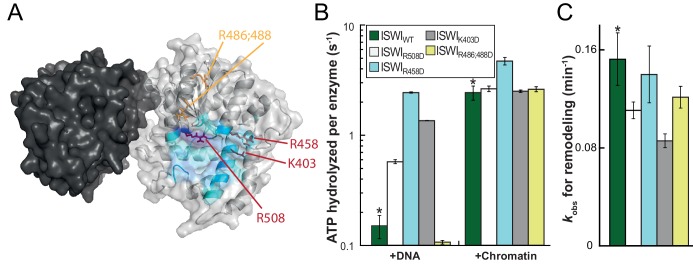
Figure 7. Validation of the predicted binding interface of AcidicN on Lobe 2.
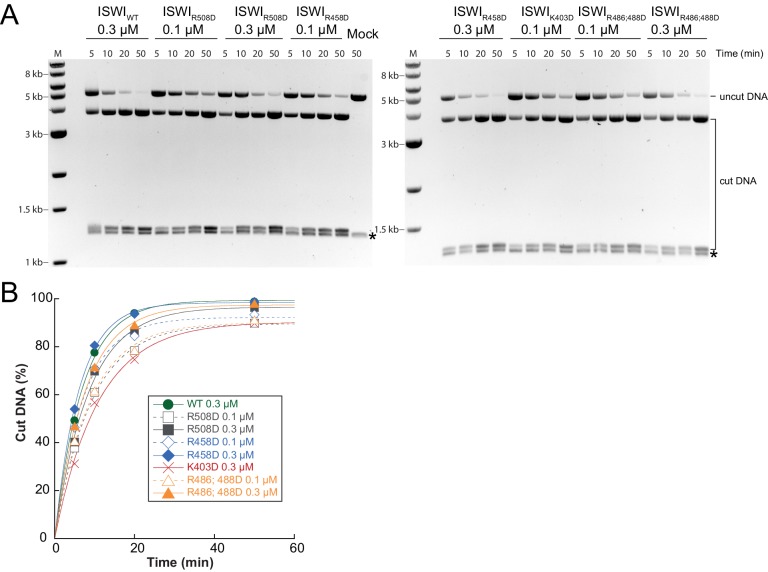
(A) Homology model of the ISWI ATPase domain. Dark and light grey, ATPase lobes 1 and 2, respectively; blue, hypothetical binding interface of AcidicN as in Figure 4—figure supplement 3A. Positively charged residues selected for mutagenesis are shown in red (AcidicN interface mutant) and orange (control mutant). (B) Mutation of the AcidicN interface (K403D, R458D and R508D) strongly upregulated DNA-stimulated ATP hydrolysis relative to ISWIWT, whereas the nucleosome-stimulated ATP turnover was similar. In contrast, a control mutation (R486; 488D) had little effect on ATP hydrolysis. Saturating concentrations of DNA and chromatin were used. Errors are s.d. for ISWIWT and minimal and maximal values of two independent measurements for all other constructs. (C) AcidicN interface variants of ISWI robustly remodeled nucleosomes within twofold of ISWIWT. Nucleosomal arrays containing wild-type H4 were used. Errors are s.d. (n ≥ 3) for ISWIWT and minimal and maximal values of two independent measurements for all other constructs. Raw data of the remodeling assay can be found in Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Color code as in (B). Results for ISWIWT (*) were replotted for comparison from Figure 3B,C.
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE of purified recombinant ISWI constructs analyzed in Figure 7.