Abstract
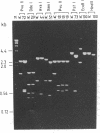
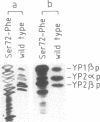
The replacement of each one of the eight serine residues present in the amino acid sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein YP2 beta (L45) by different amino acids has been performed by heteroduplex site-directed mutagenesis in the cloned gene. The mutated DNA was used to transform a yeast strain previously deprived of the original protein YP2 beta (L45) by gene disruption. The replacement of serine in position 19 by either alanine, aspartic acid, or threonine prevents in vivo phosphorylation of the protein and its interaction with the ribosome. The serine-19 mutated gene is unable to rescue the negative effect on the growth rate caused by elimination of the original protein in YP2 beta (L45) gene disrupted strains. The mutation of any one of the other seven serine residues has no effect on either the phosphorylation or the ribosome binding capacity of the protein, although replacement of serine-72 seems to increase the sensitivity of the polypeptide to degradation. These results provide strong evidence indicating that ribosomal protein phosphorylation plays an important part in the activity of the particle and that it supports the existence of a control mechanism of protein synthesis, which would regulate the level of phosphorylation of acidic proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amons R., Pluijms W., Möller W. The primary structure of ribosomal protein eL12/eL12-P from Artemia salina 80 S ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Phosphorylation of the ribosomal protein S6 is elevated in cells transformed by a variety of tumor viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):966–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.966-969.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Madsen P., Ryazanov A. G. Increased phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 during mitosis in transformed human amnion cells correlates with a decreased rate of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4231–4235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Regulation of initiation factors during translational repression caused by serum depletion. Covalent modification. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5493–5497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gressner A. M., Wool I. G. Effect of experimental diabetes and insulin on phosphorylation of rat liver ribosomal protein S6. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):148–150. doi: 10.1038/259148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman W. L., Ilan J. Analysis by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the in vivo phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins derived from free and membrane-bound polysomes. Mol Biol Rep. 1975 Oct;2(3):219–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00356991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Phosphorylation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae equivalent of ribosomal protein S6 has no detectable effect on growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1338–1345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavergne J. P., Conquet F., Reboud J. P., Reboud A. M. Role of acidic phosphoproteins in the partial reconstitution of the active 60 S ribosomal subunit. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80761-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacConnell W. P., Kaplan N. O. The activity of the acidic phosphoproteins from the 80 S rat liver ribosome. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5359–5366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Nakagawa T., Tsurugi K. On the size and the role of a free cytosolic pool of acidic ribosomal proteins in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biochem. 1988 Dec;104(6):908–911. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Tsurugi K. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of acidic ribosomal protein A1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3574–3574. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S. J., Traugh J. A. Differential stimulation of phosphorylation of initiation factors eIF-4F, eIF-4B, eIF-3, and ribosomal protein S6 by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10611–10616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Palfrey H. C. Identification of the major Mr 100,000 substrate for calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III in mammalian cells as elongation factor-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17299–17303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. H., Shimmin L. C., Yee J., Dennis P. P. A family of genes encode the multiple forms of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal proteins equivalent to the Escherichia coli L12 protein and a single form of the L10-equivalent ribosomal protein. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):579–588. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.579-588.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen E., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase differentially alters translation of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3518–3523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redpath N. T., Proud C. G. The tumour promoter okadaic acid inhibits reticulocyte-lysate protein synthesis by increasing the net phosphorylation of elongation factor 2. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):69–75. doi: 10.1042/bj2620069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacha M., Santos C., Ballesta J. P. Disruption of single-copy genes encoding acidic ribosomal proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2182–2190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacha M., Sáenz-Robles M. T., Vilella M. D., Ballesta J. P. Independent genes coding for three acidic proteins of the large ribosomal subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9094–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Shestakova E. A., Natapov P. G. Phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 by EF-2 kinase affects rate of translation. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):170–173. doi: 10.1038/334170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saenz-Robles M. T., Remacha M., Vilella M. D., Zinker S., Ballesta J. P. The acidic ribosomal proteins as regulators of the eukaryotic ribosomal activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90140-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimmin L. C., Ramirez C., Matheson A. T., Dennis P. P. Sequence alignment and evolutionary comparison of the L10 equivalent and L12 equivalent ribosomal proteins from archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eucaryotes. J Mol Evol. 1989 Nov;29(5):448–462. doi: 10.1007/BF02602915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Reyes R., Conde P., Ballesta J. P. Acidic ribosomal proteins from eukaryotic cells. Effect on ribosomal functions. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):409–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Vidales F. J., Ballesta J. P. Effect of phosphorylation on the affinity of acidic proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar;114(3):609–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Vidales F. J., Ballesta J. P. Functional role of acidic ribosomal proteins. Interchangeability of proteins from bacterial and eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3263–3266. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Ogata K. Evidence for the exchangeability of acidic ribosomal proteins on cytoplasmic ribosomes in regenerating rat liver. J Biochem. 1985 Dec;98(6):1427–1431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidales F. J., Robles M. T., Ballesta J. P. Acidic proteins of the large ribosomal subunit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Effect of phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):390–396. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilella M. D., Remacha M., Ortiz B. L., Mendez E., Ballesta J. P. Characterization of the yeast acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins using monoclonal antibodies. Proteins L44/L45 and L44' have different functional roles. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):407–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G., Chan Y. L., Glück A., Suzuki K. The primary structure of rat ribosomal proteins P0, P1, and P2 and a proposal for a uniform nomenclature for mammalian and yeast ribosomal proteins. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90127-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S. P5/P5' the acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;606(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S., Warner J. R. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Phosphorylated and exchangeable proteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1799–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven A. J., Maassen J. A., Möller W. Structure and phosphorylation of an acidic protein from 60S ribosomes and its involvement in elongation factor-2 dependent GTP hydrolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):989–998. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]