Abstract
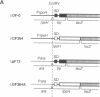
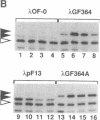
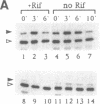
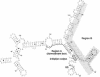
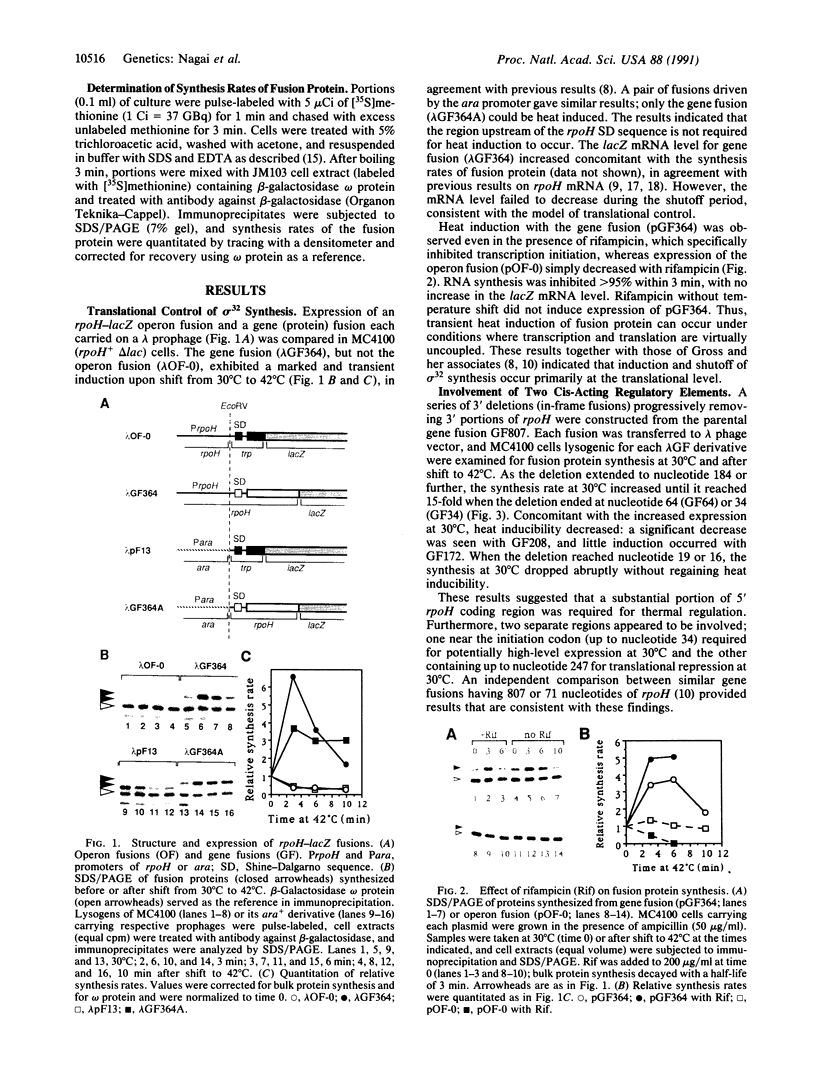
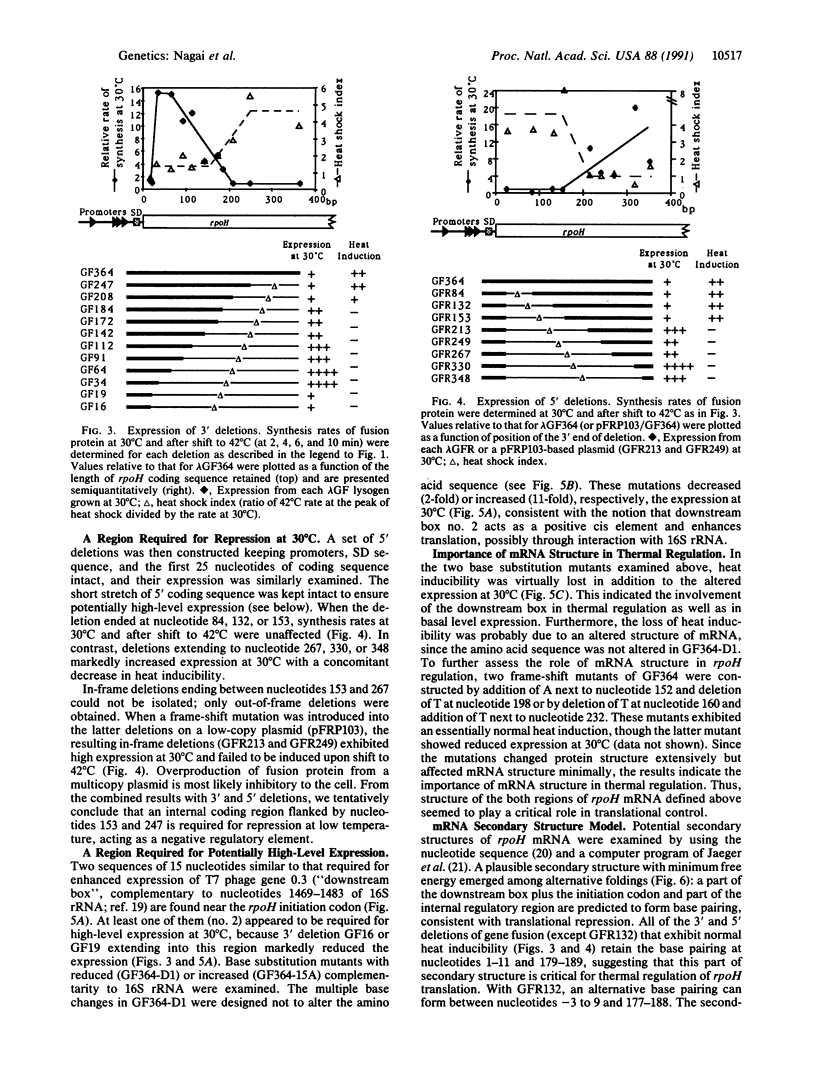
When Escherichia coli cells are transferred from 30 degrees C to 42 degrees C, transcription from specific promoters recognized by RNA polymerase containing sigma 32 (the rpoH gene product) is transiently activated, resulting in induction of heat shock proteins. Transcription from heat shock promoters is activated by an increased cellular concentration of sigma 32 due to enhanced synthesis and stabilization. We have constructed and examined the expression of mutant derivatives (deletions and base substitutions) of rpoH-lacZ gene fusion. Synthesis of a sigma 32-beta-galactosidase fusion protein was found to be regulated at the translational level involving two distinct 5'-proximal rpoH coding regions. A small region immediately downstream of the initiation codon is required for potentially high-level expression, whereas a much larger internal region is required for thermal regulation--namely, repression at low temperature or nonstress conditions. The two mRNA regions act as positive and negative cis elements, respectively, in controlling rpoH translation. We propose that an interplay between these RNA regions involving secondary structure formation is important in regulating translation initiation and that transient disruption of secondary structure represents a primary step of the heat shock response.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter-Muenchau P., Wolf R. E., Jr Growth-rate-dependent regulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase level mediated by an anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence located within the Escherichia coli gnd structural gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Vaughn V., Walter W. A., Neidhardt F. C., Gross C. A. Regulation of the promoters and transcripts of rpoH, the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):419–432. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Ishihama A. Heat-shock induction of RNA polymerase sigma-32 synthesis in Escherichia coli: transcriptional control and a multiple promoter system. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):10–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00337752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano M., Shigesada K., Imai M. Construction and characterization of plasmid and lambda phage vector systems for study of transcriptional control in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Predicting optimal and suboptimal secondary structure for RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:281–306. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamath-Loeb A. S., Gross C. A. Translational regulation of sigma 32 synthesis: requirement for an internal control element. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3904–3906. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3904-3906.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai H., Yano R., Erickson J. W., Yura T. Transcriptional regulation of the heat shock regulatory gene rpoH in Escherichia coli: involvement of a novel catabolite-sensitive promoter. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2710–2715. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2710-2715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A. Positive regulatory gene for temperature-controlled proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):894–900. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengart M. L., Fatscher H. P., Fuchs E. The initiation of translation in E. coli: apparent base pairing between the 16srRNA and downstream sequences of the mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1719–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. The heat shock response of E. coli is regulated by changes in the concentration of sigma 32. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):348–351. doi: 10.1038/329348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D., Walter W., Gross C. A. DnaK, DnaJ, and GrpE heat shock proteins negatively regulate heat shock gene expression by controlling the synthesis and stability of sigma 32. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2202–2209. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., Erickson J., Sharma S., Georgopoulos C. Heat shock regulatory gene rpoH mRNA level increases after heat shock in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1155–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1155-1158.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., Spence J., Georgopoulos C. Modulation of stability of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory factor sigma. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1585–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1585-1589.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Ito K., Yura T. Isolation and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants defective in heat-shock induction of proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00332716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Ribosomes as sensors of heat and cold shock in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5589–5593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Genetic control of heat-shock protein synthesis and its bearing on growth and thermal resistance in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):860–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Imai M., Yura T. The use of operon fusions in studies of the heat-shock response: effects of altered sigma 32 on heat-shock promoter function in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00331486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Tobe T., Ito K., Osawa T. Heat shock regulatory gene (htpR) of Escherichia coli is required for growth at high temperature but is dispensable at low temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6803–6807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]