Abstract
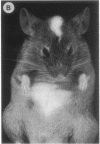
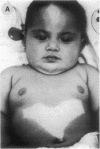
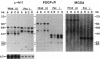
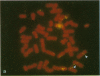
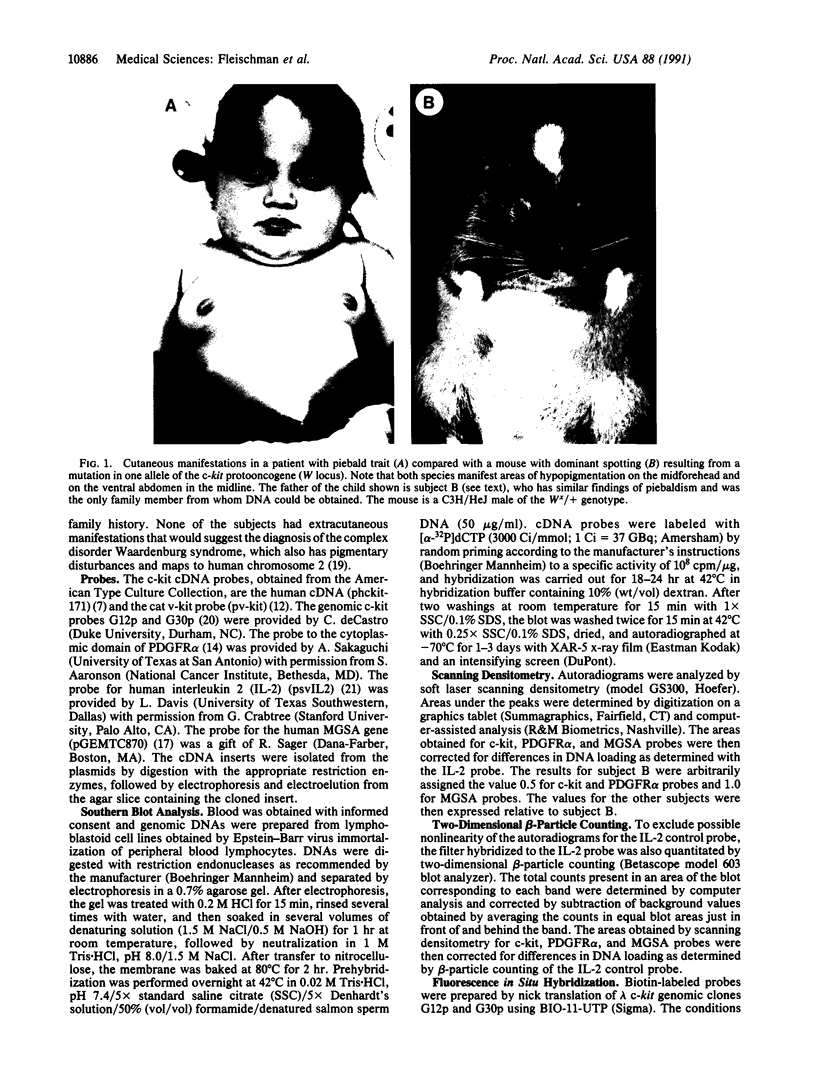
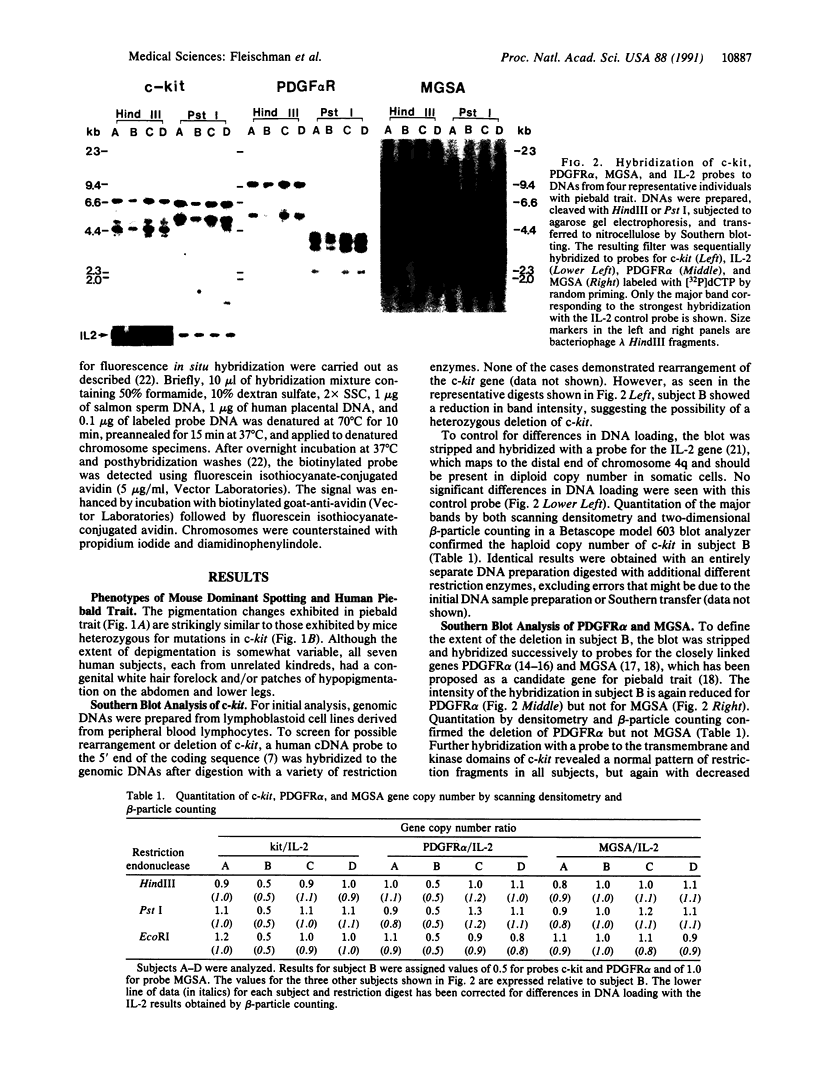
The protooncogene c-kit is critical for development of hematopoietic stem cells, germ cells, and melanoblasts in the mouse. Homozygous mutations of this gene in the mouse cause anemia, infertility, and albinism, whereas heterozygous mutant mice usually exhibit only a white forehead blaze and depigmentation of the ventral body, tail, and feet. The heterozygous mouse phenotype is very similar to human piebald trait, which is characterized by a congenital white hair forelock and ventral and extremity depigmentation. To investigate the possibility that alterations in the human c-kit gene may be a cause of piebald trait, DNA from seven unrelated affected individuals was examined by Southern blot analysis. One subject, although cytogenetically normal, has a heterozygous deletion of the c-kit protooncogene. This deletion encompasses the entire coding region for c-kit and also involves the closely linked gene for platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha. Fluorescence in situ hybridization of genomic c-kit probes to metaphase chromosomes independently confirmed the deletion in this case. These findings provide molecular evidence mapping piebald trait to the c-kit locus on chromosome 4. Although we cannot exclude the involvement of other closely linked genes, the demonstration of a genomic c-kit deletion in one subject with piebald trait and the marked concordance of the human and mouse phenotypes provide strong evidence for the role of c-kit in the development of human melanocytes and in the pathogenesis of piebald trait.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André C., d'Auriol L., Lacombe C., Gisselbrecht S., Galibert F. c-kit mRNA expression in human and murine hematopoietic cell lines. Oncogene. 1989 Aug;4(8):1047–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anisowicz A., Zajchowski D., Stenman G., Sager R. Functional diversity of gro gene expression in human fibroblasts and mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9645–9649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Cho B. C., Donovan P. J., Jenkins N. A., Cosman D., Anderson D., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E. Mast cell growth factor maps near the steel locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is deleted in a number of steel alleles. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90298-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy C., Newton V., Wellesley D., Harris R., Read A. P. Assignment of the locus for Waardenburg syndrome type I to human chromosome 2q37 and possible homology to the Splotch mouse. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1017–1023. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., McFarland E. C., Russell E. S. Analysis of pleiotropism at the dominant white-spotting (W) locus of the house mouse: a description of ten new W alleles. Genetics. 1981 Feb;97(2):337–361. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronwald R. G., Adler D. A., Kelly J. D., Disteche C. M., Bowen-Pope D. F. The human PDGF receptor alpha-subunit gene maps to chromosome 4 in close proximity to c-kit. Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;85(3):383–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00206767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Smith K. A., Fornace A. J., Jr, Comeau C. M., Wiskocil R. L., Crabtree G. R. T-cell growth factor: complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the gene in normal and malignant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1634–1638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoo J. J., Haslam R. H., van Orman C. Tentative assignment of piebald trait gene to chromosome band 4q12. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):230–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00401233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M. A., Honeyman M. M., Mayne A. J., Tarlow M. J. Homozygosity in piebald trait. J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;24(9):568–571. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.9.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Glenister P. H., Loutit J. F., Evans E. P., Peters J. A presumed deletion covering the W and Ph loci of the mouse. Genet Res. 1984 Oct;44(2):161–168. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300026367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Heidaran M., Miki T., Popescu N., La Rochelle W., Kraus M., Pierce J., Aaronson S. Isolation of a novel receptor cDNA establishes the existence of two PDGF receptor genes. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):800–804. doi: 10.1126/science.2536956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Zsebo K. M., Hogan B. L. Embryonic expression of a haematopoietic growth factor encoded by the Sl locus and the ligand for c-kit. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):667–669. doi: 10.1038/347667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer T. C. Interactions between normal and pigment cell populations mutant at the dominant-spotting (W) and steel (Sl) loci in the mouse. J Exp Zool. 1979 Oct;210(1):81–88. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402100109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang C. Y., Kelly J., Brownlee C., Jackson-Grusby L., Stiles C., Bowen-Pope D. Selective expression of PDGF A and its receptor during early mouse embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):114–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90181-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz B. Gene control of mammalian differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:411–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Avivi A., Zimmer Y., Givol D., Yarden Y., Lonai P. Developmental expression of c-kit, a proto-oncogene encoded by the W locus. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):911–923. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortonne J. P. Piebaldism, Waardenburg's syndrome, and related disorders. "Neural crest depigmentation syndromes"? Dermatol Clin. 1988 Apr;6(2):205–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. H., Ray P., Brown K., Barker P. E., Jhanwar S., Ruddle F. H., Besmer P. Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family--oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A., Balentien E., Thomas H. G., Flaggs G., Barton D. E., Spiess J., Bordoni R., Francke U., Derynck R. Molecular characterization and chromosomal mapping of melanoma growth stimulatory activity, a growth factor structurally related to beta-thromboglobulin. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2025–2033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible R. H. Clonal distribution of melanocytes in piebald-spotted and variegated mice. J Exp Zool. 1969 Oct;172(2):181–199. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401720205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle A. G., Truslove G. M. A gene triplet in the mouse. Genet Res. 1970 Apr;15(2):227–235. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. A., Seldin M. F., Martinez L., Watson M. L., Choudhury G. G., Lalley P. A., Pierce J., Aaronson S., Barker J., Naylor S. L. Mouse platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha gene is deleted in W19H and patch mutations on chromosome 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4811–4815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman G., Eriksson A., Claesson-Welsh L. Human PDGFA receptor gene maps to the same region on chromosome 4 as the KIT oncogene. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1989 Nov;1(2):155–158. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. A., Mercola M., Anderson E., Wang C. Y., Stiles C. D., Bowen-Pope D. F., Chapman V. M. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha-subunit gene (Pdgfra) is deleted in the mouse patch (Ph) mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmeyer T., Peter S., Hartmann M., Munemitsu S., Ackermann R., Ullrich A., Slamon D. J. Expression of the hst-1 and c-kit protooncogenes in human testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 1;51(7):1811–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telfer M. A., Sugar M., Jaeger E. A., Mulcahy J. Dominant piebald trait (white forelock and leukoderma) with neurological impairment. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jul;23(4):383–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Auriol L., Mattei M. G., Andre C., Galibert F. Localization of the human c-kit protooncogene on the q11-q12 region of chromosome 4. Hum Genet. 1988 Apr;78(4):374–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00291740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]