Abstract
Background
COPD often coexists with chronic conditions that may influence disease prognosis. We investigated associations between chronic (co)morbidities and exacerbations in primary care COPD patients.
Method
Retrospective cohort study based on 2012–2013 electronic health records from 179 Dutch general practices. Comorbidities from patients with physician-diagnosed COPD were categorized according to International Classification of Primary Care (ICPC) codes. Chi-squared tests, uni- and multivariable logistic, and Cox regression analyses were used to study associations with exacerbations, defined as oral corticosteroid prescriptions.
Results
Fourteen thousand six hundred three patients with COPD could be studied (mean age 67 (SD 12) years, 53% male) for two years. At baseline 12,826 (88%) suffered from ≥1 comorbidities, 3263 (22%) from ≥5. The most prevalent comorbidities were hypertension (35%), coronary heart disease (19%), and osteoarthritis (18%). Several comorbidities showed statistically significant associations with frequent (i.e., ≥2/year) exacerbations: heart failure (odds ratio [OR], 95% confidence interval: 1.72; 1.38–2.14), blindness & low vision (OR 1.46; 1.21–1.75), pulmonary cancer (OR 1.85; 1.28–2.67), depression 1.48; 1.14–1.91), prostate disorders (OR 1.50; 1.13–1.98), asthma (OR 1.36; 1.11–1.70), osteoporosis (OR 1.41; 1.11–1.80), diabetes (OR 0.80; 0.66–0.97), dyspepsia (OR 1.25; 1.03–1.50), and peripheral vascular disease (OR 1.20; 1.00–1.45). From all comorbidity categories, having another chronic respiratory disease beside COPD showed the highest risk for developing a new exacerbation (Cox hazard ratio 1.26; 1.17–1.36).
Conclusion
Chronic comorbidities are highly prevalent in primary care COPD patients. Several chronic comorbidities were associated with having frequent exacerbations and increased exacerbation risk.
Background
Although nowadays healthcare systems are largely configured to manage individual diseases rather than multimorbidity, there is an increasing awareness of the importance of comorbidities in patients with chronic conditions [1]. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a prevalent chronic respiratory condition, is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide [2]. In the past decade several studies have shown that COPD often coexists with other diseases, [3, 4] and that comorbidity is associated with poorer clinical outcomes [4, 5]. Some of these comorbidities arise independently of COPD, whereas others may be causally related, either through shared risk factors (smoking, aging) or shared pathophysiology, as a complication of COPD, or due to medication side effects.
Several associations between COPD and particular comorbidities have been shown. Cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, skeletal muscle dysfunction, osteoporosis, depression and lung cancer are all highly prevalent among patients with any severity of COPD, and cross-sectional studies have shown their significant impact on patients’ health-related quality of life [2, 6, 7]. Most of the research on comorbidity in COPD comes from studies in secondary care populations, thus representing patients in the more severe part of the COPD severity spectrum [4]. However, in most developed countries, the vast majority of patients with COPD are managed in primary care. Studies performed in general practice settings report that 21 to 74% of patients with COPD suffer from two or more additional chronic diseases [6, 8].
As COPD is a progressive disease, factors that influence its prognosis are important to consider when managing patients. Since exacerbation frequency is a known predictor of COPD progression, [2] it is important to know what the potential impact of comorbidities on the risk of exacerbations is. Recently Putcha et al.reported a model in which the number of comorbid conditions predicted dyspnea and exacerbation risk [9]. This prediction model does, however, not take into account which particular comorbid conditions are associated with exacerbation risk. Other previous studies have predominantly looked at mortality as the outcome of interest, [5, 10, 11] but from a patient management perspective it is important that physicians consider comorbidities that influence potentially modifiable prognostic factors like exacerbation rate in their treatment decisions. Therefore, the aim of the current study was to explore associations between a wide range of comorbid chronic conditions and exacerbation risk in a real-life cohort of primary care patients with COPD.
Methods
Design and dataset
The study used routine data from a general practice database from the Department of Primary and Community Care at the Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. De-identified electronic medical records from primary care patients diagnosed with COPD from 179 general practices in the eastern part of the Netherlands were available in the database.
For each registered subject, the following data were extracted: age, sex, all diagnoses using the International Classification of Primary Care (ICPC), extended with Dutch ICPC sub-codes, [12] and all prescribed medication. ICPC-2 or ICD10 coding data were recoded into ICPC-1. Medication prescriptions (i.e., prescription start and end dates, dosage, frequency, and duration) were extracted and categorized using the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classification system [13]. For the current study only the data on prescriptions for oral corticosteroids were used.
Study population
Subjects aged ≥40 years were included in the study population when they had physician-diagnosed COPD (as labeled with ICPC code R95 in the electronic medical record) before or during the study period. Asthma (ICPC R96) in addition to the COPD code was not an exclusion criterion. The follow-up period covered the years 2012 and 2013. The observation period for patients terminated either at the end of the study period (31 December 2013), or when a subject died or deregistered from the practice.
Comorbidities
The selection of chronic comorbid diseases studied was based on existing literature [1, 14], the authors’ clinical expertise and expert opinions (Nielen MM, Spronk I, Davids R, Korevaar JC, Poos MJ, Hoeymans N, Opstelten W, van der Sande MAB, Biermans MCJ, Schellevis FG, RA V: A new method for estimating morbidity rates based on routine electronic medical records in primary care, submitted). We considered all chronic diseases as comorbidities, regardless whether the disease had been diagnosed before the COPD diagnosis or thereafter. Apart from all ‘obligatory’ chronic diseases we also included several recurrent diseases (i.e., depression, anxiety, anemia, dyspepsia, urinary tract infection) which could potentially influence COPD outcomes. After reaching consensus about these recurrent comorbidities within the research team, ICPC (sub)codes were linked (see Appendix 1). Selection of the recurrent comorbidities in our population was based on the patient’s history in terms of these particular ICPC codes. To define whether a history of ICPC codes was relevant or irrelevant for the aim of the study, we added specific selection criteria based on published clinical guidelines for the respective diseases (see Appendix 1).
Finally, a total of 82 chronic comorbid conditions were selected and included in the analyses. The comorbidities were clustered and analyzed based on their ICPC codes into the following 14 categories: respiratory; cardiovascular; digestive; endocrine; metabolic/nutrition; musculoskeletal; neurologic; psychiatric; urogenital; blood (−forming organs)/lymphatics; infectious; eye/ear/skin; non-pulmonary cancer; and pulmonary cancer. Low prevalence categories were merged (see Appendix 2). To restrict ourselves, we focused on conditions with a high prevalence and cardiopulmonary comorbidities (other than COPD) with a lower prevalence (7 conditions, see Table 2). High-prevalent comorbidities (19 conditions), further referred to as ‘frequent comorbidities’, were defined as being present in ≥5% of the study population. This resulted in a total of 26 comorbidities remaining for further analyses.
Table 2.
Prevalence of frequent and cardiopulmonary comorbidity in the study population, sorted from highest to lowest prevalence rate
| Total study populationa, (n = 14,603) | Patients with <2 exacerbations/year, (n = 13,709) | Patients with ≥2 exacerbations/year, (n = 894) | p-valueb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequent comorbidity | ||||
| Hypertension | 5,116 (35 · 0) | 4,805 (35 · 2) | 311 (34 · 8) | 0 · 873 |
| Coronary heart disease | 2,759 (18 · 9) | 2,569 (18 · 7) | 191 (21 · 4) | 0 · 051 |
| Osteoarthritis | 2,570 (17 · 6) | 2,402 (17 · 5) | 168 (18 · 8) | 0 · 334 |
| Diabetes | 2,464 (16 · 9) | 2,330 17 · 0) | 134 (15 · 0) | 0 · 120 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 2,031 (13 · 9) | 1,897 (14 · 8) | 150 (16 · 8) | 0 · 006 |
| Blindness & low vision | 1,938 (13 · 3) | 1,772 (12 · 9) | 166 (18 · 6) | <0 · 001 |
| Dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux | 1,845 (12 · 6) | 1,703 (12 · 4) | 142 (15 · 9) | 0 · 003 |
| Dislipidemia | 1,703 (11 · 7) | 1,613 (11 · 8) | 90 (10 · 1) | 0 · 125 |
| Stroke & transient ischaemic attack | 1,357 (9 · 3) | 1,259 (9 · 2) | 98 (11 · 0) | 0 · 076 |
| Chronic kidney diease | 1,360 (9 · 3) | 1,263 (9 · 2) | 97 (10 · 9) | 0 · 103 |
| Asthma | 1,305 (8 · 9) | 1,202 (8 · 8) | 103 (11 · 5) | 0 · 005 |
| Hearing loss | 1,144 (7 · 8) | 1,078 (7 · 9) | 66 (7 · 4) | 0 · 604 |
| Heart failure | 1,048 (7 · 2) | 943 (6 · 9) | 105 (11 · 7) | <0 · 001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 1,044 (7 · 1) | 964 (7 · 0) | 80 (8 · 9) | 0 · 031 |
| Skin cancer | 913 (6 · 3) | 862 (6 · 3) | 51 (5 · 7) | 0 · 485 |
| Osteoporosis/osteopenia | 884 (6 · 1) | 801 (5 · 8) | 83 (9 · 3) | <0 · 001 |
| Thyroid disorder | 808 (5 · 5) | 757 (5 · 5) | 51 (5 · 9) | 0 · 817 |
| Depression | 800 (5 · 5) | 729 (5 · 3) | 71 (7 · 9) | 0 · 001 |
| Prostate disorders | 784 (5 · 4) | 719 (5 · 2) | 65 (7 · 3) | 0 · 009 |
| Cardiopulmonary comorbidity | ||||
| Heart valve disease | 568 (3 · 9) | 528 (3 · 9) | 40 (7 · 8) | 0 · 035 |
| Bronchiectasis/chronic bronchitis | 414 (2 · 8) | 379 (2 · 8) | 35 (3 · 9) | 0 · 045 |
| Pulmonary cancer | 317 (2 · 2) | 284 (2 · 1) | 33 (3 · 7) | 0 · 001 |
| Sleep apneu syndrome | 173 (1 · 2) | 161 (1 · 2) | 12 (1 · 3) | 0 · 653 |
| Other chronic pulmonary disease | 157 (1 · 1) | 148 (1 · 1) | 9 (1 · 0) | 0 · 838 |
| Recurrent sinusitis | 54 (0 · 4) | 49 (0 · 4) | 55 (6 · 2) | 0 · 335 |
| Congenital cardiovascular anomaly | 32 (0 · 2) | 28 (0 · 2) | 4 (0 · 4) | 0 · 132 |
aCOPD population with complete data available, patients lost to follow-up (n = 1,824) excluded
b p-values displayed are calculated for the difference between the subgroup <2 versus ≥2 exacerbations/year Chi-square tests for categorized variables. p < 0 · 05 was considered statistically significant
Outcomes
The outcomes for the study were (i) prevalence of comorbidities in the study population, (ii) annual rate of exacerbations (dichotomized as <2 versus ≥2 exacerbations/year based on the cumulated 2012/13 data), and (iii) time (in days) until first exacerbation. An exacerbation was defined as a prescription of oral corticosteroids (i.e., prednisolone (ATC H02AB06) or prednisone (ATC H02AB07)) with a minimum daily dose of 20 mg for a minimum duration of 5 days and a maximum duration of 15 days (based on Dutch GP guidelines for treatment of COPD exacerbations [15]). As there is no consensus in the literature regarding a cut-off to differentiate between relapse of an earlier exacerbation and a new exacerbation, [16] we considered a subsequent predniso(lo)ne prescription after an oral corticosteroid-free interval of ≥14 days since the end-date of the previous prescription as a new exacerbation.
Statistical analysis
Analyses were performed with SPSS statistical software (version 22, IBM SPSS Statistics, Feltham, Middlesex, UK) and Microsoft Excel 2007 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, Washington, US). Statistically significant results were defined as p < 0 · 05. Patients’ baseline characteristics and comorbidity prevalence rates were calculated. We performed Chi-square tests for categorized variables and independent t-tests for continuous variables to analyze differences between the subgroups with <2 and ≥2 exacerbations per year.
We explored associations between comorbidities and exacerbation risk using univariable analyses. Hazard ratios for comorbidities were calculated using Cox regression, in which the time variable consisted of time to the first exacerbation. Data from patients who died or were otherwise lost to follow up were right-censored. Subsequently, all frequent and cardiopulmonary comorbidities (Table 2), age, and gender were included as covariates in multivariate Cox regression analyses. The model was reduced through backward exclusion to produce a final model that consisted of only non-collinear, independently associated, statistically significant covariates. The same modeling approach was used for comorbidity categories using all other categories, with age and gender as covariates.
In addition, we performed multivariable logistic regression analyses to calculate odds ratio’s (ORs) with the dichotomous indicator variable for exacerbation frequency (<2 versus ≥2 exacerbations/year) as the dependent variable. Predictor variables in the logistic models were: all frequent comorbidities, all cardiopulmonary comorbidities, gender, and age. This modeling approach was also used to analyze the 14 categories of comorbidity.
Results
Study population
Overall, data of 16,427 subjects diagnosed with COPD were available for analyses. Of these patients, 1824 (11 · 1%) were lost to follow-up during the 2-year study period. Reason for loss to follow-up was known for 800 (44 · 5%) of these patients, with death being the predominant reason. Table 1 shows baseline characteristics of the patients with complete follow-up (i.e., the final study population, n = 14,603). Mean (SD) age was 66 · 5 (11 · 5) years and 53% were males. At baseline, 89 · 1% of patients suffered from ≥1 chronic comorbid conditions, while 23 · 1% had ≥5 comorbidities. Most prevalent comorbid conditions were hypertension (35 · 2%), coronary heart disease (19 · 2%), osteoarthritis (17 · 6%), diabetes (17 · 3%), and peripheral vascular disease (14 · 3%). Table 2 shows the prevalence rates of the frequent and cardiopulmonary comorbidities. Table 3 shows the prevalence of ICPC-categorized comorbidities.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the COPD study population grouped by low (<2/year) versus high (≥2/year) exacerbation rate
| Patients with full follow-up (study population)a
(n = 14,603) |
Subgroups of study population | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient characteristics | Patients with <2 exacerbations/year (n = 13,709) | Patients with ≥2 exacerbations/year (n = 894)b | |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 7,749 (53 · 1) | 7,322 (53 · 4) | 427 (47 · 8)‡ |
| Age at study baseline, years; mean (SD; range) | 66 · 5 (11 · 5; 40–110)‡ | 66 · 5 (11 · 6; 40–110) | 67 · 4 (10 · 3; 40–93)‡ |
| Full dataset available (censored data), n (%) | |||
| Full data available | 13,709 (93 · 9) | 894 (6 · 1) | |
| Deceased | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Moved | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Nursing home | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Unknown | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Comorbidity data | |||
| Number of comorbid diseasesc, mean (SD; range) | 3 · 0 (2 · 3;0–20)‡ | 3 · 0 (2 · 3;0–16) | 3 · 4 (2 · 5; 0–20)‡ |
| Number of comorbid diseases categoriesc, n (%) | |||
| 0 | 1,777 (12 · 2) | 1,700 (12 · 4) | 77 (8 · 6) |
| 1 or 2 | 5,305 (36 · 6) | 5,021 (36 · 6) | 284 (31 · 8) |
| 3 or 4 | 4,258 (29 · 2) | 3,977 (29 · 0) | 281 (31 · 4) |
| 5 and more | 3,263 (22 · 3)‡ | 3,011 (22 · 0) | 252 (28 · 2)‡ |
| Exacerbations | |||
| Number of exacerbationsd, mean (SD; range) | 0 · 75 (1 · 5;0–15)‡ | 0 · 44 (0 · 8;0–2) | 5 · 6 (2 · 0;3–15)‡ |
SD standard deviation, N/A not applicable
* p < 0.05, † p < 0.01, ‡ p < 0.001
a p-values displayed are calculated for the difference between patients lost to follow-up versus patients with full follow-up. Chi-square tests for categorized variables and independent t-tests for continuous variables. p < 0 · 05 was considered statistically significant
b p-values displayed are calculated for the difference between the subgroups <2 versus ≥2 exacerbations/year. Chi-square tests for categorized variables and independent t-tests for continuous variables. p < 0 · 05 was considered statistically significant
cpresence of any type of comorbid disease was assessed at study baseline, i.e., 1 January 2012
dMean number of exacerbations during the study period, 1 January 2012 – 31 December 2013
Baseline characteristics of the initial population of all COPD patients (n = 16,427) and those who were lost to follow-up (n = 1,824) are reported in Appendix 3
Table 3.
Prevalence of ICPC-categorized comorbidity in the COPD study population, sorted from highest to lowest prevalence rate of frequent exacerbations
| Study populationa, (n = 14,603) | Patients with <2 exacerbations/year, (n = 13,709) | Patients with ≥2 exacerbations/year (n = 894) | p-valueb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comorbidity category | ||||
| Cardiovascular | 8,516 (58 · 3) | 7,955 (58 · 0) | 561 (62 · 8) | 0 · 006 |
| Endocrine, metabolic and nutrition | 4,856 (33 · 3) | 4,568 (33 · 3) | 288 (25 · 5) | 0 · 496 |
| Musculoskeletal | 3,588 (24 · 6) | 3,337 (24 · 3) | 251 (28 · 1) | 0 · 012 |
| Eye and ear | 2,984 (20 · 4) | 2,762 (20 · 1) | 222 (24 · 8) | 0 · 001 |
| Digestive | 2,801 (19 · 2) | 2,597 (18 · 9) | 204 (22 · 8) | 0 · 004 |
| Urogenital (male and female) | 2,330 (16 · 0) | 2,146 (15 · 7) | 184 (20 · 6) | <0 · 001 |
| Psychiatric | 2,271 (15 · 6) | 2,092 (15 · 3) | 179 (20 · 0) | <0 · 001 |
| Non-pulmonary cancer | 2,203 (15 · 1) | 2,071 (15 · 1) | 132 (14 · 8) | 0 · 782 |
| Respiratory (excl · pulmonary cancer) | 1,998 (13 · 7) | 1,839 (13 · 4) | 159 (17 · 8) | <0 · 001 |
| Skin | 1,395 (9 · 6) | 1,314 (9 · 6) | 81 (9 · 1) | 0 · 605 |
| Neurological | 413 (2 · 8) | 389 (2 · 8) | 24 (2 · 7) | 0 · 789 |
| Pulmonary cancer | 317 (2 · 2) | 284 (2 · 1) | 33 (3 · 7) | 0 · 001 |
| Blood (forming organs) and lymphatics | 106 (0 · 7) | 97 (0 · 7) | 9 (1 · 0) | 0 · 307 |
| Infectious | 87 (0 · 6) | 80 (0 · 6) | 7 (0 · 8) | 0 · 453 |
ICPC International Classification of Primary Care
aTotal COPD population, with patients who were lost to follow-up (n = 1,824) excluded
b p-values displayed are calculated for the difference between the group <2 versus ≥2 exacerbations/year. We performed Chi-square tests for categorized variables. p-value <0 · 05 was considered statistically significant
During the 2-year study period the mean number of exacerbations per patient was 0.72 (SD 1 · 5). 68% of patients had no exacerbation and 5 · 7% had ≥4 exacerbations during the study period.
Associations between comorbidities and exacerbation frequency
Tables 2 and 3 show the univariable associations between comorbidities and comorbidity categories and the exacerbation frequency subgroups, respectively. Overall, patients with one or more comorbid conditions more often had ≥2 exacerbations/year compared to patients without any comorbidity (5 · 9% vs 4 · 0%, p = 0 · 001). Patients with any other chronic respiratory disease next to their COPD, (n = 2,294, 15 · 7%) more often had ≥2 exacerbations per year compared to patients without respiratory comorbidity (8 · 2% vs 5 · 7%, p < 0 · 001).
Univariable logistic regression analysis showed that COPD patients with pulmonary cancer had 1.81 higher odds for ≥2 exacerbations per year compared to patients without pulmonary cancer (Fig. 1, p = 0.002). Patients who, next to their COPD, also suffered from asthma, blindness or low vision, coronary heart disease, depression, dyspepsia, heart failure, osteoporosis or osteopenia, peripheral vascular disease, or prostate disorders, had a higher risk of having frequent exacerbations compared to those who did not suffer from these comorbid conditions (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
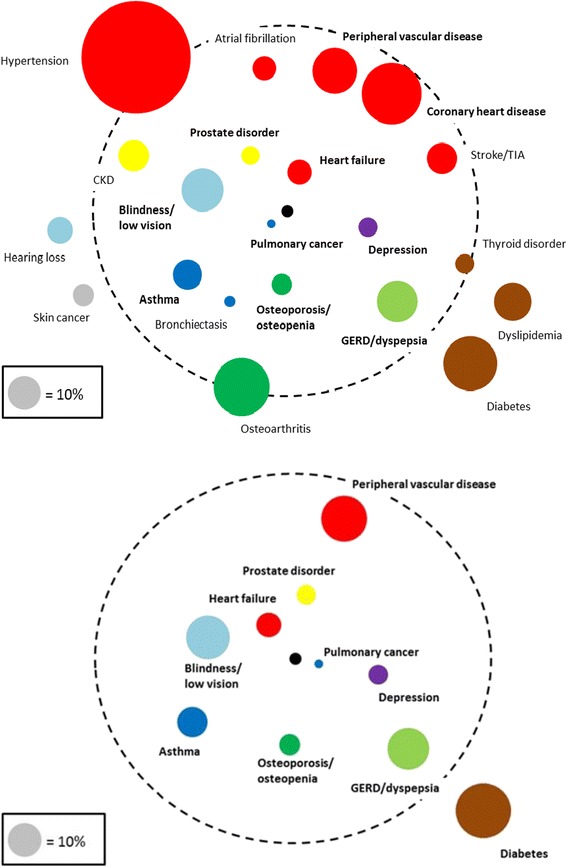
Comorbidome of comorbidities in the COPD study population (n = 14,603). Results are from univariable (upper panel) and multivariable (lower panel, corrected for age, gender and the other comorbidities) logistic regression analysis. (Diameter of the coloured circles represents the prevalence of each comorbidity. Proximity to the black centre of the circle represents stronger positive association (OR) with ≥2 exacerbation per year. The dashed circle represents an OR of 1. Comorbidities marked bold were statistically significantly (i.e., p < 0.05) associated with increased or decreased risk. In the multivariable model covariates were sequentially dropped until only statistically significant covariates remained. Comorbidities outside the dashed circle were negatively associated (i.e., ‘protective’) with ≥2 exacerbation/year. Comorbidities with prevalence <5% were not analysed). CKD: chronic kidney disease. COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease. TIA: transient ischemic attack
Table 4 lists the comorbidities and comorbidity categories significantly associated with having ≥2 exacerbation per year. In the multivariable logistic regression analysis, among the statistically significant associations, the highest ORs for having ≥2 exacerbations per year were observed for pulmonary cancer (OR 1 · 85; 95% CI 1 · 28–2 · 67), heart failure (OR 1 · 72; 1 · 38–2 · 14), prostate disorders (OR 1 · 50; 1 · 13–1 · 98) and blindness/low vision (OR 1 · 46; 1 · 21–1 · 75) as comorbid conditions (Table 4). Dislipidemia was not statistically significant, but did show a trend, with an OR of 0 · 81 (95% CI 0 · 65–1 · 01, p = 0 · 071). When looking at comorbidity categories, patients with other chronic respiratory conditions (OR 1 · 37; 1 · 15–1 · 64) and psychiatric comorbidities (OR 1 · 35; 1 · 13–1 · 60) were at highest risk for frequent exacerbations.
Table 4.
Comorbidities associated with ≥2 exacerbations/year versus <2 exacerbations/year in COPD patients, corrected for age and sex (multivariable results), sorted by p-value
| Odds ratio (95%CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| Comorbid conditionsa, b | ||
| Heart failure | 1 · 72 (1 · 38–2 · 14) | <0 · 001 |
| Blindness & low vision | 1 · 46 (1 · 21–1 · 75) | <0 · 001 |
| Pulmonary cancer | 1 · 85 (1 · 28–2 · 67) | 0 · 002 |
| Depression | 1 · 48 (1 · 14–1 · 91) | 0 · 003 |
| Prostate disorders | 1 · 50 (1 · 13–1 · 98) | 0 · 004 |
| Asthma | 1 · 36 (1 · 11–1 · 70) | 0 · 004 |
| Osteoporosis/osteopenia | 1 · 41 (1 · 11–1 · 80) | 0 · 006 |
| Diabetes | 0 · 80 (0 · 66–0 · 97) | 0 · 020 |
| Dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux | 1 · 25 (1 · 03–1 · 50) | 0 · 023 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1 · 20 (1 · 00–1 · 45) | 0 · 049 |
| Comorbidity categoriesb,c | ||
| Respiratory (excl. pulmonary cancer) | 1 · 37 (1 · 15–1 · 64) | <0 · 001 |
| Psychiatric | 1 · 35 (1 · 13–1 · 60) | <0 · 001 |
| Urogenital (male and female) | 1 · 34 (1 · 12–1 · 60) | <0 · 001 |
| Eye and ear | 1 · 25 (1 · 06–1 · 47) | 0 · 007 |
| Endocrine, metabolic and feeding | 0 · 85 (0 · 73–0 · 99) | 0 · 032 |
| Cardiovascular | 1 · 17 (1 · 01–1 · 36) | 0 · 037 |
OR odds ratio
aAll chronic comorbidities with prevalence ≥5% and cardiopulmonary comorbidities were included in the multivariable logistic regression model
bReference category was ‘comorbidity not diagnosed before study period’ (i.e., 1 January 2012)
cAll ICPC comorbidity categories were included in the multivariate logistic regression mode
Time to first exacerbation
Table 5 summarizes the results from the Cox regression analyses. Among the statistically significant associations, the comorbid conditions with the highest risk of developing a first exacerbation were recurrent sinusitis (Cox hazard ratio 1 · 53; 95% CI, 1 · 05–2 · 24), bronchiectasis/chronic bronchitis (HR = 1.50; 1.31–1.73) and heart failure (1 · 41; 1 · 29–1 · 55). For dislipidemia a non-statistically HR of 0 · 92 was observed (p = 0 · 067, 95% CI 0 · 85–1 · 00).
Table 5.
Comorbidities associated with development of a first exacerbation in the study population, corrected for age and sex (results from multivariable Cox regression analysis), sorted by p-value
| Cox hazard ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| Comorbiditya,b | ||
| Bronchiectasis/chronic bronchitis | 1 · 50 (1 · 31–1 · 73) | <0 · 001 |
| Heart failure | 1 · 41 (1 · 29–1 · 55) | <0 · 001 |
| Depression | 1 · 34 (1 · 20–1 · 50) | <0 · 001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 1 · 27 (1 · 16–1 · 40) | <0 · 001 |
| Asthma | 1 · 24 (1 · 14–1 · 36) | <0 · 001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1 · 15 (1 · 07–1 · 24) | <0 · 001 |
| Prostate disorders | 1 · 20 (1 · 04–1 · 45) | 0 · 002 |
| Blindness & low vision | 1 · 11 (1 · 03–1 · 20) | 0 · 009 |
| Coronary heart disease | 1 · 10 (1 · 02–1 · 17) | 0 · 011 |
| Dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux | 1 · 10 (1 · 02–1 · 20) | 0 · 013 |
| Pulmonary cancer | 1 · 23 (1 · 04–1 · 45) | 0 · 016 |
| Recurrent sinusitis | 1 · 53 (1 · 05–2 · 24) | 0 · 028 |
| Osteoporosis/osteopenia | 1 · 12 (1 · 01–1 · 25) | 0 · 037 |
| Comorbidity categoryb, c | ||
| Respiratory (excl. pulmonary cancer) | 1 · 26 (1 · 17–1 · 36) | <0 · 001 |
| Urogenital (male and female) | 1 · 18 (1 · 10–1 · 27) | <0 · 001 |
| Cardiovascular | 1 · 16 (1 · 08–1 · 24) | <0 · 001 |
| Mental health | 1 · 16 (1 · 08–1 · 24) | <0 · 001 |
| Eye and ear | 1 · 09 (1 · 02–1 · 16) | 0 · 013 |
| Digestive | 1 · 07 (1 · 00–1 · 15) | 0 · 042 |
aAll chronic comorbidities with prevalence ≥5% and cardiopulmonary comorbidities were included in the multivariate Cox regression model
bReference category was ‘comorbidity not diagnosed before study period’ (i.e., 1 January, 2012)
cAll ICPC comorbidity categories were included in the multivariate Cox regression model
Having another chronic respiratory disease beside COPD was also associated with risk of developing a first exacerbation (Cox hazard ratio 1 · 26; 1 · 17–1 · 36), see Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
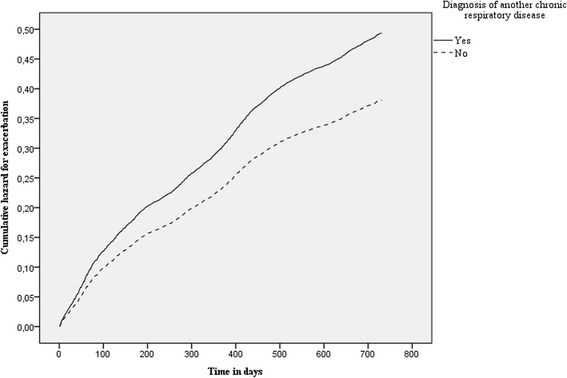
Hazard for exacerbation split by COPD patients with versus without one or more diagnoses of other chronic respiratory diseases at baseline. (Patients with another chronic respiratory disease next to their COPD showed a higher hazard rate for the development of a first exacerbation (Cox hazard ratio 1.26; 1.17–1.36) compared to patients without another chronic respiratory disease). COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Discussion
In this paper we explored the prevalence of comorbid chronic conditions and associations with exacerbation risk in a real-life cohort of primary care COPD patients. Our findings support the notion that comorbidities are rather rule than exception in patients with COPD [4], with 88% having at least one other chronic disease. Several comorbidities were associated with having frequent exacerbations, with heart failure, blindness/low vision and pulmonary cancer showing the strongest associations in terms of statistical significance. In contrast, diabetes was associated with a lower risk of having frequent exacerbations. Bronchiectasis/chronic bronchitis, heart failure and depression were the strongest predictors for developing a new exacerbation.
Comparison with existing literature
Previous research has shown that cardiovascular, psychiatric, and metabolic comorbidity are highly prevalent in COPD patients, [8, 17] and our results confirm these findings. In addition to the finding by Rutten et al. [18] that unrecognized heart failure is rather common in elderly patients with stable COPD, our data also indicate that heart failure may increase the risk of having frequent exacerbations. Recent clinical trial data have shown correlations between several comorbidities and mortality risk if a COPD patient is admitted to hospital with an acute exacerbation [19, 20]. Our observations support the association between chronic comorbidity and exacerbation risk in a primary care study population, i.e., the COPD population without selection of any kind, which is unprecedented and impossible to derive from clinical trial populations [21].
We observed a trend towards statistical significance that COPD patients with dislipidemia had less frequent exacerbations compared to patients without dislipidemia (HR 0.92; p = 0.067). This observation seems to be in line with findings by Ingebrigtsen et al., who recently reported that statin use for treatment of dislipidemia was associated with reduced odds of exacerbations in individuals with COPD [22] and findings by Chan et al. that hyperlipidemia in COPD was associated with decreased incidence of pneumonia and mortality in retrospective analyses of health insurance data [23]. Intuitively, the observed lower risk of frequent exacerbations in COPD patients with comorbid diabetes might be sought in GPs’ reluctance to prescribe oral corticosteroids in these patients because the impact this may have on glucose levels, but a survey among Dutch GPs showed that most of them do not adjust treatment of exacerbations to the presence of diabetic comorbidity [24]. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (OR = 1.25 (95% CI 1.03–1.50) in our analyses) was recognized as a significant predictor of acute exacerbations of COPD in a recent review by Lee et al [25]. A relationship between prostate disorders and exacerbations has not been described in the literature, but might be related to use of inhaled anticholinergics.
Strengths and limitations
A strength of this study is the inclusion of >14 thousand COPD patients from a real-life, unbiased primary care setting. However, the main strength is not so much the uniqueness or even the size of our dataset. Other existing general practice databases essentially contain the same, or even more detailed data regarding diagnoses and medication prescriptions, [26–29] but the meticulousness with which we have looked at ALL chronic comorbidity, including recurrent episodes of conditions that are not necessarily chronic in all patients, seems unprecedented. Moreover, other existing databases with real-life general practice COPD data mainly stem from the UK and Denmark, and now there is also one available from the Netherlands. We intentionally applied minimal exclusion criteria in order to maximize generalizability of the results. Another strength is the wide range of chronic comorbidities investigated, summing up to a total of 82 conditions. Apart from all commonly known chronic comorbid diseases, we also included several recurrent diseases (i.e., depression, anxiety, anemia, dyspepsia, urinary tract infection) and applied criteria to define their chronicity based on disease specific guidelines (see Appendix 1). Inclusion of patients with recurrent diseases seems relevant when studying risk factors for COPD exacerbations, but has not been done in previous studies.
Our study was based on patients’ medical records in general practice. Limited agreement between medical record-based and objectively identified comorbidities of COPD [30] and undiagnosed comorbidity in COPD patients is common [18, 31]. This may have resulted in underestimation of the presence of comorbidity in our study population. The use of real-life data presents limitations, for instance the fact that patients’ smoking history and lung function could not be included because this information is not consistently and uniformly documented in general practice medical records. We chose to limit the analyses to comorbidities with a relatively high (i.e., ≥5%) prevalence. This may mean that comorbidities that are related to increased exacerbation risk but have a low prevalence rate in the COPD patient population were missed.
We defined an exacerbation as an oral corticosteroid prescription, which is the recommended treatment for acute exacerbations in Dutch COPD guidelines [15]. Consequently, mild exacerbations treated with bronchodilators only are not included in our analyses. Oral steroid prescriptions during GP out-of-office hours, emergency department visits and hospitalizations, and prescriptions by pulmonary specialists may not always have been included for all patients, as these are not automatically added to patients’ medical records in all electronic patient record systems. Because there is no international consensus about a definition that discriminates relapse of an earlier exacerbation from a new one, our (arbitrary) choice to use an interval of ≥14 days since the end date of the previous oral steroid prescription may have led to under- or overestimation of the number of exacerbations. Unfortunately, the rather crude prescription information did not allow us to look at the impact of comorbidities on the duration or progression of exacerbations. Although observational studies such as ours lack the rigorous internal validity that is typical for randomized controlled trials, they provide valuable insight into comorbidity prevalence in COPD and its relation with an important outcome, i.e., exacerbations. As such, our findings should be considered in conjunction with those arising from other study designs, including randomized trials.
Clinical implications
Better knowledge about the role that comorbidity plays in COPD exacerbation risk may contribute to lower exacerbation rates in COPD patients through patient-tailored and systems medicine approaches. In turn, reduction of exacerbations may improve patients’ quality of life and prevent disability, hospitalizations, and mortality. A challenge for researchers is to find ways to enable physicians to take comorbidity into account when assessing COPD patients’ exacerbation risk. Putcha et al. developed a simple score that includes 14 comorbidities, where one point increase in comorbidity count was associated with 21% higher exacerbation risk [9]. However, their comorbidity score does not include comorbidities such as asthma, lung cancer and depression, while our results indicate that these comorbidities are also related to exacerbation risk. Neither does Putcha’s score take differences in exacerbation risk for different comorbidities into account. This highlights the importance of including a wide range of comorbid chronic conditions like we did in our study.
Beside Putcha’s comorbidity score, several prognostic indices to support COPD patient care have been developed, [32] most of them predicting prognosis in terms of mortality or hospitalization. Only few indices predict exacerbation risk and only one (the DOSE index [33]) has been developed and validated in primary care [34]. Comorbidity is not included in the existing prognostic indices, with the exception of the COTE index, which assesses mortality and not exacerbation risk [10, 11]. Our results may contribute to the development of a prognostic index that connects comorbidities with exacerbation risk to identify patients at highest risk, thereby potentially reducing disease progression.
Conclusion
We have confirmed that many patients with COPD are affected by chronic comorbidities. Several highly prevalent as well as cardiopulmonary comorbidities appear to be independently associated with the risk of suffering from frequent exacerbations in our unbiased primary care patient population. Apart from clinical COPD guidelines advising that comorbidities should be diagnosed and treated appropriately, insight in patients’ comorbidity patterns could also be used to identify those that are more likely to suffer from frequent exacerbations. Further research is needed to assess opportunities of implementation of this knowledge in routine care, so that patient-centered COPD care that also takes comorbidity into account can become the standard. Ultimately this may contribute to reducing disease progression and reduce the significant burden that COPD and its exacerbations puts on patients and healthcare systems.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the statistical support provided by Reinier Akkermans.
Funding
GlaxoSmithKline funded the study with a research grant. The sponsor was not involved in the execution of the study, interpretation of the results, or the writing of this paper. The corresponding author had full access to all data and the final responsibility to submit for publication.
Availability of data and materials
Please contact author for data requests.
Authors’ contributions
TRS initiated the study. JAMW, EM, JFMB, WT, JWHK and TRS designed the study. JAMW, EM and TRS analysed and interpreted data. JAMW and TRS wrote the initial version of the paper. JAMW, EM, JFMB, JWHK and TRS revised the report. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In the Netherlands, all patients are listed with a general practitioner (GP) and have access to specialized healthcare through this GP. For this database study, approval of an ethics committee was not required.
Abbreviations
- ATC
Anatomical therapeutic chemical
- CKD
Chronic kidney disease
- COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- GP
General practitioner
- ICPC
International classification of primary care
- N/A
Not applicable
- OR
Odds ratio
- SD
Standard deviation
- TIA
Transient ischemic attack
- UK
United Kingdom
- US
United States
Appendix 1
Table 6.
List of 82 comorbidities included in comorbidity selection, sorted by prevalence (%) in the study population
| Comorbiditiy | Prevalence (%) | Diagnosis | ICPC code | Inclusion criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | 35.2 | Hypertension | K86, K87 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Coronary heart disease | 19.2 | Myocardial infarction/other ischemic heart disease | K75, K76, K76.02, K76.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Angina Pectoris | K74, K74.01, K74.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Osteoarthritis | 17.6 | Artrose/spondylose wervelkolom | L84, L84.01, L84.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Gonartrose | L90 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Coxartrose | L89 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Osteoarhritis, other | L91 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Diabetes | 17.3 | DM1, DM2 | T90, T90.01, T90.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 14.3 | Atherosclerose | K91 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Intermittent claudication/Raynaud/Buerger | K92, K92.01, K92.02, K92.03 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Other disease cardiovascular system | K99, K99.01, K99.02, K 99.03, K99.04, K99.05, K99.06 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Blindness & low vision | 13.8 | (Diabetic/hypertensive) retinopathy | F83, F83.01, F83.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Maculadegeneratie | F84 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Blindness/amblyopia | F94 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Cataract | F92, F92.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Dyspepsia, Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) | 12.6 | Stomach ulcer | D86.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC [35] |
| Duodenal ulcer | D85 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC [35] | ||
| Peptic ulcer, other | D86 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC [35] | ||
| Oesophagus reflux with and without oesophagitis | D87, D87.01, D87.02, D84, D84.02, D84.03 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC [35] | ||
| Dislipidemia | 11.5 | Hypercholesterolemia/hypertriglyceridemia | T93, T93.01, T93.02, T93.03, T93.04 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Stroke & transient ischaemic attack | 9.7 | TIA (transient ischemic accident) | K89 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| CVA (cerebrovascular accident) | K90, K90.01, K90.02, K90.03 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Chronic kidney diease | 9.5 | Renal dysfunction | U99, U99.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Asthma | 8.5 | Asthma | R96, R96.01, R96.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [36] |
| Hearing loss | 8.1 | Deafness | H84, H86, H85 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Otosclerosis | H83 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Heart failure | 7.9 | (congestive) heart failure | K77, K77.01, K77.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Pulmonary heart disease | K82 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Atrial fibrillation | 7.5 | Atrial fibrillation/flutter | K78 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Skin cancer | 6.3 | Skin cancer | S77.01, S77.02, S77.03, S77.04, S77 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Osteoporosis/osteopenia | 6.3 | Osteoporosis/osteopenie | L95, L95.01, L95.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Depression | 5.6 | Depressive disorder | P76, P76.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [37, 38] |
| Thyroid disorder | 5.6 | Hypothyroidism | T86 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Hyperthyroidism | T85 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Psoariasis | 4.6 | Psoriasis | S91 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Obesity | 4.4 | Adipositas | T82 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Anxiety | 4.3 | Somatoform disorder | P75 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [39] |
| Phobia | P79.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [39] | ||
| Anxiety disorder | P74, P 74.01, P74.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [39] | ||
| Obsessive - compulsive disorder | P79.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [39] | ||
| (chronic) functional somatic symtoms | P01, P78 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [39] | ||
| Post traumatic stress disorder | P02.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-2012 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 24 months after first ICPC code [39] | ||
| Eczema | 4.1 | Atopic dermatitis | S87 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Heart valve disease | 3.9 | Heart valve disease | K83, K83.01, K83.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Heart valve disease (rheumatic) | K71.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Diverticular disease of intestine | 3.9 | Colonic diverticula, diverticulitis | D92 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Alcohol problems | 3.9 | Chronic alcohol abuse | P15, P15.01, P15.02, P15.03, P15.04, P15.05, P15.06 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis, other inflammatory polyarthropathies & systemic connective tissue disorders | 3.7 | Rheumatoid arthritis/ankylosing spondylarthritis | L88.01, L88.02, L88 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Bronchiectasis/chronic bronchitis | 2.8 | Bronchiectasis/Chronic bronchitis | R91.02, R91, R91.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | 2.8 | Irritable bowel syndrom | D93 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Venous insufficiency | 2.4 | Venous insufficiency | K99.04 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Varicose ulcer | S97, S97.01 | ICPC code AND (recode OR connection to episode) 3 months after first ICPC code [40] | ||
| Pulmonary cancer | 2.4 | lung/bronchial cancer | R84 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Recurrent urinary tract infection | 2.3 | Urinary tract infection, chronic/recurrent | U71, U71.01, U71.02 | ICPC code AND (recode OR connection to episode) ≥3 times/year in 2011, 2012, 2013. Years start with 1e ICPC code. Minimal 8 weeks between each episode [41] |
| Breast cancer | 2.3 | Breat cancer | X76, X76.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Glaucoma | 2.2 | Glaucoma/verhoogde oogboldruk | F93, F93.01, F93.02, F93.03, F93.04 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Gout | 2.0 | Gout | T92 | ICPC code AND (recode OR connection to episode) ≥3 times/year in 2011, 2012, 2013. Years start with 1e ICPC code. Minimal 22 days between each episode [42] |
| Prostate cancer | 1.9 | Prostate cancer | Y77 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Dementia | 1.7 | Alzheimer's disease/Senil dementia/Alzheimer/Multi-infarct dementia | P70.01, P70, P70.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Colorectal cancer | 1.7 | Colon cancer | D75 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Rectal cancer | D75 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Epilepsy | 1.4 | Epilepsy | N88 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Bladder cancer | 1.3 | Bladder cancer | U76 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Sleep apnea syndrome | 1.2 | Sleep apnea syndrome | P0601 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Underfeeding/vitamine deficiency | 1.2 | Underfeeding/vitamine deficiency | T91, T05 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 1.2 | Crohn's disease/Ulcerative colitis | D94, D94.01, D94.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Personality disorder | 1.2 | Personality disorder | P80, P80.01, P80.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Prostate disorders | 1.2 | Prostatic hyperplasia/hypertrophy | Y85 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Other chronic pulmonary disease | 1.1 | Pulmonary tuberculosis | R70 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Pneumoconiosis | R99.06 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Sarcoidosis | R83.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Chronic liver disease | 1 | Cirrose/steatose | D97, D97.04, D97.05 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Genitourinary cancer, other | 0.9 | Genitourinary cancer, other | U75, U77, X77, Y78, Y78.01, Y78.03 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Blood(forming organs) and lymphatics disorder | 0.8 | Benign non specified neoplasm blood/lymphatic disorder | B75 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC [43] |
| Haemophilia | B83.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Congenital blood/lymphatic disorder | B79 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Purpura/coagulation disorders/abnormal trombocytes | B83, B83.02, B83.06 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Schrizophrenia/non-organic psychosis/bipolar disorder | 0.8 | Schizophrenia | P72 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Psychosis non specified | P98 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Bipolar | P73.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Migraine | 0.8 | Migraine | N89 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC [44] |
| Cancer oropharynx, oesophageal, stomach | 0.8 | Cancer of the mouth/pharynx | D77.02, D77.03 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Oesophageal cancer | D77.01, D77 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Cancer of stomach | D74 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Other psychoactive substance misuse | 0.7 | Substance abuse | P19, P19.01, P19.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Parkinson's disease | 0.6 | Parkinson's disease | N87.01, N87 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Other chronic skin disease/neoplasm (sub)cutis | 0.6 | Neoplasm cutis, subcutis non specified | S80, S80.01, S81, S83, S83.01, S83.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Vitiligo/lichen planus | S99.04, S99.06 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Viral hepatitis | 0.6 | Hepatitis B | D72.02, D72.04 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Hepatitis C | D72.03, D72.05 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Hepatitis | D72 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Uterine cervical cancer | 0.5 | Uterine cervical cancer | X75 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Learning disability’/Mental retardation | 0.4 | Mental retardation | P85 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Specified learning problems | P24. P24.01, P24.02, P24.03 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Laryngeal/throat cancer | 0.4 | Laryngeal/troat cancer | R85 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Hodgkin disease | 0.4 | Hodgkin disease | B72, B72.01, B72.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Carcinoma, other | 0.4 | Carcinoma, other | D77.04, T71, W72, L71, L71.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Chronic sinusitis | 0.3 | Chronic sinusitis | R75.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Acute Sinusitis | R75.01 en R75 | ICPC code AND (recode OR connection to episode) ≥3×/year in 2011, 2012, 2013. Years start with 1e ICPC code. Minimal 29 days between each episode. [45] | ||
| Glomerulonephritis/nephrosis | 0.3 | Glomerulonephritis | U88 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Congenital cardiovascular anomaly | 0.2 | Congenital cardiovascular anomaly | K73, K73.01, K73.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Leukaemia | 0.2 | Leukaemia | B73 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Lymphoma/multiple myeloma/other blood cancer | 0.2 | Lymphoma/multiple myeloma/other blood cancer | B74.01, B74 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Anaemia | 0.1 | Pernicous/folic acid anaemia | B81, B81.01, B81.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 AND (recode OR connection to episode) 12 months after first ICPC [43] |
| Haemolytic anaemia | B78, B78.01, B78.02, B78.03 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 | ||
| Anorextia or bulimia | 0.1 | Anorexia nervosa | T06, T06.01, T06.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Coeliakie | 0.1 | Coeliakie | D99.06 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Endometrial cancer | 0.1 | Endometrial cancer | X77.01 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Metastases; unknown origin | 0.1 | Metastases; unknown origin | A79 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Multiple sclerosis | 0.1 | MS (multiple sclerosis) | N86 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Ovarian cancer | 0.1 | Ovarian cancer | X77.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 0.1 | Pancreatic cancer | D76 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Testis cancer | 0.1 | Testis cancer | Y78.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| Brain cancer (recall: Nervous system cancer) | 0 | Brain cancer (recall: Nervous system cancer) | N74 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
| HIV/AIDS | 0 | HIV; AIDS | B90, B90.01, B90.02 | ICPC code before 1-1-12 |
Appendix 2
Table 7.
List of comorbidity categories
| Categories of chronic disease | Disease |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Hypertension |
| Coronary heart disease | |
| Congenital cardiovascular anomaly | |
| Heart failure | |
| Stroke & transient ischaemic attack | |
| Atrial fibrillation | |
| Heart valve disease | |
| Venous insufficiency | |
| Peripheral vascular disease | |
| Respiratory | COPD |
| Asthma | |
| Sleep apnea syndrome | |
| Chronic sinusitis | |
| Other chronic pulmonary disease | |
| Bronchiectasis/chronic bronchitis | |
| Mental Health | Depression |
| Anxiety disorder | |
| Alcohol problems | |
| Other psychoactive substance misuse | |
| Schrizophrenia/non-organic psychosis/bipolar disorder | |
| Anorextia or bulimia | |
| Personality disorder | |
| Learning disability’/Mental retardation | |
| Musculoskeletal | Rheumatoid arthritis, other inflammatory polyarthropathies & systemic connective tissue disorders |
| Gout | |
| Osteoporosis/osteopenie | |
| Osteoarthritis | |
| Eye and Ear | Hearing loss |
| Glaucoma | |
| Blindness & low vision | |
| Urogenital (Male and female) | Chronic kidney diease |
| Glomerulonephritis/nephrosis | |
| Recurrent urinary tract infection | |
| Prostate disorders | |
| Skin | Eczema |
| Psoriasis | |
| Other chronic skin disease/neoplasm (sub)cutis | |
| Digestive | Diverticular disease of intestine |
| Dyspepsia, Gastroesophageal reflux | |
| Irritable bowel syndrom | |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | |
| Coeliakie | |
| Chronic liver disease | |
| Endocrine, metabolic and nutrition | Underfeeding/vitamine deficiency |
| Diabetes | |
| Dislipidemia | |
| Obesity | |
| Thyroid disorder | |
| Neurological | Dementia |
| Epilepsy | |
| Migraine | |
| Parkinson's disease | |
| Multiple sclerosis | |
| Blood(forming organs) and Lymphatics | Anaemia |
| Blood (forming organs) and lymphatics disorder | |
| Infectious | Viral hepatitis |
| HIV/AIDS | |
| Non-pulmonary cancer | Testis Cancer |
| Cancer oropharynx, oesophageal, stomach | |
| Cancer Colorectal | |
| Pancreatic cancer | |
| Laryngeal/troat cancer | |
| Breast cancer | |
| Ovarian cancer | |
| Endometrial cancer | |
| Uterine cervical cancer | |
| Prostate cancer | |
| Bladder cancer | |
| Genitourinary cancer, other | |
| Brain cancer (recall: Nervous system cancer) | |
| Hodgkin disease | |
| Leukaemia | |
| Lymphoma/multiple myeloma/other blood cancer | |
| Metastases; unknown origin | |
| Carcinoma, other | |
| Skin cancer | |
| Pulmonary cancer | Pulmonary cancer |
Appendix 3
Table 8.
Baseline characteristics of the initial population of all COPD patients, the patients who were lost to follow-up, and the patients with full follow-up
| All COPD patients (n=16,427) |
Patients lost to follow-up (n= 1,824) |
Patients with full follow-up (study population)a
(n=14,603) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient characteristics | |||
| Sex, male, n (%) | 8,682 (52·9) | 933 (51·2) | 7,749 (53·1) |
| Age at study baseline, years; mean (SD; range) | 66·9 (11·6; 40–111) | 70·1 (12·0; 40–111) | 66·5 (11·5; 40–110)‡ |
| Full dataset available (censored data), n (%) | |||
| Full data available | 14,603 (88·7) | ||
| Deceased | 541 (3·0) | 541 (29·7) | N/A |
| Moved | 223 (1·3) | 223 (12·2) | N/A |
| Nursing home | 36 (0·2) | 36 (2·0) | N/A |
| Unknown | 1024 (6·2) | 1024 (56·1) | N/A |
| Comorbidity data | |||
| Number of comorbid diseasesb, mean (SD; range) | 3·0 (2·3;0–20) | 3·4 (2·5; 0–16) | 3·0 (2·3;0–20)‡ |
| Number of comorbid diseases categoriesb, n (%) | |||
| 0 | 1,951 (11·9) | 174 (9·5) | 1,777 (12·2) |
| 1 or 2 | 5,891 (35·9) | 586 (32·1) | 5,305 (36·6) |
| 3 or 4 | 4,797 (29·2) | 539 (29·6) | 4,258 (29·2) |
| 5 and more | 3,788 (23·1) | 525 (28·8) | 3,263 (22·3)‡ |
| Exacerbations data | |||
| Number of exacerbations, mean (SD; range) | 0·72 (1·5;0–15)c | 0·46 (1·0;0–11)c | 0·75 (1·5;0–15) |
SD standard deviation, N/A not applicable
* p<0.05, † p<0.01, ‡ p<0.001
a p-values displayed are calculated for the difference between patients lost to follow-up versus patients with full follow-up. Chi-square tests for categorized variables and independent t-tests for continuous variables. p<0·05 was considered statistically significant
bPresence of any type of comorbid disease was assessed at study baseline, i.e. 1 January 2012
cMean number of exacerbations during the study period, 1 January 2012 – 31 December 2013. For the columns ‘all COPD patients’ and ‘Patients lost to follow-up’ these rates cannot be converted into annual rates because of incomplete observation time in the patients who were lost to follow-up
Baseline characteristics of the study population grouped by low (<2/year) versus high (≥2/year) exacerbation rate are reported in Table 1
Contributor Information
Janine A. M. Westerik, Phone: 0031 243614611, Email: Janine.westerik@radboudumc.nl
Esther I. Metting, Phone: 0031(0)50-363 3796, Email: e.i.metting@umcg.nl
Job F. M. van Boven, Email: jobvanboven@gmail.com
Waling Tiersma, Email: Waling.Tiersma@radboudumc.nl.
Janwillem W. H. Kocks, Email: j.h.w.kocks@umcg.nl
Tjard R. Schermer, Phone: 0031 243614611, Email: tjard.schermer@radboudumc.nl
References
- 1.Barnett K, Mercer SW, Norbury M, Watt G, Wyke S, Guthrie B. Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and medical education: a cross-sectional study. Lancet (London, England) 2012;380(9836):37–43. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.From the Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). 2016. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/. Accessed 16 Jan 2017.
- 3.van Manen JG, IJzermans CJ, Bindels PJ, van der Zee JS, Bottema BJ, Schade E. Prevalence of comorbidity in patients with a chronic airway obstruction and controls over the age of 40. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54(3):287–93. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(01)00346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Negewo NA, McDonald VM, Gibson PG. Comorbidity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Invest. 2015;53(6):249–58. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2015.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Putcha N, Drummond MB, Wise RA, Hansel NN. Comorbidities and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: prevalence, influence on outcomes, and management. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;36(4):575–91. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1556063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wijnhoven HA, Kriegsman DM, Hesselink AE, de Haan M, Schellevis FG. The influence of co-morbidity on health-related quality of life in asthma and COPD patients. Respir Med. 2003;97(5):468–75. doi: 10.1053/rmed.2002.1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen W, Thomas J, Sadatsafavi M, FitzGerald JM. Risk of cardiovascular comorbidity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3(8):631–9. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Garcia-Olmos L, Alberquilla A, Ayala V, Garcia-Sagredo P, Morales L, Carmona M, et al. Comorbidity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in family practice: a cross sectional study. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-14-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Putcha N, Puhan MA, Drummond MB, Han MK, Regan EA, Hanania NA, et al. A simplified score to quantify comorbidity in COPD. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e114438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Divo M, Cote C, de Torres JP, Casanova C, Marin JM, Pinto-Plata V, et al. Comorbidities and risk of mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186(2):155–61. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201201-0034OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Torres JP, Casanova C, Marin JM, Pinto-Plata V, Divo M, Zulueta JJ, et al. Prognostic evaluation of COPD patients: GOLD 2011 versus BODE and the COPD comorbidity index COTE. Thorax. 2014;69(9):799–804. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Okkes IM, Becker HW, Bernstein RM, Lamberts H. The March 2002 update of the electronic version of ICPC-2. A step forward to the use of ICD-10 as a nomenclature and a terminology for ICPC-2. Fam Pract. 2002;19(5):543–6. doi: 10.1093/fampra/19.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. 2015. Available from: http://www.whocc.no/. Accessed 16 Jan 2017.
- 14.Luijks H, Schermer T, Bor H, van Weel C, Lagro-Janssen T, Biermans M, et al. Prevalence and incidence density rates of chronic comorbidity in type 2 diabetes patients: an exploratory cohort study. BMC Med. 2012;10:128. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Snoeck-Stroband JB, Schermer TRJ, Van Schayck CP, Muris JW, Van der Molen T, In ’t Veen JCCM, Chavannes NH, Broekhuizen BDL, Barnhoorn MJM, Smeele I, Geijer RMM, Tuut MK. NHG guideline COPD (third revision). Huisarts Wet. 2015;58(4):198–211.
- 16.Seemungal TA, Donaldson GC, Bhowmik A, Jeffries DJ, Wedzicha JA. Time course and recovery of exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161(5):1608–13. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.5.9908022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Frei A, Muggensturm P, Putcha N, Siebeling L, Zoller M, Boyd CM, et al. Five comorbidities reflected the health status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the newly developed COMCOLD index. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(8):904–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rutten FH, Cramer MJ, Grobbee DE, Sachs AP, Kirkels JH, Lammers JW, et al. Unrecognized heart failure in elderly patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(18):1887–94. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Almagro P, Cabrera FJ, Diez J, Boixeda R, Alonso Ortiz MB, Murio C, et al. Comorbidities and short-term prognosis in patients hospitalized for acute exacerbation of COPD: the EPOC en Servicios de medicina interna (ESMI) study. Chest. 2012;142(5):1126–33. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xu W, Collet JP, Shapiro S, Lin Y, Yang T, Platt RW, et al. Independent effect of depression and anxiety on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations and hospitalizations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178(9):913–20. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200804-619OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kruis AL, Stallberg B, Jones RC, Tsiligianni IG, Lisspers K, van der Molen T, et al. Primary care COPD patients compared with large pharmaceutically-sponsored COPD studies: an UNLOCK validation study. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e90145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ingebrigtsen TS, Marott JL, Nordestgaard BG, Lange P, Hallas J, Vestbo J. Statin use and exacerbations in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2015;70(1):33–40. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chan MC, Lin CH, Kou YR. Hyperlipidemia in COPD is associated with decreased incidence of pneumonia and mortality a nationwide health insurance data based retrospective cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:1053–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.de Vries M, Berendsen AJ, Bosveld HE, Kerstjens HA, van der Molen T. COPD exacerbations in general practice: variability in oral prednisolone courses. BMC Fam Pract. 2012;13:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-13-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee AL, Goldstein RS. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in COPD: links and risks. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1935–49. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S77562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Price D, West D, Brusselle G, Gruffydd-Jones K, Jones R, Miravitlles M, et al. Management of COPD in the UK primary-care setting: an analysis of real-life prescribing patterns. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:889–904. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S62750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.James GD, Donaldson GC, Wedzicha JA, Nazareth I. Trends in management and outcomes of COPD patients in primary care, 2000–2009: a retrospective cohort study. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2014;24:14015. doi: 10.1038/npjpcrm.2014.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jones PW, Nadeau G, Small M, Adamek L. Characteristics of a COPD population categorised using the GOLD framework by health status and exacerbations. Respir Med. 2014;108(1):129–35. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2013.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lange P, Tottenborg SS, Sorknaes AD, Andersen JS, Sogaard M, Nielsen H, et al. Danish Register of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Epidemiol. 2016;8:673–8. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S99489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Triest FJ, Franssen FM, Spruit MA, Groenen MT, Wouters EF, Vanfleteren LE. Poor agreement between chart-based and objectively identified comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir J. 2015;46(5):1492–5. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00667-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Vanfleteren LE, Franssen FM, Uszko-Lencer NH, Spruit MA, Celis M, Gorgels AP, et al. Frequency and relevance of ischemic electrocardiographic findings in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Cardiol. 2011;108(11):1669–74. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.07.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dijk WD, Bemt L, Haak-Rongen S, Bischoff E, Weel C, Veen JC, et al. Multidimensional prognostic indices for use in COPD patient care. A systematic review. Respir Res. 2011;12:151. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jones RC, Donaldson GC, Chavannes NH, Kida K, Dickson-Spillmann M, Harding S, et al. Derivation and validation of a composite index of severity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the DOSE Index. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180(12):1189–95. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200902-0271OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rolink M, van Dijk W, van den Haak-Rongen S, Pieters W, Schermer T, van den Bemt L. Using the DOSE index to predict changes in health status of patients with COPD: a prospective cohort study. Prim Care Respir J. 2013;22(2):169–74. doi: 10.4104/pcrj.2013.00033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Numans ME, De Wit NJ, Dirven JAM, Heemstra-Borst CG, Hurenkamp GJB, Scheele ME, Burgers JS, Geijer RMM, De Jongh E. NHG guideline Stomach complaints (third revision). Huisarts Wet. 2013;56:26–3.
- 36.Smeele I, Barnhoorn MJM, Broekhuizen BDL, Chavannes NH, In ’t Veen JCCM, Van der Molen T, Muris JW, Van Schayck O, Schermer TRJ, Snoeck-Stroband JB, Geijer RMM, Tuut MK. NHG-Werkgroep Astma bij volwassenen en COPD. [NHG guideline Asthma in adults (third revision)]. Huisarts Wet. 2015;58(3):142–54.
- 37.Van Weel-Baumgarten EM, Van Gelderen MG, Grundmeijer HGLM, Licht-Strunk E, Van Marwijk HWJ, Van Rijswijk HCAM, Tjaden BR, Verduijn M, Wiersma T, Burgers JS, Van Avendonk MJP, Van der Weele GM. [NHG guideline Depression (second revision). Huisarts Wet. 2012;55(6):252–9.
- 38.Spijker J, Bockting CLH, Meeuwissen JAC, Vliet IM V, Emmelkamp PMG, Hermens MLM, Balkom ALJM V, namens de Werkgroep Multidisciplinaire richtlijnontwikkeling Angststoornissen/Depressie . Multidisciplinaire richtlijn Depressie (Derde revisie). Richtlijn voor de diagnostiek, behandeling en begeleiding van volwassen patiënten met een depressieve stoornis. Utrecht: Trimbos-instituut; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hassink-Franke LJA, Terluin B, Van Heest FB, Hekman J, Van Marwijk HWJ, Van Avendonk MJP. [NHG guideline Anxiety (second revision)]. Huisarts Wet. 2012;55(2):68-77.
- 40.Van Hof N, Balak FSR, Apeldoorn L, De Nooijer HJ, Vleesch Dubois V. Van Rijn-van Kortenhof. [NHG guideline Ulcus cruris venosum (second revision)]. Huisarts Wet. 2010;53(6):321–33.
- 41.Van Pinxteren B, Knottnerus BJ, Geerlings SE, Visser HS, Klinkhamer S, Van der Weele GM, Verduijn MM, Opstelten W, Burgers JS, Van Asselt KM. [NHG-guideline Urinary tract infections (third revision)]. Huisarts Wet. 2013;56(6):270–80.
- 42.Janssens HJEM, Lagro HAHM, Van Peet PG, Gorter KJ, Van der Pas P, Van der Paardt M, Woutersen-Koch H. [NHG guideline osteoarthritis (first version)]. Huisarts Wet. 2009;52(9):439–53.
- 43.Bouma M, Burgers J, Drost B, Den Elzen WPJ, Luchtman T, OosterhuisWP, Woutersen-Koch H, Van Wijk M; NHG-werkgroep Anemie. [NHG guideline anemia (first revision)]. Huisarts Wet. 2014;57(10):528–36.
- 44.Dekker F, Van Duijn NP, Ongering JEP, Bartelink MEL, Boelman L, Burgers JS, Bouma M, Kurver MJ. [NHG guideline Headache (third revision)]. Huisarts Wet. 2014;57(1):20–31.
- 45.Venekamp RP, De Sutter A, Sachs A, Bons SCS, Wiersma TJ, De Jongh E. [NHG guideline Acute rhinosinusitis (third revision)]. Huisarts Wet. 2014;57(10):537.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Please contact author for data requests.


