The title nitropyrrole-based compounds are intermediates used in the synthesis of modified DNA minor-groove binders. They are ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, its derivative ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide and 1-(3-azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide.
Keywords: crystal structure, nitropyrrole, minor-groove binders, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The title nitropyrrole-based compounds, C7H8N2O4, (I) (ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate), its derivative C12H14N2O4, (II) [ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate], C15H26N4O3, (III) {N-[3-(dimethyamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide}, and C20H27N9O5, (IV) {1-(3-azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide}, are intermediates used in the synthesis of modified DNA minor-groove binders. In all four compounds, the nitro groups lie in the plane of the pyrrole ring. In compounds (I) and (II), the ester groups also lie in the plane of the pyrrole ring. In compound (III), both of the other substituents lie out of the plane of the pyrrole ring. In the case of compound (IV), the coplanarity extends to the second pyrrole ring and through both amide groups. In the crystals of all four compounds, layer-like structures are formed, via a combination of N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds for (I), (III) and (IV), but by only C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds for (II).
Chemical context
Over the past two decades, the field of minor-groove binders (MGBs) has expanded vastly and now these compounds display a wide spectrum of biological activities, such as antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic and anticancer activities. A large number of structural modifications have been carried out on the original, naturally occurring compounds distamycin and netropsin, in order to optimize their biological activities (Lang et al., 2014 ▸). In addition to modifying the biological activities, structural changes have been made to the head group, tail group and the heterocyclic moieties in order to modulate their solubility, selectivity and the degree of binding to the minor groove of DNA (Alniss et al., 2014 ▸). We have recently turned to developing MGB-biotin hybrid molecules to be used as novel biochemical probes in order to determine the mechanism of action of MGBs. Structural information is important in this field, as intermolecular contacts are important for minor-groove binding and molecular conformation is relevant to structure–activity and model building (Chenoweth & Dervan, 2009 ▸). This paper details the crystal structures of a number of key building blocks that have facilitated this molecular probe development.
Structural commentary
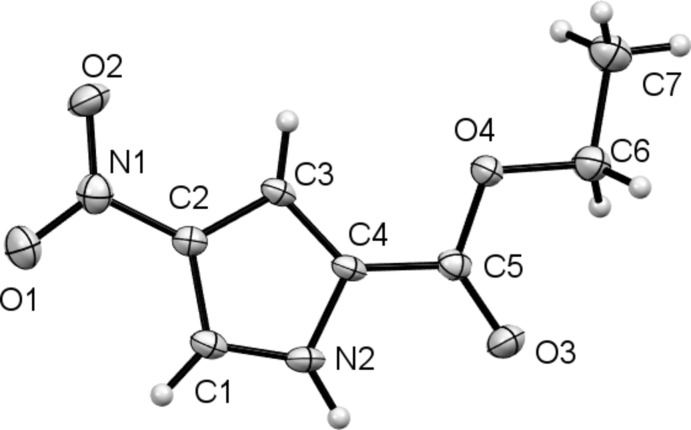
Compound (I), illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸, was produced as an intermediate in the synthesis of ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate (II). Its molecular structure is essentially planar with both the nitro and the ester functionalities coplanar with the pyrrole ring; torsion angles O1—N1—C2—C1 and N2—C4—C5—O3 are −1.5 (4) and 4.4 (4)°, respectively.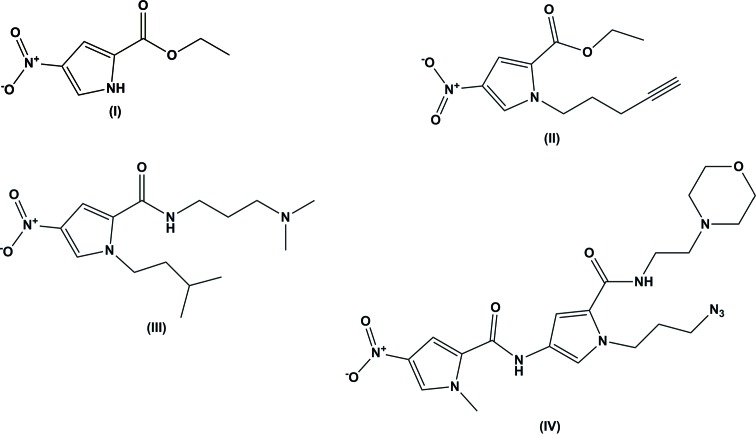
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I), with the atom labelling and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
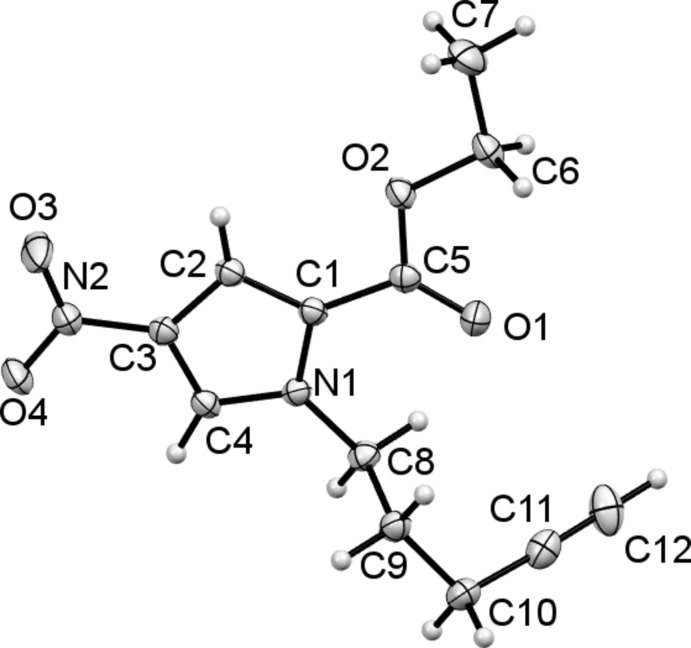
Compound (II), illustrated in Fig. 2 ▸, is an alkyne-functionalized derivative of (I) which allows for late stage diversification, and introduction of biological probe moieties, such as biotin, through application of robust click-chemistry methods. As with (I), the nitro and ester groups are approximately coplanar with the plane of the pyrrole ring. Here torsion angles O4—N2—C3—C2 and N1—C1—C5—O1 are 178.43 (14) and −8.1 (2)°, respectively. However, the overall planarity of the molecule is broken by the pentynyl function, with torsion angle C1—N1—C8—C9 being 86.21 (17)°.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II), with the atom labelling and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
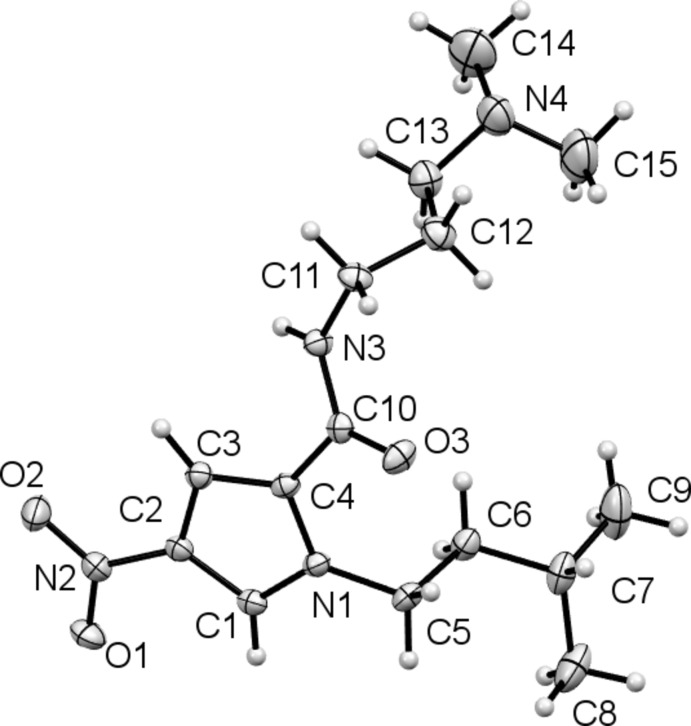
The molecular structure of compound (III) is shown in Fig. 3 ▸. It has the same 4-nitro pyrrole core as compounds (I) and (II) but has an amide substituent rather than an ester, and the pyrrole N atom now bears an iso-pentyl fragment. The introduction of the basic tail group, in this case the dimethylaminopropyl moiety, is a crucial feature for biological activity in these MGBs. The nitro group is again coplanar with the pyrrole ring, with torsion angle O2—N2—C2—C1 = 179.34 (15)°, but both the other substituents lie out of the plane of the pyrrole ring.
Figure 3.
The molecular structure of compound (III), with the atom labelling and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
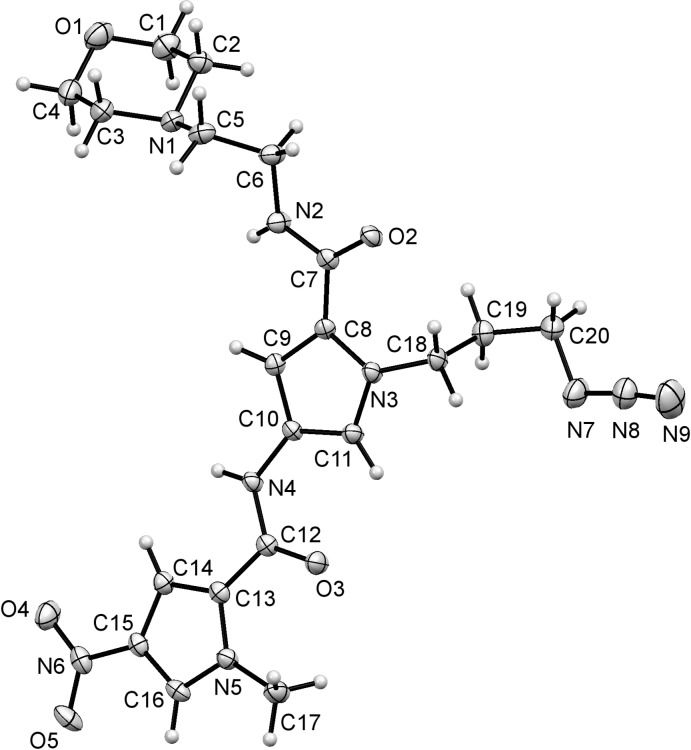
The final structure reported, compound (IV), is illustrated in Fig. 4 ▸. It is another example of a compound containing a moiety that can be functionalized with click chemistry, this time an azide. Here, there are two pyrrole rings present, one of which is a 4-nitro pyrrole as found in compounds (I), (II) and (III). As with the previous structures, the nitro group is essentially coplanar with the pyrrole ring [torsion angle O4—N6—C15—C14 = −2.8 (3)°] and this coplanarity extends to the second pyrrole ring and through both amide groups [torsion angles O3—C12—C13—N5, C12—N4—C10—C11 and O2—C7—C8—N3 are 3.1 (3), 5.5 (3) and −2.9 (3)°, respectively]. The amide O atoms and the pyrrole N atoms are all mutually syn with respect to the molecular axis running through them.
Figure 4.
The molecular structure of compound (IV), with the atom labelling and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Supramolecular features
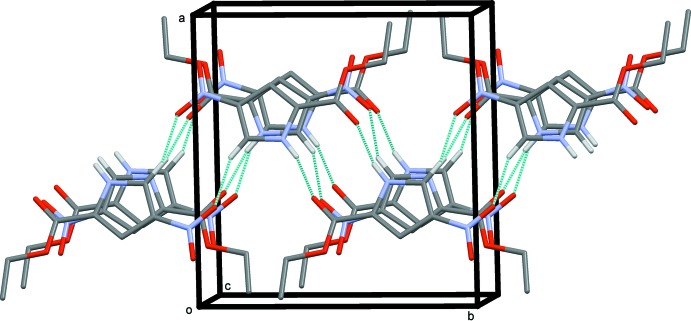
In the crystal of (I), a primary hydrogen-bonding interaction is formed, as would be expected, between the N—H donor and the carbonyl acceptor. This gives a centrosymmetric 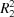 (10) motif. A weaker secondary centrosymmetric
(10) motif. A weaker secondary centrosymmetric 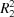 (10) hydrogen-bonding motif is also present; see Fig. 5 ▸ and Table 1 ▸. This is formed by a pyrrole C—H donor and an O atom of the nitro group. Both hydrogen-bonded ring motifs are approximately coplanar with molecular (I) and thus a two-dimensional supramolecular structure results with layers of molecules parallel to plane (10
(10) hydrogen-bonding motif is also present; see Fig. 5 ▸ and Table 1 ▸. This is formed by a pyrrole C—H donor and an O atom of the nitro group. Both hydrogen-bonded ring motifs are approximately coplanar with molecular (I) and thus a two-dimensional supramolecular structure results with layers of molecules parallel to plane (10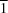 ). Interactions between the layers are both through dipole-to-dipole contacts [nitro-to-carbonyl N⋯C distance = 3.174 (4) Å] and through π–π contacts [closest C-to-C distance, C1⋯C4, is 3.304 (4) Å]. The layered structure of (I) seems to be reflected in its crystal morphology. The samples were stacked thin plates. An approximately single sample was obtained by cutting – but some degree of non-single nature is reflected in the slightly high R factors and the higher than expected residual electron density.
). Interactions between the layers are both through dipole-to-dipole contacts [nitro-to-carbonyl N⋯C distance = 3.174 (4) Å] and through π–π contacts [closest C-to-C distance, C1⋯C4, is 3.304 (4) Å]. The layered structure of (I) seems to be reflected in its crystal morphology. The samples were stacked thin plates. An approximately single sample was obtained by cutting – but some degree of non-single nature is reflected in the slightly high R factors and the higher than expected residual electron density.
Figure 5.
The crystal packing of compound (I), viewed along the c axis. The intermolecular interactions (See Table 1 ▸) are shown as dashed lines. For clarity, only the H atoms involved in these interactions have been included.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H1N⋯O3i | 0.90 (4) | 2.00 (5) | 2.872 (3) | 163 (4) |
| C1—H1⋯O1ii | 0.95 | 2.34 | 3.203 (4) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 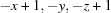 ; (ii)
; (ii) 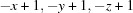 .
.
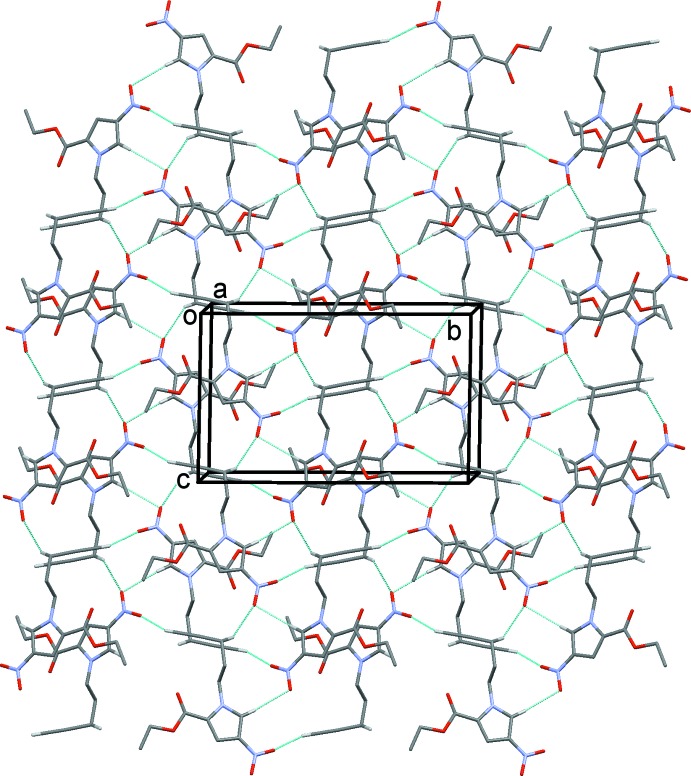
In the crystal of (II), as no strong hydrogen-bond donor is present, the supramolecular contacts are limited to non-classical C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸ and Fig. 6 ▸), which combine to give layers parallel to the bc plane, and π–π contacts [C5⋯C4i = 3.319 (2) Å; symmetry code: (i) 2 − x, −y, 1 − z] that link the layers. In contrast to (I) there are no dipole–dipole-type contacts involving the nitro group and, perhaps surprisingly, the carbonyl group is not involved in the intermolecular hydrogen bonding. There is a short intramolecular contact [O1⋯C8 = 2.925 (2), O1⋯H8A = 2.41 Å] which may disfavour intermolecular bonding here.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O3i | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.323 (2) | 141 |
| C10—H10B⋯O3ii | 0.99 | 2.51 | 3.337 (2) | 141 |
| C12—H12⋯O4iii | 0.95 | 2.40 | 3.262 (2) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 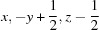 ; (ii)
; (ii) 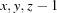 ; (iii)
; (iii) 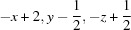 .
.
Figure 6.
The crystal packing of compound (II), viewed along the a axis. The intermolecular interactions (See Table 2 ▸) are shown as dashed lines. For clarity, only the H atoms involved in these interactions have been included.
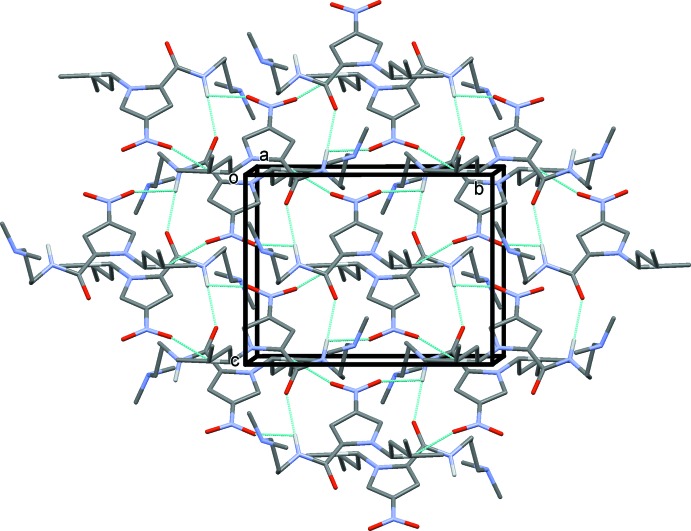
In the crystal of (III), the amide N—H group can be described as acting as a bifurcated donor giving two hydrogen bonds (Table 3 ▸ and Fig. 7 ▸), forming a short contact with the amide C=O group and a much longer contact to an O atom of a nitro group. These combine to give an 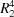 (16) motif, shown in Fig. 7 ▸. The carbonyl group also makes an intramolecular C—H-to-O contact similar to that found in the structure of (II) [O3⋯C5 = 2.970 (2), O3⋯H5A = 2.40 Å; see Table 4 ▸]; however, here, with a strong N—H hydrogen-bond donor available, this is not enough to prevent O3 taking part in other contacts. The structure of (III), composed of hydrogen-bonded layers parallel to the bc plane, features no short π–π or dipole–dipole contacts.
(16) motif, shown in Fig. 7 ▸. The carbonyl group also makes an intramolecular C—H-to-O contact similar to that found in the structure of (II) [O3⋯C5 = 2.970 (2), O3⋯H5A = 2.40 Å; see Table 4 ▸]; however, here, with a strong N—H hydrogen-bond donor available, this is not enough to prevent O3 taking part in other contacts. The structure of (III), composed of hydrogen-bonded layers parallel to the bc plane, features no short π–π or dipole–dipole contacts.
Table 3. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (III) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H1N⋯O3i | 0.91 (1) | 2.01 (1) | 2.895 (2) | 165 (2) |
| C5—H5A⋯O2ii | 0.99 | 2.54 | 3.460 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 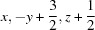 ; (ii)
; (ii) 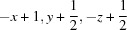 .
.
Figure 7.
The crystal packing of compound (III), viewed along the a axis. The intermolecular interactions (See Table 3 ▸) are shown as dashed lines. For clarity, only the H atoms involved in these interactions have been included.
Table 4. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (IV) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H1N⋯O5i | 0.83 (2) | 2.36 (2) | 3.176 (2) | 171 (2) |
| N4—H2N⋯O2ii | 0.88 (2) | 2.02 (2) | 2.864 (2) | 162 (2) |
| C2—H2A⋯O4iii | 0.99 | 2.53 | 3.498 (3) | 165 |
| C6—H6B⋯O3iv | 0.99 | 2.58 | 3.354 (3) | 135 |
| C9—H9⋯O5i | 0.95 | 2.43 | 3.322 (2) | 156 |
| C14—H14⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.46 | 3.317 (3) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 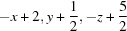 ; (ii)
; (ii) 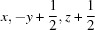 ; (iii)
; (iii) 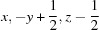 ; (iv)
; (iv) 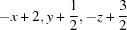 .
.
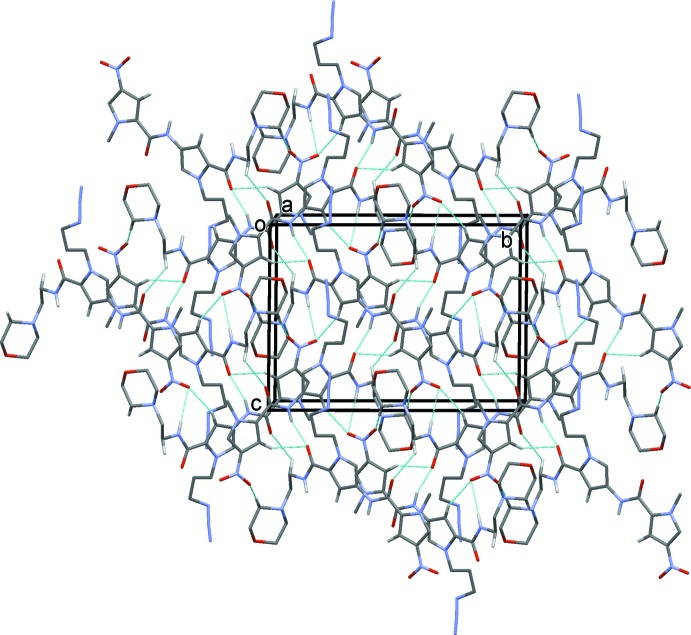
In the crystal of (IV), there are two classical N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 4 ▸ and Fig. 8 ▸) that involve both of the amide N—H groups, but surprisingly only one of the potential amide C=O acceptors. The other acceptor O atom is O5 of the nitro group. These hydrogen bonds combine to give layers parallel to the bc plane. As with (II), the reason for the second amide carbonyl group not acting as a classical hydrogen-bond acceptor may lie with a short intramolecular contact [O3⋯C11 = 2.765 (3) Å, O3⋯H11 = 2.27 Å; see Table 4 ▸]. The remaining shortest intermolecular contact involves the terminal N atom of the N3 group. This forms a short contact with the methyl carbon C17 [N9⋯C17ii 2.968 (3) Å; symmetry code: (ii) = −x + 1, −y, −z + 1) and these contacts form the primary bridges between the layers described above.
Figure 8.
The crystal packing of compound (IV), viewed along the a axis. The intermolecular interactions (See Table 4 ▸) are shown as dashed lines. For clarity, only the H atoms involved in these interactions have been included.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.37, update May 2016; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) yielded zero hits for 4-nitropyrrole-2-carboxylates and only 12 hits for 4-nitropyrrole-2-carboxamides. One of the latter, viz. dimethyl{3-[1-methyl-4-(1-methyl-4-nitropyrrole-2-carboxamido)pyrrole-2-carboxamido]propyl}ammonium chloride methanol solvate (RACBAZ; Lu et al., 2003 ▸), has a (4-nitropyrrole-2-carboxamido)pyrrole-2-carboxamide unit present, as in compound (IV). Here, the conformation of this unit is slightly more planar than that for compound (IV). For example, the two pyrrole rings are inclined to one another by 3.7 (2)° compared to 9.3 (1)° in compound (IV).
Synthesis and crystallization
Ethyl 4-nitro-1 H -pyrrole-2-carboxylate (I). 4-Nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid was dissolved in thionyl chloride (10 mL) and heated under reflux for 2 h. Excess thionyl chloride was removed under reduced pressure and the acid chloride so formed was dissolved in dichloromethane (25 mL, dry) to which ethanol (10 mL) and TEA (2 mL) were added. The stirring was continued at room temperature overnight. Solvent and excess reagents were removed under reduced pressure and the residue was partitioned between brine (50 mL) and ethyl acetate (100 mL). After the extraction, the water layer was extracted again with ethyl acetate (2 × 100 mL). The combined organic extracts were dried (Na2SO4), filtered and the solvent removed under reduced pressure. The crude product obtained was applied to a silica gel column and eluted with 1/2 ethyl acetate/n-hexane. The required product was obtained as a brown solid (1.070 g, 93%), m.p. 445–447 K [reference m.p. 447–448 K, Lee et al., 1988 ▸]. IR: 750, 775, 808, 841, 961, 1017, 1086, 1119, 1148, 1204, 1263, 1316, 1364, 1383, 1420, 14670, 1503, 1566, 1684, 3264 cm−1. 1H NMR (DMSO-d 6): 9.81(1H, br), 7.77(1H, dd, J = 3.5 Hz & J = 1.6 Hz), 7.41(1H, dd, J = 2.6 Hz & J = 1.8 Hz), 4.41(2H, qt, J = 7.1 Hz), 1.4(3H, q, J = 7.1 Hz). HRESIMS: found 185.0555; calculated 185.0557.
Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1 H -pyrrole-2-carboxylate (II). Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate (0.230 g, 1.25 mmol) was dissolved in acetone (25 mL) to which sodium carbonate (0.395 g, 3.73 mmol), tetrabutylammonium iodide (0.462 g, 1.25 mmol), and propyl bromide solution 80 weight % in toluene (1.50 mL) were added. The reaction mixture was heated under reflux for 6 h after which time it was left stirring at room temperature overnight. Water and ethyl acetate were added to the reaction mixture. After extraction, the organic layers were collected, dried (Na2SO4), filtered and the solvent removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was applied to a silica gel column and eluted with (1/4 ethyl acetate/n-hexane, R F = 0.35). The required product was obtained as a white solid (0.270 g, 83%), m.p. 335–337 K [It was obtained as a colourless oil by Satam et al., 2014 ▸]. IR: 754, 808, 864, 1018, 1084, 1107, 1165, 1188, 1250, 1285, 1312, 1364, 1383, 1422, 1497, 1533, 1717 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 7.70 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz), 7.46 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz), 4.53 (2H, t, J = 6.8 Hz), 4.35 (2H, q, J = 7.2 Hz), 2.24 (2H, dt, J = 6.7 Hz & J = 2.7 Hz), 2.09 (1H, t, J = 2.7 Hz), 2.07 (2H, qt, J = 6.7 Hz), 1.40 (3H, t, J = 7.1 Hz). HRESIMS: found 251.1010; calculated 251.1026.
N -[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1 H -pyrrole-2-carboxamide (III). Following Khalaf et al., 2004 ▸, 4-nitro-N-isopropyl-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid (0.315g, 1.39 mmol) was dissolved in thionyl chloride (5 mL) and heated at reflux for 4 h. The excess thionyl chloride was removed under reduced pressure at 323 K to give the acid chloride as a white solid that was used without further purification. 3-(Dimethylamino)propylamine (0.25 mL, 2.47 mmol) was dissolved in THF (20 mL, dry) to which N-methylmorpholine (0.25 mL) was added at room temperature with stirring. The acid chloride was dissolved in THF (5 mL, dry) and added dropwise to the amine solution at room temperature with stirring. The reaction mixture was then left stirring at room temperature overnight. Following this, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure at 323 K and then the crude product was extracted with aqueous potassium carbonate solution (25 mL, 10% w/v) and dichloromethane (2 × 50 mL). The organic layer was collected, dried (Na2SO4), and filtered, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by chromatography over silica gel using 100:100:1 methanol/ethyl acetate/triethylamine to give the required product as a pale-yellow solid (410 mg, 95%), m.p. 345–346 K. IR (KBr): 1656, 1637, 1565, 1534, 1498, 1417, 1333 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 0.95 (6H, d, J = 6.5 Hz), 1.57–1.76 (5H, m), 2.32 (6H, s), 2.51 (2H, t, J = 10.3 Hz), 3.47–3.51 (2H, quintet, J = 4.8 Hz), 4.40–4.44 (2H, q, J = 7.5 Hz), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 1.9 Hz), 7.56 (1H, d, J = 1.9 Hz), 8.61 (1H, s, br, CONH). HRESIMS: found 310.20031; calculated 310.20049.
1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1 H -pyrrole-2-carboxamido)- N -[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1 H -pyrrole-2-carboxamide (IV). 1-(3-chloropropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-(2-morpholinoethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide (100 mg, 0.214 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (5 mL, anhydrous) to which was added sodium azide (41.7 mg, 0.642 mmol). This solution was heated at 333 K overnight with stirring and then the DMF was removed in vacuo. The resulting residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate (10 mL), washed with water (3 x 10 mL) and the organic layer was reduced in volume by rotary evaporation to approximately 1 mL and the product was obtained as a crystalline solid after several hours (81 mg, 80%). IR: 3357, 3294, 3140, 2954, 2857, 2805, 2097, 1617, 1496, 1303, 1115 cm−1. 1H NMR (DMSO): 10.26 (1H, s), 8.18 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz), 8.00 (1H, t, J = 5.6 Hz), 7.58 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz), 7.27 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz), 6.85 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz), 4.34 (2H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.96 (3H, s), 3.58 (4H, t, J = 4.4 Hz), 3.25–3.30 (4H, m), 2.40–2.45 (6H, m), 1.93 (2H, pentet, J = 6.8Hz). HRESIMS: found 474.2202; calculated 474.2208.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 5 ▸. The H atoms bound to N were located in difference Fourier maps and freely refined for (I) and (IV). In compound (III), the N—H distance was restrained to be 0.93 (1) Å. For all structures, C-bound H atoms were placed in the expected geometrical positions and treated as riding: C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 5. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||||
| Chemical formula | C7H8N2O4 | C12H14N2O4 | C15H26N4O3 | C20H27N9O5 |
| M r | 184.15 | 250.25 | 310.40 | 473.51 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 123 | 123 | 123 | 123 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 11.0318 (13), 10.4108 (13), 7.1659 (8) | 7.8839 (4), 16.1443 (7), 10.2058 (5) | 17.5744 (7), 11.3718 (6), 8.7299 (4) | 11.2809 (4), 16.4528 (6), 12.5130 (5) |
| β (°) | 96.734 (10) | 104.472 (5) | 92.076 (4) | 106.542 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 817.32 (17) | 1257.78 (10) | 1743.55 (14) | 2226.32 (14) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.25 × 0.02 | 0.38 × 0.14 × 0.06 | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.04 | 0.30 × 0.28 × 0.03 |
| Data collection | ||||
| Diffractometer | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.679, 1.000 | 0.918, 1.000 | 0.995, 1.000 | 0.828, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 4995, 1604, 1240 | 6098, 2745, 2133 | 8252, 3971, 2873 | 14949, 4852, 3295 |
| R int | 0.038 | 0.025 | 0.030 | 0.038 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.617 | 0.639 | 0.650 | 0.639 |
| Refinement | ||||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.073, 0.210, 1.17 | 0.041, 0.100, 1.03 | 0.053, 0.145, 1.03 | 0.049, 0.128, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 1604 | 2745 | 3971 | 4852 |
| No. of parameters | 123 | 164 | 206 | 316 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H-atom parameters constrained | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.73, −0.30 | 0.22, −0.24 | 0.33, −0.27 | 0.29, −0.32 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, IV, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIIsup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IVsup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Patricia Keating, Gavin Bain and Craig Irving for their assistance in carrying out this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Crystal data
| C7H8N2O4 | F(000) = 384 |
| Mr = 184.15 | Dx = 1.497 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.0318 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 1975 reflections |
| b = 10.4108 (13) Å | θ = 3.2–28.3° |
| c = 7.1659 (8) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| β = 96.734 (10)° | T = 123 K |
| V = 817.32 (17) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.35 × 0.25 × 0.02 mm |
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E diffractometer | 1604 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1240 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.038 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.679, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −11→12 |
| 4995 measured reflections | l = −8→8 |
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.073 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.210 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.17 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1052P)2 + 0.5276P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1604 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 123 parameters | Δρmax = 0.73 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.6535 (2) | 0.5757 (2) | 0.6758 (3) | 0.0334 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.8216 (2) | 0.5067 (2) | 0.8325 (3) | 0.0321 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.6242 (2) | −0.0697 (2) | 0.6309 (3) | 0.0284 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.79942 (18) | −0.0218 (2) | 0.8128 (3) | 0.0225 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.7216 (2) | 0.4878 (3) | 0.7390 (3) | 0.0254 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.5700 (2) | 0.1948 (3) | 0.6026 (3) | 0.0211 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.5726 (3) | 0.3226 (3) | 0.6068 (4) | 0.0203 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.5102 | 0.3788 | 0.5530 | 0.024* | |
| C2 | 0.6831 (3) | 0.3584 (3) | 0.7041 (4) | 0.0189 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.7498 (3) | 0.2472 (3) | 0.7609 (4) | 0.0181 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.8287 | 0.2428 | 0.8300 | 0.022* | |
| C4 | 0.6769 (2) | 0.1465 (3) | 0.6954 (4) | 0.0179 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.6964 (3) | 0.0084 (3) | 0.7088 (4) | 0.0192 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.8251 (3) | −0.1596 (3) | 0.8261 (5) | 0.0290 (8) | |
| H6A | 0.8214 | −0.1978 | 0.6991 | 0.035* | |
| H6B | 0.7645 | −0.2034 | 0.8954 | 0.035* | |
| C7 | 0.9511 (3) | −0.1739 (4) | 0.9291 (5) | 0.0325 (9) | |
| H7A | 1.0100 | −0.1298 | 0.8592 | 0.049* | |
| H7B | 0.9720 | −0.2653 | 0.9406 | 0.049* | |
| H7C | 0.9533 | −0.1360 | 1.0546 | 0.049* | |
| H1N | 0.513 (4) | 0.143 (4) | 0.546 (6) | 0.055 (13)* |
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0340 (14) | 0.0233 (14) | 0.0415 (14) | 0.0062 (10) | −0.0014 (10) | 0.0016 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0239 (12) | 0.0294 (14) | 0.0408 (13) | −0.0063 (10) | −0.0050 (10) | −0.0058 (10) |
| O3 | 0.0227 (12) | 0.0247 (13) | 0.0359 (13) | −0.0045 (10) | −0.0039 (9) | −0.0034 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0213 (11) | 0.0189 (12) | 0.0253 (11) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0053 (8) | 0.0002 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0263 (14) | 0.0236 (15) | 0.0270 (14) | 0.0008 (12) | 0.0057 (11) | 0.0002 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0139 (12) | 0.0293 (16) | 0.0189 (12) | −0.0021 (11) | −0.0031 (9) | −0.0010 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0167 (14) | 0.0271 (18) | 0.0164 (14) | 0.0020 (13) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0031 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0165 (14) | 0.0216 (17) | 0.0182 (14) | 0.0004 (12) | −0.0002 (11) | −0.0002 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0134 (14) | 0.0238 (17) | 0.0166 (13) | 0.0028 (11) | −0.0007 (11) | 0.0024 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0136 (13) | 0.0249 (17) | 0.0144 (13) | 0.0017 (12) | −0.0019 (10) | 0.0029 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0181 (14) | 0.0230 (17) | 0.0165 (13) | −0.0004 (13) | 0.0015 (11) | 0.0020 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0251 (17) | 0.0252 (18) | 0.0348 (18) | 0.0019 (14) | −0.0047 (13) | −0.0023 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0238 (17) | 0.033 (2) | 0.0397 (19) | 0.0033 (15) | −0.0013 (14) | 0.0006 (15) |
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—N1 | 1.236 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.406 (4) |
| O2—N1 | 1.237 (3) | C3—C4 | 1.371 (4) |
| O3—C5 | 1.225 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| O4—C5 | 1.322 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.455 (4) |
| O4—C6 | 1.464 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.502 (4) |
| N1—C2 | 1.426 (4) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| N2—C1 | 1.331 (5) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C4 | 1.380 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| N2—H1N | 0.90 (4) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (4) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | ||
| C5—O4—C6 | 114.6 (2) | C3—C4—C5 | 131.1 (3) |
| O1—N1—O2 | 123.1 (3) | N2—C4—C5 | 120.3 (3) |
| O1—N1—C2 | 118.7 (3) | O3—C5—O4 | 124.7 (3) |
| O2—N1—C2 | 118.2 (3) | O3—C5—C4 | 122.8 (3) |
| C1—N2—C4 | 109.8 (2) | O4—C5—C4 | 112.5 (2) |
| C1—N2—H1N | 129 (3) | O4—C6—C7 | 106.9 (3) |
| C4—N2—H1N | 121 (3) | O4—C6—H6A | 110.3 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 107.2 (3) | C7—C6—H6A | 110.3 |
| N2—C1—H1 | 126.4 | O4—C6—H6B | 110.3 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 126.4 | C7—C6—H6B | 110.3 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 109.0 (3) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.6 |
| C1—C2—N1 | 124.7 (3) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—N1 | 126.3 (3) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 105.3 (3) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 127.3 | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 127.3 | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—N2 | 108.7 (3) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C4—N2—C1—C2 | 0.0 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 179.4 (3) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (3) | C1—N2—C4—C3 | 0.0 (3) |
| N2—C1—C2—N1 | 179.8 (3) | C1—N2—C4—C5 | −179.5 (2) |
| O1—N1—C2—C1 | −1.5 (4) | C6—O4—C5—O3 | 1.7 (4) |
| O2—N1—C2—C1 | 178.1 (3) | C6—O4—C5—C4 | −178.3 (2) |
| O1—N1—C2—C3 | 178.3 (3) | C3—C4—C5—O3 | −175.0 (3) |
| O2—N1—C2—C3 | −2.1 (4) | N2—C4—C5—O3 | 4.4 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.1 (3) | C3—C4—C5—O4 | 4.9 (4) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.8 (3) | N2—C4—C5—O4 | −175.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | −0.1 (3) | C5—O4—C6—C7 | 173.4 (3) |
(I) Ethyl 4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H1N···O3i | 0.90 (4) | 2.00 (5) | 2.872 (3) | 163 (4) |
| C1—H1···O1ii | 0.95 | 2.34 | 3.203 (4) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Crystal data
| C12H14N2O4 | F(000) = 528 |
| Mr = 250.25 | Dx = 1.322 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2521 reflections |
| a = 7.8839 (4) Å | θ = 3.2–29.3° |
| b = 16.1443 (7) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 10.2058 (5) Å | T = 123 K |
| β = 104.472 (5)° | Rod, colourless |
| V = 1257.78 (10) Å3 | 0.38 × 0.14 × 0.06 mm |
| Z = 4 |
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E diffractometer | 2745 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2133 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.025 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.0°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010) | h = −10→9 |
| Tmin = 0.918, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −20→17 |
| 6098 measured reflections | l = −13→12 |
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0359P)2 + 0.3332P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2745 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 164 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.67236 (15) | −0.08852 (7) | 0.29527 (11) | 0.0320 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.66323 (13) | −0.10194 (6) | 0.51291 (11) | 0.0242 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.8949 (2) | 0.18072 (8) | 0.77978 (13) | 0.0489 (4) | |
| O4 | 1.00887 (15) | 0.25558 (7) | 0.64857 (12) | 0.0325 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.84828 (15) | 0.07104 (8) | 0.37170 (12) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.93141 (17) | 0.19300 (8) | 0.67172 (14) | 0.0261 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.77664 (17) | 0.01969 (9) | 0.45352 (15) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.79676 (18) | 0.05720 (9) | 0.57710 (15) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.7608 | 0.0365 | 0.6530 | 0.024* | |
| C3 | 0.88142 (18) | 0.13247 (9) | 0.56798 (15) | 0.0203 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.91140 (18) | 0.13959 (9) | 0.44135 (15) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.9667 | 0.1848 | 0.4091 | 0.024* | |
| C5 | 0.69928 (18) | −0.06124 (9) | 0.40866 (15) | 0.0210 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.5915 (2) | −0.18454 (9) | 0.48267 (17) | 0.0276 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.6748 | −0.2201 | 0.4501 | 0.033* | |
| H6B | 0.4800 | −0.1822 | 0.4117 | 0.033* | |
| C7 | 0.5610 (2) | −0.21857 (11) | 0.61188 (19) | 0.0391 (5) | |
| H7A | 0.6723 | −0.2205 | 0.6811 | 0.059* | |
| H7B | 0.5123 | −0.2746 | 0.5959 | 0.059* | |
| H7C | 0.4785 | −0.1828 | 0.6430 | 0.059* | |
| C8 | 0.86099 (19) | 0.05609 (10) | 0.23232 (15) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.8812 | −0.0037 | 0.2205 | 0.027* | |
| H8B | 0.9626 | 0.0869 | 0.2164 | 0.027* | |
| C9 | 0.69648 (19) | 0.08289 (10) | 0.12910 (15) | 0.0237 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.6743 | 0.1423 | 0.1423 | 0.028* | |
| H9B | 0.5953 | 0.0509 | 0.1431 | 0.028* | |
| C10 | 0.7135 (2) | 0.06919 (10) | −0.01578 (16) | 0.0285 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.6022 | 0.0852 | −0.0801 | 0.034* | |
| H10B | 0.8069 | 0.1057 | −0.0323 | 0.034* | |
| C11 | 0.75444 (19) | −0.01676 (11) | −0.04200 (16) | 0.0285 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.7889 (2) | −0.08626 (12) | −0.0585 (2) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.8167 | −0.1424 | −0.0718 | 0.045* |
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0447 (7) | 0.0269 (6) | 0.0227 (6) | −0.0082 (5) | 0.0050 (5) | −0.0042 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0289 (5) | 0.0186 (5) | 0.0261 (6) | −0.0061 (4) | 0.0089 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0915 (11) | 0.0352 (8) | 0.0284 (7) | −0.0224 (7) | 0.0306 (7) | −0.0113 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0192 (6) | 0.0359 (7) | −0.0106 (5) | 0.0112 (5) | −0.0032 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0202 (6) | 0.0199 (6) | 0.0171 (7) | 0.0005 (5) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0256 (8) | −0.0030 (6) | 0.0078 (6) | −0.0017 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0194 (7) | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0197 (8) | 0.0006 (6) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0180 (7) | 0.0212 (8) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0208 (8) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0195 (7) | 0.0162 (7) | 0.0237 (8) | −0.0013 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0200 (7) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0356 (10) | −0.0048 (6) | 0.0072 (7) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0462 (10) | 0.0295 (10) | 0.0397 (11) | −0.0126 (8) | 0.0073 (8) | 0.0070 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0244 (7) | 0.0247 (8) | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0069 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0266 (7) | 0.0234 (8) | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0288 (9) | 0.0192 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0035 (7) | 0.0010 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0374 (10) | 0.0238 (9) | −0.0022 (7) | 0.0058 (6) | −0.0050 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0326 (9) | 0.0337 (10) | 0.0506 (12) | −0.0030 (8) | 0.0173 (8) | −0.0146 (9) |
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C5 | 1.2064 (18) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| O2—C5 | 1.3399 (18) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| O2—C6 | 1.4512 (18) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| O3—N2 | 1.2235 (17) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| O4—N2 | 1.2336 (16) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C4 | 1.3420 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.515 (2) |
| N1—C1 | 1.3926 (18) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C8 | 1.4707 (18) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C3 | 1.4221 (19) | C9—C10 | 1.534 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.372 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C5 | 1.466 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.401 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.464 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.376 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C11—C12 | 1.177 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.502 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C5—O2—C6 | 115.49 (12) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.6 |
| C4—N1—C1 | 109.00 (12) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C4—N1—C8 | 122.81 (12) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C8 | 128.18 (12) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| O3—N2—O4 | 122.99 (13) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| O3—N2—C3 | 118.42 (13) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| O4—N2—C3 | 118.59 (13) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 108.50 (13) | N1—C8—C9 | 111.85 (11) |
| C2—C1—C5 | 128.60 (13) | N1—C8—H8A | 109.2 |
| N1—C1—C5 | 122.87 (13) | C9—C8—H8A | 109.2 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 105.63 (13) | N1—C8—H8B | 109.2 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 127.2 | C9—C8—H8B | 109.2 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 127.2 | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 109.36 (13) | C8—C9—C10 | 111.30 (12) |
| C4—C3—N2 | 124.15 (13) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.4 |
| C2—C3—N2 | 126.49 (14) | C10—C9—H9A | 109.4 |
| N1—C4—C3 | 107.50 (12) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.4 |
| N1—C4—H4 | 126.2 | C10—C9—H9B | 109.4 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 126.2 | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.0 |
| O1—C5—O2 | 124.15 (14) | C11—C10—C9 | 112.91 (13) |
| O1—C5—C1 | 125.78 (14) | C11—C10—H10A | 109.0 |
| O2—C5—C1 | 110.08 (13) | C9—C10—H10A | 109.0 |
| O2—C6—C7 | 106.78 (13) | C11—C10—H10B | 109.0 |
| O2—C6—H6A | 110.4 | C9—C10—H10B | 109.0 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 110.4 | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.8 |
| O2—C6—H6B | 110.4 | C12—C11—C10 | 177.77 (19) |
| C7—C6—H6B | 110.4 | C11—C12—H12 | 180.0 |
| C4—N1—C1—C2 | −0.32 (16) | C2—C3—C4—N1 | −0.11 (16) |
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | 178.42 (13) | N2—C3—C4—N1 | 179.47 (13) |
| C4—N1—C1—C5 | −178.80 (13) | C6—O2—C5—O1 | 1.6 (2) |
| C8—N1—C1—C5 | −0.1 (2) | C6—O2—C5—C1 | −177.89 (11) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.25 (15) | C2—C1—C5—O1 | 173.80 (15) |
| C5—C1—C2—C3 | 178.61 (14) | N1—C1—C5—O1 | −8.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.09 (16) | C2—C1—C5—O2 | −6.8 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—N2 | −179.65 (14) | N1—C1—C5—O2 | 171.39 (12) |
| O3—N2—C3—C4 | 178.63 (15) | C5—O2—C6—C7 | −179.97 (13) |
| O4—N2—C3—C4 | −1.1 (2) | C4—N1—C8—C9 | −95.21 (16) |
| O3—N2—C3—C2 | −1.9 (2) | C1—N1—C8—C9 | 86.21 (17) |
| O4—N2—C3—C2 | 178.43 (14) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | 178.43 (12) |
| C1—N1—C4—C3 | 0.26 (16) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 56.43 (18) |
| C8—N1—C4—C3 | −178.56 (12) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −16 (4) |
(II) Ethyl 4-nitro-1-(4-pentynyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O3i | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.323 (2) | 141 |
| C10—H10B···O3ii | 0.99 | 2.51 | 3.337 (2) | 141 |
| C12—H12···O4iii | 0.95 | 2.40 | 3.262 (2) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) x, y, z−1; (iii) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Crystal data
| C15H26N4O3 | F(000) = 672 |
| Mr = 310.40 | Dx = 1.182 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2708 reflections |
| a = 17.5744 (7) Å | θ = 3.2–28.8° |
| b = 11.3718 (6) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 8.7299 (4) Å | T = 123 K |
| β = 92.076 (4)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 1743.55 (14) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.04 mm |
| Z = 4 |
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E diffractometer | 3971 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2873 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.030 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010) | h = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.995, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −13→14 |
| 8252 measured reflections | l = −11→10 |
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.053 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.145 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0606P)2 + 0.6893P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3971 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 206 parameters | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.43676 (7) | 1.01567 (12) | 0.38580 (15) | 0.0292 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.43689 (8) | 0.82473 (12) | 0.37406 (17) | 0.0343 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.67675 (7) | 0.84955 (11) | −0.16325 (14) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.60351 (8) | 0.99423 (12) | 0.07012 (16) | 0.0183 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.46097 (8) | 0.92217 (13) | 0.33535 (17) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.67714 (8) | 0.70166 (13) | 0.01195 (17) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| H1N | 0.6676 (11) | 0.6851 (17) | 0.1111 (12) | 0.024* | |
| N4 | 0.91585 (10) | 0.56415 (18) | 0.0944 (2) | 0.0422 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.55171 (9) | 1.02695 (15) | 0.1723 (2) | 0.0195 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.5396 | 1.1052 | 0.2008 | 0.023* | |
| C2 | 0.51972 (9) | 0.92543 (15) | 0.22736 (19) | 0.0187 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.55292 (9) | 0.82769 (15) | 0.15765 (19) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.5412 | 0.7472 | 0.1738 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 0.60561 (9) | 0.87244 (15) | 0.06166 (19) | 0.0174 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.65546 (10) | 1.07684 (15) | −0.0027 (2) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.6340 | 1.1573 | 0.0008 | 0.026* | |
| H5B | 0.6606 | 1.0549 | −0.1116 | 0.026* | |
| C6 | 0.73347 (10) | 1.07512 (17) | 0.0790 (2) | 0.0244 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.7536 | 0.9939 | 0.0775 | 0.029* | |
| H6B | 0.7276 | 1.0976 | 0.1875 | 0.029* | |
| C7 | 0.79112 (11) | 1.15716 (18) | 0.0085 (2) | 0.0308 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.7960 | 1.1345 | −0.1014 | 0.037* | |
| C8 | 0.76633 (14) | 1.2851 (2) | 0.0139 (3) | 0.0456 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.7200 | 1.2957 | −0.0504 | 0.068* | |
| H8B | 0.8069 | 1.3352 | −0.0242 | 0.068* | |
| H8C | 0.7562 | 1.3068 | 0.1198 | 0.068* | |
| C9 | 0.86909 (13) | 1.1411 (3) | 0.0907 (3) | 0.0517 (7) | |
| H9A | 0.9071 | 1.1890 | 0.0398 | 0.078* | |
| H9B | 0.8839 | 1.0581 | 0.0869 | 0.078* | |
| H9C | 0.8661 | 1.1659 | 0.1978 | 0.078* | |
| C10 | 0.65675 (9) | 0.80817 (15) | −0.04016 (19) | 0.0185 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.71803 (10) | 0.61821 (16) | −0.0811 (2) | 0.0233 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.7028 | 0.6309 | −0.1901 | 0.028* | |
| H11B | 0.7023 | 0.5376 | −0.0534 | 0.028* | |
| C12 | 0.80398 (11) | 0.62648 (19) | −0.0639 (2) | 0.0303 (5) | |
| H12A | 0.8268 | 0.5728 | −0.1389 | 0.036* | |
| H12B | 0.8198 | 0.7076 | −0.0891 | 0.036* | |
| C13 | 0.83521 (11) | 0.59597 (19) | 0.0947 (2) | 0.0318 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.8286 | 0.6642 | 0.1634 | 0.038* | |
| H13B | 0.8059 | 0.5294 | 0.1355 | 0.038* | |
| C14 | 0.94033 (15) | 0.5120 (3) | 0.2399 (3) | 0.0619 (8) | |
| H14A | 0.9326 | 0.5684 | 0.3228 | 0.093* | |
| H14B | 0.9944 | 0.4916 | 0.2373 | 0.093* | |
| H14C | 0.9105 | 0.4408 | 0.2578 | 0.093* | |
| C15 | 0.96397 (14) | 0.6629 (3) | 0.0604 (4) | 0.0631 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.9505 | 0.6927 | −0.0424 | 0.095* | |
| H15B | 1.0174 | 0.6378 | 0.0645 | 0.095* | |
| H15C | 0.9567 | 0.7253 | 0.1359 | 0.095* |
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0269 (7) | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0346 (8) | 0.0097 (6) | 0.0057 (6) | −0.0033 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0338 (7) | 0.0252 (8) | 0.0452 (9) | −0.0027 (6) | 0.0168 (6) | 0.0024 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0375 (7) | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0167 (6) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0043 (5) | 0.0010 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0191 (7) | 0.0147 (7) | 0.0207 (7) | −0.0002 (6) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0014 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0192 (7) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0244 (7) | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0031 (6) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0003 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0286 (9) | 0.0492 (12) | 0.0484 (12) | −0.0016 (8) | −0.0035 (8) | 0.0092 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0180 (9) | 0.0219 (9) | 0.0033 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0205 (8) | 0.0023 (7) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0008 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0174 (9) | 0.0213 (9) | 0.0002 (7) | −0.0013 (6) | 0.0004 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0191 (8) | 0.0158 (8) | 0.0171 (8) | −0.0001 (7) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0265 (9) | 0.0162 (8) | 0.0211 (9) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0033 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0256 (9) | 0.0240 (10) | 0.0235 (9) | −0.0056 (8) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0044 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0317 (10) | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0253 (10) | −0.0127 (9) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0041 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0592 (15) | 0.0333 (12) | 0.0448 (14) | −0.0203 (11) | 0.0108 (11) | 0.0026 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0332 (12) | 0.0749 (19) | 0.0469 (14) | −0.0221 (12) | −0.0010 (10) | 0.0124 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0205 (9) | 0.0177 (8) | −0.0029 (7) | −0.0020 (6) | −0.0020 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0221 (9) | 0.0219 (9) | 0.0049 (7) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0042 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0287 (10) | 0.0318 (11) | 0.0307 (11) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0056 (8) | −0.0027 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0359 (11) | 0.0314 (11) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0011 (8) | −0.0004 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0435 (14) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0645 (18) | −0.0022 (14) | −0.0170 (13) | 0.0193 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0366 (13) | 0.074 (2) | 0.079 (2) | −0.0156 (13) | −0.0038 (13) | 0.0177 (16) |
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—N2 | 1.2325 (19) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| O2—N2 | 1.2375 (19) | C7—C8 | 1.520 (3) |
| O3—C10 | 1.236 (2) | C7—C9 | 1.535 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.350 (2) | C7—H7 | 1.0000 |
| N1—C4 | 1.388 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C5 | 1.471 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| N2—C2 | 1.424 (2) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| N3—C10 | 1.338 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| N3—C11 | 1.456 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| N3—H1N | 0.908 (9) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| N4—C15 | 1.443 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.515 (3) |
| N4—C14 | 1.453 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| N4—C13 | 1.463 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.378 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.511 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.404 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.369 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C10 | 1.480 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.523 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9900 | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9900 | C15—H15A | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.524 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9900 | C15—H15C | 0.9800 |
| C1—N1—C4 | 109.28 (14) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 123.63 (14) | C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C4—N1—C5 | 126.63 (14) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O1—N2—O2 | 123.30 (15) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O1—N2—C2 | 118.82 (15) | C7—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| O2—N2—C2 | 117.88 (15) | C7—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C10—N3—C11 | 122.14 (15) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C10—N3—H1N | 117.1 (13) | C7—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C11—N3—H1N | 120.6 (13) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C15—N4—C14 | 109.9 (2) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C15—N4—C13 | 112.51 (19) | O3—C10—N3 | 124.00 (16) |
| C14—N4—C13 | 110.86 (19) | O3—C10—C4 | 122.17 (16) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 107.04 (15) | N3—C10—C4 | 113.82 (15) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 126.5 | N3—C11—C12 | 114.51 (15) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 126.5 | N3—C11—H11A | 108.6 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 109.31 (15) | C12—C11—H11A | 108.6 |
| C1—C2—N2 | 124.59 (15) | N3—C11—H11B | 108.6 |
| C3—C2—N2 | 126.09 (15) | C12—C11—H11B | 108.6 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 105.77 (15) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 127.1 | C13—C12—C11 | 113.83 (16) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 127.1 | C13—C12—H12A | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—N1 | 108.58 (15) | C11—C12—H12A | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—C10 | 128.54 (16) | C13—C12—H12B | 108.8 |
| N1—C4—C10 | 122.87 (15) | C11—C12—H12B | 108.8 |
| N1—C5—C6 | 110.60 (14) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.7 |
| N1—C5—H5A | 109.5 | N4—C13—C12 | 112.04 (17) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.5 | N4—C13—H13A | 109.2 |
| N1—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13A | 109.2 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.5 | N4—C13—H13B | 109.2 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.1 | C12—C13—H13B | 109.2 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 113.79 (15) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.9 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 108.8 | N4—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 108.8 | N4—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6B | 108.8 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6B | 108.8 | N4—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.7 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 112.21 (17) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C9 | 110.58 (19) | N4—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C9 | 109.48 (17) | N4—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 108.1 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 108.1 | N4—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C9—C7—H7 | 108.1 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | ||
| C4—N1—C1—C2 | −0.96 (18) | C1—N1—C5—C6 | 98.60 (19) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | −173.61 (14) | C4—N1—C5—C6 | −72.7 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.21 (18) | N1—C5—C6—C7 | 179.02 (15) |
| N1—C1—C2—N2 | −178.42 (15) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 61.5 (2) |
| O1—N2—C2—C1 | −0.8 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C9 | −175.33 (18) |
| O2—N2—C2—C1 | 179.34 (15) | C11—N3—C10—O3 | −7.4 (3) |
| O1—N2—C2—C3 | −179.22 (15) | C11—N3—C10—C4 | 171.01 (14) |
| O2—N2—C2—C3 | 0.9 (3) | C3—C4—C10—O3 | 148.08 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.63 (18) | N1—C4—C10—O3 | −30.3 (2) |
| N2—C2—C3—C4 | 179.23 (15) | C3—C4—C10—N3 | −30.4 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | −1.20 (18) | N1—C4—C10—N3 | 151.23 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C10 | −179.77 (15) | C10—N3—C11—C12 | 90.8 (2) |
| C1—N1—C4—C3 | 1.39 (18) | N3—C11—C12—C13 | 64.5 (2) |
| C5—N1—C4—C3 | 173.75 (15) | C15—N4—C13—C12 | 68.4 (3) |
| C1—N1—C4—C10 | −179.95 (14) | C14—N4—C13—C12 | −168.0 (2) |
| C5—N1—C4—C10 | −7.6 (2) | C11—C12—C13—N4 | 159.69 (17) |
(III) N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-isopentyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H1N···O3i | 0.91 (1) | 2.01 (1) | 2.895 (2) | 165 (2) |
| C5—H5A···O2ii | 0.99 | 2.54 | 3.460 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Crystal data
| C20H27N9O5 | F(000) = 1000 |
| Mr = 473.51 | Dx = 1.413 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4332 reflections |
| a = 11.2809 (4) Å | θ = 3.3–29.5° |
| b = 16.4528 (6) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 12.5130 (5) Å | T = 123 K |
| β = 106.542 (4)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 2226.32 (14) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.28 × 0.03 mm |
| Z = 4 |
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E diffractometer | 4852 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3295 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.038 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.0°, θmin = 3.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.828, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −21→20 |
| 14949 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.128 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0544P)2 + 0.8101P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4852 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 316 parameters | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3 |
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 1.41300 (15) | 0.56045 (11) | 1.22578 (13) | 0.0398 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.98973 (13) | 0.34257 (9) | 0.69343 (11) | 0.0258 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.74904 (13) | −0.00393 (9) | 0.86469 (11) | 0.0283 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.97289 (14) | −0.07180 (11) | 1.39704 (12) | 0.0368 (4) | |
| O5 | 0.86665 (15) | −0.18352 (10) | 1.36804 (12) | 0.0340 (4) | |
| N1 | 1.30194 (15) | 0.45013 (11) | 1.04738 (14) | 0.0241 (4) | |
| N2 | 1.09195 (16) | 0.35509 (11) | 0.87526 (14) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.84913 (15) | 0.20896 (10) | 0.74083 (13) | 0.0200 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.88041 (15) | 0.08236 (11) | 0.98173 (14) | 0.0198 (4) | |
| N5 | 0.76427 (15) | −0.11643 (11) | 1.04131 (13) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| N6 | 0.90337 (16) | −0.12010 (12) | 1.33493 (14) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| N7 | 0.53925 (18) | 0.24820 (15) | 0.46339 (15) | 0.0422 (6) | |
| N8 | 0.49433 (18) | 0.24723 (13) | 0.36178 (16) | 0.0379 (5) | |
| N9 | 0.4479 (2) | 0.24057 (16) | 0.26908 (19) | 0.0575 (7) | |
| C1 | 1.2953 (2) | 0.57601 (15) | 1.14934 (18) | 0.0345 (6) | |
| H1A | 1.2826 | 0.6354 | 1.1404 | 0.041* | |
| H1B | 1.2299 | 0.5537 | 1.1795 | 0.041* | |
| C2 | 1.2846 (2) | 0.53840 (13) | 1.03754 (17) | 0.0272 (5) | |
| H2A | 1.2020 | 0.5506 | 0.9861 | 0.033* | |
| H2B | 1.3476 | 0.5623 | 1.0058 | 0.033* | |
| C3 | 1.42227 (19) | 0.43408 (15) | 1.12873 (18) | 0.0312 (5) | |
| H3A | 1.4892 | 0.4540 | 1.0987 | 0.037* | |
| H3B | 1.4331 | 0.3747 | 1.1406 | 0.037* | |
| C4 | 1.4324 (2) | 0.47497 (16) | 1.23829 (19) | 0.0373 (6) | |
| H4A | 1.3704 | 0.4513 | 1.2716 | 0.045* | |
| H4B | 1.5154 | 0.4645 | 1.2899 | 0.045* | |
| C5 | 1.30008 (19) | 0.41485 (14) | 0.93966 (17) | 0.0271 (5) | |
| H5A | 1.3284 | 0.3577 | 0.9515 | 0.032* | |
| H5B | 1.3598 | 0.4447 | 0.9097 | 0.032* | |
| C6 | 1.1751 (2) | 0.41652 (14) | 0.85378 (17) | 0.0280 (5) | |
| H6A | 1.1376 | 0.4709 | 0.8539 | 0.034* | |
| H6B | 1.1860 | 0.4073 | 0.7789 | 0.034* | |
| C7 | 1.00628 (18) | 0.32014 (12) | 0.79114 (15) | 0.0194 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.93886 (17) | 0.25098 (12) | 0.81991 (15) | 0.0180 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.96041 (17) | 0.20919 (12) | 0.91950 (15) | 0.0187 (4) | |
| H9 | 1.0175 | 0.2240 | 0.9885 | 0.022* | |
| C10 | 0.88249 (17) | 0.14092 (12) | 0.90005 (15) | 0.0178 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.81442 (18) | 0.14275 (13) | 0.78955 (15) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.7534 | 0.1042 | 0.7535 | 0.025* | |
| C12 | 0.81419 (17) | 0.01299 (13) | 0.95888 (15) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.82387 (17) | −0.04175 (12) | 1.05467 (16) | 0.0196 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.88497 (18) | −0.03205 (13) | 1.16576 (16) | 0.0211 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.9339 | 0.0131 | 1.1995 | 0.025* | |
| C15 | 0.86064 (18) | −0.10201 (13) | 1.21902 (15) | 0.0209 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.78689 (18) | −0.15307 (13) | 1.14111 (16) | 0.0226 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.7573 | −0.2049 | 1.1552 | 0.027* | |
| C17 | 0.6959 (2) | −0.15598 (14) | 0.93648 (17) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| H17A | 0.6654 | −0.2090 | 0.9529 | 0.044* | |
| H17B | 0.7509 | −0.1636 | 0.8892 | 0.044* | |
| H17C | 0.6258 | −0.1218 | 0.8975 | 0.044* | |
| C18 | 0.78428 (19) | 0.23250 (13) | 0.62593 (15) | 0.0233 (5) | |
| H18A | 0.7383 | 0.1850 | 0.5861 | 0.028* | |
| H18B | 0.8458 | 0.2488 | 0.5872 | 0.028* | |
| C19 | 0.69467 (19) | 0.30212 (14) | 0.62105 (16) | 0.0266 (5) | |
| H19A | 0.6400 | 0.2886 | 0.6679 | 0.032* | |
| H19B | 0.7419 | 0.3515 | 0.6524 | 0.032* | |
| C20 | 0.6165 (2) | 0.31976 (15) | 0.50420 (18) | 0.0321 (5) | |
| H20A | 0.5637 | 0.3679 | 0.5039 | 0.039* | |
| H20B | 0.6699 | 0.3312 | 0.4555 | 0.039* | |
| H1N | 1.094 (2) | 0.3458 (14) | 0.9407 (19) | 0.025 (6)* | |
| H2N | 0.922 (2) | 0.0947 (15) | 1.051 (2) | 0.035 (7)* |
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0397 (9) | 0.0420 (11) | 0.0339 (9) | −0.0102 (9) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0090 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0354 (8) | 0.0221 (8) | 0.0175 (7) | −0.0041 (7) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0044 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0364 (8) | 0.0263 (8) | 0.0184 (8) | −0.0069 (7) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0497 (11) | 0.0211 (8) | −0.0107 (9) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0016 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0510 (10) | 0.0254 (9) | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0052 (8) | 0.0139 (7) | 0.0106 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0229 (8) | 0.0221 (10) | 0.0252 (9) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0037 (7) | 0.0000 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0331 (10) | 0.0261 (10) | 0.0145 (9) | −0.0090 (9) | 0.0067 (7) | −0.0014 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0263 (9) | 0.0180 (9) | 0.0140 (8) | −0.0012 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0003 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0178 (9) | 0.0146 (9) | −0.0011 (8) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0013 (7) |
| N5 | 0.0253 (8) | 0.0180 (9) | 0.0203 (9) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0067 (7) | 0.0005 (7) |
| N6 | 0.0280 (9) | 0.0294 (11) | 0.0215 (9) | 0.0081 (9) | 0.0081 (8) | 0.0067 (8) |
| N7 | 0.0405 (11) | 0.0530 (15) | 0.0259 (11) | −0.0132 (11) | −0.0019 (9) | 0.0015 (10) |
| N8 | 0.0345 (10) | 0.0428 (13) | 0.0322 (12) | 0.0017 (10) | 0.0028 (9) | −0.0026 (10) |
| N9 | 0.0693 (16) | 0.0580 (17) | 0.0339 (13) | 0.0029 (14) | −0.0036 (12) | −0.0083 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0333 (14) | 0.0329 (13) | −0.0019 (12) | 0.0098 (10) | −0.0066 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0289 (11) | 0.0217 (12) | 0.0307 (12) | −0.0011 (10) | 0.0078 (9) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0237 (10) | 0.0291 (13) | 0.0367 (13) | −0.0033 (10) | 0.0018 (9) | 0.0059 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0312 (12) | 0.0444 (16) | 0.0306 (13) | −0.0089 (12) | −0.0003 (10) | 0.0073 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0280 (11) | 0.0218 (11) | 0.0320 (12) | −0.0047 (10) | 0.0095 (9) | −0.0034 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0358 (12) | 0.0243 (12) | 0.0238 (11) | −0.0107 (10) | 0.0082 (9) | −0.0011 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0172 (10) | 0.0182 (10) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0069 (8) | −0.0012 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0154 (10) | 0.0162 (9) | 0.0020 (9) | 0.0047 (7) | −0.0035 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0209 (9) | 0.0190 (10) | 0.0161 (9) | 0.0016 (9) | 0.0053 (8) | −0.0022 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0160 (10) | 0.0157 (9) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0057 (8) | 0.0013 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0256 (10) | 0.0178 (11) | 0.0192 (10) | −0.0026 (9) | 0.0048 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0213 (9) | 0.0188 (10) | 0.0181 (10) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0071 (8) | −0.0005 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0209 (9) | 0.0190 (11) | 0.0199 (10) | 0.0026 (9) | 0.0074 (8) | 0.0006 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0235 (10) | 0.0213 (11) | 0.0188 (10) | 0.0016 (9) | 0.0064 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0228 (10) | 0.0224 (11) | 0.0185 (10) | 0.0041 (9) | 0.0072 (8) | 0.0027 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0280 (10) | 0.0179 (11) | 0.0245 (11) | 0.0032 (9) | 0.0118 (9) | 0.0054 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0386 (12) | 0.0230 (12) | 0.0248 (11) | −0.0068 (11) | 0.0052 (9) | −0.0013 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0300 (11) | 0.0234 (11) | 0.0133 (10) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0264 (10) | 0.0290 (13) | 0.0230 (11) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0045 (9) | 0.0013 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0266 (11) | 0.0348 (14) | 0.0312 (12) | −0.0027 (11) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0072 (10) |
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.421 (3) | C3—H3B | 0.9900 |
| O1—C4 | 1.425 (3) | C4—H4A | 0.9900 |
| O2—C7 | 1.239 (2) | C4—H4B | 0.9900 |
| O3—C12 | 1.230 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.510 (3) |
| O4—N6 | 1.226 (2) | C5—H5A | 0.9900 |
| O5—N6 | 1.237 (2) | C5—H5B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C5 | 1.462 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C2 | 1.466 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C3 | 1.470 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.469 (3) |
| N2—C7 | 1.339 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.383 (3) |
| N2—C6 | 1.455 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.404 (3) |
| N2—H1N | 0.83 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C11 | 1.359 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.378 (3) |
| N3—C8 | 1.383 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C18 | 1.467 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.478 (3) |
| N4—C12 | 1.349 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.374 (3) |
| N4—C10 | 1.410 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.396 (3) |
| N4—H2N | 0.88 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| N5—C16 | 1.344 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.374 (3) |
| N5—C13 | 1.388 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| N5—C17 | 1.471 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| N6—C15 | 1.424 (2) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| N7—N8 | 1.227 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| N7—C20 | 1.467 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.517 (3) |
| N8—N9 | 1.134 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.503 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C19—C20 | 1.505 (3) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C19—H19A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C19—H19B | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C20—H20A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.502 (3) | C20—H20B | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | ||
| C1—O1—C4 | 109.65 (18) | H6A—C6—H6B | 107.9 |
| C5—N1—C2 | 110.46 (17) | O2—C7—N2 | 121.32 (19) |
| C5—N1—C3 | 109.57 (17) | O2—C7—C8 | 121.96 (17) |
| C2—N1—C3 | 108.13 (17) | N2—C7—C8 | 116.62 (16) |
| C7—N2—C6 | 120.80 (17) | N3—C8—C9 | 107.54 (17) |
| C7—N2—H1N | 120.7 (16) | N3—C8—C7 | 122.45 (16) |
| C6—N2—H1N | 118.2 (16) | C9—C8—C7 | 129.45 (17) |
| C11—N3—C8 | 109.00 (16) | C8—C9—C10 | 107.51 (17) |
| C11—N3—C18 | 121.61 (16) | C8—C9—H9 | 126.2 |
| C8—N3—C18 | 128.93 (17) | C10—C9—H9 | 126.2 |
| C12—N4—C10 | 123.17 (17) | C11—C10—C9 | 107.40 (17) |
| C12—N4—H2N | 120.6 (16) | C11—C10—N4 | 128.53 (18) |
| C10—N4—H2N | 116.1 (16) | C9—C10—N4 | 124.06 (17) |
| C16—N5—C13 | 109.14 (17) | N3—C11—C10 | 108.55 (17) |
| C16—N5—C17 | 122.87 (18) | N3—C11—H11 | 125.7 |
| C13—N5—C17 | 127.76 (17) | C10—C11—H11 | 125.7 |
| O4—N6—O5 | 123.31 (17) | O3—C12—N4 | 122.55 (18) |
| O4—N6—C15 | 118.70 (18) | O3—C12—C13 | 121.67 (19) |
| O5—N6—C15 | 117.98 (18) | N4—C12—C13 | 115.78 (17) |
| N8—N7—C20 | 113.6 (2) | C14—C13—N5 | 108.13 (17) |
| N9—N8—N7 | 174.3 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 130.51 (19) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 111.39 (19) | N5—C13—C12 | 121.36 (17) |
| O1—C1—H1A | 109.3 | C13—C14—C15 | 106.08 (18) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.3 | C13—C14—H14 | 127.0 |
| O1—C1—H1B | 109.3 | C15—C14—H14 | 127.0 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.3 | C16—C15—C14 | 109.09 (17) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.0 | C16—C15—N6 | 123.80 (19) |
| N1—C2—C1 | 110.88 (18) | C14—C15—N6 | 127.11 (19) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | N5—C16—C15 | 107.55 (19) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | N5—C16—H16 | 126.2 |
| N1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 126.2 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | N5—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.1 | N5—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—C4 | 111.51 (19) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—H3A | 109.3 | N5—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109.3 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—H3B | 109.3 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 109.3 | N3—C18—C19 | 112.29 (16) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.0 | N3—C18—H18A | 109.1 |
| O1—C4—C3 | 111.86 (19) | C19—C18—H18A | 109.1 |
| O1—C4—H4A | 109.2 | N3—C18—H18B | 109.1 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.2 | C19—C18—H18B | 109.1 |
| O1—C4—H4B | 109.2 | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.9 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.2 | C20—C19—C18 | 112.59 (18) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.9 | C20—C19—H19A | 109.1 |
| N1—C5—C6 | 114.48 (18) | C18—C19—H19A | 109.1 |
| N1—C5—H5A | 108.6 | C20—C19—H19B | 109.1 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 108.6 | C18—C19—H19B | 109.1 |
| N1—C5—H5B | 108.6 | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.8 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 108.6 | N7—C20—C19 | 108.00 (19) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 107.6 | N7—C20—H20A | 110.1 |
| N2—C6—C5 | 112.10 (18) | C19—C20—H20A | 110.1 |
| N2—C6—H6A | 109.2 | N7—C20—H20B | 110.1 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.2 | C19—C20—H20B | 110.1 |
| N2—C6—H6B | 109.2 | H20A—C20—H20B | 108.4 |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.2 | ||
| C20—N7—N8—N9 | −177 (3) | C18—N3—C11—C10 | −173.55 (17) |
| C4—O1—C1—C2 | −58.5 (2) | C9—C10—C11—N3 | 0.7 (2) |
| C5—N1—C2—C1 | −175.98 (17) | N4—C10—C11—N3 | −178.01 (18) |
| C3—N1—C2—C1 | −56.1 (2) | C10—N4—C12—O3 | −0.9 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—N1 | 59.5 (2) | C10—N4—C12—C13 | 179.47 (17) |
| C5—N1—C3—C4 | 175.41 (19) | C16—N5—C13—C14 | 0.0 (2) |
| C2—N1—C3—C4 | 55.0 (2) | C17—N5—C13—C14 | −174.61 (18) |
| C1—O1—C4—C3 | 57.3 (2) | C16—N5—C13—C12 | −179.14 (17) |
| N1—C3—C4—O1 | −56.8 (3) | C17—N5—C13—C12 | 6.2 (3) |
| C2—N1—C5—C6 | −69.5 (2) | O3—C12—C13—C14 | −175.9 (2) |
| C3—N1—C5—C6 | 171.44 (18) | N4—C12—C13—C14 | 3.7 (3) |
| C7—N2—C6—C5 | −148.35 (19) | O3—C12—C13—N5 | 3.1 (3) |
| N1—C5—C6—N2 | −75.6 (2) | N4—C12—C13—N5 | −177.36 (17) |
| C6—N2—C7—O2 | −4.8 (3) | N5—C13—C14—C15 | −0.3 (2) |
| C6—N2—C7—C8 | 171.58 (18) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 178.8 (2) |
| C11—N3—C8—C9 | 0.4 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.4 (2) |
| C18—N3—C8—C9 | 172.56 (18) | C13—C14—C15—N6 | −179.62 (18) |
| C11—N3—C8—C7 | 172.58 (17) | O4—N6—C15—C16 | 177.15 (19) |
| C18—N3—C8—C7 | −15.3 (3) | O5—N6—C15—C16 | −3.9 (3) |
| O2—C7—C8—N3 | −2.9 (3) | O4—N6—C15—C14 | −2.8 (3) |
| N2—C7—C8—N3 | −179.27 (18) | O5—N6—C15—C14 | 176.11 (19) |
| O2—C7—C8—C9 | 167.3 (2) | C13—N5—C16—C15 | 0.2 (2) |
| N2—C7—C8—C9 | −9.0 (3) | C17—N5—C16—C15 | 175.17 (17) |
| N3—C8—C9—C10 | 0.0 (2) | C14—C15—C16—N5 | −0.4 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −171.38 (19) | N6—C15—C16—N5 | 179.63 (17) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.5 (2) | C11—N3—C18—C19 | 101.0 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—N4 | 178.35 (17) | C8—N3—C18—C19 | −70.2 (3) |
| C12—N4—C10—C11 | 5.5 (3) | N3—C18—C19—C20 | −172.88 (17) |
| C12—N4—C10—C9 | −173.06 (18) | N8—N7—C20—C19 | −163.3 (2) |
| C8—N3—C11—C10 | −0.7 (2) | C18—C19—C20—N7 | 63.8 (2) |
(IV) 1-(3-Azidopropyl)-4-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamido)-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H1N···O5i | 0.83 (2) | 2.36 (2) | 3.176 (2) | 171 (2) |
| N4—H2N···O2ii | 0.88 (2) | 2.02 (2) | 2.864 (2) | 162 (2) |
| C2—H2A···O4iii | 0.99 | 2.53 | 3.498 (3) | 165 |
| C6—H6B···O3iv | 0.99 | 2.58 | 3.354 (3) | 135 |
| C9—H9···O5i | 0.95 | 2.43 | 3.322 (2) | 156 |
| C14—H14···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.46 | 3.317 (3) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+5/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iv) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
References
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Alniss, H. Y., Salvia, M., Sadikov, M., Golovchenko, I., Anthony, N. G., Khalaf, A. I., MacKay, S. P., Suckling, C. J. & Parkinson, J. A. (2014). ChemBioChem, 15, 1978–1990. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Burla, M. C., Polidori, G. & Camalli, M. (1994). J. Appl. Cryst. 27, 435.
- Chenoweth, D. M. & Dervan, P. B. (2009). PNAS, 106, 13175–1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Khalaf, A. I., Waigh, R. D., Drummond, A. J., Pringle, B., McGroarty, I., Skellern, G. G. & Suckling, C. J. (2004). J. Med. Chem. 47, 2133–2156. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lang, S., Khalaf, A. I., Breen, D., Huggan, J. K., Clements, C. J., MacKay, S. P. & Suckling, C. J. (2014). Med. Chem. Res. 23, 1170–1179.
- Lee, M., Coulter, D. M. & Lown, J. W. (1988). J. Org. Chem. 53, 1855–1859.
- Lu, L., Zhu, M., Li, J. & Yang, P. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o417–o419.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Oxford Diffraction (2010). CrysAlis PRO. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, England.
- Satam, V., Patil, P., Babu, B., Rice, T., Porte, A., Alger, S., Zeller, M. & Lee, M. (2014). Synth. Commun. 44, 968–975.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, IV, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IIIsup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017001177/su5346IVsup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report