Abstract
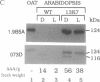
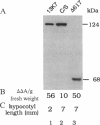
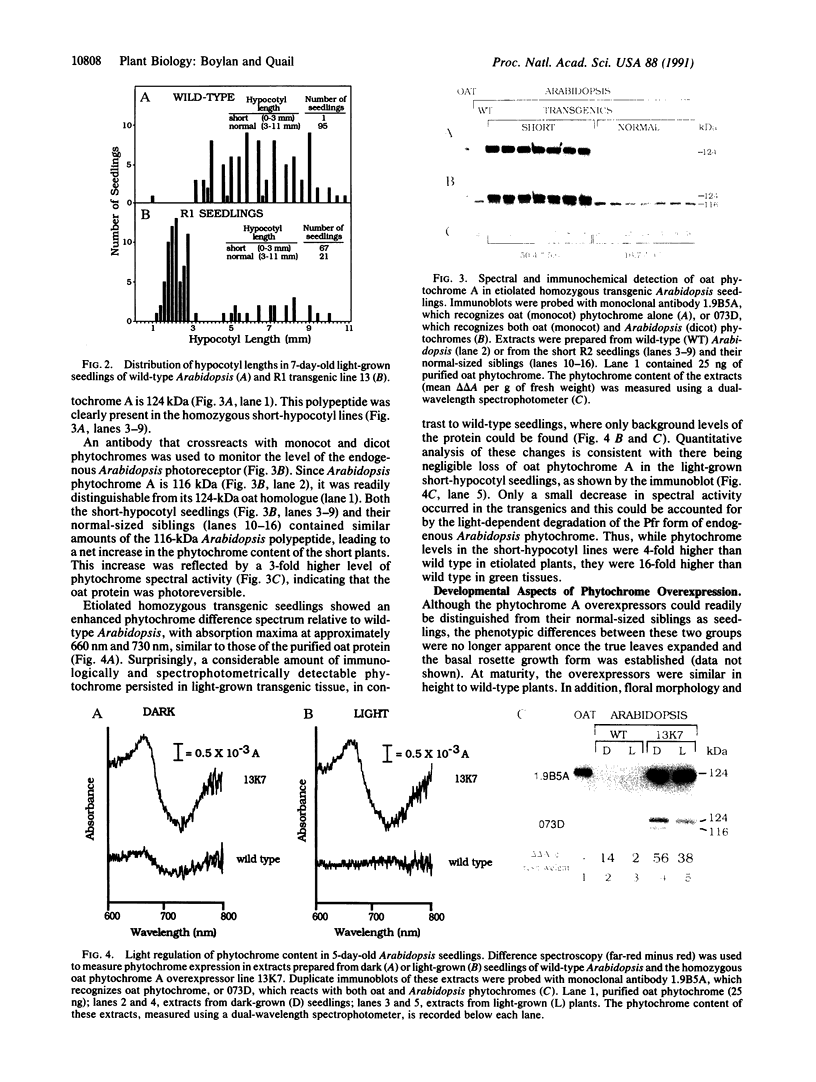
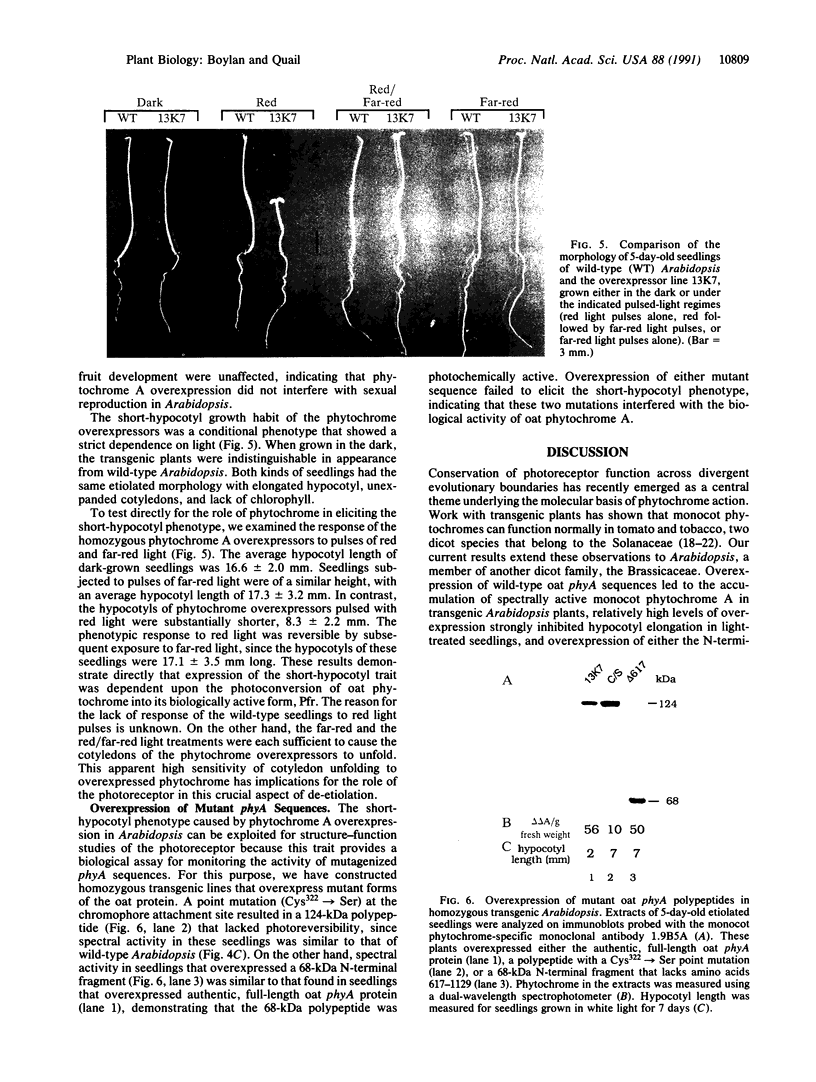
To develop a model plant system for efficient functional analysis of mutagenized phytochrome polypeptides, we have overexpressed oat phytochrome A in Arabidopsis thaliana. R1 seedlings from selfed primary transformants segregated for hypocotyl length, when grown in the light, with a ratio of 3 short to 1 of normal length. When homozygous lines were established from these two size classes, accumulation of immunologically detectable oat phytochrome cosegregated with the short-hypocotyl trait. The short-hypocotyl seedlings contained substantially more spectrally active phytochrome than their normal-sized siblings, indicating that the introduced oat protein was photoreversible. The short-hypocotyl phenotype was strictly light-dependent, since no morphological effects of phytochrome overexpression could be seen in etiolated seedlings. Overexpression of only the chromophore-bearing, N-terminal domain of phytochrome A did not induce short hypocotyls in light-grown seedlings, indicating that additional sequence is essential for photoreceptor function. Similarly, overexpression of a full-length sequence mutated at the chromophore attachment site had no effect on phenotype, indicating the absence of any detectable dominant negative effect of the chromophoreless polypeptide on the activity of endogenous Arabidopsis phytochrome. Thus, the readily scorable short-hypocotyl phenotype of Arabidopsis seedlings overexpressing phytochrome A provides a simple visual assay for rapidly monitoring the biological activity of mutagenized phytochrome A polypeptides.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boylan M. T., Quail P. H. Oat Phytochrome Is Biologically Active in Transgenic Tomatoes. Plant Cell. 1989 Aug;1(8):765–773. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.8.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. R., Hershey H. P., Vierstra R. D. Characterization of Tobacco Expressing Functional Oat Phytochrome : Domains Responsible for the Rapid Degradation of Pfr Are Conserved between Monocots and Dicots. Plant Physiol. 1991 Jul;96(3):775–785. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Peto C. A., Ashbaugh M., Saganich R., Pratt L., Ausubel F. Different Roles for Phytochrome in Etiolated and Green Plants Deduced from Characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana Mutants. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):867–880. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. M., Quail P. H. Monoclonal antibodies to three separate domains on 124 kilodalton phytochrome from Avena. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):622–626. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehesh K., Tepperman J., Christensen A. H., Quail P. H. phyB is evolutionarily conserved and constitutively expressed in rice seedling shoots. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Feb;225(2):305–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00269863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya M. Molecular properties and biogenesis of phytochrome I and II. Adv Biophys. 1989;25:133–167. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. A., Nagatani A., Keith B., Deak M., Furuya M., Chua N. H. Rice Phytochrome Is Biologically Active in Transgenic Tobacco. Plant Cell. 1989 Aug;1(8):775–782. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.8.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Shanklin J., Vierstra R. D., Hershey H. P. Expression of a functional monocotyledonous phytochrome in transgenic tobacco. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1005–1012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy D. W., Pratt L. H. Immunogold electron microscopy of phytochrome in Avena: identification of intracellular sites responsible for phytochrome sequestering and enhanced pelletability. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2541–2550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani A., Kay S. A., Deak M., Chua N. H., Furuya M. Rice type I phytochrome regulates hypocotyl elongation in transgenic tobacco seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5207–5211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H. Phytochrome: a light-activated molecular switch that regulates plant gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:389–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock R. A., Quail P. H. Novel phytochrome sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana: structure, evolution, and differential expression of a plant regulatory photoreceptor family. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1745–1757. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valvekens D., Van Montagu M., Van Lijsebettens M. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana root explants by using kanamycin selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5536–5540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]