Significance
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) are an urgent threat: as an increasing cause of disease and as the staging ground for resistance to “last line” drugs. Thus, we must understand how CRE evolve, diversify, and spread and especially the potential for asymptomatic transmission without outbreaks. Our broad sample of species and genetic determinants that defined four hospital CRE communities over 16 mo revealed a significant degree of CRE diversity, with little evidence for clonal spread but extensive movement of resistance determinants. We provide evidence for considerable asymptomatic carriage and unrecognizable mechanisms of carbapenem resistance that, together, indicate continued innovation by these organisms to thwart the action of this important class of antibiotics and underscore the need for continued surveillance of CRE.
Keywords: carbapenem resistance, Enterobacteriaceae, comparative genomics, whole-genome sequencing, molecular evolution
Abstract
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) are among the most severe threats to the antibiotic era. Multiple different species can exhibit resistance due to many different mechanisms, and many different mobile elements are capable of transferring resistance between lineages. We prospectively sampled CRE from hospitalized patients from three Boston-area hospitals, together with a collection of CRE from a single California hospital, to define the frequency and characteristics of outbreaks and determine whether there is evidence for transfer of strains within and between hospitals and the frequency with which resistance is transferred between lineages or species. We found eight species exhibiting resistance, with the majority of our sample being the sequence type 258 (ST258) lineage of Klebsiella pneumoniae. There was very little evidence of extensive hospital outbreaks, but a great deal of variation in resistance mechanisms and the genomic backgrounds carrying these mechanisms. Local transmission was evident in clear phylogeographic structure between the samples from the two coasts. The most common resistance mechanisms were KPC (K. pneumoniae carbapenemases) beta-lactamases encoded by blaKPC2, blaKPC3, and blaKPC4, which were transferred between strains and species by seven distinct subgroups of the Tn4401 element. We also found evidence for previously unrecognized resistance mechanisms that produced resistance when transformed into a susceptible genomic background. The extensive variation, together with evidence of transmission beyond limited clonal outbreaks, points to multiple unsampled transmission chains throughout the continuum of care, including asymptomatic carriage and transmission of CRE. This finding suggests that to control this threat, we need an aggressive approach to surveillance and isolation.
Infections with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) are associated with high rates of complications and mortality (1, 2). As much as 11% of all device-related nosocomial infections are attributable to CRE (3), and the incidence of CRE infections is rising. Treating these infections is challenging and, depending on the presence of other resistance elements, may not be even possible; hence, it is important to understand their epidemiology to develop appropriate infection control and public health strategies to slow or contain the spread of CRE. It is especially important to understand how resistance elements spread between strains and the extent of transmission that goes undetected between cases.
CRE typically harbor genes that encode carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamases or carbapenemases (4). Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPCs) are the most common in the United States. KPCs are encoded by the blaKPC gene, which is typically plasmid-associated and located on the transposable element Tn4401. Although originally observed in K. pneumoniae strains, KPCs are found in a wide variety of plasmids and observed in other Enterobacteriaceae (5).
The increasing incidence of CRE has been attributed largely to the spread of a single K. pneumoniae clone, ST258 (6). In the United States, the majority of carbapenem resistance is due to these and other KPC-containing strains of Enterobacteriaceae (7), but a feature of carbapenem resistance is the diversity of genetic elements that are capable of producing it (4, 8, 9). Outside the United States, other carbapenemase genes have been reported to be common, including the oxacillin hydrolyzing beta-lactamase gene blaOXA-48 (North Africa and West Europe), blaVIM (Mediterranean countries), and blaNDM (Pakistan, Bangladesh, and India) (10). These variants have been infrequently reported within US institutions to date (11). An increasing number of reports have identified strains with low levels of carbapenem resistance attributable to mutations in genes encoding porins (12), sometimes in combination with the expression of extended spectrum or AmpC beta-lactamases (13–15).
Several recent retrospective studies have examined the molecular epidemiology of hospital-associated CRE, with a focus on outbreaks (5, 16–20). The higher resolution offered by genomic methods provides advantages when rigorously defining outbreaks and transmission, because distinct clones may be indistinguishable by other methods. However, the few published multi-institutional reports have relied primarily on less discriminating, non–genomic-typing methods (21, 22). In this study, we obtained genome sequences of 122 carbapenem nonsusceptible and 141 susceptible bacterial isolates from four large referral hospitals in the United States in an effort to obtain a snapshot of the genetic diversity of CREs among and within multiple institutions and implications for transmission and to determine the mechanisms that have spread resistance within and between species and geographic areas.
Results
Isolates Causing Clinical Disease in Boston Area Hospitals Cannot Be Linked by Clonal Spread: Evidence for Unsampled Transmission.
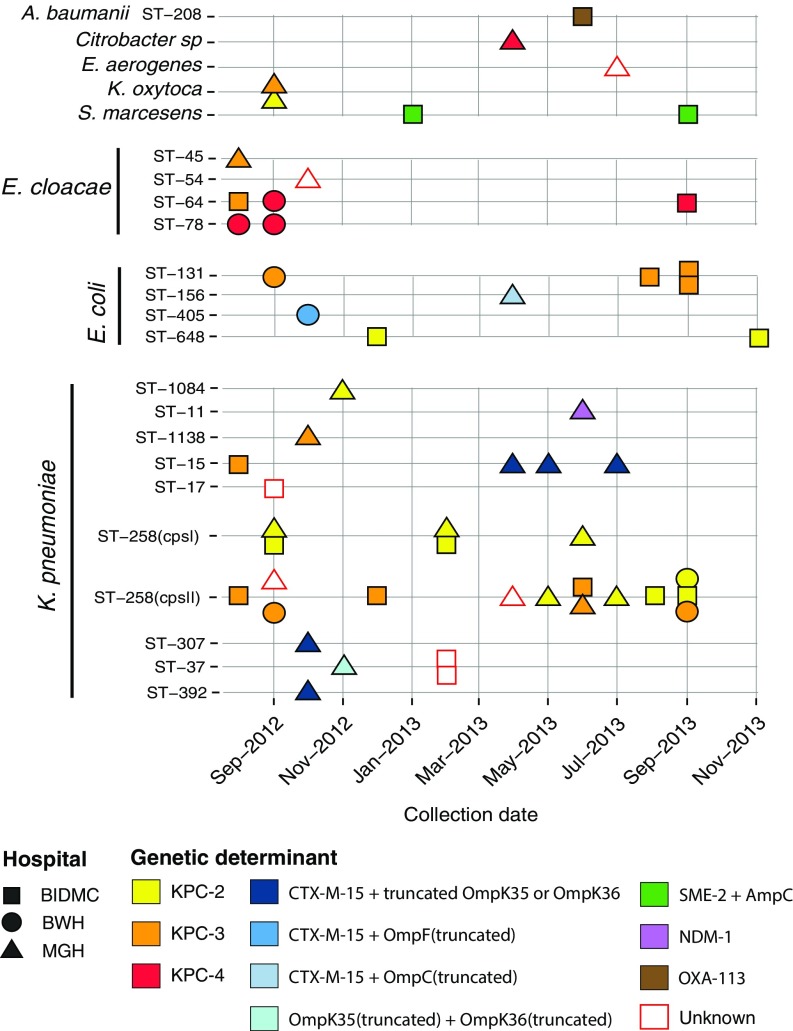
We prospectively collected and sequenced nonsusceptible Enterobacteriaceae with a meropenem minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ≥2 μg/mL (23) isolated from patient samples at three Boston hospitals over a 16-mo period in 2012 and 2013 [Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH); together these form the Boston Prospective Collection]. CRE were obtained from patient samples including blood (11%), wounds (11%), and the respiratory tract (16%), but the majority (44%) were isolated from urine, consistent with previous reports (SI Appendix, Table S1) (24). Fig. 1 provides an overview of the collection. Samples are plotted by month of isolation, hospital, and species. If a multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme was available, the ST is indicated. The three most common resistant species, and the only ones isolated from all three hospitals, were K. pneumoniae (Fig. 1 and SI Appendix, Fig. S4), Escherichia coli (SI Appendix, Fig. S5), and Enterobacter cloacae (SI Appendix, Fig. S6), with K. pneumoniae being the most common (55% of total nonsusceptible isolates). These isolates may be further subdivided by MLST into 17 STs (Fig. 1), the majority of which were restricted to one hospital and many found only once, suggesting limited transmission among the sampled hospitals; only 5 of 17 STs were found in two or more hospitals (ST64, ST131, ST15, ST258, and ST37). K. pneumoniae ST258 was the most frequently isolated ST. For comparison, we collected susceptible controls that were matched by species, time, and hospital (149 isolates in total making up the Boston Prospective Collection; SI Appendix, Tables S1 and S3). As expected, the susceptible population was more diverse than the nonsusceptible population (SI Appendix, Fig. S2 and Table S3).
Fig. 1.
Carbapenem-nonsusceptible Enterobacteriaceae from three Boston-area hospitals. Isolates are shown as squares (BIDMC), circles (BWH), and triangles (MGH). Isolates are stratified based on species and MLST (vertical axis) and with respect to time of collection (horizontal axis). Color indicates the predicted genetic determinant for meropenem nonsusceptibility. Isolates for which no genetic determinant was predicted are outline in red. Each rectangle on December 2012 represents two specimens collected from the same patient.
Unknown Mechanisms of Carbapenem Resistance.
Among known resistance loci, we detected blaKPC in 4 distinct species totaling 65% (36 of 55) of nonsusceptible isolates, and, among the 19 non-blaKPC carriers, known resistance mechanisms could be identified in 12, including combinations of beta-lactamases and inactivated porins (SI Appendix, Table S14; also see Materials and Methods). These are summarized together with all genes associated with antibiotic resistance identified in the genomes of susceptible and nonsusceptible isolates in SI Appendix, Table S1 and S5, the meropenem MIC associated with each genetic determinant (SI Appendix, Fig. S3), and the predicted plasmid harboring those, when identified, in SI Appendix, Table S15 (see SI Appendix, SI Material and Methods, Annotation for details). With minor differences, recognizable resistance mechanisms were similar to those seen in a retrospective collection of 48 CRE collected from 2007 to 2012 (Boston Historical Collection; SI Appendix).
Among the seven isolates from the Boston Prospective Collection with unexplained resistance (more details are in SI Appendix, Table S13) were MGH_31 and MGH_59; two ST258 isolates collected 8 mo apart from the same hospital. These isolates are found in distinct regions of the phylogeny after removing SNPs in predicted regions of recombination (SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S9) so appear to have evolved resistance independently. Retesting confirmed resistance to meropenem (MIC ≥4 μg/mL) and lack of blaKPC, the genetic determinant explaining all nonsusceptible ST258 isolates in this collection (Fig. 2 and SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S4). To determine whether the unrecognized resistance factor in MGH_31 and MGH_59 was plasmid-encoded, we transformed a susceptible K. pneumoniae isolate with the plasmid content from MGH_31 or MGH_59. Recipients of plasmid material from either isolate developed the resistant phenotype (MIC ≥ 4 μg/mL; MIC of susceptible recipient: 0.06 μg/mL). The plasmid sequence from these two isolates belonged to similar but distinct incompatibility groups (SI Appendix, Table S6), and shared 39 orthologous groups of genes (SI Appendix, Table S7), most of which were associated with transposition and plasmid stability. None of the predicted plasmid-encoded genes had an obvious role in carbapenem resistance. Although both MGH_31 and MGH_59 contained two blaTEM homologs, these had high amino acid identity with each other as well as to blaTEM from carbapenem-susceptible isolates, suggesting that they are unlikely to have a role in resistance. Because accurate prediction of plasmid sequences from draft genomes is still challenging, we also examined genes shared by these two isolates regardless of their predicted location (chromosomal or plasmid). Although this examination revealed some chromosomal beta-lactamases and metallo-beta-lactamases, we found no single gene that could explain the resistance that we observed, and porins were predicted to be fully intact (SI Appendix, Table S9).
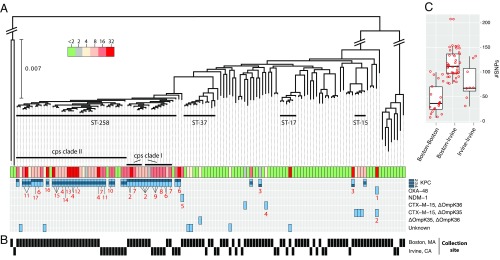
Fig. 2.
K. pneumoniae diversity. (A) Phylogeny of K. pneumoniae core genomes across all collections. Diagonal bars crossing major branches represent scale breaks. Horizontal thick black bars show clusters associated with a single MLST and containing resistant strains. The MIC of meropenem in micrograms per milliliter for each isolate is shown together with the predicted genetic determinant of resistance from the list of alternative genotypes located on the right. Numbers in red indicate predicted location of resistance determinants, including the predicted incompatibility group and name of closest replicon at GenBank and accession, if detected: 1, IncL/M(pOXA-48); 2, IncR; 3, IncN [pBK31551]; 4, chromosome; 5, IncFII(pKPX1) [accession no. KF727591.2]; 6, IncFIB(pQil); 7, IncFIB(K); 8, IncN; 9, IncN [accession no. FJ223607.1]; 10, IncFIA(HI1); 11, ColRNAI; 12, IncR [accession no. CP006657.1]; 13, two genomic locations: chromosome; IncI2 [pBK15692]; 14, IncI2 [pBK15692]; 15, IncFIA(HI1) [pBK30683]; 16, [pKpS90]; and 17, IncFIB(K) [pBK32179]. (B) Black rectangles indicate the city in which the isolate was collected. (C) Box plot of the distribution of SNPs (after removing recombination) separating closest pairs of ST258 from the same or different cities. Whiskers correspond to 1.5× the interquartile range (distance between the first and the third quartile). Red circles indicate the number of SNPs between each pair evaluated.
K. pneumoniae BIDMC_35 (ST17) also exhibited a high MIC (≥32 μg/mL), for which no genetic cause could be identified (SI Appendix, Table S13). With the exception of BIDMC_35, all ST17 isolates in our sample were susceptible to meropenem. High-level meropenem resistance (MIC ≥ 32 μg/mL) could be introduced to a susceptible E. coli strain by transformation with BIDMC_35 plasmid content. Although we did not detect genes implicated in carbapenem resistance in any BIDMC_35 plasmid scaffold (SI Appendix, Table S8), we identified a single gene on a predicted plasmid that varied at one site compared with a known class D beta-lactamase, blaOXA-10, which has not been implicated in clinical carbapenem resistance (SI Appendix, Fig. S7). Although comparison with the nonredundant database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) suggests that BIDMC_35’s blaOXA-10 is a unique blaOXA-10 variant, the mutation impacts the signal sequence of the protein and is unlikely to confer a change to OXA-10 function.
Phylogeographic Structure of the CRE Population.
If CRE transmission predominantly occurs over relatively short distances, we expect the population to show strong phylogeographic structure. We compared the collection described above with isolates from a hospital in Irvine, CA, collected in an identical manner to the Boston-based hospitals over the same 16-mo time period (Irvine Prospective Collection). The resulting sample contained 20 nonsusceptible and 45 susceptible isolates (summarized in SI Appendix, Tables S1 and S3). Consistent with results from the Boston-area hospitals, only two STs were widespread enough to be found on both coasts. First, K. pneumoniae ST258 was the most frequently isolated nonsusceptible ST in Irvine: 12 of 14 (86%) of K. pneumoniae and 12 of 20 (60%) of all nonsusceptible isolates. The vast majority of ST258 on both coasts carried blaKPC genes, the variants of which correlated well with membership in previously described cps clades (25) (SI Appendix, Table S1). Second, E. coli ST131, recently described as both successful and of high pathogenic potential (26), was isolated from one patient in Irvine during the same sampling period (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). The ST131 isolates from Boston and Irvine had different MICs and resistance determinants (SI Appendix, Table S1 and Fig. S5), suggesting that these geographically separated lineages acquired resistance independently.
The ST258 phylogeny gave us the opportunity to compare the relatedness of isolates across hospitals within and between geographic regions (Fig. 2B). Because K. pneumoniae is known to undergo recombination (25) and because recombination can impact phylogenetic reconstruction, we constructed an ST258-specific phylogeny based on the core genome of this group lacking predicted recombined sites (SI Appendix, Fig. S9 and SI Materials and Methods). A pairwise SNP distance matrix is given in SI Appendix, Table S16. We calculated the number of SNPs separating each isolate from its closest relative in the same geographic location (Boston vs. Boston or Irvine vs. Irvine) and the other (Boston vs. Irvine); the results are shown in Fig. 2C. ST258 isolates from the same coast tended to cluster and were significantly more closely related to each other than strains from the other coast (Boston–Boston vs. Boston–Irvine: P = 7.622 × 10−9; Irvine–Irvine vs. Boston-Irvine: P = 0.01; Wilcoxon rank sum test), indicating local spread of this ST. The distribution of close relatives shows that isolates are typically separated by dozens of SNPs, although it should be noted that two isolates from the same host (BIDMC_42A and B) differed at 29 sites in a recombination-free alignment, suggesting considerable diversity may exist within individual hosts.
Transfer of Resistance Elements by Diverse Tn4401 Elements.
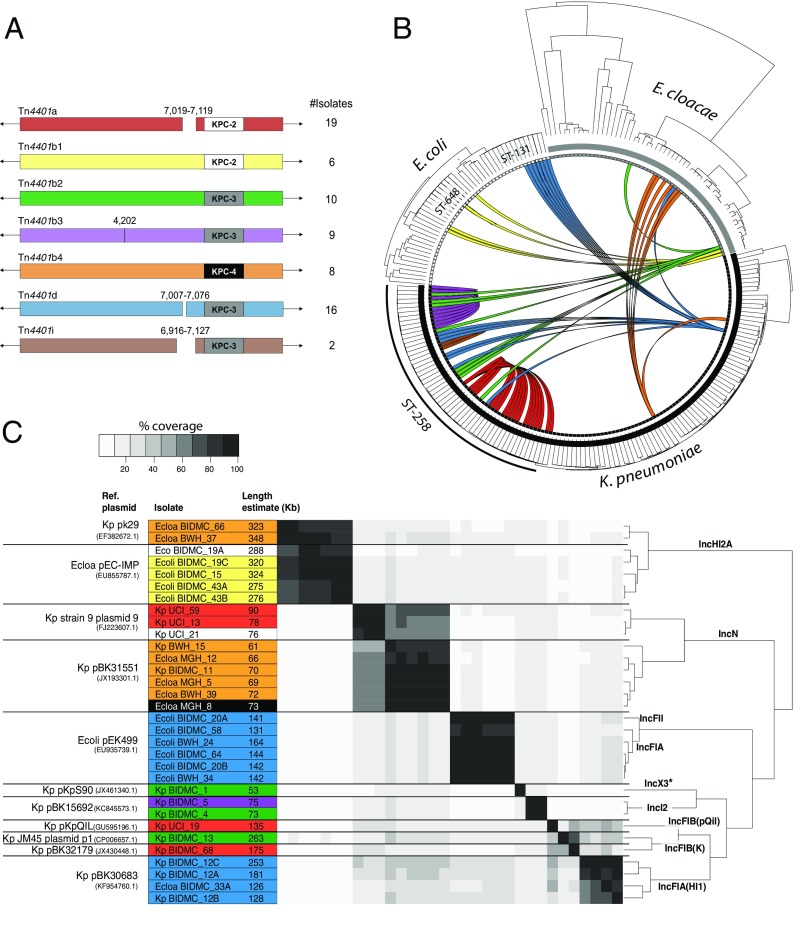
The transposable element Tn4401 mediates movement of KPC genes between strains and can insert into the chromosome or plasmids (5). In all cases, Tn4401 and KPC were physically linked in the genome. Fig. 3A shows the Tn4401b isoforms (27, 28) and subtypes (distinct blaKPC or single substitutions between instances) found in this study (Fig. 3B and SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S8) and illustrates the distribution of Tn4401 among lineages of the three most prevalent species. Cases in which identical Tn4401 sequences were found in divergent genomes are illustrated (Fig. 3B; also see SI Appendix, Table S1). K. pneumoniae harbored six of the seven Tn4401 isoforms shown in Fig. 3A, and five of these were present in ST258 isolates. We also identified an isoform, that we have called Tn4401i, containing a 210-nt deletion upstream of blaKPC-3, which was manually confirmed (Materials and Methods and SI Appendix, Fig. S10) and detected in two closely related ST258 isolates (UCI_67 and UCI_1) (Fig. 3B and SI Appendix, Fig. S8).
Fig. 3.
CRE Tn4401 isoforms. (A) The coordinates of indels (gaps in the rectangle) and substitutions (vertical line) are based on alignment against Tn4401b, the longest subtype identified. Only identical transposons within a single scaffold and found in more than one isolate were considered. The number of isolates with each form is listed to the right of the figure. The blaKPC associated with each transposon is indicated. (B) The phylogeny of each species is depicted in the outer radius. Colored arcs indicate isolates with identical Tn4401 sequences and are consistent with colors used in A. (C) Similarity among plasmids harboring the blaKPC gene. The name for the best matching reference plasmid at NCBI, the species associated with it (Kp for K. pneumoniae, Ecoli for E. coli, and Ecloa for E. cloacae), and GenBank accession number is given for each group in the first column. Species and isolate names are given alongside the estimated length of their predicted plasmid. Color indicates Tn4401 isoform encoded by plasmid according to A, and white cells are unique and unnamed isoforms. Black cells are truncated transposons. Pairwise percentage coverage between plasmids is shown in gray scale. Dendrogram depicts hierarchical clustering of plasmids based on their pairwise identity and coverage, and labels along branches indicate the plasmid incompatibility group assigned to each group. Nonchromosomal scaffolds that did not have sufficient identity to a previously reported plasmid are not included. *IncX3 incompatibility group was inferred from best-match plasmid: pKpS90 (accession no. JX461340.1).
Plasmids are also important in transferring resistance loci between lineages, so we searched all scaffolds from isolates containing Tn4401 to identify plasmid-associated sequence (Materials and Methods), which we then clustered to identify related plasmid groups (Fig. 3C). For the 32 strains with matches to known plasmids, we identified 11 plasmid groups containing sequences with high identity and coverage that belonged to 9 incompatibility groups. K. pneumoniae carried eight different plasmid groups, compared with two groups for E. coli and three groups for E. cloacae. Similar KPC-containing plasmids may encode distinct Tn4401 subtypes [for example, the ST258 strains BIDMC_5 and BIDMC_4 (Fig. 3C)], whereas plasmids belonging to different incompatibility groups may harbor the same Tn4401 isoform [for example, pEK499-like and pBK30683-like both carry copies of Tn4401d (Fig. 3C)]. Nine other ST258 strains contained chromosomal copies of Tn4401b2 and Tn4401b3. Examination of 5-Kb flanking regions revealed four distinct chromosomal integration sites (SI Appendix), and integration was validated for one by SMRT sequencing long reads spanning the integration site. The isolates with chromosomal Tn4401 were sampled in different months, and all were collected from the same Boston-area hospital, except one that was isolated from a hospital 0.5 miles away.
Discussion
Antibiotic resistance is extraordinarily diverse in terms of the species, mechanisms, and genes involved. This characteristic is especially true of CRE, which comprise many different species brought together by their ability to harbor genes that confer high levels of resistance to some of the most important antibiotics remaining in our arsenal. This paper considers this diversity in two cities and multiple local samples from hospitals in the Boston area and has prospectively collected and sequenced the vast majority of CRE isolates from multiple institutions outside of an outbreak setting.
Contrary to what would have been expected in the case of restricted outbreaks with a small number of lineages, the individual hospitals that we surveyed harbored multiple combinations of CRE species, sequence types, resistance determinants, plasmids, and transposons. In fact, only a limited subset of closely related strains were shared among multiple hospitals, notably the ST258 lineage of K. pneumoniae, which was previously noted as among the most frequent causes of CRE infection in the United States (1, 2, 29). The reasons for the success of this lineage, and its association with many resistance determinants and mobile elements, are not clear but may reflect its prominence in settings where resistance may be acquired, a higher recombination rate (30), or adaptation through compensatory mutations that limit any fitness costs associated with mechanisms conferring carbapenem resistance, as suggested by Bowers et al. (31). Five isolates of ST258 were meropenem-susceptible. These susceptible strains were not basal in the ST258 phylogenetic tree, suggesting that these strains lost their relevant determinants at some point during their evolution, possibly implying a fitness cost.
The diversity in species that we detected was echoed by the multiplicity of specific resistance determinants, as well as the different isoforms of Tn4401 we define in Fig. 3, which transfer these determinants between strains. Adding Tn4401 to non–whole-genome sequencing-based CRE surveys may help to reveal transmission events that could not be detected by MLST or examination of chromosomal DNA alone. The reasons for the observed distribution of Tn4401 as well as other mobile genetic elements in this and other studies are unclear, but we speculate that the observed distribution of resistance loci likely reflects the product of at least two processes: the transmissibility of the mobile element itself and the impact it has on the fitness of the recipient genome, both of which may be different in vitro in comparison with the hospital environment (32). Notably, ST258 is not only a frequent cause of CRE infection but also carries more combinations of resistance loci and transposons than any other lineage. It has been speculated that lineages that seem to have a propensity to take up resistance genes may undergo more recombination, including at sites not involved in resistance (30).
Using genome sequences to infer recent transmission is not trivial and requires some estimate of the expected SNP distance that occurs between and within infections (33). Our dataset sheds light on diversity within an infection in the form of two isolates retrieved from the same patient (BIDMC_42A and B) that were separated by 29 SNPs in a recombination free genome alignment (SI Appendix, Table S16). There are only two pairs of isolates in the prospective collection that are more closely related and that might reflect recent transmission. One of these pairs (BIDMC_60 and BIDMC_68) was separated by 13 SNPs, and the isolates were sampled in the same institution one month apart, whereas the other (BIDMC_34 and BIDMC_45) was divergent at 19 SNPs but were sampled 5 mo apart. The former is a plausible case of transmission, whereas the latter is less so. We do not have sufficient data at present to definitively determine the genetic distance associated with transmission, but it should be noted that the great majority of isolates in the prospective dataset do not have plausible donors in the sample when considering the date of isolation and the genetic distance (SI Appendix, Table S16). This result may suggest multiple unsampled transmission chains throughout the continuum of care, consistent with recent reports of asymptomatic carriage (34), which we know can continue for months after discharge (35). The hypothesis that CRE transmission occurs undetected throughout the continuum of care will need to be addressed by enhanced surveillance.
A recent study of the emergence and spread of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae suggested relatively rapid dissemination of ST258 (31). Our data support this model, because ST258 isolates from both coasts shared recent common ancestors, including from both cps clades. However, the ST258 isolates in our sample from the East and West Coasts were clearly distinct, indicating that, unsurprisingly, the majority of spread is local. The closest relationship we observed between isolates from different coasts was between two isolates, BIDMC_2A and UCI_1, which were separated by 76 SNPs in their core genome after accounting for recombined regions that might falsely inflate genetic distances (SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S9). The mean distance between isolates sampled in Boston and Irvine was considerably and significantly greater than that of isolates collected on the same coast (Fig. 2C).
Our sampling strategy, which collected CRE in general, rather than individual species, clones or resistance mechanisms, gave us the opportunity to ascertain the diversity of mechanisms and to identify cases of resistance where the molecular mechanisms were unrecognizable. In addition to blaKPCs, we found multiple changes in porins that, alone, or in combination with beta-lactamases, were likely to cause resistance, as previously reported (12–15). Taken together, isolates with porin mutations account for more than 20% of the Boston Prospective Collection (including two isolates with a previously unreported combination of blaTEM-1 and a truncated OmpK36). Given that beta-lactamases are more widespread that carbapenemases, and porins are ubiquitous, this is an accessible route to diminished susceptibility not requiring the acquisition of additional loci.
We also found evidence for combinations of plasmid-borne resistance mechanisms that could not be recognized based on current knowledge. The limitations of our approach might have caused us to miss the mechanisms responsible and include the difficulty in confidently distinguishing chromosomal and plasmid scaffolds, although we did search all scaffolds and reads for evidence of common determinants. We also examined the presence or absence of genes using a database of previously described resistance mechanisms, which could miss subtle changes impacting protein function or expression. Finally, the mechanisms could act at the translational or posttranslational levels, which would be obscured by our emphasis on coding sequences (36).
Although not all mechanisms have been revealed, the fact that these unexplained mechanisms of CRE exist is a critical result and shows that there are many ways to achieve carbapenem resistance and that we should be vigilant as new ones emerge. From a clinical perspective, this observation means that diagnostic methods that target certain genes and that are now on the market (blaKPC gene detection) will fail to detect a significant fraction of CRE, and the limitations of these diagnostics should, therefore, be understood by clinicians when making therapeutic decisions. Our raw data are available for comparison with the results of other researchers investigating currently unknown resistance mechanisms.
We have shown many different CRE lineages in multiple species, generated by multiple mechanisms and genetic determinants. Few of the isolates that we collected were closely related, as would be expected of a short transmission chain, but carried identical or nearly identical resistance elements and plasmids. Ultimately, to combat CRE, we need to continue whole-genome-based surveillance studies, such as this one, to better define the expanse of the problem with respect to CRE strain diversity and the molecular mechanisms driving resistance. However, studies based on clinical cultures from hospitalized patients alone are insufficient to fully identify and interrupt transmission; therefore, we must extend these studies further to include isolates from outside of tertiary hospital settings and from asymptomatic carriers.
Materials and Methods
Specimen Collection and Phenotypic Assessment.
Enterobacteriaceae with meropenem MIC of ≥2 μg/mL, nonsusceptible according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (23), were collected from patients from four hospitals over a 16-mo period (August 2012 through November 2013), together with species- and date-matched carbapenem-susceptible controls, when available. Three participating hospitals were located in Boston (Boston Prospective Collection), and another was located in Irvine (Irvine Prospective Collection). For context and comparison, carbapenem-resistant bacteria that had been sporadically archived from three Boston-area hospitals between 2006 and 2012 were also collected (Historical Collection). A full list of isolates and characteristics is provided in SI Appendix, Table S1 and summarized in SI Appendix, Table S2. Genome sequences were determined for a total of 263 isolates. Details of DNA extraction, sequencing, assembly, annotation, and phylogeny reconstruction are presented in the SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods. Genomic sequences were deposited in the BioProject database under the BioProject “Carbapenem Resistance” (accession no. PRJNA202876). Institutional review board (IRB) approval was granted by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Committee on the Use of Humans as Experimental Subjects. Samples were collected with informed consent under study approvals of the IRB committees of the participating institutions: Partners Healthcare (covering both MGH and BWH); Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston; University of California, Irvine; and Carolinas HealthCare System.
cps Gene Analysis and Clade Classification.
ST258 isolates may be further divided on the basis of divergent capsular loci into cps clades I and II (SI Appendix, Fig. S1 and Table S1). We determined the clade for each ST258 isolate by comparing wzy orthologs from our collection to wzy reference sequences of cps clades I and II (37, 38) (AHJ80448.1 and AHJ80492.1, respectively). Details are given in the SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods.
Plasmid Identification.
Plasmid scaffolds were defined when >70% of scaffold length matched the previous published plasmid sequence, and <30% matched to either mobile element or chromosomal sequences. Reference plasmids having ≥70% overall coverage by scaffolds of one isolate were considered as present in that isolate. Incompatibility groups were defined based on greater than 94% identity to replicons in PlasmidFinder database (39).
Transposon Tn4401 Annotation.
Copies were identified by similarity with Tn4401 transposon sequence from plasmid pKPC_FCF/3SP (GenBank accession no. NC_021660.2). Isoforms present in more than one genome were annotated according to the appropriate nomenclature (27, 28). Isoforms not meeting this criterion were annotated as “unique” (SI Appendix, Table S1). Copies containing different variants of blaKPC or containing a single-nucleotide substitution were considered as distinct Tn4401b subtypes. The sites of chromosomal integration were examined by comparing concatenates of 5-Kb flanking regions (10 Kb total), and those with more than 90% coverage and 90% identity were considered as the same integration site. Assembly of the Tn4401i isoform (210-nt deletion upstream of blaKPC-3) was confirmed by inspecting the alignment of reads to draft assemblies including those predicted to not contain the deletion. Further details are available in SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods.
Identifying Additional Resistance Determinants.
Based on a separate annotation of resistance genes (SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods), we constructed a matrix showing the presence and absence of all predicted resistance genes across all isolates. Isolates encoding known carbapenem resistance determinants (e.g., blaKPC were removed), and additional determinants were identified by manually searching for genes with a presence/absence pattern specific for meropenem resistant isolates. In addition, for all strains with unexplained resistance, we aligned reads to a reference database of antibiotic-resistance determinants to verify absence of known mechanisms (SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods). Putative inactivated porins were identified by searching for porin orthologs with less than 80% similarity to reference porin gene sequences and then manually inspecting hits for mutations that would likely impact function (e.g., disruption by insertion elements). For isolates having unexplained resistance, we also manually inspected all encoded porins and compared porin variants with those encoded by susceptible isolates having similar beta-lactamase content. Manual inspection did not identify any additional putative resistance-conferring porin variants.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Kaye D. Evans (School of Medicine, University of California Irvine) and Jean Spargo (Massachusetts General Hospital) for assistance with isolates. This project has been funded, in whole or in part, with Federal funds from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), NIH, Department of Health and Human Services, under Contract HHSN272200900018C and Grant U19AI110818 to the Broad Institute. This work was supported by NIH/NIAID Grant K08AI104767 (to Y.H.G.) and NIH/NIAID Grants R21AI112694 and R21AI119114 (to J.E.K.). J.L.R.-C. was supported by a Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel fellowship (Process 99999.010768/2014-09). The contents of this publication are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
Data deposition: Genomic sequences have been deposited in the BioProject database, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject (accession no. PRJNA202876).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1616248114/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2013. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013 (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta). Available at: www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013. Accessed July 25, 2014.
- 2.Schwaber MJM, et al. Predictors of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae acquisition among hospitalized adults and effect of acquisition on mortality. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52(3):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01020-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hidron AI, et al. National Healthcare Safety Network Team; Participating National Healthcare Safety Network Facilities NHSN annual update: antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: annual summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006-2007. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2008;29(11):996–1011. doi: 10.1086/591861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nordmann P, Dortet L, Poirel L. Carbapenem resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: here is the storm! Trends Mol Med. 2012;18(5):263–272. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Conlan S, et al. Single-molecule sequencing to track plasmid diversity of hospital-associated carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(254):254ra126. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Munoz-Price LS, et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(9):785–796. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70190-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gupta N, Limbago BM, Patel JB, Kallen AJ. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: epidemiology and prevention. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53(1):60–67. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Walther-Rasmussen J, Høiby N. OXA-type carbapenemases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;57(3):373–383. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Warner DM, et al. Involvement of MarR and YedS in carbapenem resistance in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli from China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(4):1935–1937. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02445-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nordmann P, Naas T, Poirel L. Global spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17(10):1791–1798. doi: 10.3201/eid1710.110655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lyman M, et al. Notes from the Field: Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae producing OXA-48-like carbapenemases--United States, 2010-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(47):1315–1316. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6447a3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Doménech-Sánchez A, et al. Role of Klebsiella pneumoniae OmpK35 porin in antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47(10):3332–3335. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.10.3332-3335.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Findlay J, Hamouda A, Dancer SJ, Amyes SGB. Rapid acquisition of decreased carbapenem susceptibility in a strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae arising during meropenem therapy. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(2):140–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Elliott E, et al. In vivo development of ertapenem resistance in a patient with pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae with an extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42(11):e95–e98. doi: 10.1086/503264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Novais A, et al. Spread of an OmpK36-modified ST15 Klebsiella pneumoniae variant during an outbreak involving multiple carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae species and clones. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;31(11):3057–3063. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1665-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Marchaim D, et al. Outbreak of colistin-resistant, carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in metropolitan Detroit, Michigan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55(2):593–599. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01020-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Epson EE, et al. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae producing New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase at an acute care hospital, Colorado, 2012. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2014;35(4):390–397. doi: 10.1086/675607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Snitkin ES, et al. Tracking a hospital outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with whole-genome sequencing. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(148):148ra116. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bratu S, et al. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Brooklyn, NY: molecular epidemiology and in vitro activity of polymyxin B and other agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56(1):128–132. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen L, et al. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: molecular and genetic decoding. Trends Microbiol. 2014;22(12):686–696. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mathers AJA, et al. Molecular dissection of an outbreak of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae reveals Intergenus KPC carbapenemase transmission through a promiscuous plasmid. MBio. 2011;2(6):e00204–e00211. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00204-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Leavitt A, et al. Molecular epidemiology, sequence types, and plasmid analyses of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in Israel. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54(7):3002–3006. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01818-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . M100S: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 26th Ed Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; Wayne, PA: 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guh AY, et al. Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in 7 US communities, 2012-2013. JAMA. 2015;314(14):1479–1487. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.12480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen L, Mathema B, Pitout JDD, DeLeo FR, Kreiswirth BN. Epidemic Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 is a hybrid strain. MBio. 2014;5(3):e01355-e14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01355-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nicolas-Chanoine M-H, Bertrand X, Madec J-Y. Escherichia coli ST131, an intriguing clonal group. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014;27(3):543–574. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00125-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang L, et al. Complete sequences of KPC-2-encoding plasmid p628-KPC and CTX-M-55-encoding p628-CTXM coexisted in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:838. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Martinez T, Martinez I, Vazquez GJ, Aquino EE, Robledo IE. Genetic environment of the KPC gene in Acinetobacter baumannii ST2 clone from Puerto Rico and genomic insights into its drug resistance. J Med Microbiol. 2016;65(8):784–792. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kitchel B, et al. Molecular epidemiology of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in the United States: clonal expansion of multilocus sequence type 258. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(8):3365–3370. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00126-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hanage WP, Fraser C, Tang J, Connor TR, Corander J. Hyper-recombination, diversity, and antibiotic resistance in pneumococcus. Science. 2009;324(5933):1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.1171908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bowers JR, et al. Genomic analysis of the emergence and rapid global dissemination of the clonal group 258 Klebsiella pneumoniae pandemic. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0133727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Benenson S, et al. Comparison of two carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clones: from a contained outbreak in a paediatric population and from a national epidemic. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67(7):1651–1654. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Worby CJ, Chang H-H, Hanage WP, Lipsitch M. The distribution of pairwise genetic distances: a tool for investigating disease transmission. Genetics. 2014;198(4):1395–1404. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.171538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Turner P, et al. High prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant Gram-negative colonization in hospitalized Cambodian infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2016;35(8):856–861. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zimmerman FS, et al. Duration of carriage of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae following hospital discharge. Am J Infect Control. 2013;41(3):190–194. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2012.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsai Y-K, Liou C-H, Fung C-P, Lin J-C, Siu LK. Single or in combination antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of Klebsiella pneumoniae contribute to varied susceptibility to different carbapenems. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Deleo FR, et al. Molecular dissection of the evolution of carbapenem-resistant multilocus sequence type 258 Klebsiella pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(13):4988–4993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321364111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chen L, et al. Multiplex PCR for identification of two capsular types in epidemic KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(7):4196–4199. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02673-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Carattoli A, et al. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(7):3895–3903. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02412-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.