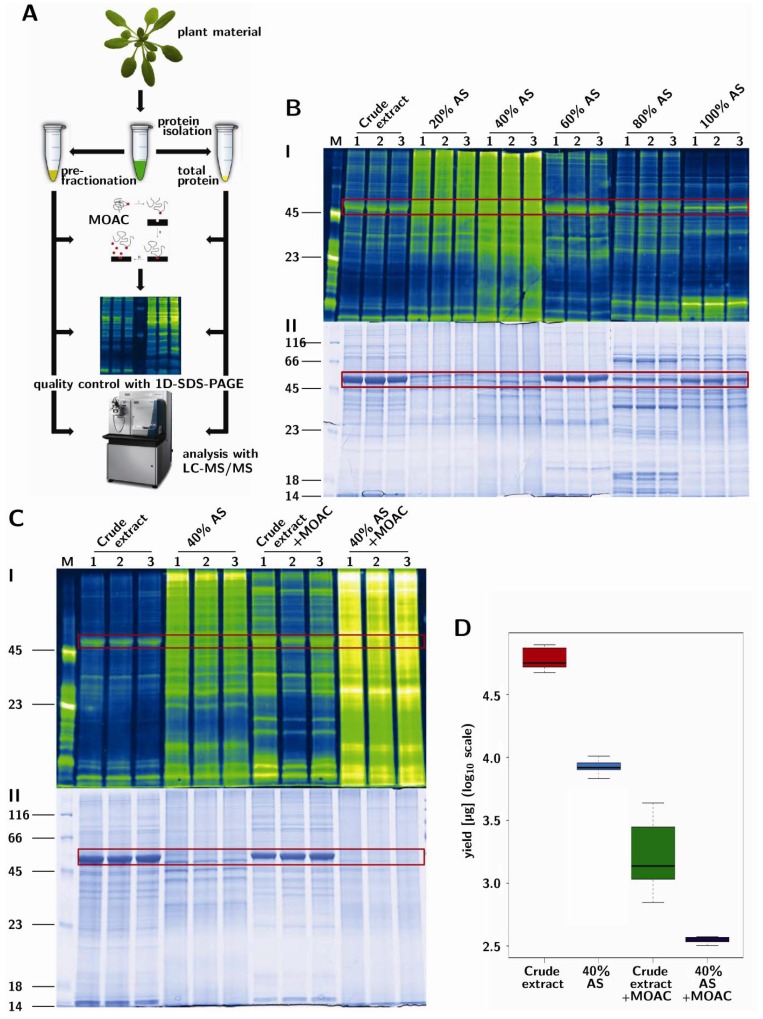
Figure 1.
Prefractionation-assisted phosphoprotein enrichment (PAPE). (A) Experimental setup. Arabidopsis soluble leaf proteins were either extracted with phenol to obtain the crude extract (total protein) or pre-fractionated by 40% ammonium sulfate precipitation. Subsequently, phosphoproteins were enriched using metal oxide affinity chromatography (MOAC). Quality control was assessed with SDS-PAGE and phospho-specific Pro-Q Diamond staining. Mass spectrometry analysis was performed with on-line nano-LC (Easy-nLC II) FT-mass spectrometry (LTQ Orbitrap Velos); (B) SDS-PAGE showing the crude extract and stepwise ammonium sulfate (AS) fractionations. Each step was performed three times (lanes labeled 1, 2 and 3). Visualization of proteins was achieved with (I) Pro-Q Diamond phosphoprotein staining in false-color representation and (II) colloidal coomassie staining. Protein molecular weights are indicated on the left-hand margin. (C) SDS-PAGE of different extraction and phosphoprotein enrichment steps, with visualization of the proteins as described above. Boxed areas mark the position of the large subunit of RuBisCO. (D) Boxplot depiction of protein yield (log10 microgram of proteins) from 25 g of leaf material (n = 6).