Abstract
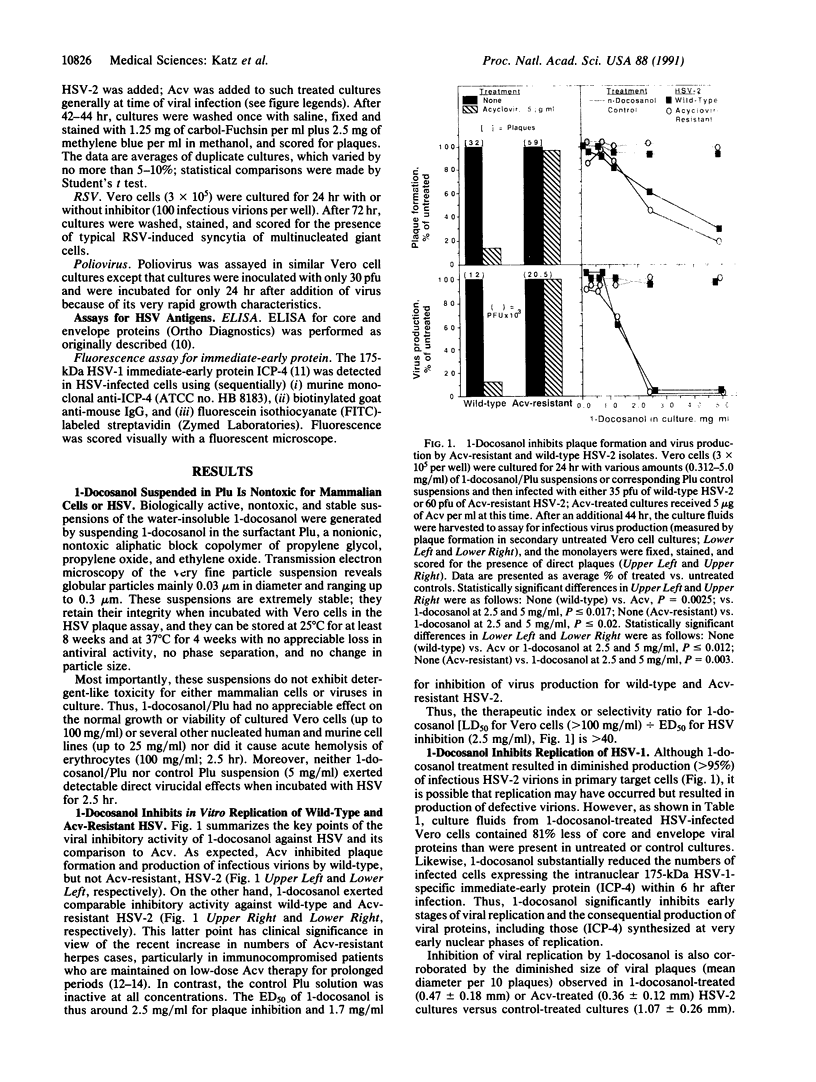
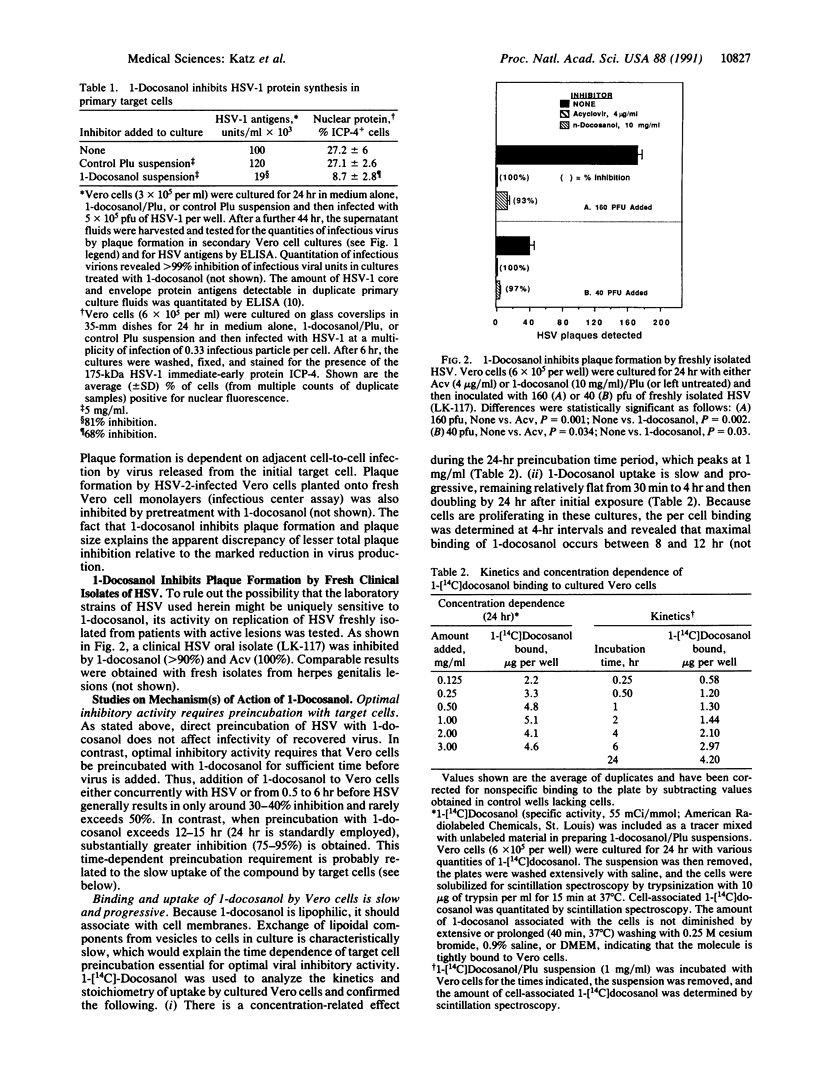
This article reports that 1-docosanol, a 22-carbon-long saturated alcohol, exerts a substantial inhibitory effect on replication of certain viruses (e.g., herpes simplex virus and respiratory syncytial virus) within primary target cells in vitro. To study the basis for its viral inhibitory activity, a suspension of 1-docosanol was formulated in an inert and nontoxic surfactant, Pluronic F-68; this suspension exerted potent inhibitory activity on the ability of susceptible viruses to infect cultured target cells. Susceptible viruses included wild-type herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 as well as acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus 2 and also respiratory syncytial virus--all of which are lipid-enveloped. In contrast, nonenveloped poliovirus was not susceptible to the inhibitory action of 1-docosanol. Although the precise mechanism has yet to be defined, current evidence suggests that 1-docosanol inhibits viral replication by interfering with the early intracellular events surrounding viral entry into target cells. It is possible that interaction between the highly lipophilic compound and components of target cell membranes renders such target cells less susceptible to viral fusion and/or entry. If this mechanism proves to be correct, 1-docosanol may provide a broad spectrum activity against many different viruses, especially those with lipid-containing envelopes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatis P. A., Miller C. H., Schrager L. E., Crumpacker C. S. Successful treatment with foscarnet of an acyclovir-resistant mucocutaneous infection with herpes simplex virus in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):297–300. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich K. S., Mills J., Chatis P., Mertz G. J., Busch D. F., Follansbee S. E., Grant R. M., Crumpacker C. S. Acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):293–296. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maugh T. H., 2nd Chemotherapy: antiviral agents come of age. Science. 1976 Apr 9;192(4235):128–132. doi: 10.1126/science.192.4235.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride P. T., Clark L., Krueger G. G. Evaluation of triacontanol-containing compounds as anti-inflammatory agents using guinea pig models. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Oct;89(4):380–383. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12471763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rose H. M., Mednis B. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. I. Entry. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):507–516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.507-516.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safrin S., Assaykeen T., Follansbee S., Mills J. Foscarnet therapy for acyclovir-resistant mucocutaneous herpes simplex virus infection in 26 AIDS patients: preliminary data. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1078–1084. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J., Auperin D., Snipes W. Extreme sensitivity of enveloped viruses, including herpes simplex, to long-chain unsaturated monoglycerides and alcohols. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snipes W., Person S., Keller G., Taylor W., Keith A. Inactivation of lipid-containing viruses by long-chain alcohols. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler T., Meurman O. H., Arstila P. P., Halonen P. E. Solid-phase enzyme-immunoassay for the detection of herpes simplex virus antigens in clinical specimens. J Virol Methods. 1983 Jul;7(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(83)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]