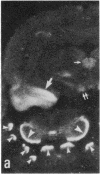
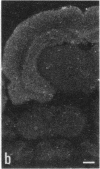
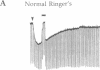
Abstract
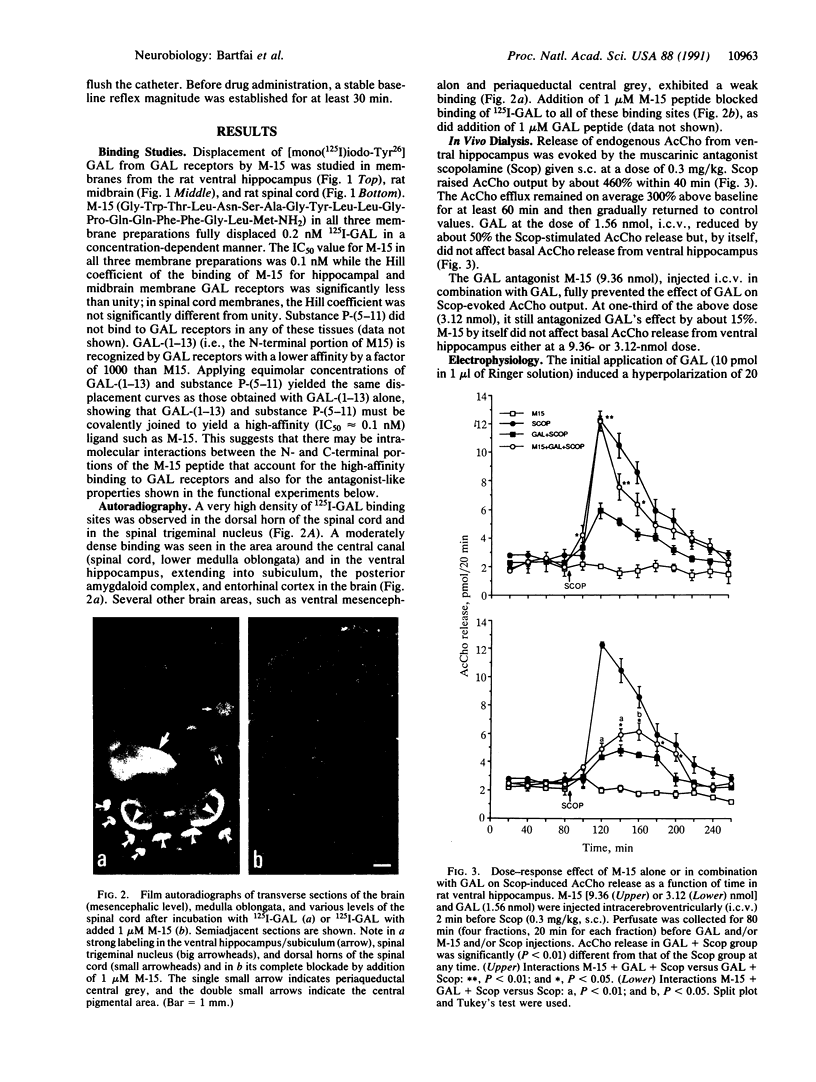
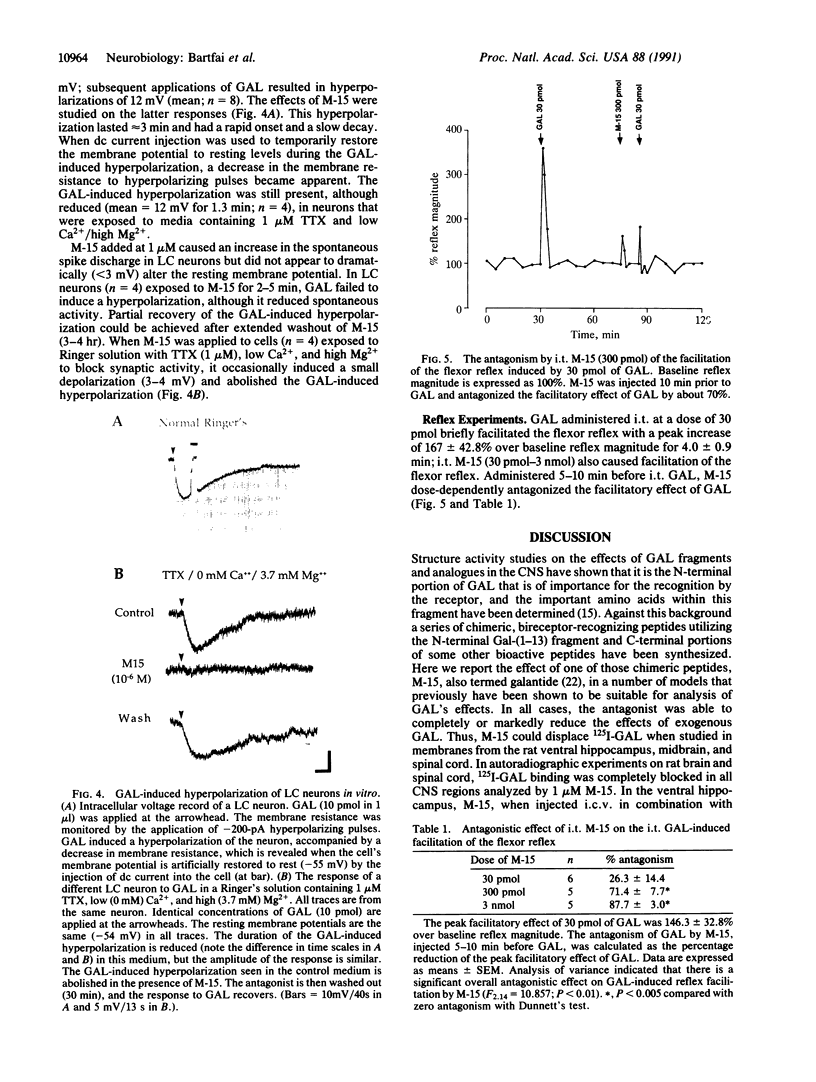
The 20-amino acid peptide M-15 binds with high affinity (IC50 approximately 0.1 nM) to 125I-labeled galanin (125I-GAL) binding sites in membranes from the ventral hippocampus, midbrain, and rat spinal cord. Receptor autoradiographic studies show that M-15 can displace 125I-GAL from all labeled sites. M-15 acts as a reversible high-affinity antagonist in blocking the inhibitory effects of GAL on the evoked release of acetylcholine in vivo in the hippocampus and on the GAL-induced hyperpolarization of locus coeruleus neurons in slices. M-15 also blocks the facilitatory effects of GAL on the spinal flexor reflex. Thus, the chimeric peptide M-15 [GAL-(1-13)-substance P-(5-11)amide] represents the first antagonist to the neuronal actions of GAL.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghajanian G. K., Cedarbaum J. M., Wang R. Y. Evidence for norepinephrine-mediated collateral inhibition of locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 18;136(3):570–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Lamour Y., Nicoll R. A. Galanin blocks the slow cholinergic EPSP in CA1 pyramidal neurons from ventral hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 19;164(2):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis M., Aston-Jones G. Evidence for self- and neighbor-mediated postactivation inhibition of locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res. 1986 May 28;374(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Berthold M., Bedecs K., Undén A., Bartfai T., Bertorelli R., Consolo S., Crawley J., Martin B., Nilsson S. N-terminal galanin-(1-16) fragment is an agonist at the hippocampal galanin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9588–9591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Wu C. F., Consolo S., Nordström O., Brynne N., Bartfai T., Melander T., Hökfelt T. Galanin inhibits acetylcholine release in the ventral hippocampus of the rat: histochemical, autoradiographic, in vivo, and in vitro studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7339–7343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves P. M., Wilson C. J. Fine structure of rat locus coeruleus. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Oct 15;193(4):841–852. doi: 10.1002/cne.901930402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves P. M., Wilson C. J. Monoaminergic presynaptic axons and dendrites in rat locus coeruleus seen in reconstructions of serial sections. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Oct 15;193(4):853–862. doi: 10.1002/cne.901930403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagny-Pourmir I., Lorinet A. M., Yanaihara N., Laburthe M. Structural requirements for galanin interaction with receptors from pancreatic beta cells and from brain tissue of the rat. Peptides. 1989 Jul-Aug;10(4):757–761. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastropaolo J., Nadi N. S., Ostrowski N. L., Crawley J. N. Galanin antagonizes acetylcholine on a memory task in basal forebrain-lesioned rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9841–9845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Nilsson S., Brodin E. Visualization of galanin binding sites in the rat central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 May 27;124(3):381–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Cuello A. C., Oertel W. H., Verhofstad A., Goldstein M. Coexistence of galanin-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines, 5-hydroxytryptamine, GABA and neuropeptides in the rat CNS. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3640–3654. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03640.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Köhler C., Nilsson S., Hökfelt T., Brodin E., Theodorsson E., Bartfai T. Autoradiographic quantitation and anatomical mapping of 125I-galanin binding sites in the rat central nervous system. J Chem Neuroanat. 1988 Jul-Aug;1(4):213–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Staines W. A., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Eckenstein F., Salvaterra P. M., Wainer B. H. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in cholinergic neurons of the septum-basal forebrain complex projecting to the hippocampus of the rat. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 23;360(1-2):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seutin V., Verbanck P., Massotte L., Dresse A. Galanin decreases the activity of locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 19;164(2):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Sills M. A., Jacobowitz D. M. Autoradiographic distribution of 125I-galanin binding sites in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):1029–1042. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström E., Archer T., Melander T., Hökfelt T. Galanin impairs acquisition but not retrieval of spatial memory in rats studied in the Morris swim maze. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 7;88(3):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Villar M. J., Hökfelt T. The effects of intrathecal galanin and C-fiber stimulation on the flexor reflex in the rat. Brain Res. 1989 May 8;486(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., North R. A., Shefner S. A., Nishi S., Egan T. M. Membrane properties of rat locus coeruleus neurones. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):137–156. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90265-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X.-J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Villar M. J., Fahrenkrug J., Hökfelt T. On the Role of Galanin, Substance P and Other Neuropeptides in Primary Sensory Neurons of the Rat: Studies on Spinal Reflex Excitability and Peripheral Axotomy. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(9):733–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]