Abstract
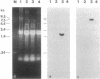
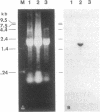
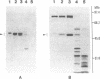
We report a phenomenon previously unknown for oviparous animals; in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes a serine carboxypeptidase is synthesized extraovarially and then internalized by oocytes. The cDNA encoding mosquito vitellogenic carboxypeptidase (VCP) was cloned and sequenced. The VCP cDNA hybridizes to a 1.5-kilobase mRNA present only in the fat body of vitellogenic females. The deduced amino acid sequence of VCP shares significant homology with members of the serine carboxypeptidase family. Binding assays using a serine protease inhibitor, [3H]diisopropyl fluorophosphate, showed that VCP is activated in eggs at the onset of embryonic development. Activation of VCP is associated with the reduction in its size from 53 kDa (inactive proenzyme) to 48 kDa (active enzyme). The active, 48-kDa, form of VCP is maximally present at the middle of embryonic development and disappears by the end.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baulcombe D. C., Barker R. F., Jarvis M. G. A gibberellin responsive wheat gene has homology to yeast carboxypeptidase Y. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13726–13735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S. G., Raikhel A. S. Mosquito vitellogenin subunits originate from a common precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):436–442. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhadialla T. S., Raikhel A. S. Biosynthesis of mosquito vitellogenin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9924–9933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmochowska A., Dignard D., Henning D., Thomas D. Y., Bussey H. Yeast KEX1 gene encodes a putative protease with a carboxypeptidase B-like function involved in killer toxin and alpha-factor precursor processing. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galjart N. J., Gillemans N., Harris A., van der Horst G. T., Verheijen F. W., Galjaard H., d'Azzo A. Expression of cDNA encoding the human "protective protein" associated with lysosomal beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase: homology to yeast proteases. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):755–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90999-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galjart N. J., Gillemans N., Meijer D., d'Azzo A. Mouse "protective protein". cDNA cloning, sequence comparison, and expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4678–4684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R., Moore S., Stein W. H. Serine at the active center of yeast carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8366–8369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indrasith L. S., Sasaki T., Yamashita O. A unique protease responsible for selective degradation of a yolk protein in Bombyx mori. Purification, characterization, and cleavage profile. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1045–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama T., Takahashi S. Y. Purification and characterization of a cysteine proteinase from silkworm eggs. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 5;193(1):203–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawooya J. K., Osir E. O., Law J. H. Physical and chemical properties of microvitellogenin. A protein from the egg of the tobacco hornworm moth, Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10844–10849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Wu X. W., Gibbs R. A., Cook R. G., Muzny D. M., Caskey C. T. Generation of cDNA probes directed by amino acid sequence: cloning of urate oxidase. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1288–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.3344434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina M., León P., Vallejo C. G. Drosophila cathepsin B-like proteinase: a suggested role in yolk degradation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jun;263(2):355–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90646-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raikhel A. S., Dhadialla T. S. Accumulation of yolk proteins in insect oocytes. Annu Rev Entomol. 1992;37:217–251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai N., Mori S., Izumi S., Haino-Fukushima K., Ogura T., Maekawa H., Tomino S. Structures and expression of mRNAs coding for major plasma proteins of Bombyx mori. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 28;949(2):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner C. J., Quigley J. P. Detection, identification, and partial characterization of serine proteases and esterases in biological systems. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 1;122(1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valls L. A., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Protein sorting in yeast: the localization determinant of yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y resides in the propeptide. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W. Evolution and expression of vitellogenin genes. Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. Y., Cole K. D., Law J. H. The nucleotide sequence of a microvitellogenin encoding gene from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Gene. 1989 Aug 15;80(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. Y., Cole K. D., Law J. H. cDNA cloning and deduced amino acid sequence of microvitellogenin, a female specific hemolymph and egg protein from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8851–8855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. P., Liao D. I., Bullock T., Remington S. J., Breddam K. Crystallization of serine carboxypeptidases. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):301–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90352-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]