Significance
Decoupling stiffness, pore size, and cell infiltration is a critical hurdle in biomaterials design. Here, by adding ultrasoft colloidal hydrogels to polymerizing fibrin, the particles are driven into a percolated three-dimensional tunnel-like structure throughout the fibrin network. The colloidal particles remain embedded, in stark contrast to the fate of a sacrificial porogen. Yet, cells use the long-time flow behavior of the colloidal network within the tunnels to migrate. Importantly, the colloidal volume fraction, ϕ, defines the critical physical dimensions of the network, which can thus be tuned. Additionally, the stiffness of the constituent particles affects the viscous flow of the colloidal network, affecting cell migration rates. This simplistic approach makes its potential applicability in clinical settings highly tractable.
Keywords: fibrin, microgels, colloidal assemblies, porosity, cell migration
Abstract
In regenerative medicine, natural protein-based polymers offer enhanced endogenous bioactivity and potential for seamless integration with tissue, yet form weak hydrogels that lack the physical robustness required for surgical manipulation, making them difficult to apply in practice. The use of higher concentrations of protein, exogenous cross-linkers, and blending synthetic polymers has all been applied to form more mechanically robust networks. Each relies on generating a smaller network mesh size, which increases the elastic modulus and robustness, but critically inhibits cell spreading and migration, hampering tissue regeneration. Here we report two unique observations; first, that colloidal suspensions, at sufficiently high volume fraction (ϕ), dynamically assemble into a fully percolated 3D network within high-concentration protein polymers. Second, cells appear capable of leveraging these unique domains for highly efficient cell migration throughout the composite construct. In contrast to porogens, the particles in our system remain embedded within the bulk polymer, creating a network of particle-filled tunnels. Whereas this would normally physically restrict cell motility, when the particulate network is created using ultralow cross-linked microgels, the colloidal suspension displays viscous behavior on the same timescale as cell spreading and migration and thus enables efficient cell infiltration of the construct through the colloidal-filled tunnels.
Decoupling stiffness, pore size, and cell infiltration is a critical hurdle in biomaterials design and has been previously addressed in synthetic hydrogels by enabling cell-mediated degradation via protease-specific peptide cross-linkers (1–4). However, even in these highly engineered systems, compared with native extracellular matrices (ECMs), the mesh size remains a critical limiting factor in host integration; this is because cells are incapable of nonproteolytic, i.e., degradation-independent, migration through such small mesh sizes (5), as illustrated in Fig. 1A.
Fig. 1.
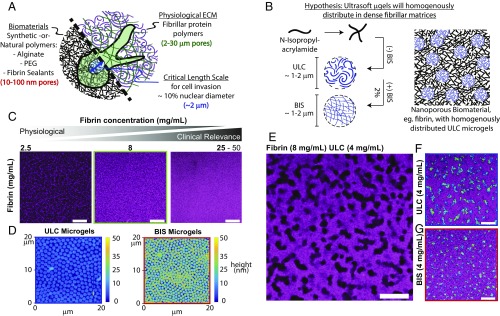
μGels form discrete tunnels of space-filling colloidal assemblies within fibrin matrices. (A) An illustration: Synthetic and natural material systems routinely used in regenerative medicine display pore sizes on the order of 10–100 nm, whereas physiological ECM has characteristic pore sizes ranging from 2 to 30 μm. Cells are incapable of penetrating through pores that are less than ∼10% of their nuclear size (∼2 μm), making invasion of traditional biomaterial systems dependent on degradation of the polymer. (B) We hypothesized that μgels introduced within a protein-fiber polymerizing solution would (i) homogeneously distribute throughout the polymer and (ii) relax the dense, submicrometer-scale mesh size. Ultrasoft μgels were used because their lack of particle stiffness would better enable cell spreading. (C) Fibrin gels (2.5, 8, 25 mg/mL) were polymerized with fluorescently labeled fibrinogen AF647 (magenta). A significant and physiologically impactful decrease in the mesh size is apparent in fibrin polymers made from solutions with supraphysiological concentrations routinely used in clinical applications. (D) ULC and BIS cross-linked μgels deposited onto glass surfaces demonstrate their differences in deformability. In solution these particles are ∼1.1 μm and 0.9 μm, respectively, yet the ULC μgels deform to a much greater extent than the 2 mol % BIS cross-linked μgels. (E–G) Fibrin (8 mg/mL) gels polymerized with 4 mg/mL μgels [(E) unlabeled ULC μgels; (F) fluorescently labeled ULC μgels; (G) fluorescently labeled BIS cross-linked μgels]. Contrary to our original hypothesis, μgels did not distribute homogeneously throughout the fibrin polymer, but rather organized into large structures comprising many μgels. A mixture of AF488 (green) and AF555 (blue) μgels was used to assist in the discrimination of individual particles within the resultant colloidal assembly. (Scale bars, 20 μm.)
Protein-based biomaterials derived from native ECM represent an attractive alternative to synthetic hydrogels, offering significant benefits through their enhanced endogenous bioactivity. The native ECM and its derivatives act as growth factor/cytokine depots, thus providing a multivalent endogenous binding site for growth factor delivery (6). A classic example of this type of biomaterial is fibrin, the endogenous provisional matrix formed at sites of vascular injury as a result of blood coagulation (7, 8). Clinically, to reach desirable mechanical properties for sealing tissues/wounds, fibrin is used at supraphysiological concentrations typically containing ∼10× more fibrinogen than physiological concentrations (9–12). When used at these artificially high concentrations, the characteristic mesh size of the network is unfortunately similar to that of synthetic PEG polymers, which is on the order of tens of nanometers, making it physically impossible for cells to infiltrate without significant degradation of the polymer (10, 11, 13, 14). Others have tried to overcome the porosity/invasion barrier of dense fibrin, and of other high-concentration ECM-based polymers, through inclusion of sacrificial porogens within the matrix. However, in these cases the polymer requires additional processing to remove the porogens, limiting the potential for in situ application (15).
Cells are incapable of nonproteolytically invading/migrating into polymers or matrices that present mesh sizes less than ∼2 μm. Introducing large open pores, via porogens, can enable cell invasion by creating a new and much larger length scale within the material. This approach, however, greatly softens the network. Here we show a unique method for enabling cell migration within dense protein-based polymers, like fibrin, by generating tunnels filled with highly deformable, ultralow cross-linked (ULC) microgel particles (μgels). The μgel suspension inside the tunnels is viscoelastic; it is solid-like at short timescales and liquid-like at long timescales. Interestingly, the structural relaxation of the ULC μgel colloidal network, which characterizes its long-time flow behavior, is on the same timescale as cell migration, thus enabling efficient cell migration without the extraction of the particle network from the fibrin matrix.
Results
Generation of Fibrin-μGel Constructs.
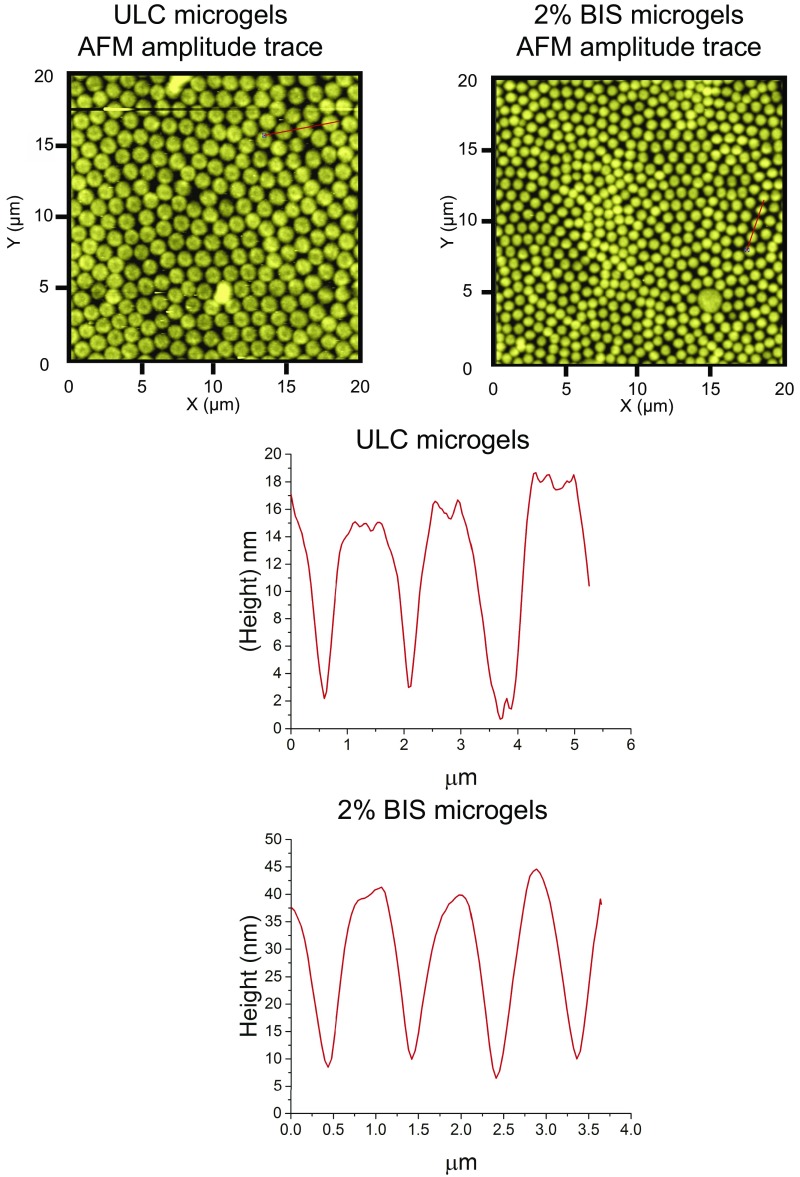
ULC μgels are composed of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (pNIPAM) copolymerized with acrylic acid (AAc) and synthesized in the absence of exogenous cross-linker. Cross-linking and branching of the polymer chains forming these unique particles occurs via rare parasitic chain transfer reactions (16) rendering extremely deformable particles (17). When deposited on a glass surface, as shown in Fig. 1D and Fig. S1, they spread to radius/height ratios of ∼690 nm/∼13 nm. In contrast, “soft” cross-linked particles synthesized with 2 mol % methylene-bisacrylamide (BIS μgels) spread less and retain their spherical shape with a lower radius/height ratio of ∼470 nm/∼33 nm. Both particles display similar diameter in solution, ∼1 μm.
Fig. S1.
μGel (ULC and 2 mol % BIS) amplitude and height traces measured using AFM along the straight lines within the images.
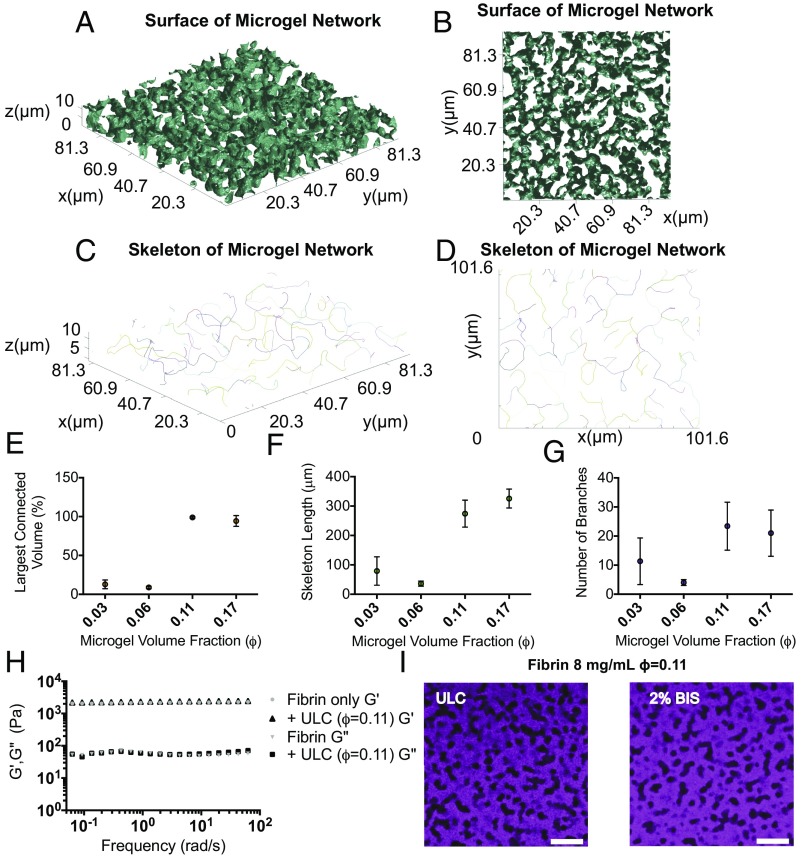
Fibrin networks are uniform fibrous matrices, which become increasingly dense at high fibrinogen concentrations (Fig. 1C). However, when μgels are incorporated into polymerizing fibrin networks we observe that, instead of remaining homogeneously dispersed as originally hypothesized and illustrated in Fig. 1B, the μgels form tubular-like networks of “pores” filled with μgel particles, as shown in Fig. 1 E–G. ULC and BIS μgels form different structures at the same concentration, as shown in Fig. 1 F and G. However, when the μgel volume fraction (ϕ) is controlled, as in Fig. 2I, similar structures are formed irrespective of μgel cross-linking density, highlighting the important role of ϕ in the structure of the composite. Through quantitative microscopic analysis of these 3D tubular structures, shown in Fig. 2 A–D, we determine a mean tubular radius of ∼5 μm. Somewhat surprisingly, in an almost digital manner, the μgels form one fully connected network above a critical initial ϕc ∼ 0.11, as shown in Fig. 2E. The number of branches and mean length per branch of this primary colloidal domain also increases above ϕc, as shown in Fig. 2 F and G. The ϕ of μgels increases from ∼0.11 in the prepolymerized solution to (locally) ∼0.6 within the fibrin-embedded, percolated colloidal network (Movie S1). μGel suspensions at this “final” ϕ ∼ 0.6 are weakly elastic with a plateau modulus of ∼2 Pa (Fig. 4F), 3 orders of magnitude less than that of the fibrin network. This suggests that the fibrin, which occupies ∼82% of the final volume, dominates the mechanical properties of the composite.
Fig. 2.
μGels form an interconnected network at a critical volume fraction (ϕ) within the bulk polymer while maintaining overall mechanical properties. (A and B) MATLAB-generated isosurfaces of μgel networks within fibrin and (C and D) representative skeletons of μgel networks in 8 mg/mL fibrin with 4 mg/mL ULC μgels (ϕ > 0.1) were generated from confocal microscopy stacks. The isosurface and skeleton were analyzed for the number of connected μgel volumes. (E) Volume of the largest connected domain relative to the total volume occupied by the μgels as a function of initial ϕ. (F) Skeleton length in micrometers and (G) number of branches of the of the largest connected μgel domain as a function of initial ϕ (average of three independent measures). (H) Storage (G′) and loss (G′′) moduli of fibrin (8 mg/mL) gels with and without ULC μgels (ϕ ∼ 0.1) via oscillatory rheology (constant strain = 0.5%; 0.06–62.83 rad/s). No significant differences are observed in elastic (G′) and viscous (G′′) moduli between samples. G′ is frequency independent and more than an order of magnitude larger than G′′, attesting to the elastic character of the material. Averaging the elastic modulus at all frequencies confirms G′ is identical in the presence or absence of μgels (Fig. S2). (I) Fibrin gels (8 mg/mL) were polymerized with ULC or BIS cross-linked μgels at equivalent initial ϕ = 0.11. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) These images display observable similarities in structure. Thus, ϕ of the particles, as opposed to the concentration, dictates the dimensionality of the final colloidal assembly within fibrin, suggesting the phenomenon observed is universal and not specific to the ULC μgels.
Fig. 4.
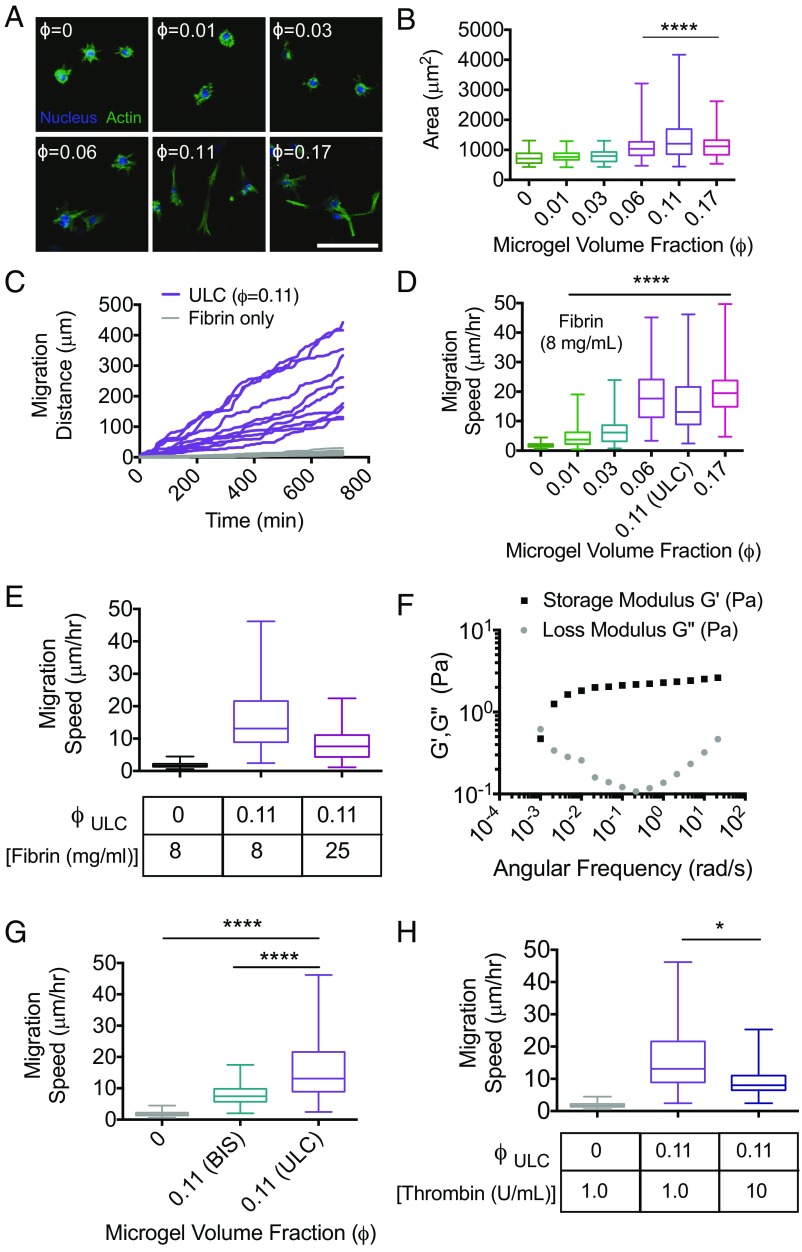
μGel-filled, percolated colloidal assemblies enable enhanced cell spreading and invasion of dense, nonpermissive fibrin polymers. Fibroblast morphology and motility were analyzed in a variety of fibrin–μgel formulations (ULC μgels unless otherwise noted). (A) Representative maximum intensity projections of confocal image slices of the actin cytoskeleton and nuclei of fibroblasts embedded in fibrin (8 mg/mL) with increasing ϕ. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) These images indicate that fibroblasts do not appreciably spread until ϕ approaches ϕc. (B) Quantitation of cell spread area indicates maximum spreading is observed at ϕc. A partial transition to a spread state is observed at ϕ = 0.06, before full network percolation, whereas cells also appear less well spread at ϕ that far exceeds the critical threshold for percolation. (C) Representative cumulative distance vs. time for cell migration in formulations at ϕc demonstrate cumulative distances that span the overall dimensions of the colloidal network. (D) Average migration speed was measured at increasing ϕ. In correlation with spread area, cell migration speeds increase significantly as ϕ approaches ϕc. (E) Average migration speeds of fibroblasts decrease in formulations made with 25 mg/mL fibrin, compared with 8 mg/mL, but remained higher than fibrin-only formulations at lower concentrations (8 mg/mL). Whereas elastic deformation of individual μgels cannot account for the motility observed, cells could use the long-time viscous behavior of the μgel suspension, thus (F) μgel suspensions at ϕfinal = 0.6 were tested with rheology to measure G′, G′′ as a function of angular frequency to determine the timescale of their structural relaxation. Furthermore, (G) cell migration speed as a function of μgel cross-linking density and (H) thrombin concentrations were measured. All data are represented as box and whiskers plots (25th to 75th percentile) with a line at the median and error bars to the minimum and maximum values. A Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons posttest was used for B, D–G. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001. Cells could phagocytize some μgels to initially enter the tunnel structure although there is no evidence for phagocytosis in our experiments. Subsequent phagocytosis assays show no evidence of cell uptake. The long migration distances also suggest that the cells rather exploit the long-time viscous behavior of the μgel suspension.
Fig. S2.
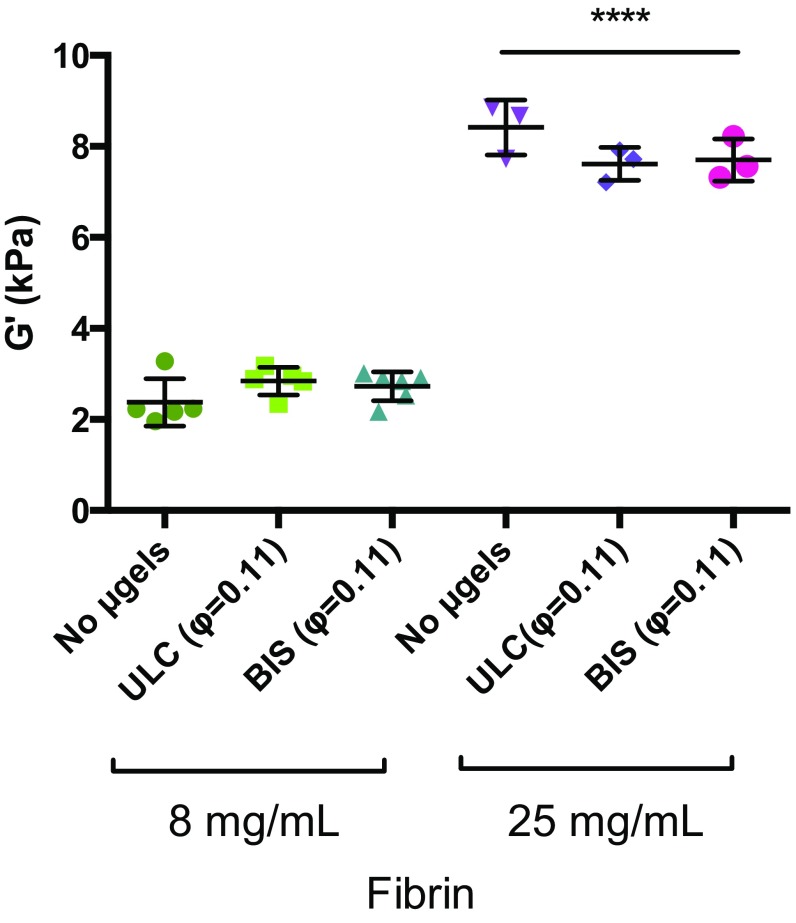
μGels do not significantly alter the mechanical properties of fibrin gels. The average storage modulus from n = 3–5 gels was calculated from frequency sweeps (from 0.06 to 62.83 rad/s) of composite fibrin–μgel networks. No statistically significant differences were found between μgel-containing and fibrin-only groups within the same fibrin concentration. ****P ≤ 0.0001.
Mechanism of Colloidal Network Formation.
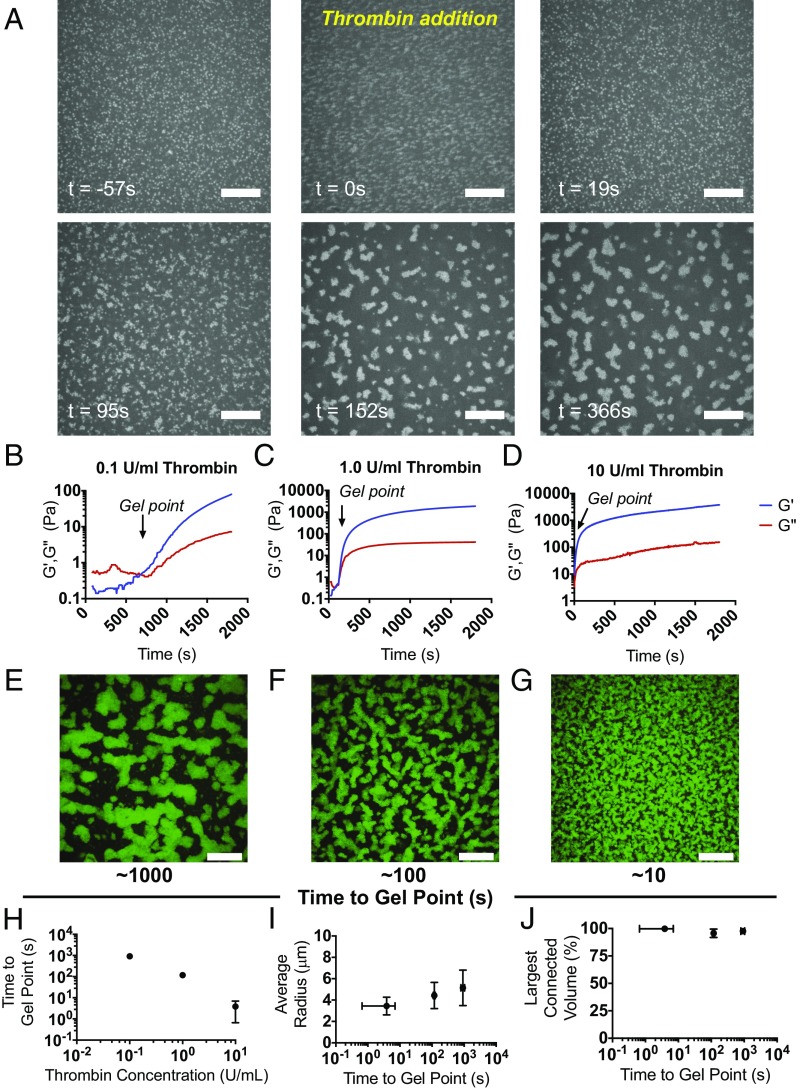
The formation of the colloidal network seen experimentally could either result from particle–particle interactions or be driven by the polymerizing fibrin. The first scenario would require attractive interparticle attractions and induced demixing. Under the conditions of fibrin formation used here, the μgels are swollen. They display a hydrodynamic radius that is significantly greater than their fully deswollen state at low pH and high temperature. Given their solvent swollen state, their dielectric function is very similar to that of the surrounding solvent. Thus, the Hamaker constant associated with the van der Waals attraction between the particles is essentially negligible, and as a result, the presence of an attractive force driving phase separation can be ruled out. Consistent with this expectation, μgel suspensions observed before fibrin polymerization remain stable and homogeneously dispersed, and do not phase separate (Fig. 3A). Furthermore, ULC μgels within significantly less-dense fibrin polymers freely diffuse and do not exhibit restricted motion or any clustering phenomena with other μgels or with fibrin polymer fibers (Movie S2). We then hypothesize that fibrin polymerization kinetics drive assembly of the colloidal network. In this case, the polymerizing fibrin, which grows from fibrin monomers into branched and rigid rod-like structures, progressively restricts the volume available to the μgels, causing them to cluster into large domains that ultimately connect and percolate through the polymerized fibrin network (Fig. 3A). If true, increasing the concentration of thrombin, which enzymatically activates the fibrin monomer thus increasing the rate of polymerization, would alter the μgel clustering dynamics. To test this, we fix ϕ above ϕc and visualize the μgel particles during fibrin polymerization for thrombin concentrations ct = 10, 1.0, 0.1 U/mL. The gelation times, tgp, for fibrin in these conditions are found from the time dependence of G′ and G′′ in the linear regime by identifying the time where the moduli cross (Fig. 3 B–D); we find tgp < 10 s for ct = 10 U/mL, tgp ∼ 102 s for ct = 1.0 U/mL, and tgp ∼103 s for ct = 0.1 U/mL (Fig. 3H). Consistent with our expectations, before fibrin polymerization the μgels are homogeneously dispersed and do not aggregate or phase separate, as shown in Fig. 3A (t = −57 s) and Movie S3. Subsequently, after adding thrombin, they are driven into colloidal domains on the same timescale as fibrin polymerization (Fig. 3A, t = 95 s and Movies S4–S6). However, the radial dimension of the tunnel structures formed by the μgels is visibly and quantifiably smaller as the gelation time of fibrin decreases (Fig. 3 E–G, J). Interestingly, the connectivity of the tubular structures is maintained (Fig. 3I). Thus, we conclude that fibrin polymerization predominantly drives the formation of the colloidal network seen experimentally whereas ϕ controls the extent of percolation of this network.
Fig. 3.
Polymerization of the bulk polymer drives μgel network formation. Fluorescently labeled μgels were imaged over time in polymerizing fibrin gels to visualize their network organization. (A) μGels are freely mobile in the fibrinogen solution (t = −57 s), thrombin is then added to initiate polymerization (t = 0 s), and then fibrin formation occurs over the next ∼100 s until the gel forms. (B–D) The elastic and viscous moduli G′ and G′′ of fibrinogen (8 mg/mL) containing μgels (ϕ = 0.11) were monitored at constant frequency and strain (0.5%, 6.28 rad/s) as a function of time, for increasing activity units of the fibrin polymerization initiator, thrombin. The average of the three independent measurements of G′ and G′′ is displayed for (B) 0.1, (C) 1.0, and (D) 10 U/mL thrombin. Order-of-magnitude increasing titrations of thrombin units lead predictably to order-of-magnitude decreases in the fibrin gel point. (E–G) Representative maximum intensity projections are shown of confocal image slices of unlabeled fibrin (8 mg/mL) with AF488-ULC μgels at ϕ = 0.11 with either (E) 0.1, (F) 1.0, or (G) 10 U/mL thrombin acquired at the end of a real-time polymerization experiment. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (H) The time to gel point of fibrin is plotted versus thrombin concentration, demonstrating that they are approximately inversely proportional to each other. Hence as thrombin concentration increases, the gelation time decreases. Representative data of the (I) average μgel tunnel radius within a network is shown as a function of time to gel point and (J) volume occupied by the main connected μgel domain relative to the total volume occupied by the μgels. Whereas the speed of fibrin polymerization had no effect on the connectivity of the colloidal network, it did alter the dimensions of the tunnels with slower fibrin polymerization leading to larger tunnel radius.
Further evidence that μgel particles themselves do not play a dominant role in the formation of the colloidal network comes from observations with BIS μgels. We find that for equivalent ϕ, the resultant colloidal network is identical compared with that obtained with ULC μgels (Fig. 2I), illustrating that the formation of percolated colloidal networks is not specific to the ULC μgels, but rather driven by fibrin polymerization in the absence of any known or observed specific fiber–μgel and μgel–μgel interactions (18). Furthermore, the observed μgel domain organization also enables the fibrin in the μgel-free regions to essentially remain free of distortions due to the particles, a fact that is expected to be favorable given the rigid character of the fibrin fibers. Consistent with this, whereas there is a striking change in the overall structure of the fibrin composite, we see no significant differences in the fiber structure of the fibrin across the various conditions used in our experiments.
Cell Invasion Through μGel Domains.
Given the highly interconnected nature of the μgel domains, the ultrasoft, deformable nature of the individual μgel units comprising those domains, and the dimensionality of the domains, we hypothesize that cells might use the μgel-filled tunnels to navigate the fibrin composite matrices. We examine cell morphology and spreading in previously reported nonpermissive fibrin formulations at concentrations of 8 mg/mL. In accord with previous reports (19, 20), cells in the fibrin-only samples display a round morphology, as shown in Fig. 4A. Within these dense polymer scaffolds the cells must degrade the matrix around them to spread due to the small, restrictive mesh size of the network. However, when the interconnected tunnels comprising ULC μgels are incorporated into the fibrin network, cell spreading increases as ϕ increases; the cells progressively lose their circularity, become more elliptical, and exhibit an increased overall spread area, as shown in Fig. 4B. This indicates that cells are indeed able to use these unique domains to extend protrusions and spread in three dimensions. Of note is the observation that cells display marked heterogeneity in their spread state in μgel-tunnel-containing fibrin. This appears to be due to the various locations of cells proximal or distal to a colloidal-filled tunnel structure.
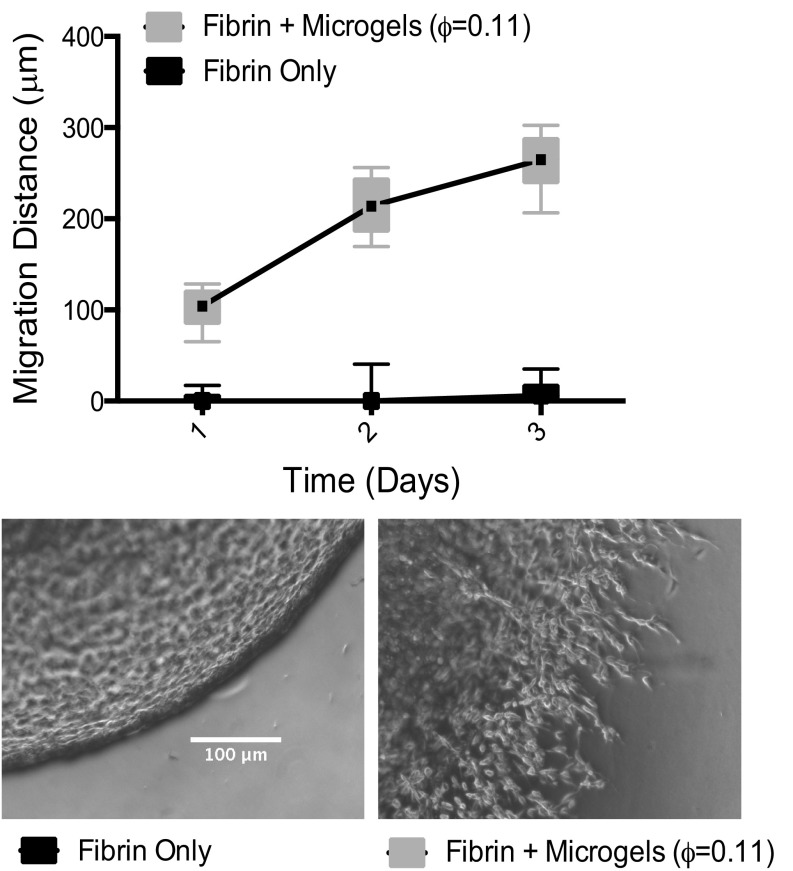
By time-lapse microscopy, we observe that cells migrate an overall distance that is significantly larger than their characteristic size and that the migration distance increases linearly with time, as shown in Fig. 4C and Fig. S3. We also find that migration speed is considerably larger for samples containing μgel tunnels compared with fibrin-only controls, as shown in Fig. 4 C and D. In particular, the migration speed increases eightfold in the sample with ϕ = ϕc compared with the μgel-free sample. Furthermore, the average cell speeds in physiological fibrin concentrations, i.e., concentrations expected in native blood clots (∼2.5 mg/mL), are 6.6 μm/h, which is a factor of ∼2.5× lower than the migration speeds observed in normally restrictive fibrin formulations (i.e., 8 mg/mL) containing fully connected ULC μgel tunnels. Importantly, at the clinically used fibrin concentrations (∼25 mg/mL) an increase in migration speed to 8.2 μm/h was observed at ϕc (Fig. 4E), confirming the key role played by the μgel tunnel structure and connectivity.
Fig. S3.
μGels enable enhanced cell infiltration in dense fibrin ECMs compared with fibrin-only controls. Average migration speeds are shown for cells polymerized in fibrin alone, or various fibrin–μgel hybrid constructs. Box and whiskers plot shown, migration distance averaged from 5 measurements from n = 12 gels from 2 independent biological replicates (represented as median with 75th to 25th percentile with minimum and maximum). A two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test was performed and statistically significant differences were found between ±μgels (P < 0.0001) at each time point.
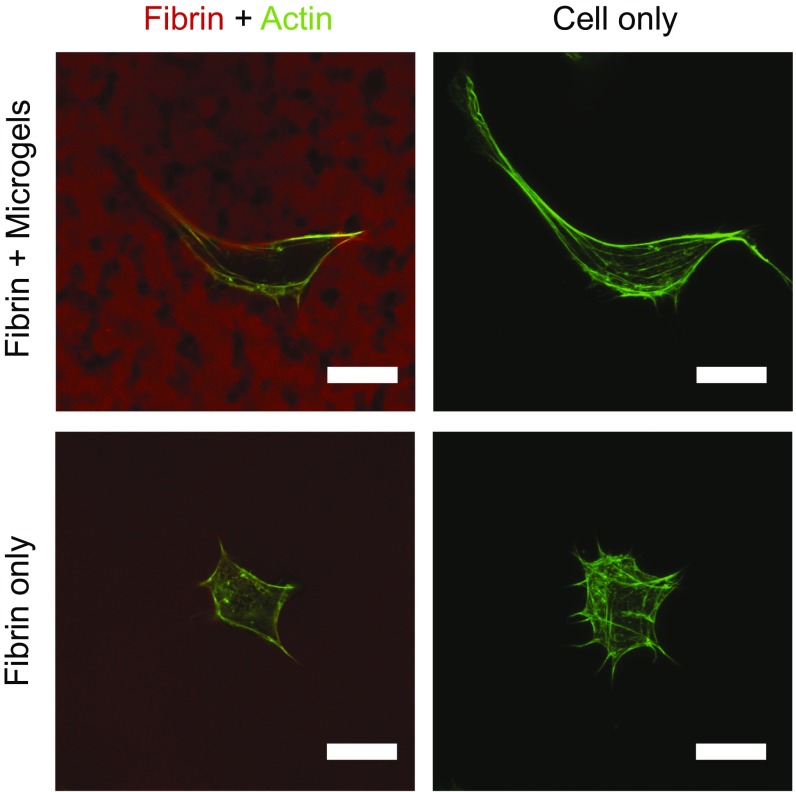
We initially hypothesized that cells would use the structural relaxation of the ultrasoft colloidal assembly, which enables the long-time flow behavior of the suspension. To address this, we calculate the μgel ϕ inside the tunnels. We find a ϕ(final) of ∼0.6. Hard particles at this ϕ are either crystalline or glassy. In contrast, the ULC μgel suspension exhibits a structural relaxation at an angular frequency of ω ∼ 1.2*10–3 rad/s, as shown in Fig. 4F, corresponding to a time scale of 2π/ω ∼1.5 h. Thus, whereas cells cannot penetrate pore sizes less than 10% of their nuclear diameter, they are capable of moving through the μgel network exploiting its structural relaxation. We confirm this by estimating a characteristic migration timescale for the cells from the measured speed (median of 13 μm/h at ϕc) and the typical cell size used in our experiments (∼20 μm). We obtain a time of ∼1.5 h, consistent with the structural relaxation time of the suspension. The scenario that emerges from our results is that cells migrate through the composite matrix by using the tunnels within fibrin. We observe that individual cells are in contact with several μgel network structures, as shown in Fig. S4, and may extend protrusions through them to spread and ultimately migrate.
Fig. S4.
Microgel tunnels enable enhanced cell spreading in dense fibrin ECMs compared with fibrin-only controls. Voids in fibrin generated by μgels allow cells to extend protrusions and spread in these matrices compared with fibrin-only constructs, which fully encapsulate the cells. NIH/3T3s were incubated overnight in gels with (Top Row) or without (Bottom Row) ULC μgels (ϕ = 0.11) containing labeled fibrinogen (red). Cells were then fixed and stained with phalloidin (green) to visualize the actin cytoskeleton. Individual z slices of the cell and fibrin are shown. (Scale bars, 20 μm.)
The cross-link density, and thus stiffness, of the individual particles comprising a colloidal suspension determines the suspension viscosity; at equivalent ϕ, colloidal dispersions of hard particles are more viscous than dispersions of soft particles (21). Thus, particle cross-linking could dictate the maximum possible migration speed by establishing the characteristic structural relaxation timescale of the colloidal-filled tunnel structures. In support of this, when μgels cross-linked with 2 mol % BIS are used to form composites (Fig. 4G), the average migration speed still increases fourfold compared with fibrin alone. However, this speed is ∼1/2 that observed for the ULC μgels at the same ϕ. The dimensionality of colloidal tunnel structures obtained in both situations is essentially identical (Fig. 2I).
Discussion
We have reported that microparticles at sufficiently high ϕ are driven into a single, interconnected μgel network in response to fibrillar biomatrix polymerization. When ultrasoft, deformable μgels are used, cells exploit the long-time viscous behavior of the particulate network for enhanced invasion and migration. The addition of an interconnected, fully percolated colloidal domain of μgels within fibrin polymers made at supraphysiological concentrations can overcome the natural limitations of the base natural polymer system associated with a restrictive mesh size. The potential transformative nature of this work lies in both the tunability of the microparticles being used and the inherent simplicity of the approach. In addition, our data indicate that ϕ and not the particle specifics determine the formation of the colloidal network. Therefore, microparticles of varying chemistries and those that present selected biomolecules, such as growth factors and adhesion factors, could easily be used for further control of cell phenotype. Such a simple approach is highly tractable in the clinical setting while solving a complicated fundamental materials problem: decoupling polymer mechanics and porosity from important cellular functions like material invasion.
Materials and Methods
μGel Synthesis.
Sterile filtered solutions of N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid (95 mol % NIPAM) monomer (recrystallized from n-hexanes) and acrylic acid (5 mol % AAc) were mixed at 450 rpm in a reaction vessel at 70 °C before the addition of an initiator, ammonium persulfate (APS) in the presence or absence of 2 mol % N,N'-methylene(bisacrylamide) (BIS) (16–18, 22). Purified μgels were labeled with AlexaFluor dyes and lyophilized for future use.
Atomic Force Microscopy Characterization of μGels.
μGel particles were deposited on cleaned and APTMS (aminopropyltrimethoxysilane)-treated coverslips by immersion followed by centrifugation for 10 min at 2,200 × g. The coverslips were removed, rinsed with deionized water, dried with nitrogen, imaged with an MFP3D Asylum Research atomic force microscope (AFM), and processed using MFP3D software (WaveMetrics Inc.).
Fibrin/Composite Gel Formation.
For the formation of fibrin and fibrin–μgel polymers, fibrinogen (CSL Behring) was mixed with 25 mM Hepes 150 mM NaCl (Hepes buffer) pH 7.4, and 5 mM CaCl2 with or without ULC or BIS μgels before the addition of thrombin (0.1, 1, or 10 U/mL). Gels were allowed to polymerize for 1 h before imaging. For fluorescence microscopy, 5 mol % labeled fibrinogen (AlexaFluor 555 or 647) was incorporated during polymerization.
Confocal Microscopy.
Image stacks (20 μm) were acquired on an LSM 700 (Carl Zeiss Microscopy Ltd.) using a 63× objective lens. A Cell Observer Spinning Disk (SD) confocal (Carl Zeiss Microscopy Ltd.) was used for the acquisition of time-lapse videos of real-time μgel network formation in 3D composite gels with varying thrombin concentrations.
μGel Network Analysis.
Using a custom in-house–built script in MATLAB, images were run through a median filter and then binarized using the Otsu method to find the threshold value. A skeleton of the structure was obtained by solving the eikonal equation and detecting all its singularities using the fast marching method; these form a set corresponding to the sought skeleton and give accurate results in Cartesian coordinates (23, 24). Connectivity of the sample was determined by the number and location of all branches within the skeleton, and the branch number and total length of the branches in each connected μgel volume.
Rheology.
(i) A Physica MCR 501 cone and plate rheometer (Anton-Paar) was used (2.014° cone angle, and 24.960-mm tool diameter) to measure the viscoelastic properties of the various fibrin and fibrin–μgel composites. Strain sweeps from 0.1 to 100% at 6.28 rad/s were performed to establish the linear regime. Frequency sweeps from 0.06 to 62.83 rad/s were then performed to obtain the frequency dependence of the storage (G′) and loss (G′′) moduli. Average storage moduli were calculated from the average value over the frequency range for three different, identically prepared constructs. Measurements for gel point were acquired by time sweep at a fixed strain of 0.5% every second, while monitoring G′ and G′′. (ii) For experiments on μgel suspensions, ULC μgels were resuspended in 25 mM Hepes buffer with 150 mM NaCl at ϕ = 0.6. Before measurements, samples were presheared at a shear rate of 25 s−1 for 15 min with an equilibration time of at least 3 h. Frequency sweeps were performed at 1% strain from 0.001 to 21.5 rad/s to determine the viscoelastic properties of the suspension.
Cell Culture.
NIH/3T3 fibroblasts (American Type Culture Collection, ATCC) were cultured in DMEM with 4.5 g/L glucose, l-glutamine, sodium pyruvate, and supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin and 10% (vol/vol) bovine calf serum.
Cell Morphological Analysis.
NIH/3T3s were incorporated into fibrin-only and fibrin–μgel gels in media at a density of 1,000,000 cells/mL comprising 10% of the gel volume (10 μL in 100 μL gel). After incubation overnight, the samples were rinsed with cold 1× PBS, fixed with 4% (wt/vol) formaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich) for 20 min, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 10 min, rinsed again with 1× PBS, and incubated with AF488 Phalloidin (Life Technologies) and Hoechst 33258 (Life Technologies). Confocal z stacks (100 μm) were imaged with a 10× objective. Cell area, circularity, and elliptical factor were measured using NIS Elements Software (Nikon) from at least 50 different cells in 3 different gels.
Live Cell Migration.
NIH/3T3s were fluorescently labeled using CMFDA Cell Tracker Green (Life Technologies). Cells were incorporated into fibrin and fibrin–μgel gels at a density of 1,000,000 cells/mL comprising 10% of the gel volume (10 μL in 100 μL gel). The cells were incubated overnight and live-cell imaging was performed with a Nikon BioStation IM-Q Live-Cell microscope. Images of cells at least 50 μm above the polymer–TC plate interface were acquired with a 10× objective in phase contrast and FITC every 10 min over the course of 12 h for 6–10 regions from 2 to 3 independent experiments. Images were imported into FIJI (ImageJ) and cells were manually tracked over the duration of the experiment with distance over time and average instantaneous speed calculated. Dividing cells and cells that moved out of the viewing field for more than half of the experimental duration were neglected. At least 50–100 cells were tracked per experimental and control group from 2 to 3 independent experiments.
Statistical Analysis.
All statistical analyses were performed using the Prism software program (GraphPad). Storage moduli between groups measured were analyzed using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison posttest. For cell morphology, a one-way ANOVA was performed with Tukey’s multiple comparisons posttest. For cell spread area, elongation, and migration speed a Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test was used with Dunn’s posttest for multiple comparisons. Cell infiltration in the outgrowth assay was analyzed with a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Data are represented in box and whisker plots, which extend from the 25th to 75th percentiles with a line at the median and error bars to the minimum and maximum values.
Materials and Methods
Microgel Synthesis.
ULC μgels of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) (95 mol % NIPAM/5 mol % AAc) were synthesized from standard precipitation polymerization techniques as previously described (16–18, 22). Briefly, sterile filtered solutions of NIPAm monomer (recrystallized from n-hexanes) and acrylic acid were mixed at 450 rpm in a reaction vessel at 70 °C before the addition of an initiator, APS. For BIS cross-linked μgels, 2 mol % N,N'-methylene(bisacrylamide) was added to the reaction as an exogenous cross-linker. In both cases, the reaction proceeded for 6 h, after which the solution of μgels was cooled, filtered through glass wool, and purified by ultracentrifugation. Purified μgels were lyophilized for future use. Fluorescent μgels were generated through labeling of AAc groups with cadaverine conjugates of AlexaFluor dyes (cadaverine AF488, 555, 647, Life Technologies) via carbodiimide chemistry with EDC (1-ethyl-3-(-3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride) and Sulfo-NHS (N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide). ULC μgels were resuspended in 25 mM Hepes 150 mM NaCl pH 7.4 (Hepes buffer).
AFM Characterization of μGels.
Glass coverslips were cleaned thoroughly by following a sequential solvent sonication protocol developed previously developed in the laboratory. Once clean, the coverslips were treated for 2 h with a 1 vol/vol % solution of APTMS in absolute ethanol (200 proof). The coverslips were rinsed with absolute ethanol and dionized water and then dried with nitrogen. μGel particles were deposited by placing the functionalized coverslips in six-well plates and then immersing them in a 0.5 mg/mL solution of μgel particles (ULC, 2 mol % BIS) in 1× Hepes buffer. The well plate was centrifuged at for 10 min at 2,200 × g. Finally, the coverslips were removed, rinsed with deionized water, and then dried with nitrogen. The samples were imaged with an MFP3D Asylum Research AFM and processed using MFP3D software under the IgorPro interactive software environment (WaveMetrics Inc.). Aluminum-coated silicon nitride cantilevers were used (NanoWorld; force constant = 42 N/m, resonance frequency = 320 kHz).
Fibrin/Composite Gel Formation.
Fibrinogen (CSL Behring) purified from human plasma containing FXIII and fibronectin was used at various concentrations throughout the study. For the formation of fibrin clots, fibrinogen was mixed with 25 mM Hepes 150 mM NaCl (Hepes buffer) pH 7.4, and 5 mM CaCl2 before the addition of thrombin (0.1, 1, or 10 U/mL). Composite gels were formed through mixing of ULC μgels with the fibrinogen/Hepes/CaCl2 mixture before the addition of thrombin (0.1, 1, or 10 U/mL). Gels were allowed to polymerize for 1 h before imaging. For fluorescence microscopy, 5 mol % labeled fibrinogen (AlexaFluor 555 or 647) was incorporated during polymerization.
Confocal Microscopy.
An LSM 700 series fluorescent confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss Microscopy Ltd.) was used for imaging of 3D composite gel structures. Image stacks (20 μm) were acquired using a 63× objective lens. A Cell Observer SD confocal (Carl Zeiss Microscopy Ltd.) was used for the acquisition of time-lapse videos of real-time μgel network formation in 3D composite gels with varying thrombin concentrations.
μGel Network Analysis.
Three-dimensional confocal images were imported into MATLAB for custom processing and analysis. Using a custom in-house–built script, images were run through a median filter and then binarized using the Otsu method to find the threshold value. Next, the skeleton of the structure was obtained, which consisted of a central line having the same topology, branching, and overall shape of the initial structure. The skeleton was calculated by solving the eikonal equation and detecting all its singularities; these form a set corresponding to the sought skeleton (23). To solve the eikonal equation, we used the fast marching method, which gives very accurate results in Cartesian coordinates (24). We also quantified the connectivity of the sample. In particular, we determined the number and location of all branches within the skeleton, and the branch number and total length of the branches in each connected μgel volume. For quantitative analysis, we used 200 × 200 pixel regions in the center of the image stacks to expedite computing time and eliminate imaging aberrations due to uneven illumination at the edges of the images.
Rheology.
(i) A Physica MCR 501 cone and plate rheometer (Anton-Paar) was used (2.014° cone angle, and 24.960-mm tool diameter) to measure the viscoelastic properties of the various fibrin and fibrin–μgel composites, which were formulated as described above. Strain sweeps from 0.1% to 100% at 6.28 rad/s were performed to establish the linear regime, from which a strain of 0.5% was chosen. Frequency sweeps from 0.06 to 62.83 rad/s were then performed to obtain the frequency dependence of the storage (G′) and loss (G′′) moduli. Average storage moduli were calculated from the average value over the frequency range for three different, identically prepared constructs. For gel-point measurements, a time sweep was performed after the addition of thrombin to the μgel-containing fibrinogen solution. Measurements for gel point were acquired at a fixed strain of 0.5% every second, while monitoring G′ and G′′. The results shown are the average of three independent measurements. The gel point was measured as the point where G′ and G′′ cross. (ii) For experiments on μgel suspensions, ULC μgels were resuspended in 25 mM Hepes buffer with 150 mM NaCl. To mimic the volume fraction of the μgels inside of the composites, suspensions at ϕ = 0.6 were tested, corresponding to a concentration of 21.8 mg/mL. A double gap tool was used with a solvent trap to prevent evaporation of the sample. Before measurements, samples were presheared at a shear rate of 25 s−1 for 15 min with an equilibration time of at least 3 h. Frequency sweeps were performed at 1% strain from 0.001 to 21.5 rad/s to determine the viscoelastic properties of the suspension.
Cell Culture.
NIH/3T3 fibroblasts (ATCC) were cultured in DMEM DMEM with 4.5 g/L glucose, l-glutamine, sodium pyruvate and supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin and 10% (vol/vol) bovine calf serum.
Cell Morphological Analysis.
For cell-spreading assays, NIH/3T3s were incorporated into polymerizing fibrin only and fibrin–μgel gels in media at a density of 1,000,000 cells per mL comprising 10% of the gel volume. Gels were formed as described previously with fibrin alone or fibrin with ULC μgels (ϕ = 0.01, 0.03, 0.06, 0.11, or 0.17). After incubation overnight, the samples were rinsed with cold 1× PBS, fixed with 4% (wt/vol) formaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich) for 20 min, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 10 min, rinsed again with 1× PBS, and incubated with AF488 Phalloidin (Life Technologies) to stain the actin cytoskeleton and Hoechst 33258 (Life Technologies) to stain the nucleus. Confocal z stacks (100 μm) were imaged with a 10× objective and maximum intensity projections were created. Cell area was measured using NIS Elements Software (Nikon) and various other parameters were calculated including circularity (=4*π*area/perimeter2) and elliptical factor (major/minor axis), which were measured from at least 50 different cells in 3 different gels.
Live Cell Migration.
For cell motility experiments, NIH/3T3s were fluorescently labeled using a cytoplasmic dye CMFDA Cell Tracker Green (Life Technologies) according to manufacturer's instructions. Cells were incorporated into polymerizing fibrin and fibrin–μgel gels in media at a density of 1,000,000 cells/mL comprising 10% of the gel volume (10 μL in 100 μL gel). Two gels (fibrin with or without μgels, ϕ = 0.01, 0.03, 0.06, 0.11, 0.17, or BIS X-link μgels ϕ = 0.11) per experiment were formed in a 35-mm dish side by side and were allowed to polymerize at 37 °C in the incubator for 1 h before the addition of media on top of the composite gels. The cells were incubated overnight and live cell imaging was performed with a Nikon BioStation IM-Q Live-Cell incubation chamber and microscope. Images of cells at least 50 μm above the interface were acquired with a 10× objective in phase contrast and FITC every 10 min over the course of 12 h for 6–10 regions from 2–3 independent experiments.
Migration Quantification.
Fluorescent images of labeled cells were imported into FIJI (ImageJ) and cells were manually tracked (recording x- and y coordinates) over the duration of the experiment. Distance over time and average instantaneous speed was calculated for each cell and plotted. Dividing cells and cells that moved out of the viewing field for more than one-half of the experimental duration were neglected. At least 50–100 cells were tracked per experimental and control group from 2–3 independent experiments.
Statistical Analysis.
All statistical analyses for rheological measurements, cell migration, and cell infiltration were performed using the Prism software program (GraphPad). For rheology, different storage moduli between groups measured were analyzed using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison posttest. For cell morphology––specifically, circularity––a one-way ANOVA was performed with Tukey’s multiple comparisons posttest. For cell spread area and elongation, the data were not normally distributed and thus a Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test was used with Dunn’s posttest for multiple comparisons. For analyzing cell infiltration in the outgrowth assay, a two-way ANOVA was performed with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. For migration speed, the data did not fit a normal Gaussian distribution and thus the Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test was used with Dunn’s posttest for multiple comparisons. Data are represented in box and whisker plots, which extend from the 25th to 75th percentiles with a line at the median and error bars to the minimum and maximum values.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge John M. Nicosia for support in performing MATLAB image analysis for figure preparation. We acknowledge funding from the Department of Defense (Award W81XWH-15-1-0485), the National Institutes of Health (Grant R01HL130918), and the National Science Foundation (Grant DMR-1609841). We also acknowledge the American Heart Association for support of A.M.D. through a Predoctoral Fellowship and the National Science Foundation (NSF) Stem Cell Biomanufacturing training grant (NSF DGE 0965945, to A.M.D.). We thank the Parker H. Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience and Georgia Tech/Children's Healthcare of Atlanta (GT/CHOA) Center for Pediatric Nanomedicine for additional funding for this project.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1607350114/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Lutolf MP, et al. Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive hydrogels for the conduction of tissue regeneration: Engineering cell-invasion characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(9):5413–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0737381100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lutolf MP, Hubbell JA. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(1):47–55. doi: 10.1038/nbt1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Raeber GP, Lutolf MP, Hubbell JA. Molecularly engineered PEG hydrogels: A novel model system for proteolytically mediated cell migration. Biophys J. 2005;89(2):1374–1388. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.050682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lutolf MP, Raeber GP, Zisch AH, Tirelli N, Hubbell JA. Cell-responsive synthetic hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2003;15(11):888–892. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wolf K, et al. Physical limits of cell migration: Control by ECM space and nuclear deformation and tuning by proteolysis and traction force. J Cell Biol. 2013;201(7):1069–1084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201210152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 24):4195–4200. doi: 10.1242/jcs.023820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mosesson MW. Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(8):1894–1904. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Doolittle RF. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53(1):195–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nürnberger S, et al. Properties and potential alternative applications of fibrin glue. In: von Byern J, Grunwald I, editors. Biological Adhesive Systems. Springer; Vienna: 2010. pp. 237–259. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ferguson J, Nürnberger S, Redl H. Fibrin: The very first biomimetic glue — still a great tool. In: von Byern J, Grunwald I, editors. Biological Adhesive Systems. Springer; Vienna: 2010. pp. 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hedrich HC, et al. Fibrin chain cross-linking, fibrinolysis, and in vivo sealing efficacy of differently structured fibrin sealants. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(6):1507–1512. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.32719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Janmey PA, Winer JP, Weisel JW. Fibrin gels and their clinical and bioengineering applications. J R Soc Interface. 2009;6(30):1–10. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ghajar CM, et al. The effect of matrix density on the regulation of 3-D capillary morphogenesis. Biophys J. 2008;94(5):1930–1941. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.120774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hanson AJ, Quinn MT. Effect of fibrin sealant composition on human neutrophil chemotaxis. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;61(3):474–481. doi: 10.1002/jbm.10196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nair A, et al. Novel polymeric scaffolds using protein microbubbles as porogen and growth factor carriers. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(1):23–32. doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2009.0094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gao J, Frisken BJ. Cross-linker-free N-Isopropylacrylamide gel nanospheres. Langmuir. 2003;19(13):5212–5216. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bachman H, et al. Ultrasoft, highly deformable microgels. Soft Matter. 2015;11(10):2018–2028. doi: 10.1039/c5sm00047e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brown AC, et al. Ultrasoft microgels displaying emergent platelet-like behaviours. Nat Mater. 2014;13(12):1108–1114; advance online publication. doi: 10.1038/nmat4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cox S, Cole M, Tawil B. Behavior of human dermal fibroblasts in three-dimensional fibrin clots: Dependence on fibrinogen and thrombin concentration. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(5-6):942–954. doi: 10.1089/1076327041348392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hwang CM, et al. Assessments of injectable alginate particle-embedded fibrin hydrogels for soft tissue reconstruction. Biomed Mater. 2013;8(1):014105. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/8/1/014105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mattsson J, et al. Soft colloids make strong glasses. Nature. 2009;462(7269):83–86. doi: 10.1038/nature08457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gao J, Frisken BJ. Influence of reaction conditions on the synthesis of self-cross-linked N-Isopropylacrylamide microgels. Langmuir. 2003;19(13):5217–5222. doi: 10.1021/la0485982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Torsello A, Hancock ER. A skeletal measure of 2D shape similarity. Comput Vis Image Underst. 2004;95(1):1–29. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hassouna MS, Farag AA. Multi-stencils fast marching methods: A highly accurate solution to the eikonal equation on Cartesian domains. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2007;29(9):1563–1574. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.