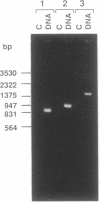
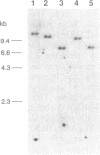
Abstract
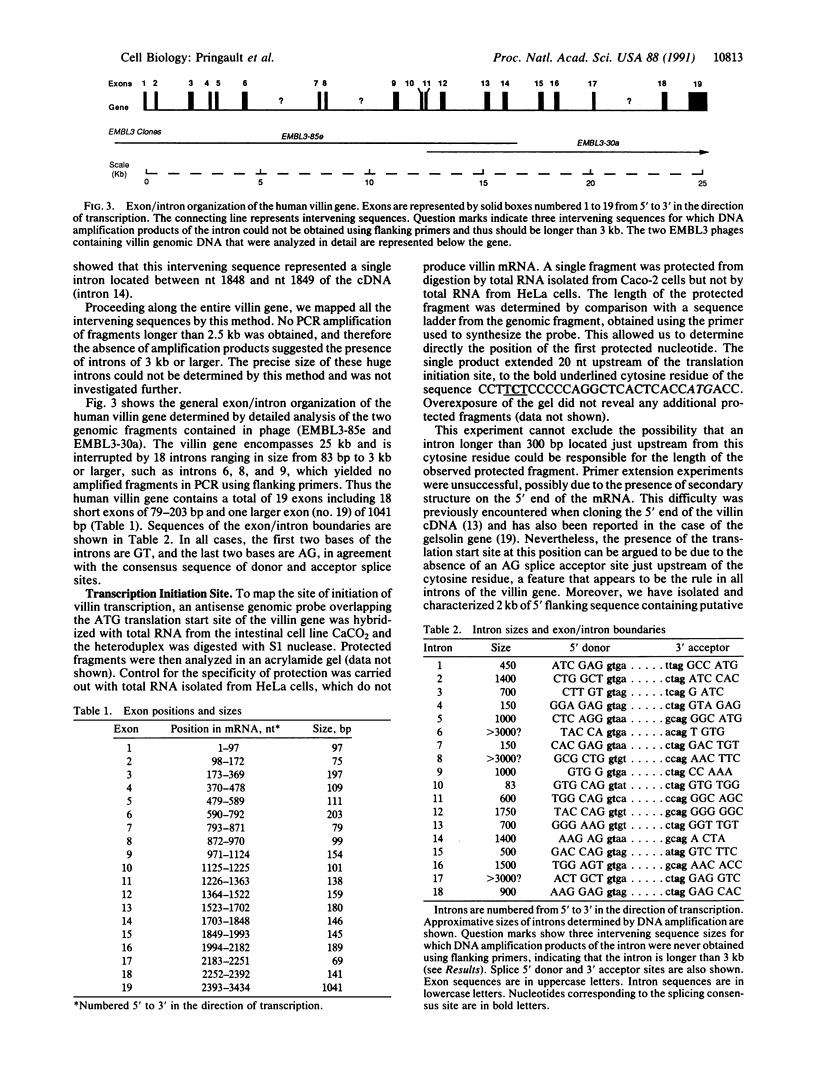
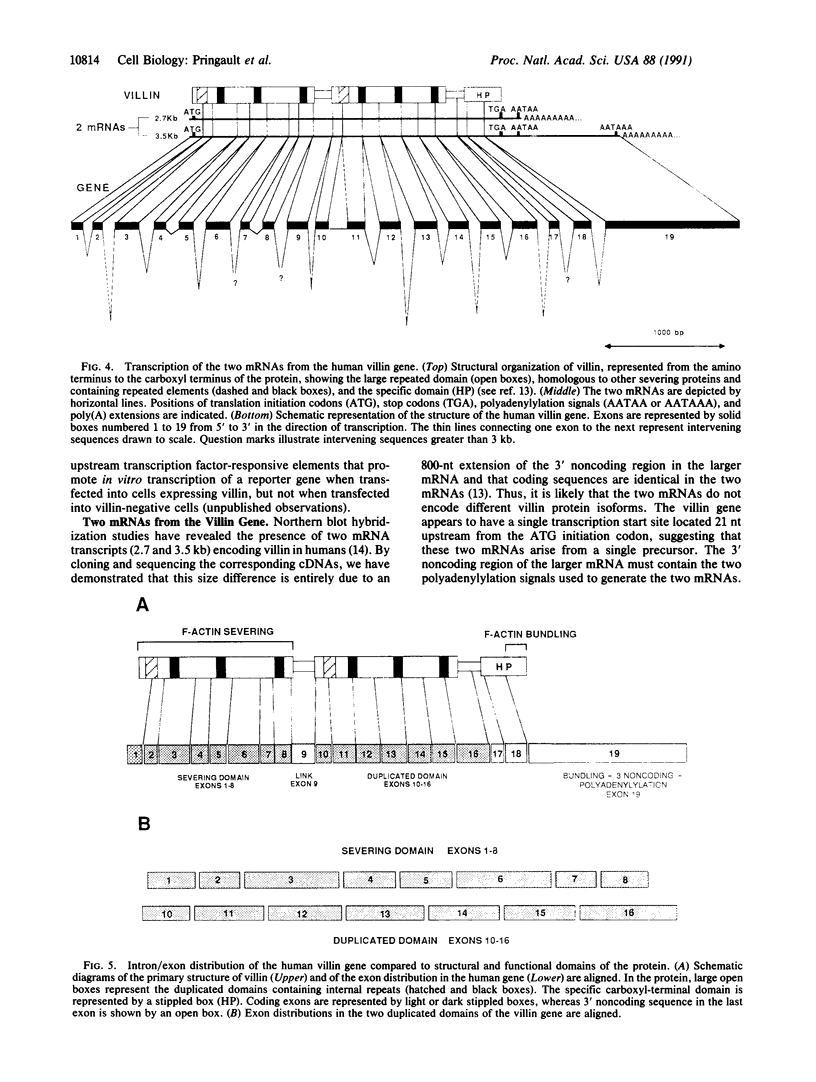
We have isolated and characterized the complete human villin gene. The villin gene is located on chromosome 2q35-36 in humans and on chromosome 1 in mice. Villin belongs to a family of calcium-regulated actin-binding proteins that share structural and functional homologies. The villin gene is expressed mainly in cells that develop a brush border, such as mucosal cells of the small and large intestine and epithelial cells of the kidney proximal tubules. Villin gene expression is strictly regulated during adult life and embryonic development in the digestive and urogenital tracts and, thus, may be used as a marker of the digestive and renal cell lineages. The human villin gene has one copy per haploid genome, encompasses about 25 kilobases, and contains 19 exons. Analysis of the structural organization of this gene shows that the two mRNAs that encode villin in humans arise by alternative choice of one of the two polyadenylylation signals located within the last exon. The overall organization of the exons reflects the gene duplication event from which this family of actin-binding proteins originated.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J. The F-actin capping proteins of Physarum polycephalum: cap42(a) is very similar, if not identical, to fragmin and is structurally and functionally very homologous to gelsolin; cap42(b) is Physarum actin. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4149–4157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- André E., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M., Noegel A. Severin, gelsolin, and villin share a homologous sequence in regions presumed to contain F-actin severing domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):722–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpin M., Pringault E., Finidori J., Garcia A., Jeltsch J. M., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. Sequence of human villin: a large duplicated domain homologous with other actin-severing proteins and a unique small carboxy-terminal domain related to villin specificity. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1759–1766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller K., Arpin M., Pringault E., Mangeat P., Reggio H. Differential distribution of villin and villin MRNA in mouse intestinal epithelial cells. Differentiation. 1988 Nov;39(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin: the major microfilament-associated protein of the intestinal microvillus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2321–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Powell L. D. Regulation of actin polymerization by villin, a 95,000 dalton cytoskeletal component of intestinal brush borders. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):739–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90550-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezzell R. M., Chafel M. M., Matsudaira P. T. Differential localization of villin and fimbrin during development of the mouse visceral endoderm and intestinal epithelium. Development. 1989 Jun;106(2):407–419. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Huet C., Arpin M., Louvard D. Villin induces microvilli growth and actin redistribution in transfected fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Geisler N., Kaulfus P., Weber K. Demonstration of at least two different actin-binding sites in villin, a calcium-regulated modulator of F-actin organization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8156–8161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Weber K. Calcium control of microfilaments: uncoupling of the F-actin-severing and -bundling activity of villin by limited proteolysis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2810–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Matsudaira P. T. Functional comparison of villin and gelsolin. Effects of Ca2+, KCl, and polyphosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16738–16743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Mehl R., Yin H. L. Genomic organization and biosynthesis of secreted and cytoplasmic forms of gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):375–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Stossel T. P., Orkin S. H., Mole J. E., Colten H. R., Yin H. L. Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):455–458. doi: 10.1038/323455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunoury R., Robine S., Pringault E., Huet C., Guénet J. L., Gaillard J. A., Louvard D. Villin expression in the visceral endoderm and in the gut anlage during early mouse embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A., Wharton K. A., Falco N., Howe C. L. Regulation of microvillus structure: calcium-dependent solation and cross-linking of actin filaments in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):809–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringault E., Arpin M., Garcia A., Finidori J., Louvard D. A human villin cDNA clone to investigate the differentiation of intestinal and kidney cells in vivo and in culture. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3119–3124. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robine S., Huet C., Moll R., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Coudrier E., Zweibaum A., Louvard D. Can villin be used to identify malignant and undifferentiated normal digestive epithelial cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8488–8492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau-Merck M. F., Simon-Chazottes D., Arpin M., Pringault E., Louvard D., Guénet J. L., Berger R. Localization of the villin gene on human chromosome 2q35-q36 and on mouse chromosome 1. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):130–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00278181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]