Abstract
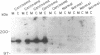
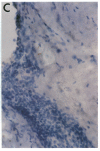
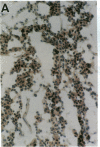
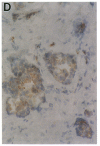
Phospholipase C-gamma 1 (PLC-gamma 1) is a substrate for several receptor tyrosine kinases and its catalytic activity is increased by tyrosine phosphorylation. However, the biological significance of this molecule in normal or malignant human epithelial cell proliferation is unknown. We determined the relative content of PLC-gamma 1 in primary human mammary carcinomas and in nonmalignant mammary tissues. By Western blot and immunohistochemistry, considerably higher levels of PLC-gamma 1 protein were detectable in the majority of carcinomas and in one of two benign fibroadenomas compared to normal breast tissues. In 18 of 21 carcinomas that contained high levels of PLC-gamma 1, the presence of phosphotyrosine on PLC-gamma 1 could also be detected. All carcinomas in which tyrosine phosphorylated PLC-gamma 1 was present also expressed detectable levels of the epidermal growth factor receptor or erbB-2, two tyrosine kinases known to phosphorylate this enzyme. Thus, a high percentage of mammary carcinomas concomitantly display increased levels of receptor tyrosine kinases and a direct tyrosine phosphorylation substrate, thereby potentially amplifying two successive steps in a signal transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bronzert D. A., Pantazis P., Antoniades H. N., Kasid A., Davidson N., Dickson R. B., Lippman M. E. Synthesis and secretion of platelet-derived growth factor by human breast cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5763–5767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Dionne C. A., Kaplow J., Mudd R., Friesel R., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J., Jaye M. Characterization and cDNA cloning of phospholipase C-gamma, a major substrate for heparin-binding growth factor 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor)-activated tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4770–4777. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuadrado A., Molloy C. J. Overexpression of phospholipase C-gamma in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts results in increased phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in response to platelet-derived growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6069–6072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Segatto O., Lonardo F., Fazioli F., Pierce J. H., Aaronson S. A. The carboxy-terminal domains of erbB-2 and epidermal growth factor receptor exert different regulatory effects on intrinsic receptor tyrosine kinase function and transforming activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2749–2756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Margolis B. L., Zilberstein A., Ashmun R. A., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J., Schlessinger J. Phospholipase C-gamma, a substrate for PDGF receptor kinase, is not phosphorylated on tyrosine during the mitogenic response to CSF-1. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3345–3350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Homma Y., Sorimachi H., Kawasaki H., Nakanishi O., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. A second type of rat phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C containing a src-related sequence not essential for phosphoinositide-hydrolyzing activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21885–21890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazioli F., Kim U. H., Rhee S. G., Molloy C. J., Segatto O., Di Fiore P. P. The erbB-2 mitogenic signaling pathway: tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma and GTPase-activating protein does not correlate with erbB-2 mitogenic potency. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2040–2048. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami K., Matsuoka K., Nakanishi O., Yamakawa A., Kawai S., Takenawa T. Antibody to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate inhibits oncogene-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9057–9061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guérin M., Gabillot M., Mathieu M. C., Travagli J. P., Spielmann M., Andrieu N., Riou G. Structure and expression of c-erbB-2 and EGF receptor genes in inflammatory and non-inflammatory breast cancer: prognostic significance. Int J Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;43(2):201–208. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock A., Ellis I. O., Robertson J. F., Gilmour A., Bell J., Elston C. W., Blamey R. W. An observation of DNA ploidy, histological grade, and immunoreactivity for tumour-related antigens in primary and metastatic breast carcinoma. J Pathol. 1989 Oct;159(2):129–134. doi: 10.1002/path.1711590207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsfall D. J., Tilley W. D., Orell S. R., Marshall V. R., Cant E. L. Relationship between ploidy and steroid hormone receptors in primary invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1986 Jan;53(1):23–28. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Sato J. D., Le A., Polikoff J., Sato G. H., Mendelsohn J. Growth stimulation of A431 cells by epidermal growth factor: identification of high-affinity receptors for epidermal growth factor by an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1337–1341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U. H., Fink D., Jr, Kim H. S., Park D. J., Contreras M. L., Guroff G., Rhee S. G. Nerve growth factor stimulates phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumjian D. A., Barnstein A., Rhee S. G., Daniel T. O. Phospholipase C gamma complexes with ligand-activated platelet-derived growth factor receptors. An intermediate implicated in phospholipase activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3973–3980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Green N., Alexander H., Liu F. T., Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M. Chemically synthesized peptides predicted from the nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome elicit antibodies reactive with the native envelope protein of Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3403–3407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Zilberstein A., Franks C., Felder S., Kremer S., Ullrich A., Rhee S. G., Skorecki K., Schlessinger J. Effect of phospholipase C-gamma overexpression on PDGF-induced second messengers and mitogenesis. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):607–610. doi: 10.1126/science.2333512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., Dressler L. G. Emerging impact of flow cytometry in predicting recurrence and survival in breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Sep;75(3):405–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S., Halcrow P., Sainsbury J. R., Angus B., Chambers P., Farndon J. R., Harris A. L. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) status associated with failure of primary endocrine therapy in elderly postmenopausal patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1988 Dec;58(6):810–814. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II in vitro by the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10335–10338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Wedegaertner P. B., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G., Kim J. J. Selectivity of phospholipase C phosphorylation by the epidermal growth factor receptor, the insulin receptor, and their cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):424–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury J. R., Farndon J. R., Needham G. K., Malcolm A. J., Harris A. L. Epidermal-growth-factor receptor status as predictor of early recurrence of and death from breast cancer. Lancet. 1987 Jun 20;1(8547):1398–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90593-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban E., Sitaras N. M., Antoniades H. N., Kufe D. W., Pantazis P. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-related transcripts and synthesis of biologically active PDGF-like proteins by human malignant epithelial cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1157–1164. doi: 10.1172/JCI113712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Liu Y. L., Kim H., Rhee S. G., Kung H. F. Inhibition of serum- and ras-stimulated DNA synthesis by antibodies to phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1074–1077. doi: 10.1126/science.2408147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoscheck C. M., Carpenter G. Characteristics of antibodies to the epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Dec;227(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon A. K., Clark G. M., Chamness G. C., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. HER-2/neu oncogene protein and prognosis in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Aug;7(8):1120–1128. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.8.1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. H., Dowle C., Williams M. R., Elston C. W., Ellis I. O., Hinton C. P., Blamey R. W., Haybittle J. L. Confirmation of a prognostic index in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1987 Oct;56(4):489–492. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Daniel T. O., Carpenter G. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A-431 cells. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.2457254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Kim J. W., Kim H., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Identification of two epidermal growth factor-sensitive tyrosine phosphorylation sites of phospholipase C-gamma in intact HSC-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3944–3948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Olashaw N. E., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Pledger W. J., Carpenter G. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2934–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]