Abstract
The thymus is a lymphatic organ that undergoes dynamic changes with age and disease. It is important to be familiar with these physiological changes in the thymus gland to be able to identify pathology and make an accurate diagnosis. The thymus may be involved in multisystem disorders or show focal isolated lesions. The aim of this article is to review the radiological anatomy of the thymus, normal variants, and pathology including hyperplasia and benign/malignant lesions involving the thymus gland in the pediatric age group. We also propose an algorithmic approach for imaging evaluation of a suspected thymic mass on the basis of morphologic features.
Keywords: Thymus, Pediatric, Thymus hyperplasia, Thymus neoplasms, Mediastinum
Core tip: It is important for clinicians to be able to identify normal variations in thymic appearance and avoid over-investigation. However, it is equally important to have a high index of suspicion for abnormal thymus especially in multisystem disorders. We discuss normal variants, hyperplasia and focal masses; and propose an algorithmic approach to the evaluation of a suspected thymic mass based on imaging morphology.
INTRODUCTION
The thymus is a lymphatic organ which is responsible for T cell immunological function. It is the first of the lymphoid organs to be formed and grows considerably in infancy[1]. It attains maximum weight at puberty and gradually becomes replaced by fat and involutes with age. Fibrofatty atrophy occurs more rapidly in young adult men than women[2]. However, it can grow back at any time in life especially after periods of stress[3].
As the thymus undergoes dynamic changes more so in the pediatric population, familiarity with the embryology, anatomy and pathology of the thymus gland is essential for radiologists to make an accurate diagnosis and avoid unnecessary biopsies and interventions.
The aim of this article is to review the radiological anatomy of the thymus, normal variants, and pathology including hyperplasia and benign/malignant lesions involving the thymus gland in the pediatric age group and propose an algorithmic approach for imaging evaluation of a suspected thymic mass.
IMAGING MODALITIES
Conventional radiography
The thymus gland is usually visible but difficult to differentiate from the cardiac silhouette on frontal chest radiographs in young children; and also may be mistaken for a mass lesion.
The normal thymus has a soft tissue density and smooth borders and numerous radiological signs have been described to aid its differentiation from a mediastinal mass. The “thymic sail sign” is seen as a triangular extension of the normal thymus laterally. The right lobe of the thymus has a convex lateral margin and the straight inferior border gets demarcated by the minor fissure which gives the sail like appearance (Figure 1). The anterior reflections of the ribs produce a wavy contour of the thymus known as the “thymus wave sign” (Figure 2)[4]. It has no mass effect on vascular structures or airway. The inferior margin of the thymus merges with the margin of the cardiac silhouette, producing the “notch sign” (Figure 3)[5].
Figure 1.
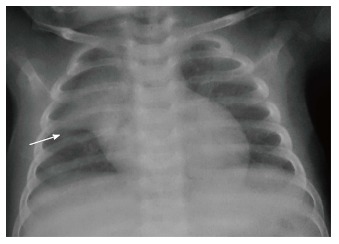
Frontal chest radiograph in an 11-mo-old boy with mild respiratory distress reveals normal thymus with characteristic “sail sign” (arrow).
Figure 2.
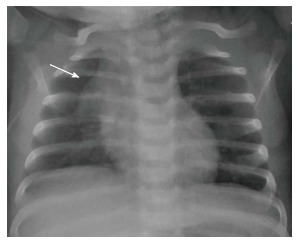
Frontal chest radiograph of a 2-mo-old girl with cough. The thymus gland is prominent but normal. Note the impression of the anterior ribs on the thymus producing the “wave sign” (arrow).
Figure 3.
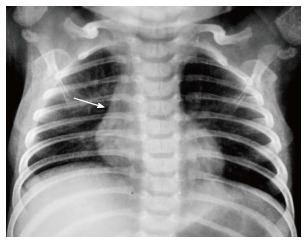
Frontal chest radiograph of a 2-year-old boy showing the inferior margin of the thymus merging with the cardiac silhouette - the “notch sign”(arrow).
The imaging appearance of thymic masses on conventional radiographs can be variable from that of an anterior mediastinal mass to a hilar mass. Small masses may be seen as subtle mediastinal widening or a paratracheal bulge whereas larger masses can even extend up to the cardiophrenic angle.
Ultrasound
On ultrasound, the thymus appears homogenous with echo texture similar to the liver but less than the muscle[6] and shows multiple echogenic foci or strands. These hyperchoic foci give a “starry sky” appearance (Figure 4) and help to identify thymic tissue[3]. The characteristic ultrasound appearance is also helpful to identify normal anatomical variants like cervical or retrocaval extension of the thymus. The shape of the thymus can be seen to vary with cardiac and respiratory movements on real-time ultrasound, and this finding helps to differentiate it from solid tumors and infiltrative diseases[3].
Figure 4.
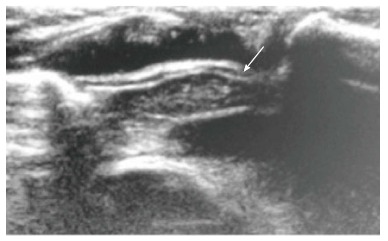
Normal sonographic (longitudinal view) appearance of the thymus gland in a 2-year-old boy with suspected mediastinal widening on chest radiograph. The thymus is hypoechoic with multiple internal echogenic foci giving the characteristic “starry sky” appearance (arrow).
Ultrasound also helps to identify the solid or cystic nature of a suspected thymic mass and the presence of any fat or calcification within[7]. It is also useful for image guided aspiration or biopsies of thymic masses. Being a low cost, portable and easily available modality with lack of ionizing radiation, sonography is useful as first line investigation for the evaluation of suspected thymic pathology[8].
Computed tomography
The thymus is seen in the anterior mediastinum as a quadrilateral shaped soft tissue density structure with convex margins (Figure 5). It is located anterior to the proximal ascending aorta, the pulmonary outflow tract, and the distal superior vena cava[9]. With increasing age (Figure 6), it becomes triangular in shape with straight or concave margins.
Figure 5.
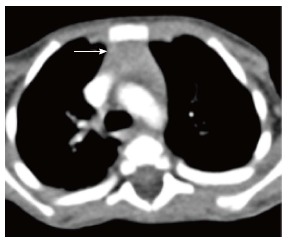
Normal appearance of the thymus on computed tomography scan of a 3-year-old boy. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography section shows homogenous soft tissue density structure (arrow) in the anterior mediastinum. Note that there is no compression of the vascular structures or airway.
Figure 6.
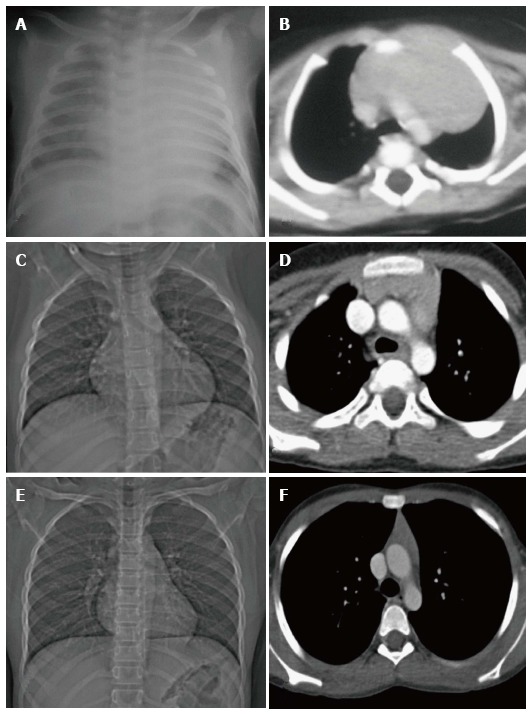
Normal variation in the appearance of the thymus with age. Frontal radiographs and CECT axial images at ages of (A, B) 2 mo, (C, D) 7 years and (E, F) 12 years. Note that the initial prominent bilobed thymus in a neonate assumes a quadrilateral shape with convex margins in early childhood. Gradually it assumes a triangular configuration with straight margins. The CT density also decreases with age with fatty replacement occurring in adults.
The size of the thymus (Figure 6) also varies with age and has been extensively studied by cross-sectional imaging[9,10]. The mean thickness of a normal thymus can vary from 0.5 to 1.1 cm as reported by Baron et al[9]. Computed tomography (CT) density of the thymus has also been reported to decrease with age in children (from 80 HU to 56 HU) likely due to fatty replacement and cellular involution[11].
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evaluation of the thymus includes T1- and T2-weighted image acquisition in the axial plane and either sagittal or coronal or both planes. Cardiac gating is usually not required. Appropriate coil as per the age of the patient is selected - quadrature knee coil for small infants, head coil for small children, or surface coils as needed[8].
The signal intensity of the thymus gland appears homogeneous and is greater than that of the muscle on T1-weighted images and of intermediate signal intensity on T2-weighted images (Figure 7). Fat saturation does not decrease the signal intensity of the thymus; however, chemical shift imaging has been used to assess the fatty replacement of the thymus and identify infiltrative disorders[12]. MRI is able to define size more accurately because of better contrast resolution. The thickness has been found to be greater at MRI than CT scan (15-20 mm between ages 20 and 70 years) as reported by de Geer et al[10].
Figure 7.
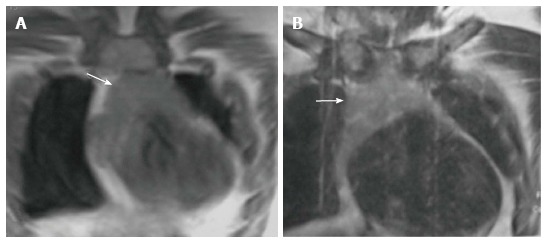
Normal appearance of the thymus on magnetic resonance imaging in a 1-year-old boy. Coronal T1WI (A) and T2WI (B) show that the signal intensity of the thymus gland is homogeneous (arrow in A and B), greater than that of the muscle on T1WI and isointense to that of fat on T2WI.
THYMIC DISORDERS
Thymic lesions may be seen in systemic disorders or as a part of manifestation of specific disease entities (Table 1), like myasthenia gravis and immunodeficiencies. However, most of the thymic lesions are seen as incidental findings while imaging for other causes[13].
Table 1.
Significance of imaging the thymus in various clinical settings
| Clinical setting | Possible imaging finding(s) |
| Myasthenia gravis | Thymoma |
| Thymic hyperplasia | |
| Suspected immunodeficiency disorder | Thymic hypoplasia |
| Thymic aplasia | |
| Incidental detection while imaging for other causes | Thymic cyst |
| Thymic hyperplasia | |
| Lymphangioma | |
| Vascular malformation | |
| Castleman’s disease | |
| Thymolipoma | |
| Fever evaluation | Lymphoma |
| Abscess | |
| Detected during evaluation of other multisystem disorders | Lymphoma |
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
We have classified thymic disorders into those presenting with small or enlarged thymus enabling the use of an imaging based approach (Table 2) in the diagnosis of thymic disorders.
Table 2.
Classification of thymic disorders according to the imaging appearance
| Appearance/size of thymus | Diseases |
| Small thymus | Physiological |
| Age related involution | |
| Treatment related atrophy | |
| Ectopic thymus | |
| Immunodeficiency disorders | |
| Hypoplasia | |
| Aplasia | |
| Large thymus | Hyperplasia |
| True hyperplasia | |
| Follicular hyperplasia | |
| Masses | |
| Cystic | |
| Thymic cyst | |
| Lymphatic malformation | |
| Germ cell tumor | |
| Solid | |
| Mild/moderate enhancement | |
| Lymphoma | |
| Thymoma | |
| Thymolipoma | |
| Thymic carcinoma | |
| Intense enhancement | |
| Hemangioma | |
| Castleman’s disease | |
| Thymic carcinoid | |
| Mixed | |
| Infections (abscess/ tuberculosis) | |
| Germ cell tumor | |
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
SMALL THYMUS
In a neonate, the normal thymic shadow on the frontal radiograph should be more than twice the width of the third dorsal vertebra. Smaller dimensions characterize thymic involution or hypoplasia[5].
Involution
Involution is seen normally as an age related decrease in the thymic size[8]. When the normal size thymus gland decreases in size in response to any stress (e.g., sepsis, major surgery, use of steroids or other immunosuppressants), it is known as thymic atrophy. It is usually transient and the thymus returns to normal after the stress resolves[8]. The thymus may decrease in size up to 40% of its original volume varying according to the severity and duration of the stress[14].
Thymic hypoplasia and aplasia
Thymic hypoplasia and aplasia indicate a small or absent thymus (Figure 8) seen in immune deficiencies[15]. These terms are most commonly used with DiGeorge syndrome. DiGeorge syndrome is due to the abnormal development of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches and is characterised by variable T-cell deficiency. Cross-sectional imaging in this setting is useful mainly for the evaluation of cardiovascular anomalies. Immunodeficiencies with T-cell abnormalities like ataxia telangiectasia or severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome are also associated with thymic aplasia or dysplasia[16].
Figure 8.
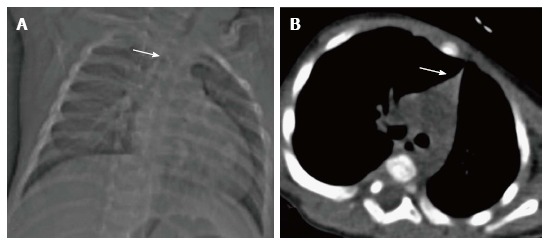
Thymic hypoplasia in a 3-mo-old male infant with primary immunodeficiency. CT scanogram (A) reveals small size of the thymus, i.e., less than twice the width of the third thoracic vertebra (arrow). NCCT chest axial section (B) shows triangular configuration of the thymus (arrow) with straight margins (normal appearance in adolescents). Compare this with the normal appearance of the thymus in a 2-mo-old infant (Figure 6A and B).
Ectopic and accessory thymic remnants
Ectopic and accessory thymic remnants can be found anywhere along the course of migration of the thymopharyngeal duct from the third and fourth branchial arches to the superior mediastinum. These can be solid or cystic in appearance and should be kept in the differentiation of pediatric neck swellings. In cases of ectopic location of the thymus, the mediastinal thymus may be small or absent. Accessory thymic tissue may be seen in the lower neck where anatomical contiguity with the relatively small mediastinal thymus can be established on imaging (Figure 9)[3,12,13].
Figure 9.
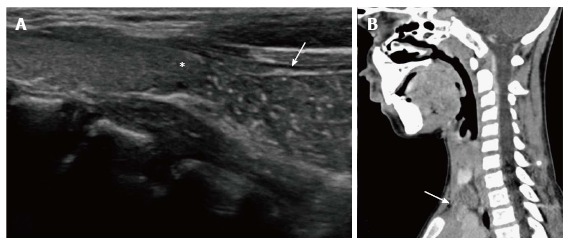
Cervical extension of the thymus in a 7-year-old male presenting with a lump in the neck. USG (A) shows the characteristic “starry sky appearance” of the left lower cervical swelling (arrow) lying near the inferior pole of the left lobe of the thyroid (asterisk). CECT sagittal reformatted image (B) documents the anatomical contiguity (arrow) of this swelling with the mediastinal thymus.
Large thymus
Large thymus may be seen in hyperplasia or masses (which can be cystic, solid or mixed).
THYMIC HYPERPLASIA
There are two patterns of thymic hyperplasia histologically- true hyperplasia and lymphoid (follicular) hyperplasia.
True thymic hyperplasia
True thymic hyperplasia is characterized by an enlarged thymus gland which retains its organised structure. The shape of the gland may change from bilobed to oval[17]. It is commonly seen in patients recovering from a recent stress such as infections, corticosteroid therapy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, major surgery or burns. The thymus undergoes atrophy in response to stress; however, it can increase to its original size within 9 mo and may even increase in size to 50% or larger (Figure 10). This is known as rebound hyperplasia and is commonly seen in the pediatric population. True hyperplasia may also be seen in patients with systemic disorders like hyperthyroidism, sarcoidosis, or pure red cell aplasia[14].
Figure 10.
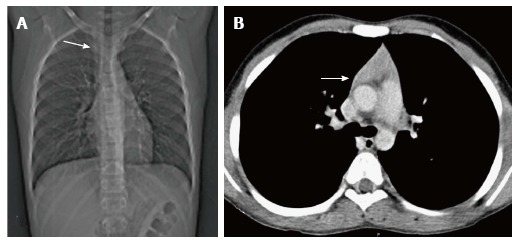
Thymic hyperplasia in a 12-year-old boy treated for Hodgkin’s lymphoma for 8 mo. CT scanogram (A) shows subtle mediastinal widening (arrow). CECT axial section (B) shows mild thymic enlargement with convex margins and homogenous density (arrow) consistent with rebound hyperplasia.
Lymphoid (follicular) hyperplasia
Lymphoid (follicular) hyperplasia is characterised by an increased number of lymphoid follicles and may not always be associated with thymic enlargement[3]. It is associated with immunologically mediated disorders, including myasthenia gravis (Figure 11), systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, vasculitis, thyrotoxicosis, and Graves’ disease[3,12]. On conventional radiographs the thymus is usually of normal size and on CT it may appear normal (45% of cases), enlarged (35%) or as a focal mass (20%)[14].
Figure 11.
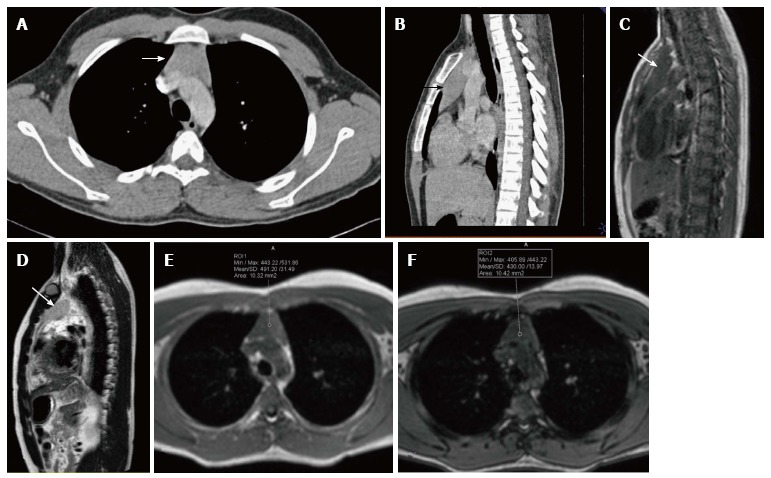
A 16-year-old male patient with myasthenia gravis. CECT axial (A) and sagittal (B) sections showing mild diffuse symmetric enlargement of the thymus gland with a smooth contour (arrow in A and B). Sagittal T1WI (C) and T2WI (D) of the chest show that the thymus (arrow in C and D) is of homogenous signal intensity (isointense to skeletal muscle on T1WI and hyperintense on T2WI). Axial T1WI show a decrease in signal on opposed-phase image (F) when compared with in-phase image (E). The findings are consistent with thymic hyperplasia.
Identifying thymic hyperplasia and differentiating it from neoplasms
It is important to be able to identify thymic hyperplasia and differentiate it from neoplasms (Table 3). In thymic rebound hyperplasia there is a diffuse symmetric enlargement of the thymus gland, with a smooth contour and normal vessels. Thymic neoplasia, however, presents as a focal mass with nodular contour, contrast enhancement and heterogenous appearance with areas of necrosis or calcification[18].
Table 3.
Key morphologic features for differentiation of thymic hyperplasia from a thymic mass
| Morphologic criteria | Hyperplasia | Mass |
| Enlargement | Diffuse, symmetric | Focal, asymmetric |
| Symmetrical | ||
| Contour | Smooth | Nodular |
| Vessels | Normal | Random branching, encased |
| Necrosis | Absent | Maybe present |
| Calcification | Absent | May be present |
| Microscopic fat (on chemical shift MRI) | Present | Absent |
The normal thymus and thymic hyperplasia have microscopic fat, which is detected on chemical shift MRI. Thymic hyperplasia thus demonstrates a decrease in signal on opposed-phase images when compared with in-phase images. Thymic tumours do not contain microscopic fat and there is no drop in signal on the opposed phase images[2]. The chemical shift ratio (CSR) is calculated to assess the presence of microscopic fat and tissue within the same voxel and a CSR less than 0.9 is considered diagnostic for microscopic fat within a thymic lesion[19].
CYSTIC THYMIC MASSES
Thymic cyst
Thymic cysts are fluid containing lesions, usually found in adults. Of all the mediastinal masses in children, thymic cysts account for less than 1%[8]. These can be congenital or acquired. The congenital cysts are found along the course of the thymopharyngeal duct in the neck or anterior mediastinum. Acquired cysts can be seen post radiotherapy for Hodgkin’s lymphoma, after thoracotomy or as a cystic change in thymic tumours with inflammatory cysts usually seen in autoimmune disorders[20]. On plain radiographs, thymic cysts are seen as homogenous, well-circumscribed masses of water density. CT reveals a homogenous fluid attenuating lesion with thin smooth walls and no solid component (Figure 12). There may be occasional internal septations or mural calcification. Presence of proteinaceous contents or hemorrhage results in increased attenuation and on MRI, an increase in T1 signal intensity[12,14].
Figure 12.
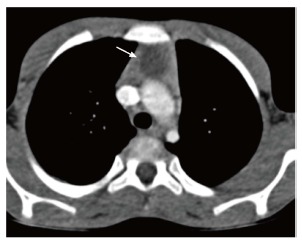
Thymic cyst in a 14-year-old boy treated for Hodgkin’s lymphoma. CECT axial section reveals a small well-defined fluid-attenuating lesion (arrow) suggestive of cyst in the thymus.
Lymphatic malformation
Lymphatic malformation (previously known as lymphangioma or cystic hygroma) consists of cysts lined by the endothelium and containing lymph. Commonly seen in the cervical region, these lesions present with neck swelling early in life. The cervical lesions may have a mediastinal extension with occasional involvement of the thymus. Cross sectional imaging shows a well-defined, multilocular cystic mass with multiple septations. CT density can be variable within the locules, with high density seen in case of hemorrhage or proteinaceous content (Figure 13). The signal intensity of such locules is high on T1WI and intermediate on T2WI. Post contrast imaging shows enhancement of the wall and septations but not of the internal contents (Figure 14)[21].
Figure 13.
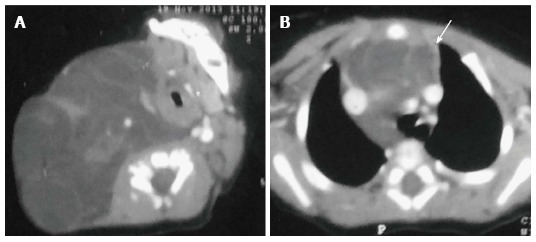
Thymic involvement by a large lymphatic malformation in a neonate diagnosed antenatally with cystic neck swelling. A: Contrast-enhanced CT scan shows a large right-sided poorly circumscribed, multiloculated low attenuation mass in the infrahyoid neck with extension into the posterior cervical and retropharyngeal space; B: Axial sections at the level of origin of arch vessels reveal involvement of the thymus (arrow) by this mass and extension into the anterior and middle mediastinum.
Figure 14.
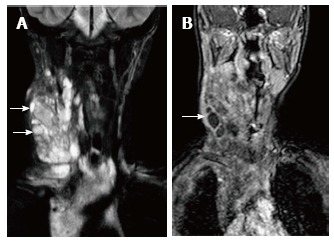
Lymphatic malformation in 13-year-old female patient. Coronal T2WI (A) shows a large, multilocular cystic neck mass with multiple septations. The mass is extending into the superior and anterior mediastinum. Note the variable signal intensity in different locules (arrows). On coronal post contrast T1WI (B), there is enhancement of the wall and internal septations (arrow).
Mature germ cell tumour
Germ cell tumours arise from the primitive germ cells and can occur anywhere along their path of migration to the gonads. The most common location of extragonadal germ cell tumours is the anterior mediastinum, where they can develop within or near the thymus. It is believed that the cellular origin of mediastinal teratomas may lie within the embryonic thymic tissue[22]. In the pediatric age group, germ cell tumours account for about 25% of the mediastinal tumours[3]. Approximately 80% of these are benign or mature teratomas[14].
Mature teratomas are usually asymptomatic and seen as an incidental finding on chest radiograph. However, symptoms may occur because of mass effect or complications. These include chest pain, hemoptysis, fever and rarely trichoptysis[22].
On plain radiographs, both benign and malignant tumours are seen as round, lobulated and sharply marginated masses located in the anterior mediastinum. Calcification, teeth or fat lucency may be identified within the mass[3].
On cross sectional imaging, teratomas are seen as cystic masses with the presence of fat, teeth, bone or calcification. Mature teratomas are well-defined, lobulated fluid attenuating masses with a thin enhancing capsule and fat/calcification on CT. On MRI, the signal intensity varies according to the internal contents. Fat component has a high T1 and intermediate T2 signal intensity whereas fluid has a low T1 and high T2 signal[3]. Calcific foci show evidence of blooming on gradient images.
Spontaneous rupture into the lung, tracheobronchial tree, pleural or pericardial space can occur, resulting in adjacent consolidation, atelectasis, pleural or pericardial effusion (Figure 15). In addition to these findings, the presence of internal inhomogenous densities within the mass, irregular tumor margins and bursting configuration of fat globules should raise the possibility of rupture[23,24]. It is important for radiologists to identify these signs of rupture and guide clinicians in planning proper surgical management[25].
Figure 15.
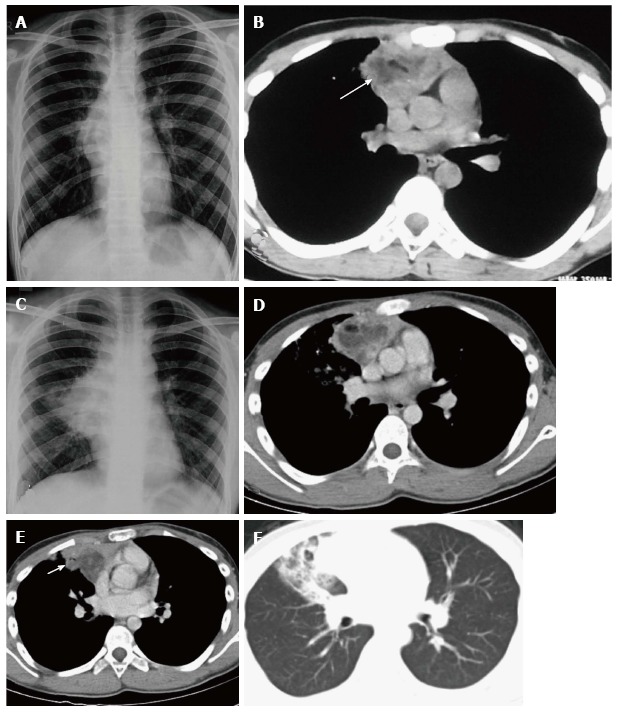
Ruptured anterior mediastinal teratoma in a 14-year-old male. Chest radiograph (A) shows a lobulated soft tissue mass in the right hilar region with obscured inferior margin. CECT axial section (B) shows a heterogenous mass in the anterior mediastinum with soft tissue, fluid and fat suggestive of anterior mediastinal teratoma. The patient refused surgery and presented 5 mo later, with complaint of cough and expectoration of foul smelling material. Chest radiograph (C) shows a large right hilar mass with irregular margins and patchy consolidation in the adjacent right mid zone. CECT (D) also demonstrates the increase in the size of the mass and irregular margins. There is evidence of small air foci (arrow in E) within this mass with adjacent consolidation suggestive of rupture into the tracheobronchial tree. Axial CT lung window (F) shows the adjacent ground glass and consolidation in the right middle lobe.
Teratomas are well encapsulated lesions and usually can be completely resected. Surgical resection is indicated even in asymptomatic patients with incidentally detected mediastinal teratomas. This is because of the potential of pulmonary extension or rupture. Rupture of teratomas usually leads to adjacent inflammation and adhesions, which may complicate the surgery. Chemotherapy or radiotherapy is given in cases of malignant teratomas and imaging is required for evaluation of residual or recurrent disease[22].
SOLID MASSES WITH MILD/ MODERATE ENHANCEMENT
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is the most common primary tumor in the pediatric age group followed by germ cell neoplasm[26,27].
Thymic involvement in lymphomas and leukemias is rare and mostly associated with a systemic disease. It is more commonly seen in Hodgkin’s disease compared to non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma[2,3].
Patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma have intrathoracic involvement in approximately 85% of cases. This can be in the form of nodal involvement, multiple pulmonary nodules or areas of consolidation. However, intrathoracic involvement is seen in only about 50% of cases of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Along with the enlarged mediastinal nodes there may be associated pulmonary nodules, consolidation, interstitial thickening, pleural effusion and pleural masses[21].
When infiltrated by lymphomatous cells, the thymus gland is homogeneously enlarged. Imaging findings include diffuse thymic enlargement, solitary mass or multiple masses in the presence of mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy (Figure 16). In approximately 20% of cases, cystic change and calcification may be detected by pretreatment CT[14].
Figure 16.
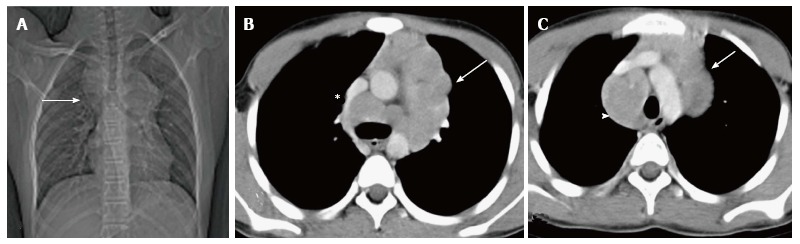
Hodgkin lymphoma in a 12-year-old boy presenting with fever and weight loss for 6 mo. CT scanogram (A) shows mediastinal widening (arrow) with lobulated contour. Axial CECT sections (B and C) reveal multiple, enlarged, homogenous lymph nodes in the region of the thymus (arrow in B and C) and paratracheal location (arrowhead in C). Note mild compression of SVC by this anterior mediastinal nodal mass (asterisk in B).
On MRI, lymphomas are of low signal intensity on T1 and variable signal intensity on T2 weighted images[14]. Usually, thymic involvement and nodal masses resolve after chemotherapy. However, in cases of a residual mass, low T2 signal intensity is suggestive of fibrosis and high signal intensity is suggestive of a residual tumour.
It is difficult to differentiate between a recurrent tumour and thymic rebound hyperplasia. Usually, thymic rebound hyperplasia has a symmetrical, smooth and homogenous appearance whereas a recurrent tumor is nodular and heterogenous[3].
Thymoma
Thymoma is a thymic epithelial tumor usually benign or of low-grade malignancy. It is usually seen in adults and is rare in children, accounting for less than 5% of the pediatric mediastinal tumours[27].
Usually asymptomatic, thymomas are picked up as an incidental finding on chest radiographs. Association with myasthenia gravis is seen in 5% to 15% of the pediatric patients[28]. Other associated conditions include pure red cell aplasia, hypogammaglobulinemia, connective tissue diseases and inflammatory bowel disease[14].
On plain radiographs, thymoma appears as a well-defined mass of increased opacity in the retrosternal location with lobulated margins. CT reveals a homogenous, soft tissue density mass with sharp margins (Figure 17). The shape may be oval, round or lobulated. Calcification and cystic degeneration may occasionally be seen.
Figure 17.
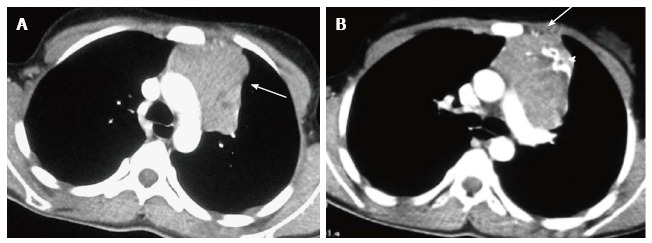
Invasive thymoma in a 13-year-old girl presenting with cough and chest pain. CECT axial images reveal a heterogenously enhancing anterior mediastinal mass with irregular margins (arrow in A) and peripheral calcification (arrowhead in B). There is evidence of focal area of extension to subpleural region anteriorly (arrow in B).
It is clinically important to differentiate invasive from non-invasive thymomas, as invasive thymomas require neo-adjuvant chemotherapy. The CT findings, which suggest invasion, include ill-defined margins, an irregular tumour-lung interface, encasement of vessels and other mediastinal structures, and nodular pleural thickening. Intra-abdominal extension may occur via the retrocrural space[29]. It is difficult to differentiate invasive thymomas from thymic carcinomas. Thymic carcinomas are more aggressive with lymphadenopathy and distant metastases being more common than in thymomas[3].
On MR imaging, thymomas are of low signal intensity on T1 and high signal intensity on T2 weighted images with homogenous enhancement post contrast.
Thymomas are FDG avid and PET imaging can be used in detection of metastases and postoperative recurrence. However, FDG-PET scanning is not able to differentiate between normal thymus, thymic hyperplasia and thymoma as all show FDG uptake[30].
Thymolipoma
Thymolipomas are rare tumours seen in any age group with a mean age of 21 years[3]. They are soft, pliable tumors with predominant fatty content. They can be very large, occupying the entire hemithorax (Figure 18). On plain radiographs, the density of the mass is less than that of soft tissue. On CT, they are of fat attenuation with intervening fibrous septa and normal thymic tissue. MRI reveals an anterior mediastinal mass with high T1 and T2 signal intensity with intervening low signal intensity fibrous strands[3].
Figure 18.
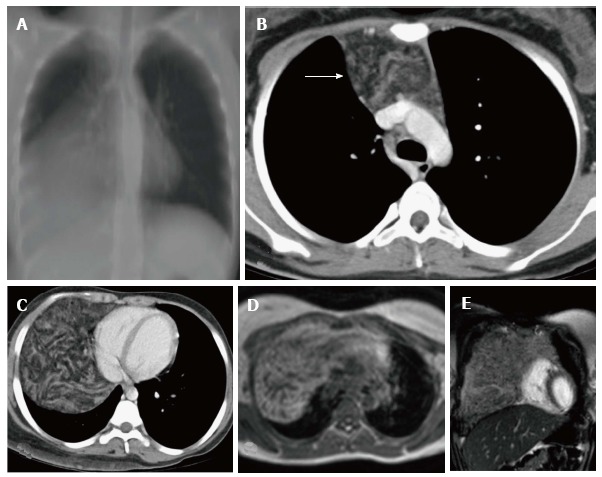
Thymolipoma in 17-year-old female. Thick MPR (multiplanar reconstruction) in the coronal plane (A) shows a large anterior and middle mediastinal mass with low attenuation and sharp margins. CECT axial images (B and C) reveal a large anterior mediastinal mass lesion extending into the right hemithorax. The mass is predominantly of fat attenuation (arrow in A). Note that there is no displacement of the heart or great vessels. Axial T1WI (D) and coronal T2WI (E) show a large heterogenous fat containing mass with intervening fibrous septa. The mass has predominantly hyperintense signal on T1WI and intermediate signal on T2WI consistent with fat.
Thymic carcinoma
Thymic carcinomas are rare in children and usually present in the fifth to sixth decades[3]. They are more aggressive than thymomas and 50%-65% of patients have metastases at the time of diagnosis[31].
SOLID MASSES WITH INTENSE ENHANCEMENT
Hemangioma
Infantile hemangioma in the anterior mediastinum involving the thymus is rare. It is usually seen in infants and young children. The imaging findings include a well defined, echogenic mass with internal vascularity and high diastolic flow on ultrasonography (USG). On CT, it is a lobulated, noncalcified mass with intense post contrast enhancement (Figure 19). The mass is isointense on T1WI and hyperintense on T2WI with internal flow voids and marked enhancement[13]. Cavernous hemangiomas in older children also shows intense enhancement but can have central heterogeneity. The differential differentiation of such avidly enhancing mass would include metastases from hypervascular primaries (thyroid, neuroendocrine tumours, and renal cell carcinoma) and Castleman’s disease.
Figure 19.
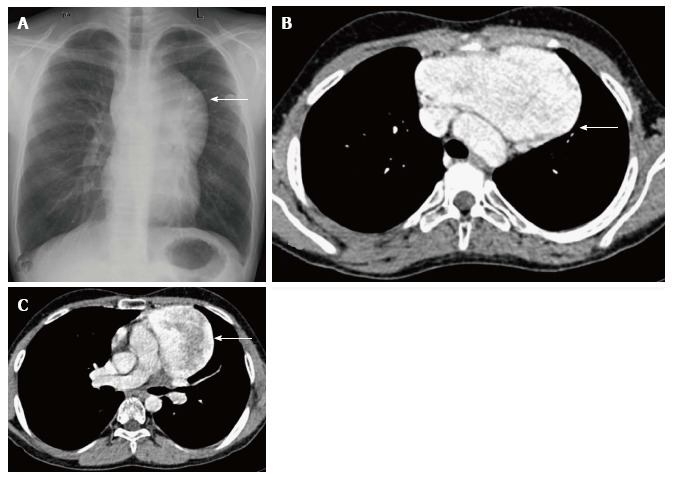
Incidentally detected cavernous hemangioma in 16-year-old male. Frontal chest radiograph (A) reveals a well-defined, lobulated soft tissue density mass (arrow) with broad base towards the mediastinum and positive hilum overlay sign. CECT axial sections (B and C) show a sharply marginated mass lesion (arrow in B) anterior to the arch of the aorta. Note the intense post contrast enhancement with central heterogeneity (arrow in C).
Castleman’s disease
Castleman’s disease is a nonclonal lymph node hyperplasia with approximately 70% of cases occuring in the chest[32]. On imaging it is seen as an intensely enhancing mediastinal nodal mass with associated prominent feeding vessels. Calcification may be seen in 10% of the cases and is usually coarse or in a branching pattern[33].
Thymic carcinoid
Thymic carcinoids are rare neuroendocrine tumors arising from cells of neural crest origin. They are usually seen in adults and patients can present with endocrine abnormalities like Cushing syndrome or syndrome of inappropriate secretion of anti-diuretic hormone[31,34]. They are more aggressive tumors with a poor prognosis and non-specific imaging features.
MIXED DENSITY MASSES
Infections
The thymus may be involved as a part of mediastinitis with heterogenous appearance on imaging. Focal abscess is seen as a rim enhancing lesion with surrounding hypodensity suggestive of edema.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is commonly seen in mediastinal lymph nodes and can secondarily involve the thymus gland. Multiple nodes may be involved with evidence of matting and conglomeration. They are hypodense with peripheral rim enhancement and central necrosis (Figure 20). Tuberculosis of the thymus is rare and is seen as an inhomogenously enhancing mass lesion in the region of the thymus gland[35]. It is important to keep it in the differential differentiation of heterogenous thymus, especially with evidence of tuberculosis elsewhere.
Figure 20.
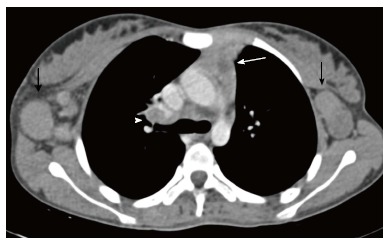
Tuberculosis in a 12-year-old girl presenting with fever and loss of weight and appetite for 3 mo. CECT axial section reveals heterogenous appearance of the thymus with central low attenuation areas (arrow). There is presence of necrotic right hilar lymph node (arrowhead) and enlarged bilateral axillary lymph nodes (black arrows).
Immature germ cell tumors
Approximately 20% of the mediastinal germ cell tumors are immature teratomas[14]. These are malignant or potentially malignant masses and usually demonstrate a solid enhancing component on imaging. On conventional radiographs, it is difficult to differentiate these from mature teratomas. However, on cross-sectional imaging (Figure 21), immature teratomas have a nodular outline, more solid component and areas of haemorrhage or necrosis. These tend to invade the surrounding structures rather than displace them as is seen in the case of mature teratomas[21,22].
Figure 21.
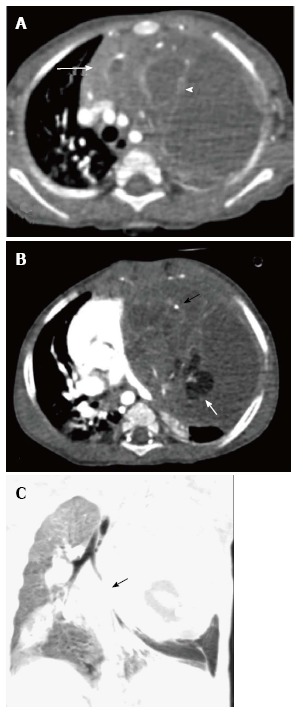
Immature teratoma in a 1-year-old boy. CECT axial sections (A and B) reveal a large cystic mass in the anterior mediastinum. The mass has enhancing solid component (arrow in A), internal septations (arrowhead in A), fat (white arrow in B), and calcific foci (black arrow in B). Note the mass effect on heart and mediastinal vascular structures. Coronal minimum intensity projection image (C) shows the narrowing of left lower lobe bronchus (arrow) and basal atelectasis.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare multi-system disease characterised by the proliferation of monoclonal dendritic cells. Thymic involvement (Figure 22) can present as an increase in size with a nodular outline and heterogenous appearance (due to cystic change and calcification). In a study by Lakatos et al[36], it was concluded that the presence of calcifications and /or cysts in a normal or enlarged thymus in a case of biopsy proven LCH is diagnostic for thymic involvement. They recommended screening USG for thymic involvement in all patients with diagnosed LCH. These findings usually resolve after chemotherapy[3,36].
Figure 22.
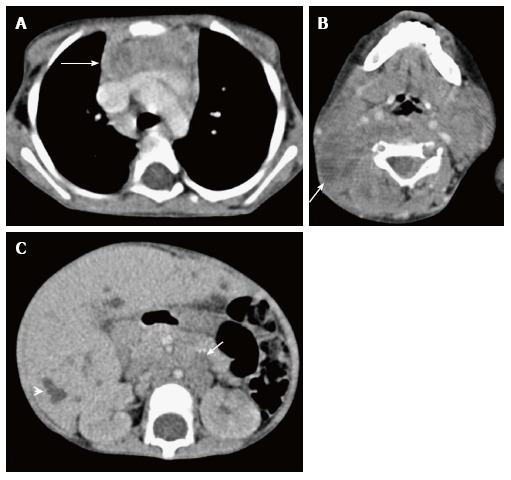
Thymic involvement in systemic Langerhans cell histiocytosis in a 2-year-old girl. CECT axial section at the level of the arch of the aorta (A) shows heterogenous appearance of the thymus with a nodular outline (arrow). Axial section of the suprahyoid neck (B) shows multiple bilateral enlarged lymph nodes with cystic change (arrow). CECT of the abdomen (C) reveals hepatomegaly with multiple small focal hypodense lesions (arrowhead) in both lobes of the liver and enlarged retroperitoneal lymph nodes (arrow).
CONCLUSION
It is important for clinicians to be able to identify normal variations in thymic appearance and avoid over-investigation. However, it is equally important to have a high index of suspicion for abnormal thymus especially in multisystem disorders. We discuss normal variants, hyperplasia and focal masses; and propose an algorithmic approach (Figure 23) to the evaluation of a suspected thymic mass based on imaging morphology.
Figure 23.
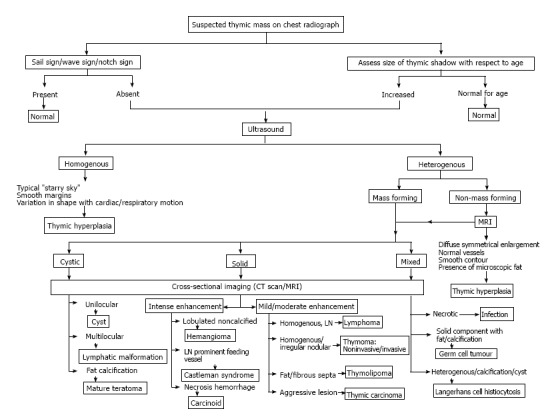
Imaging approach to the evaluation of a suspected thymic mass.
The normal thymus has a variable appearance and awareness of these anatomical variations is important to prevent unnecessary investigations and invasive procedures. The thymus may be involved in benign and malignant conditions and it is essential to know this spectrum of involvement to be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest statement: There is no conflict of interest associated with any of the senior author or other coauthors contributing their efforts in this manuscript.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Pediatrics
Country of origin: India
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
Peer-review started: May 10, 2016
First decision: July 25, 2016
Article in press: November 22, 2016
P- Reviewer: Chow J, Watanabe T S- Editor: Kong JX L- Editor: A E- Editor: Lu YJ
References
- 1.Pearse G. Normal structure, function and histology of the thymus. Toxicol Pathol. 2006;34:504–514. doi: 10.1080/01926230600865549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goldstein AJ, Oliva I, Honarpisheh H, Rubinowitz A. A tour of the thymus: a review of thymic lesions with radiologic and pathologic correlation. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2015;66:5–15. doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2013.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nasseri F, Eftekhari F. Clinical and radiologic review of the normal and abnormal thymus: pearls and pitfalls. Radiographics. 2010;30:413–428. doi: 10.1148/rg.302095131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alves ND, Sousa M. Images in pediatrics: the thymic sail sign and thymic wave sign. Eur J Pediatr. 2013;172:133. doi: 10.1007/s00431-012-1870-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Avares BR, Pereira CMR, Neto SAA, Sakuma ETI. Normal findings on chest Xray of neonates. Radiol Bras. 2006;39:435–440. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ben-Ami TE, O'Donovan JC, Yousefzadeh DK. Sonography of the chest in children. Radiol Clin North Am. 1993;31:517–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Newman B. Ultrasound body applications in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2011;41 Suppl 2:555–561. doi: 10.1007/s00247-011-2107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frush DP. Imaging evaluation of the thymus and thymic disorders in children. Pediatric chest imaging. In: Lucaya J, Strife JL, eds, editors. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2008. pp. 215–240. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baron RL, Lee JK, Sagel SS, Peterson RR. Computed tomography of the normal thymus. Radiology. 1982;142:121–125. doi: 10.1148/radiology.142.1.7053521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.de Geer G, Webb WR, Gamsu G. Normal thymus: assessment with MR and CT. Radiology. 1986;158:313–317. doi: 10.1148/radiology.158.2.3941858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sklair-Levy M, Agid R, Sella T, Strauss-Liviatan N, Bar-Ziv J. Age-related changes in CT attenuation of the thymus in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30:566–569. doi: 10.1007/s002470000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nishino M, Ashiku SK, Kocher ON, Thurer RL, Boiselle PM, Hatabu H. The thymus: a comprehensive review. Radiographics. 2006;26:335–348. doi: 10.1148/rg.262045213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.LaPlante JK, Pierson NS, Hedlund GL. Common pediatric head and neck congenital/developmental anomalies. Radiol Clin North Am. 2015;53:181–196. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2014.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Webb RW. The mediastinum: mediastinal masses. Thoracic imaging: pulmonary and cardiovascular radiology. In: Webb RW, Higgins C, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. pp. 212–270. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jana M, Bhalla AS, Gupta AK. Approach to Pediatric Chest Radiograph. Indian J Pediatr. 2016;83:533–542. doi: 10.1007/s12098-015-1980-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yin EZ, Frush DP, Donnelly LF, Buckley RH. Primary immunodeficiency disorders in pediatric patients: clinical features and imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:1541–1552. doi: 10.2214/ajr.176.6.1761541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ricci C, Pescarmona E, Rendina EA, Venuta F, Ruco LP, Baroni CD. True thymic hyperplasia: a clinicopathological study. Ann Thorac Surg. 1989;47:741–745. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(89)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kissin CM, Husband JE, Nicholas D, Eversman W. Benign thymic enlargement in adults after chemotherapy: CT demonstration. Radiology. 1987;163:67–70. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.1.3823458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Inaoka T, Takahashi K, Mineta M, Yamada T, Shuke N, Okizaki A, Nagasawa K, Sugimori H, Aburano T. Thymic hyperplasia and thymus gland tumors: differentiation with chemical shift MR imaging. Radiology. 2007;243:869–876. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2433060797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Strollo DC, Rosado-de-Christenson ML. Tumors of the thymus. J Thorac Imaging. 1999;14:152–171. doi: 10.1097/00005382-199907000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ranganath SH, Lee EY, Restrepo R, Eisenberg RL. Mediastinal masses in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198:W197–W216. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.7027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Patel IJ, Hsiao E, Ahmad AH, Schroeder C, Gilkeson RC. AIRP best cases in radiologic-pathologic correlation: mediastinal mature cystic teratoma. Radiographics. 2013;33:797–801. doi: 10.1148/rg.333125088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bachh AA, Haq I, Gupta R, Boinapally RM, Sudhakar S. Benign mediastinal teratoma with intrapulmonary extension presenting with trichoptysis. Respir Med CME. 2010;3:189–191. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Madhusudhan KS, Sharma R, Gadodia A, Kumar A. Spontaneous rupture of benign mediastinal teratoma: A report of two cases. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2012;33:123–125. doi: 10.4103/0971-5851.99750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Escalon JG, Arkin J, Chaump M, Harkin TJ, Wolf AS, Legasto A. Ruptured anterior mediastinal teratoma with radiologic, pathologic, and bronchoscopic correlation. Clin Imaging. 2015;39:689–691. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2015.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mullen B, Richardson JD. Primary anterior mediastinal tumors in children and adults. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986;42:338–345. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Siegel MJ, Coley B. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. The core curriculum: pediatric imaging; pp. 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fonseca AL, Ozgediz DE, Christison-Lagay ER, Detterbeck FC, Caty MG. Pediatric thymomas: report of two cases and comprehensive review of the literature. Pediatr Surg Int. 2014;30:275–286. doi: 10.1007/s00383-013-3438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bogot NR, Quint LE. Imaging of thymic disorders. Cancer Imaging. 2005;5:139–149. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2005.0107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wittram C, Fischman AJ, Mark E, Ko J, Shepard JA. Thymic enlargement and FDG uptake in three patients: CT and FDG positron emission tomography correlated with pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180:519–522. doi: 10.2214/ajr.180.2.1800519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jung KJ, Lee KS, Han J, Kim J, Kim TS, Kim EA. Malignant thymic epithelial tumors: CT-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:433–439. doi: 10.2214/ajr.176.2.1760433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bonekamp D, Horton KM, Hruban RH, Fishman EK. Castleman disease: the great mimic. Radiographics. 2011;31:1793–1807. doi: 10.1148/rg.316115502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ko SF, Hsieh MJ, Ng SH, Lin JW, Wan YL, Lee TY, Chen WJ, Chen MC. Imaging spectrum of Castleman‘s disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182:769–775. doi: 10.2214/ajr.182.3.1820769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Restrepo CS, Pandit M, Rojas IC, Villamil MA, Gordillo H, Lemos D, Mastrogiovanni L, Diethelm L. Imaging findings of expansile lesions of the thymus. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2005;34:22–34. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Saieg MT, Bernardi Fdel C, Gonçalves R, Botter M, Saad Junior R, Pozzan G. Tuberculosis of the thymus. J Bras Pneumol. 2007;33:355–357. doi: 10.1590/s1806-37132007000300020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lakatos K, Herbrüggen H, Pötschger U, Prosch H, Minkov M. Radiological features of thymic langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013;60:E143–E145. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


