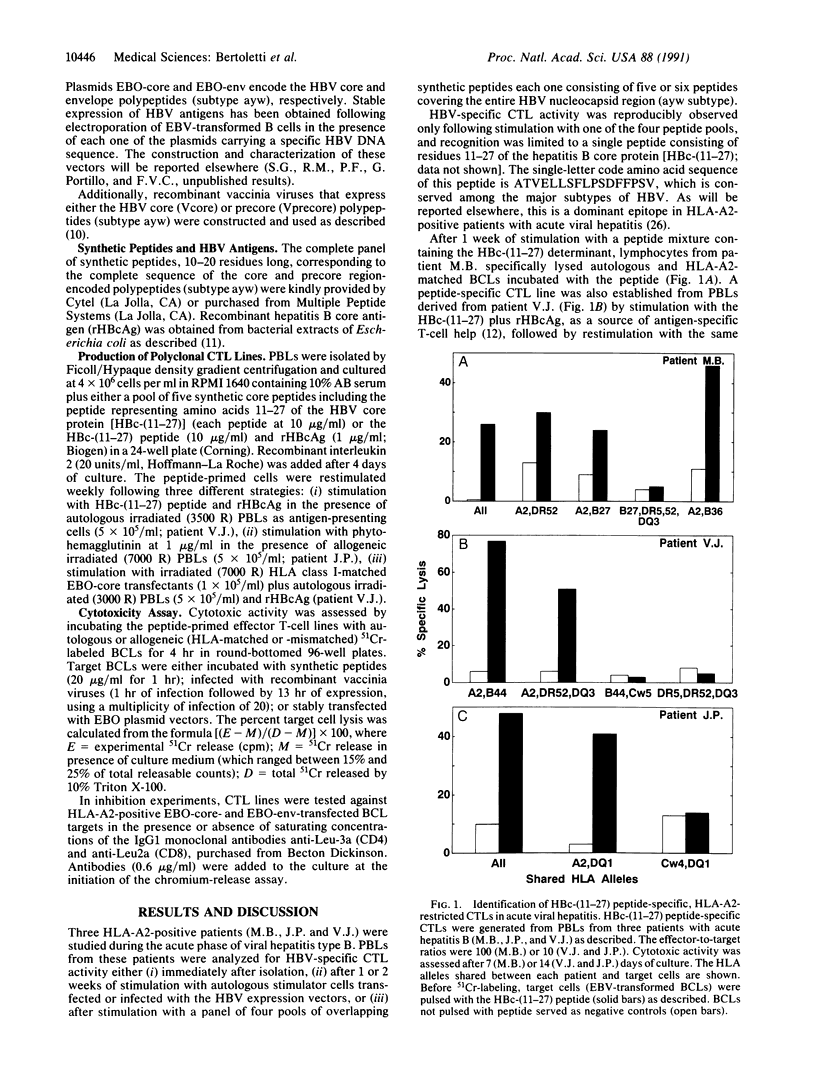
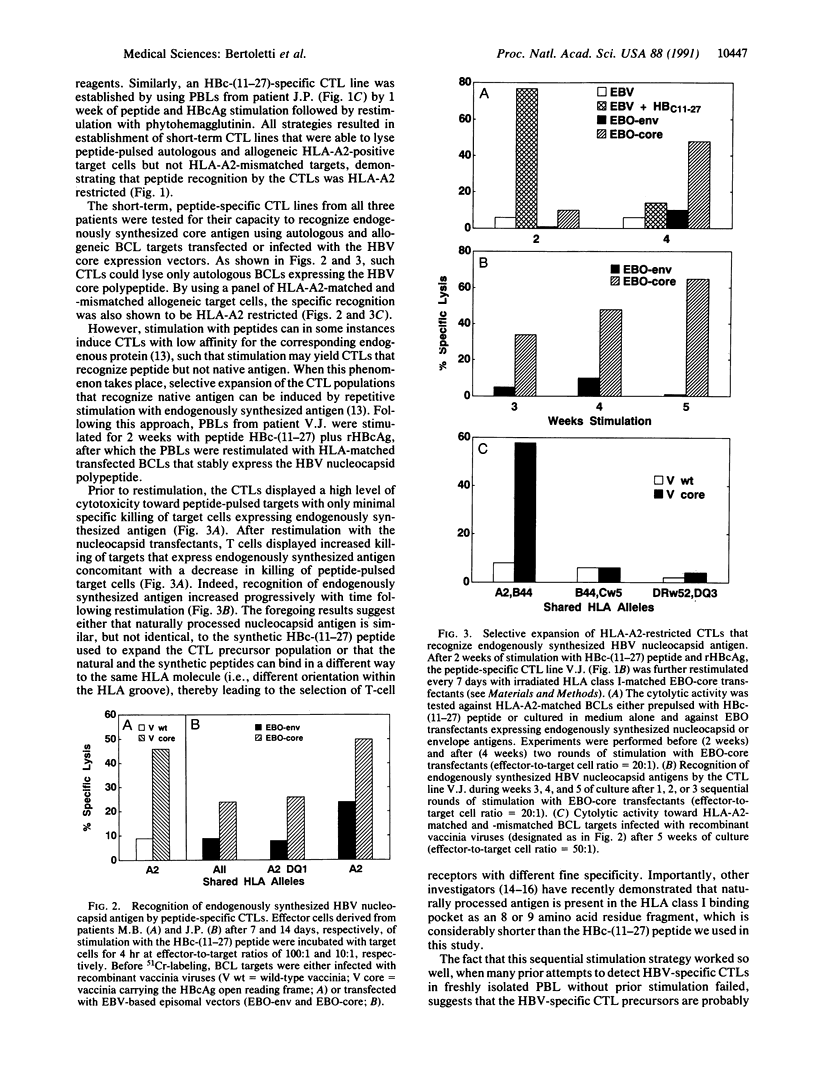
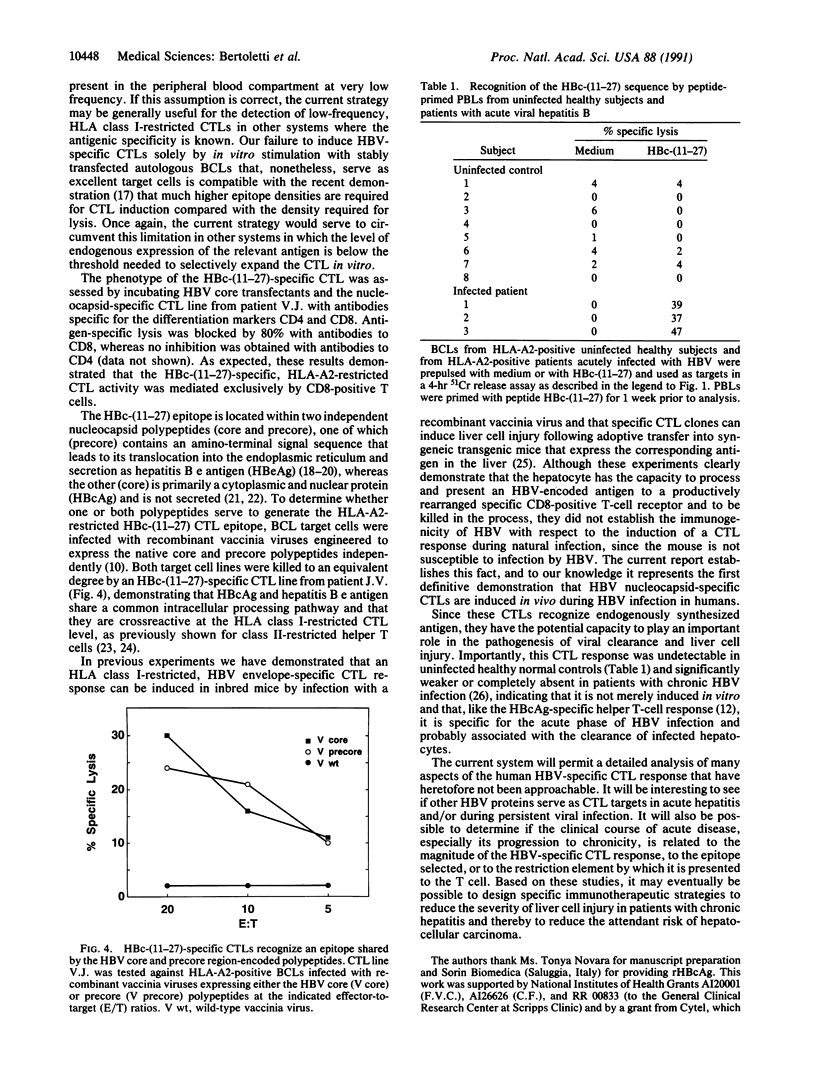
Abstract
Knowledge of the immune effector mechanisms responsible for clearance of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected cells has been severely limited by the absence of reproducible systems to selectively expand and to characterize HBV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in the peripheral blood of patients with viral hepatitis. By using a strategy involving sequential stimulation with HBV nucleocapsid synthetic peptides followed by autologous, or HLA class I-matched, HBV nucleocapsid transfectants, we now report the existence of CTLs able to lyse target cells that express endogenously synthesized HBV nucleocapsid antigen in the peripheral blood of patients with acute viral hepatitis B. The CTL response is HLA-A2 restricted, mediated by CD8-positive T cells, and specific for a single epitope, located between amino acid residues 11 and 27 of HBV core protein; these residues are shared with the secretable precore-derived hepatitis B e antigen. Equivalent lysis of target cells that express each of these proteins suggests that their intracellular trafficking pathways may intersect. The current report provides definitive evidence that HLA class I-restricted, CD8-positive CTLs that recognize endogenously synthesized HBV nucleocapsid antigen are induced during acute HBV infection in humans and establishes a strategy that should permit a detailed analysis of the role played by HBV-specific CTLs in the immunopathogenesis of viral hepatitis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. A., Damico C. A., Wieties K. M., Hansen T. H., Connolly J. M. Correlation between CD8 dependency and determinant density using peptide-induced, Ld-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):849–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnaba V., Franco A., Alberti A., Balsano C., Benvenuto R., Balsano F. Recognition of hepatitis B virus envelope proteins by liver-infiltrating T lymphocytes in chronic HBV infection. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2650–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield V., Emanuel J. R., Spickofsky N., Levenson R., Margolskee R. F. Ouabain-resistant mutants of the rat Na,K-ATPase alpha 2 isoform identified by using an episomal expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1367–1372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone F. R., Moore M. W., Sheil J. M., Bevan M. J. Induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes by primary in vitro stimulation with peptides. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1767–1779. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Ferrari C., Mondelli M. U. Hepatitis B virus structure and biology. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):311–325. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. T-cell-mediated immunopathology in viral infections. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):89–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Bertoletti A., Penna A., Cavalli A., Valli A., Missale G., Pilli M., Fowler P., Giuberti T., Chisari F. V. Identification of immunodominant T cell epitopes of the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid antigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):214–222. doi: 10.1172/JCI115280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Bertoletti A., Valli A., Antoni A. D., Giuberti T., Cavalli A., Petit M. A., Fiaccadori F. Cellular immune response to hepatitis B virus-encoded antigens in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3442–3449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Giuberti T., Tong M. J., Ribera E., Fiaccadori F., Chisari F. V. Intrahepatic, nucleocapsid antigen-specific T cells in chronic active hepatitis B. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2050–2058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A., Milich D. R., Raney A. K., Riggs M. G., Hughes J. L., Sorge J., Chisari F. V. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface and core antigens: influences of pre-S and precore sequences. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.683-692.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Moriarty A., Thornton G. B. Immune response to hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBcAg): localization of T cell recognition sites within HBcAg/HBeAg. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1223–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M. U., Bortolotti F., Pontisso P., Rondanelli E. G., Williams R., Realdi G., Alberti A., Eddleston A. L. Definition of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific target antigens recognized by cytotoxic T cells in acute HBV infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):242–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Guilhot S., Klopchin K., Moss B., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Kanagawa O., Chisari F. V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):361–364. doi: 10.1126/science.1691527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Ahmed R., Byrne J., Buchmeier M. J., Riviere Y., Southern P. Virus and immune responses: lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus as a prototype model of viral pathogenesis. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jan;41(1):70–74. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossinck M. J., Jameel S., Loukin S. H., Siddiqui A. Expression of hepatitis B viral core region in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1393–1400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossinck M. J., Siddiqui A. In vivo phosphorylation and protein analysis of hepatitis B virus core antigen. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):955–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.955-961.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rötzschke O., Falk K., Deres K., Schild H., Norda M., Metzger J., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Isolation and analysis of naturally processed viral peptides as recognized by cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):252–254. doi: 10.1038/348252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Schaller H. The secretory core protein of human hepatitis B virus is expressed on the cell surface. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5399–5404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5399-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Masiarz F. R., Rutter W. J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uy A., Bruss V., Gerlich W. H., Köchel H. G., Thomssen R. Precore sequence of hepatitis B virus inducing e antigen and membrane association of the viral core protein. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. Isolation of an endogenously processed immunodominant viral peptide from the class I H-2Kb molecule. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):213–216. doi: 10.1038/348213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



