast protein-1 and bovine interferon-alpha II. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;3(1):127–139. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Sielecki A. R. Molecular structure of an aspartic proteinase zymogen, porcine pepsinogen, at 1.8 A resolution. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):33–38. doi: 10.1038/319033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama T., Takahashi K. The complete amino acid sequence of monkey pepsinogen A. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4395–4405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X. L., Wong R. N., Tang J. Synthesis, purification, and active site mutagenesis of recombinant porcine pepsinogen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4482–4489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. G., Hansen P. J., Drost M., Gogolin-Ewens K. J. Expression of major histocompatibility complex antigens on the bovine placenta. J Reprod Fertil. 1990 Sep;90(1):235–243. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0900235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki H., Fukamizu A., Hirose S., Hayashi T., Hori H., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Murakami K. Structure of the human renin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5999–6003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruder C. A., Stellflug J. N., Dahmen J. J., Sasser R. G. Detection of pregnancy in sheep by radioimmunoassay of sera for pregnancy-specific protein B. Theriogenology. 1988 Apr;29(4):905–912. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(88)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasser R. G., Crock J., Ruder-Montgomery C. A. Characteristics of pregnancy-specific protein B in cattle. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1989;37:109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasser R. G., Ruder C. A., Ivani K. A., Butler J. E., Hamilton W. C. Detection of pregnancy by radioimmunoassay of a novel pregnancy-specific protein in serum of cows and a profile of serum concentrations during gestation. Biol Reprod. 1986 Nov;35(4):936–942. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod35.4.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Mizukami Y., Ichihara Y., Takahashi K. Primary structure of human pepsinogen gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5306–5311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., Wong R. N. Evolution in the structure and function of aspartic proteases. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Jan;33(1):53–63. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wango E. O., Wooding F. B., Heap R. B. The role of trophoblast binucleate cells in implantation in the goat: a quantitative study. Placenta. 1990 Sep-Oct;11(5):381–394. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. C., Liang R., Krivi G. G., Siegel N. R., Anthony R. V. Purification and structural characterization of ovine placental lactogen. J Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;126(1):141–149. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1260141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooding F. B. Localization of ovine placental lactogen in sheep placentomes by electron microscope immunocytochemistry. J Reprod Fertil. 1981 May;62(1):15–19. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0620015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooding F. B., Wathes D. C. Binucleate cell migration in the bovine placentome. J Reprod Fertil. 1980 Jul;59(2):425–430. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0590425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoli A. P., Beckers J. F., Wouters-Ballman P., Closset J., Falmagne P., Ectors F. Purification and characterization of a bovine pregnancy-associated glycoprotein. Biol Reprod. 1991 Jul;45(1):1–10. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod45.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]