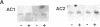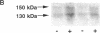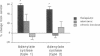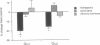Abstract
A possible role for adenylate cyclase and guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) in contributing to the chronic actions of lithium on brain function was investigated in rat cerebral cortex. It was found that chronic treatment of rats with lithium (with therapeutically relevant serum levels of approximately 1 mM) increased levels of mRNA and protein for the calmodulin-sensitive (type 1) and calmodulin-insensitive (type 2) forms of adenylate cyclase and decreased levels of mRNA and protein for the inhibitory G-protein subunits Gi alpha 1 and Gi alpha 2. Chronic lithium did not alter levels of other G-protein subunits, including Go alpha, Gs alpha, and G beta. Lithium regulation of adenylate cyclase and Gi alpha was not seen in response to short-term lithium treatment (with final serum levels of approximately 1 mM) or in response to chronic treatment at a lower dose of lithium (with serum levels of approximately 0.5 mM). The results suggest that up-regulation of adenylate cyclase and down-regulation of Gi alpha could represent part of the molecular mechanism by which lithium alters brain function and exerts its clinical actions in the treatment of affective disorders.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avissar S., Schreiber G., Danon A., Belmaker R. H. Lithium inhibits adrenergic and cholinergic increases in GTP binding in rat cortex. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):440–442. doi: 10.1038/331440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Neural and developmental actions of lithium: a unifying hypothesis. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duman R. S., Terwilliger R. Z., Nestler E. J., Tallman J. F. Sodium and potassium regulation of guanine nucleotide-stimulated adenylate cyclase in brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 15;38(12):1909–1914. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90488-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebstein R. P., Hermoni M., Belmaker R. H. The effect of lithium on noradrenaline-induced cyclic AMP accumulation in rat brain: inhibition after chronic treatment and absence of supersensitivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Apr;213(1):161–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis R. B., Nestler E. J., Aghajanian G. K. Evidence for G protein mediation of serotonin- and GABAB-induced hyperpolarization of rat dorsal raphe neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 30;459(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Acute and chronic lithium treatments influence agonist and depolarization-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):1023–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Coussen F., Bakalyar H. A., Tang W. J., Feinstein P. G., Orth K., Slaughter C., Reed R. R., Gilman A. G. Adenylyl cyclase amino acid sequence: possible channel- or transporter-like structure. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1558–1564. doi: 10.1126/science.2472670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masana M. I., Bitran J. A., Hsiao J. K., Mefford I. N., Potter W. Z. Lithium effects on noradrenergic-linked adenylate cyclase activity in intact rat brain: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res. 1991 Jan 11;538(2):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90450-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollner S., Pfeuffer T. Two different adenylyl cyclases in brain distinguished by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):265–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneron A., Ladant D., d'Alayer J., Bellalou J., Bârzu O., Ullmann A. Immunological relatedness between Bordetella pertussis and rat brain adenylyl cyclases. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):536–539. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mørk A., Geisler A. Mode of action of lithium on the catalytic unit of adenylate cyclase from rat brain. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987 Apr;60(4):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1987.tb01745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. E., Belmaker R. H. Effects of lithium in vitro and ex vivo on components of the adenylate cyclase system in membranes from the cerebral cortex of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Feb-Mar;26(2-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. B., Storm D. R. Immunological distinction between calmodulin-sensitive and calmodulin-insensitive adenylate cyclases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7623–7628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito N., Guitart X., Hayward M., Tallman J. F., Duman R. S., Nestler E. J. Corticosterone differentially regulates the expression of Gs alpha and Gi alpha messenger RNA and protein in rat cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3906–3910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulser F. New perspectives on the molecular pharmacology of affective disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci. 1989;238(5-6):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00449803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger R. Z., Beitner-Johnson D., Sevarino K. A., Crain S. M., Nestler E. J. A general role for adaptations in G-proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function. Brain Res. 1991 May 10;548(1-2):100–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91111-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treiser S. L., Cascio C. S., O'Donohue T. L., Thoa N. B., Jacobowitz D. M., Kellar K. J. Lithium increases serotonin release and decreases serotonin receptors in the hippocampus. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1529–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.6269180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]