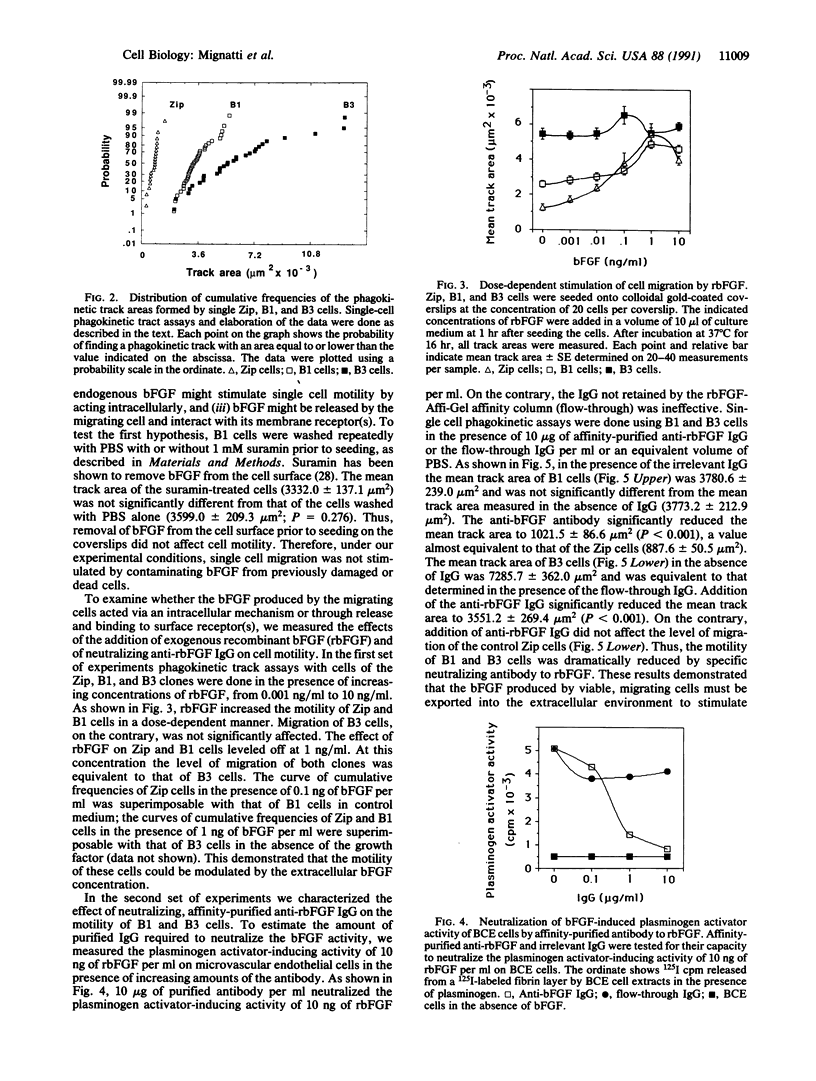
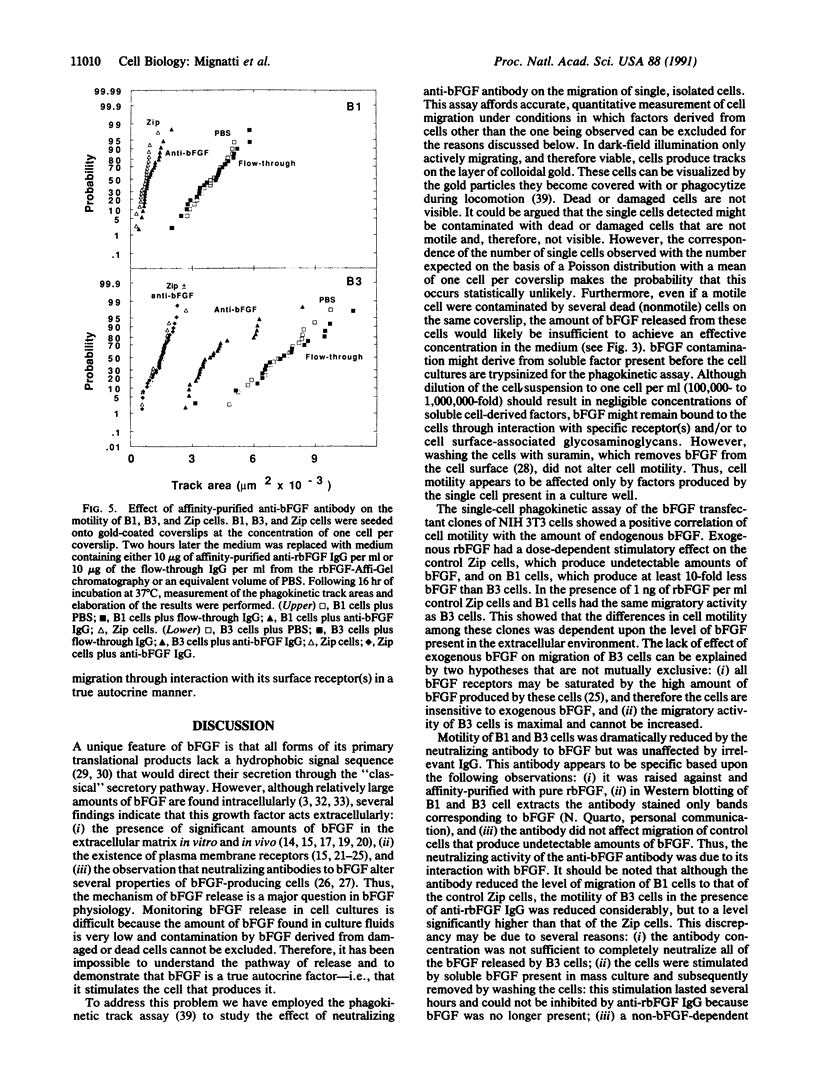
Abstract
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), a protein with angiogenic, mitogenic, and chemotactic properties, lacks a signal sequence and is not secreted via the classical secretory pathway. However, the growth factor is known to act extracellularly. Since no defined mechanism for bFGF release has been described, it has been suggested that this growth factor is released from dead or damaged cells. To test this hypothesis we characterized the effect of exogenously added bFGF and neutralizing antibody on the migration of single, isolated NIH 3T3 cells transfected with bFGF cDNA. Under these conditions the observed cell cannot be affected by bFGF derived from other cells. Cells were seeded onto colloidal gold-coated coverslips at a density of one cell per coverslip. A cell migrating on this substrate produces a track free of refringent gold particles that is measured by an image analyzer. The results showed that cell motility directly correlated with the amount of bFGF released from the migrating cells. Affinity-purified anti-bFGF antibody, but not irrelevant IgG, reduced the level of migration of the bFGF transfectants to that of the control cells transfected with the vector alone, showing that bFGF stimulates migration of the cell that releases it. Thus, bFGF is secreted by viable cells and mediates cell functions via a "true" autocrine mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht-Buehler G. The phagokinetic tracks of 3T3 cells. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Esch F., Mormède P., Ueno N., Ling N., Böhlen P., Ying S. Y., Wehrenberg W. B., Guillemin R. Molecular characterization of fibroblast growth factor: distribution and biological activities in various tissues. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1986;42:143–205. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571142-5.50008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashkin P., Doctrow S., Klagsbrun M., Svahn C. M., Folkman J., Vlodavsky I. Basic fibroblast growth factor binds to subendothelial extracellular matrix and is released by heparitinase and heparin-like molecules. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1737–1743. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Leof E. B., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Suramin inhibition of growth factor receptor binding and mitogenicity in AKR-2B cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jul;132(1):143–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. A., Rifkin D. B. Studies on the role of basic fibroblast growth factor in vivo: inability of neutralizing antibodies to block tumor growth. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):84–98. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMario J., Buffinger N., Yamada S., Strohman R. C. Fibroblast growth factor in the extracellular matrix of dystrophic (mdx) mouse muscle. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):688–690. doi: 10.1126/science.2717945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. C., Zetter B. R. Long-term culture of capillary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Wadzinski M., Ingber D., Vlodavsky I. A heparin-binding angiogenic protein--basic fibroblast growth factor--is stored within basement membrane. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):393–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Ferrara N., Schweigerer L., Neufeld G. Structural characterization and biological functions of fibroblast growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1987 May;8(2):95–114. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Moscatelli D., Jaffe E. A., Rifkin D. B. Plasminogen activator and collagenase production by cultured capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):974–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek A., Culler F. L., Beattie G. M., Lopez A. D., Cuevas P., Baird A. An in vivo model for study of the angiogenic effects of basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):876–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph-Silverstein J., Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. The development of a quantitative RIA for basic fibroblast growth factor using polyclonal antibodies against the 157 amino acid form of human bFGF. The identification of bFGF in adherent elicited murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jun 13;110(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Muthukrishnan L., Warder E., D'Amore P. A. Growth factors are released by mechanically wounded endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Tsuboi R., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):671–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenner M., Chevallier B., Badet J., Barritault D. Evidence and characterization of the receptor to eye-derived growth factor I, the retinal form of basic fibroblast growth factor, on bovine epithelial lens cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5024–5028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Both normal and tumor cells produce basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Nov;129(2):273–276. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Quarto N. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells with basic fibroblast growth factor or the hst/K-fgf oncogene causes downregulation of the fibroblast growth factor receptor: reversal of morphological transformation and restoration of receptor number by suramin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2519–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. Identification of the fibroblast growth factor receptor in human vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):537–542. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. The identification and partial characterization of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of baby hamster kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13860–13868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Identification of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of Swiss 3T3 cells and mouse skeletal muscle myoblasts. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3487–3492. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Belin D., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteolytic and angiogenic properties of endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Purification from a human hepatoma cell line of a basic fibroblast growth factor-like molecule that stimulates capillary endothelial cell plasminogen activator production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarto N., Talarico D., Sommer A., Florkiewicz R., Basilico C., Rifkin D. B. Transformation by basic fibroblast growth factor requires high levels of expression: comparison with transformation by hst/K-fgf. Oncogene Res. 1989;5(2):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Fanning P., Klagsbrun M. Basic fibroblast growth factor fused to a signal peptide transforms cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):173–175. doi: 10.1038/331173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubartelli A., Cozzolino F., Talio M., Sitia R. A novel secretory pathway for interleukin-1 beta, a protein lacking a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1503–1510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08268.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. The opposing effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta on the regulation of plasminogen activator activity in capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):957–963. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Moscatelli D., Sommer A., Rifkin D. B. Endothelial cell-derived heparan sulfate binds basic fibroblast growth factor and protects it from proteolytic degradation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):743–751. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Release of basic fibroblast growth factor-heparan sulfate complexes from endothelial cells by plasminogen activator-mediated proteolytic activity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):767–775. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasada R., Kurokawa T., Iwane M., Igarashi K. Transformation of mouse BALB/c 3T3 cells with human basic fibroblast growth factor cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):588–594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Neufeld G., Friedman J., Abraham J. A., Fiddes J. C., Gospodarowicz D. Capillary endothelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor, a mitogen that promotes their own growth. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):257–259. doi: 10.1038/325257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togari A., Dickens G., Kuzuya H., Guroff G. The effect of fibroblast growth factor on PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):307–316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00307.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fridman R., Sullivan R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Aortic endothelial cells synthesize basic fibroblast growth factor which remains cell associated and platelet-derived growth factor-like protein which is secreted. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jun;131(3):402–408. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A., D'Amore P. A. Neurite outgrowth induced by an endothelial cell mitogen isolated from retina. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1363–1367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



