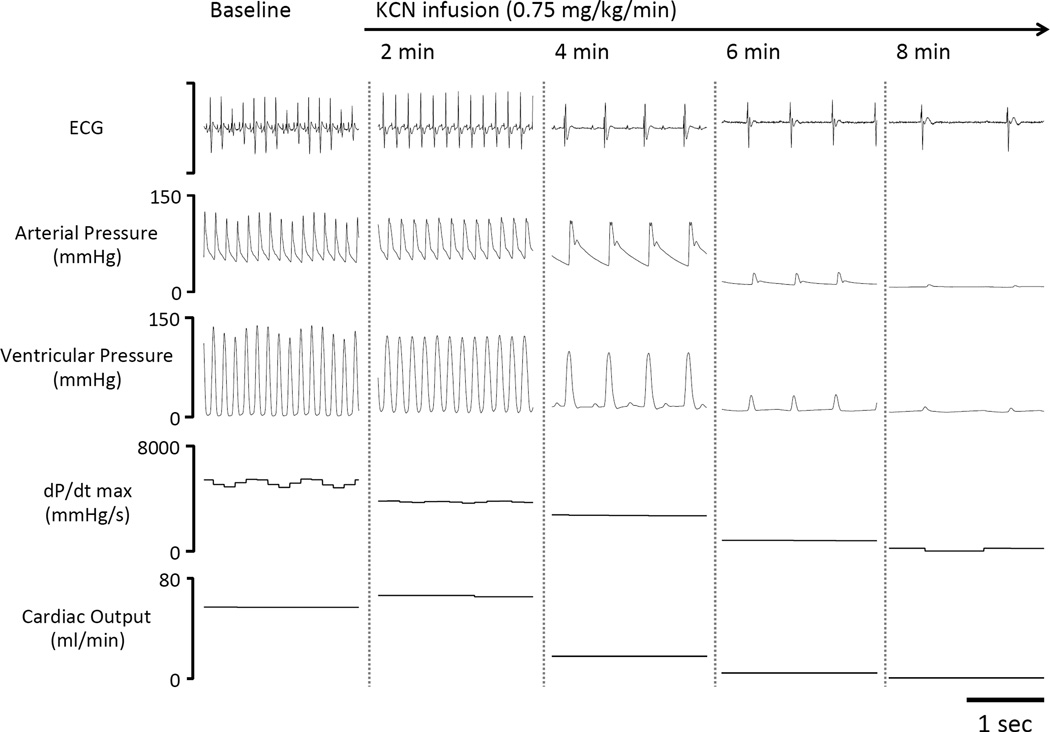
Figure 9.
Recording in one mechanically ventilated rat displaying the electrocardiogram signal (ECG), arterial pressure, ventricular pressure, dP/dt max and computed cardiac output at various times during KCN infusion at a higher dose (0.75 mg/kg/min). In this example, cardiac output (CO) started to decrease between 3 and 4 min into KCN infusion along with an abrupt drop in HR and dP/dt max, rapidly leading to a severe cardiogenic shock and a pulseless electrical activity, as demonstrated by the persistence of an ECG signal without effective cardiac contractions.