Figure 6. A model depicting the mechanism of action of LCL161/OBX in MM cells.
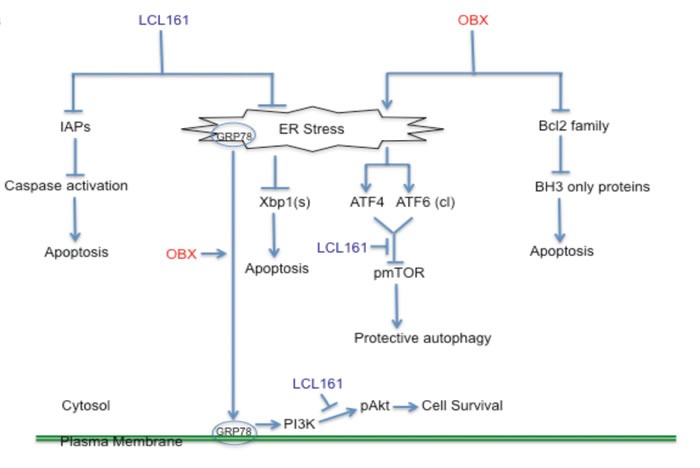
LCL161 binds and inhibits the functions of IAPs causing activation of caspases and apoptosis induction. OBX modulates the binding of the pro-apoptotic Bcl2 family proteins with the anti- apoptotic Bcl2 family proteins and causes the activation of BH3 only proteins, which eventually leads to apoptosis induction. In addition, both OBX and LCL161 modulate ER stress and the subsequent activation of specific branches of the UPR pathway. OBX activates the PERK/peif2α/ATF4 and ATF6 branches of the UPR pathway. One or both of these possibly contribute to pmTOR inhibition, which leads to protective autophagy. OBX also causes cell surface localization of GRP78, which then activates Akt through a PI3K dependent mechanism. LCL161, on the other hand, causes reduction in Xbp1 splicing. In addition, LCL161 blocks OBX induced pAkt, which then sensitizes cells to OBX treatment. We also observed that pS6 (a protein downstream of mTOR) down regulation by OBX was largely prevented by LCL161. Thus, LCL161/OBX combination induces synergistic apoptosis in MM cells through numerous mechanisms.
