Abstract
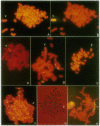
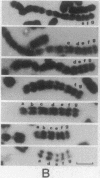
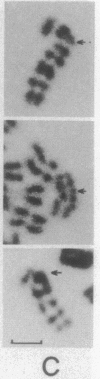
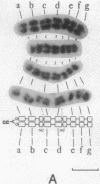
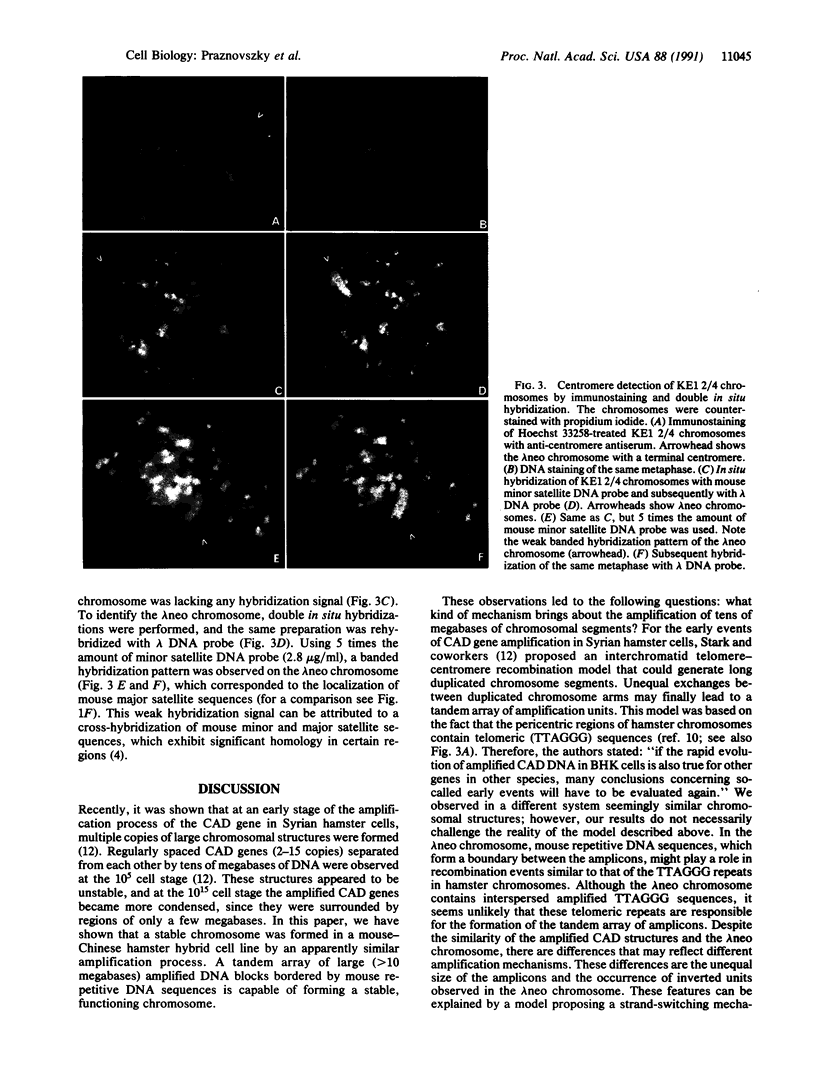
A hybrid cell line was produced by the fusion of an EC3/7 mouse cell with a Chinese hamster ovary cell. The EC3/7 cell carries a dicentric chromosome with a functional marker centromere. This marker centromere contains human, lambda, and bacterial vector DNA sequences and a dominant selectable gene (aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase type II; neo). In the hybrid, the marker centromere separated from the dicentric chromosome and formed a full-sized chromosome (lambda neo). The newly formed chromosome is stable, even under nonselective culture conditions. This functional chromosome, which is the result of an amplification process, is composed of seven large, different-sized amplicons. Each amplicon contains multiple copies of human, lambda, neo, and mouse telomeric DNA sequences. Individual amplicons are separated from each other by mouse major satellite DNA sequences. The marker centromere was localized to a terminal amplicon by anticentromere immunostaining. The number of amplicons in the newly formed chromosome is remarkably consistent. This finding suggests that the length of the newly formed chromosome is highly constrained.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cross S., Lindsey J., Fantes J., McKay S., McGill N., Cooke H. The structure of a subterminal repeated sequence present on many human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6649–6657. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Gerald P. S. Improved techniques for the induction of mammalian cell hybridization by polyethylene glycol. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01542629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlaczky G., Praznovszky T., Cserpán I., Keresö J., Péterfy M., Kelemen I., Atalay E., Szeles A., Szelei J., Tubak V. Centromere formation in mouse cells cotransformed with human DNA and a dominant marker gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8106–8110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlaczky G., Praznovszky T., Rasko I., Kereso J. Centromere proteins. I. Mitosis specific centromere antigen recognized by anti-centromere autoantibodies. Chromosoma. 1989 Jan;97(4):282–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00371967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilwig I., Gropp A. Decondensation of constitutive heterochromatin in L cell chromosomes by a benzimidazole compound ("33258 Hoechst"). Exp Cell Res. 1973 Oct;81(2):474–477. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Debatisse M., Buttin G., de Saint Vincent B. R. The multicopy appearance of a large inverted duplication and the sequence at the inversion joint suggest a new model for gene amplification. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):407–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02828.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyne J., Baker R. J., Hobart H. H., Hsu T. C., Ryder O. A., Ward O. G., Wiley J. E., Wurster-Hill D. H., Yates T. L., Moyzis R. K. Distribution of non-telomeric sites of the (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequence in vertebrate chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1990 Apr;99(1):3–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01737283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Moyzis R. K. Conservation of the human telomere sequence (TTAGGG)n among vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7049–7053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Gorman P. A., Stark M. B., Groves R. P., Stark G. R. Distinctive chromosomal structures are formed very early in the amplification of CAD genes in Syrian hamster cells. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1219–1227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90417-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Debatisse M., Giulotto E., Wahl G. M. Recent progress in understanding mechanisms of mammalian DNA amplification. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong A. K., Rattner J. B. Sequence organization and cytological localization of the minor satellite of mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11645–11661. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]