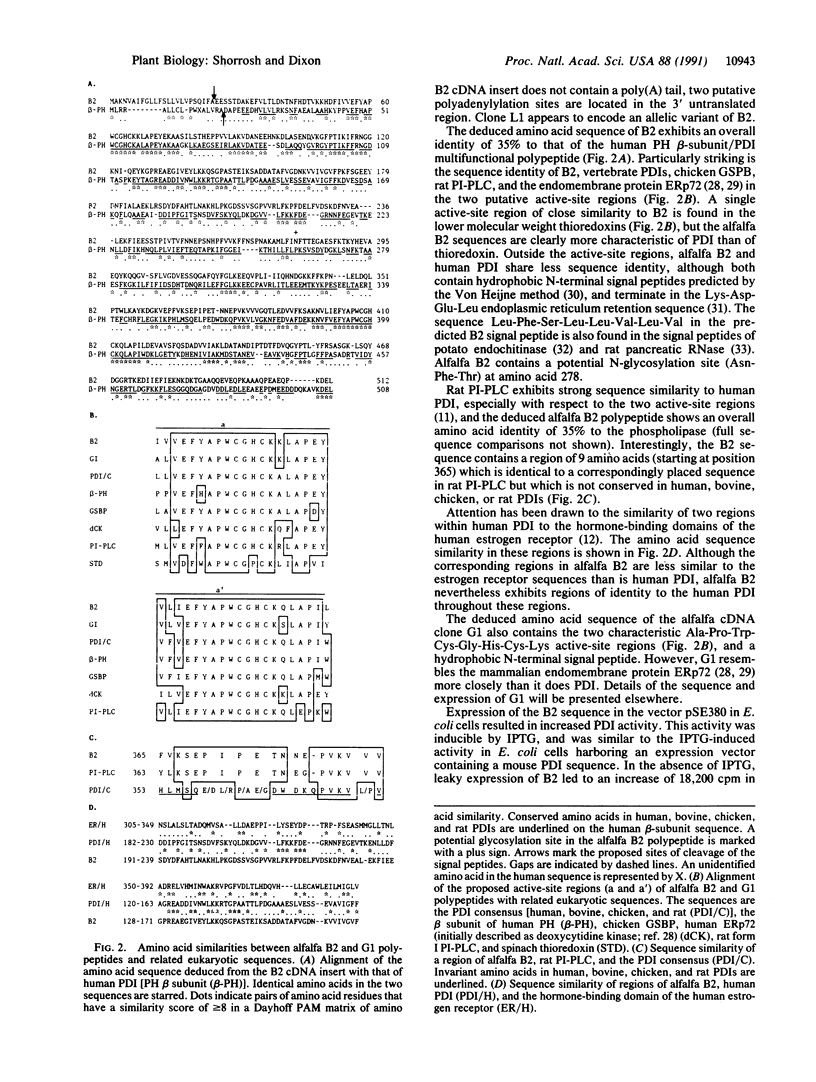
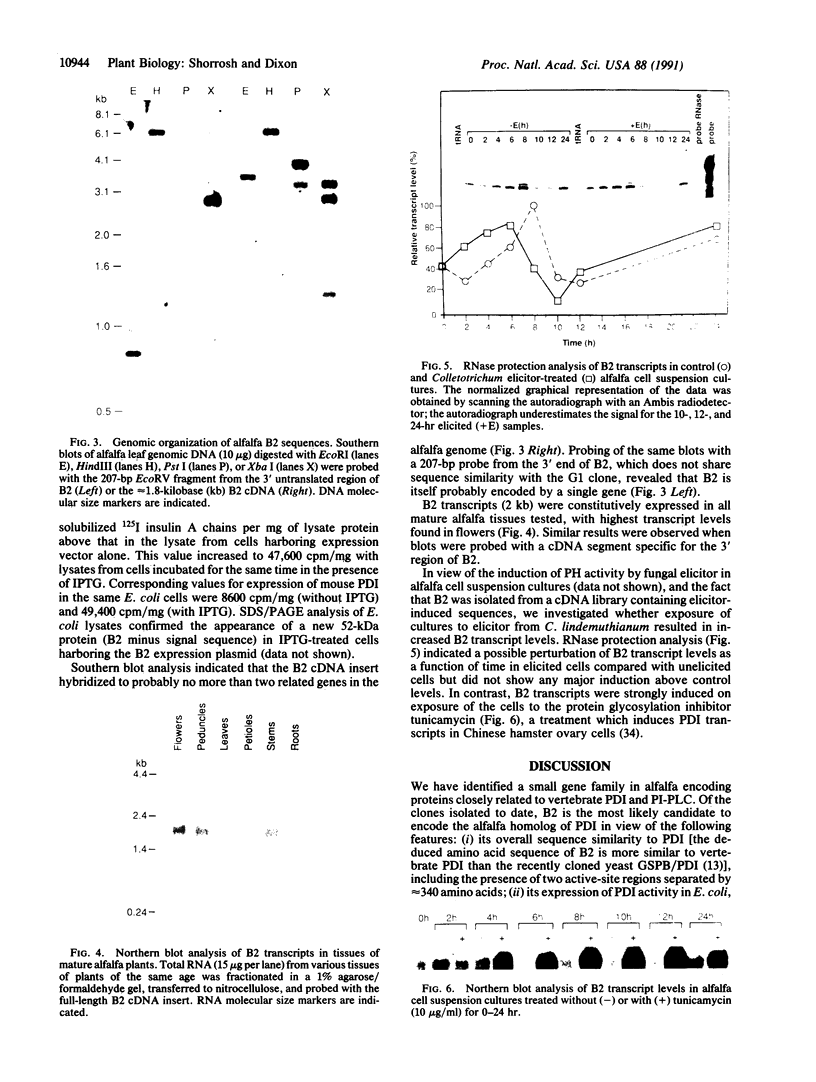
Abstract
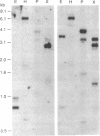
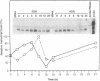
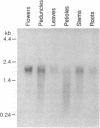
cDNA clones containing sequence similarity to the multifunctional vertebrate protein disulfide-isomerase (PDI, EC 5.3.4.1) were isolated from an alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cDNA library by screening with a cDNA sequence encoding human PDI. The polypeptide encoded by a clone designated B2 consisted of 512 amino acids and was characterized by a 24-amino acid hydrophobic leader sequence, two regions with absolute identity to the vertebrate PDI active site (Ala-Pro-Trp-Cys-Gly-His-Cys-Lys), and a C-terminal endoplasmic reticulum retention signal (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu). The overall identity of the B2 sequence to that of human PDI was 35% at the amino acid level (79% when conservative substitutions were included) and 39% at the nucleotide level; this included homology between B2 and the region of human PDI believed to be involved in binding estrogens. The deduced amino acid sequence of B2 was also 35% identical to that of a rat form I phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Lysates from Escherichia coli cells harboring an expression plasmid bearing the B2 sequence contained significantly elevated levels of PDI activity. Southern analysis indicated the presence of a small PDI-related gene family in alfalfa, of which B2 appeared to correspond to a single gene. An approximately 2-kilobase B2 transcript was expressed in all alfalfa organs tested. In alfalfa cell suspension cultures, B2 transcripts were strongly induced by tunicamycin but not by exposure to fungal elicitor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett C. F., Balcarek J. M., Varrichio A., Crooke S. T. Molecular cloning and complete amino-acid sequence of form-I phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):268–270. doi: 10.1038/334268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Superpolylinkers in cloning and expression vectors. DNA. 1989 Dec;8(10):759–777. doi: 10.1089/dna.1989.8.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Morin J. E., Dixon J. E. Purification and characterization of a thiol:protein disulfide oxidoreductase from bovine liver. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7163–7167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Inukai M., Inouye M. Dual functions of the signal peptide in protein transfer across the membrane. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalkin K., Edwards R., Edington B., Dixon R. A. Stress Responses in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): I. Induction of Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis and Hydrolytic Enzymes in Elicitor-Treated Cell Suspension Cultures. Plant Physiol. 1990 Feb;92(2):440–446. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Wasley L. C., Raney P., Haugejorden S., Green M., Kaufman R. J. The stress response in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Regulation of ERp72 and protein disulfide isomerase expression and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):22029–22034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Ellis L., Blacher R. W., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Sequence of protein disulphide isomerase and implications of its relationship to thioredoxin. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):267–270. doi: 10.1038/317267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B. Protein disulfide isomerase: multiple roles in the modification of nascent secretory proteins. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. Protein chemistry. Folding into the right shape. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):196–197. doi: 10.1038/329196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor J. J. Primary structure of an endochitinase mRNA from Solanum tuberosum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5210–5210. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geetha-Habib M., Noiva R., Kaplan H. A., Lennarz W. J. Glycosylation site binding protein, a component of oligosaccharyl transferase, is highly similar to three other 57 kd luminal proteins of the ER. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1053–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins H. C., Blackburn E. C., Freedman R. B. Comparison of the activities of protein disulphide-isomerase and thioredoxin in catalysing disulphide isomerization in a protein substrate. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):349–353. doi: 10.1042/bj2750349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. H., Tomich J. M., Wu H., Jong A., Holcenberg J. Human deoxycytidine kinase. Sequence of cDNA clones and analysis of expression in cell lines with and without enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5353–5353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaska D. D., Günzler V., Kivirikko K. I., Myllylä R. Characterization of a low-relative-molecular-mass prolyl 4-hydroxylase from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):483–490. doi: 10.1042/bj2410483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaska D. D., Kivirikko K. I., Myllylä R. Purification and characterization of protein disulphide-isomerase from the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardii. A 120 kDa dimer antigenically distinct from the vertebrate enzyme. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):63–68. doi: 10.1042/bj2680063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMantia M., Miura T., Tachikawa H., Kaplan H. A., Lennarz W. J., Mizunaga T. Glycosylation site binding protein and protein disulfide isomerase are identical and essential for cell viability in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4453–4457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Stary S. J., Swift G. H. Rat pancreatic ribonuclease messenger RNA. The nucleotide sequence of the entire mRNA and the derived amino acid sequence of the pre-enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14582–14585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavandad M., Edwards R., Liang X., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. Effects of trans-Cinnamic Acid on Expression of the Bean Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Gene Family. Plant Physiol. 1990 Oct;94(2):671–680. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella R. A., Srinivasan M., Haugejorden S. M., Green M. ERp72, an abundant luminal endoplasmic reticulum protein, contains three copies of the active site sequences of protein disulfide isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1094–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkonen T., Kivirikko K. I., Pihlajaniemi T. Molecular cloning of a multifunctional chicken protein acting as the prolyl 4-hydroxylase beta-subunit, protein disulphide-isomerase and a cellular thyroid-hormone-binding protein. Comparison of cDNA-deduced amino acid sequences with those in other species. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):1005–1011. doi: 10.1042/bj2561005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Helaakoski T., Tasanen K., Myllylä R., Huhtala M. L., Koivu J., Kivirikko K. I. Molecular cloning of the beta-subunit of human prolyl 4-hydroxylase. This subunit and protein disulphide isomerase are products of the same gene. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):643–649. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate B. F., Schaller G. E., Sussman M. R., Crain R. C. Characterization of a Polyphosphoinositide Phospholipase C from the Plasma Membrane of Avena sativa. Plant Physiol. 1989 Dec;91(4):1275–1279. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.4.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsibris J. C., Hunt L. T., Ballejo G., Barker W. C., Toney L. J., Spellacy W. N. Selective inhibition of protein disulfide isomerase by estrogens. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13967–13970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterau J. R., Combs K. A., Spinner S. N., Joiner B. J. Protein disulfide isomerase is a component of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9800–9807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Yamamoto T., Hayashi H., Koya S., Takikawa H., Toyoshima K., Horiuchi R. Sequence of membrane-associated thyroid hormone binding protein from bovine liver: its identity with protein disulphide isomerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1485–1492. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90817-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]