Abstract
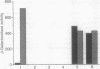
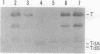
Taz1 is a hybrid signal-transducing membrane receptor between Tar, an aspartate chemoreceptor, and EnvZ, an osmosensor of Escherichia coli that is able to induce ompC expression by phosphorylating OmpR (a transcriptional activator) in response to aspartate. When the Taz1 His-277, the proposed autophosphorylation site in the cytoplasmic EnvZ domain, was replaced with a valine residue, the mutant Taz1 was unable to induce ompC expression. Similarly, when approximately two-thirds of the EnvZ domain was deleted, Taz1 was nonfunctional. However, when these two defective Taz1 proteins were coexpressed in a cell, ompC was constitutively expressed. Coinciding with this result, two mutant Taz1 molecules were able to intermolecularly complement each other to restore the OmpR kinase activity but not phosphatase activity in vitro. The identical result was also obtained with EnvZ. The present results suggest that the autophosphorylation of Taz1 and EnvZ is an intermolecular phosphorylation reaction, requiring formation of a dimer (or oligomer), and that ligand-dependent ompC expression requires not only kinase but also phosphatase activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Transfer of phosphoryl group between two regulatory proteins involved in osmoregulatory expression of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8563–8567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Mizuno T. Phosphorylation of a bacterial activator protein, OmpR, by a protein kinase, EnvZ, stimulates the transcription of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80626-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Nakasai F., Mizushima S., Mizuno T. Evidence for the physiological importance of the phosphotransfer between the two regulatory components, EnvZ and OmpR, in osmoregulation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14090–14094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballotti R., Lammers R., Scimeca J. C., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Van Obberghen E. Intermolecular transphosphorylation between insulin receptors and EGF-insulin receptor chimerae. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3303–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissette R. E., Tsung K. L., Inouye M. Suppression of a mutation in OmpR at the putative phosphorylation center by a mutant EnvZ protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):601–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.601-608.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Koshland D. E., Jr Global flexibility in a sensory receptor: a site-directed cross-linking approach. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1596–1600. doi: 10.1126/science.2820061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Comeau D., Norioka S., Inouye M. Localization and membrane topology of EnvZ, a protein involved in osmoregulation of OmpF and OmpC in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16433–16438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Delgado J., Inouye M. Phosphorylation of OmpR by the osmosensor EnvZ modulates expression of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6052–6056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Inouye M. Environmentally regulated gene expression for membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:21–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Kris R. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Ninfa A. J., Stock J. B., Silhavy T. J. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a bacterial transcriptional activator by a transmembrane receptor. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1725–1734. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Silhavy T. J. EnvZ, a transmembrane environmental sensor of Escherichia coli K-12, is phosphorylated in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5971–5973. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5971-5973.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Inouye M. Up-promoter mutations in the lpp gene of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3101–3110. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamaru K., Aiba H., Mizuno T. Transmembrane signal transduction and osmoregulation in Escherichia coli: I. Analysis by site-directed mutagenesis of the amino acid residues involved in phosphotransfer between the two regulatory components, EnvZ and OmpR. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):483–487. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose R. E. The nucleotide sequence of pACYC184. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):355–355. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokishita S., Yamada H., Aiba H., Mizuno T. Transmembrane signal transduction and osmoregulation in Escherichia coli: II. The osmotic sensor, EnvZ, located in the isolated cytoplasmic membrane displays its phosphorylation and dephosphorylation abilities as to the activator protein, OmpR. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):488–493. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadway J. L., Morrison B. D., Soos M. A., Siddle K., Olefsky J., Ullrich A., McClain D. A., Pessin J. E. Transdominant inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity in mutant insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi R., Brissette R. E., Rampersaud A., Forst S. A., Oosawa K., Inouye M. Activation of bacterial porin gene expression by a chimeric signal transducer in response to aspartate. Science. 1989 Sep 15;245(4923):1246–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.2476847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]