Abstract
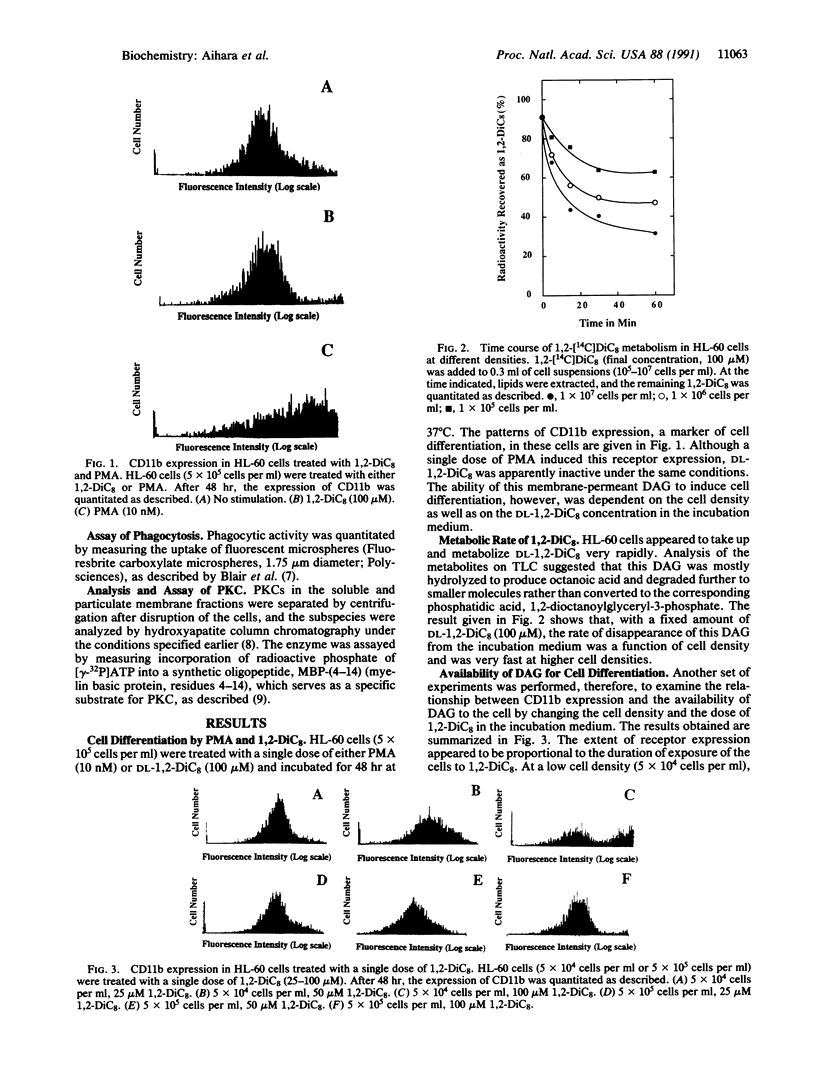
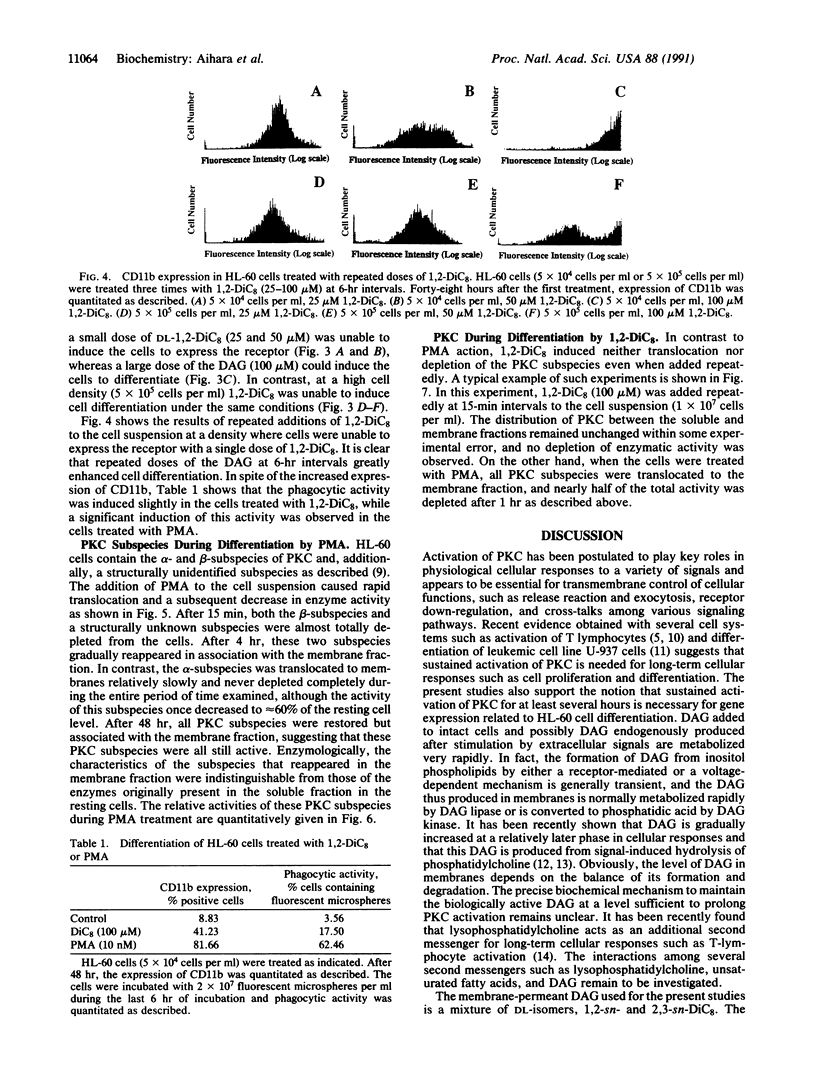
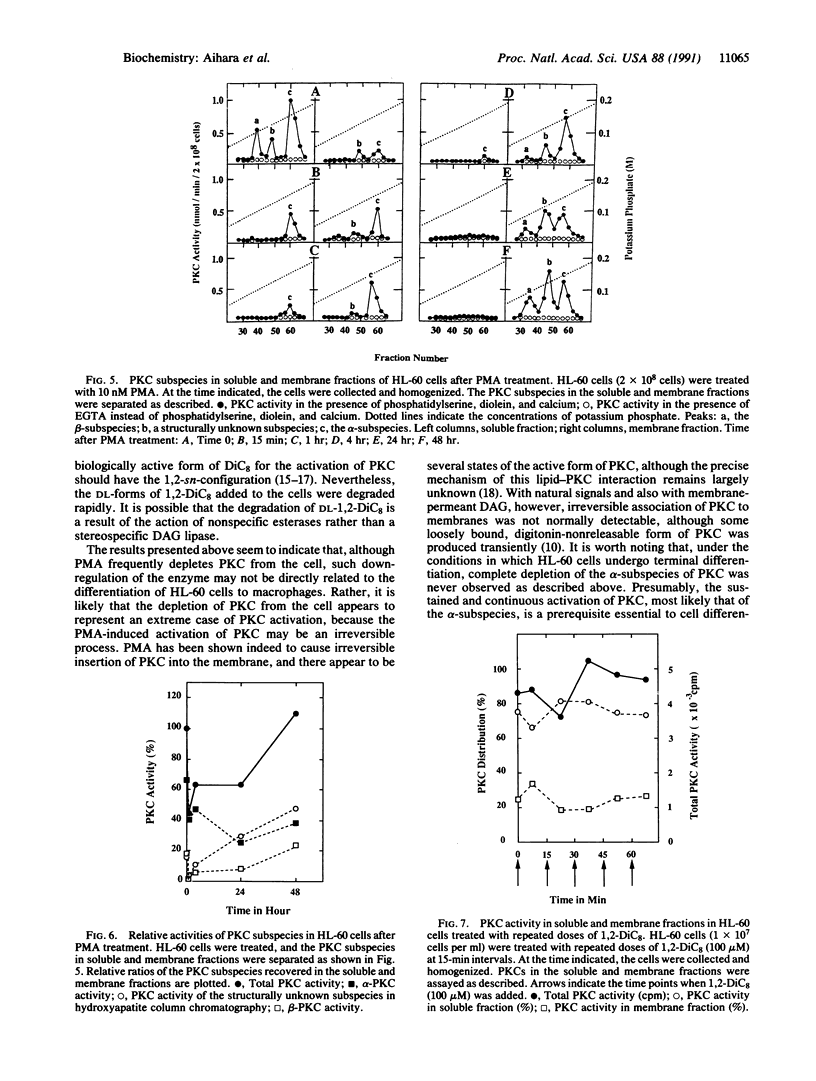
Although a single dose of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) allowed HL-60 cells to differentiate to macrophages, a single dose of membrane-permeant diacylglycerol (DAG), 1,2-dioctanoylglycerol (1,2-DiC8), was normally insufficient to differentiate these cells. These cells metabolized 1,2-DiC8 very rapidly, and 1,2-DiC8 available to protein kinase C (PKC) activation was removed from the incubation medium at a rate proportional to cell density. However, increasing the duration of exposure of HL-60 cells to this DAG either by its repeated addition or by decreasing the cell density greatly enhanced their differentiation to macrophages as measured by CD11b expression. During this differentiation induced by DAG, neither measurable translocation nor depletion (down-regulation) of PKC was observed. When the cells were exposed to PMA, on the other hand, some PKC subspecies were instantaneously translocated to membranes and subsequently disappeared very quickly, whereas the alpha-subspecies was decreased to the level of approximately 60% of the resting cell, but thereafter its activity was maintained at a nearly constant level in membranes. After approximately 4 hr, the PKC subspecies, once depleted, reappeared gradually in the membrane fraction. The results suggest that sustained activation of PKC is essential to differentiation of HL-60 cells to macrophages, and depletion of the enzyme is not needed. Perhaps translocation of PKC represents an extreme state of the active form of the enzyme, which may result from PMA action, and the alpha-subspecies presumably plays a key role in HL-60 cell differentiation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asaoka Y., Oka M., Yoshida K., Nishizuka Y. Lysophosphatidylcholine as a possible second messenger synergistic to diacylglycerol and calcium ion for T-lymphocyte activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1378–1385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91046-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asaoka Y., Oka M., Yoshida K., Nishizuka Y. Metabolic rate of membrane-permeant diacylglycerol and its relation to human resting T-lymphocyte activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8681–8685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Differences in the effects of phorbol esters and diacylglycerols on protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9317–9323. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry N., Ase K., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. Activation of resting human T cells requires prolonged stimulation of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair O. C., Carbone R., Sartorelli A. C. Differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells: simultaneous determination of phagocytic activity and cell cycle distribution by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1986 Mar;7(2):171–177. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni L. T., Rando R. R. The nature of protein kinase C activation by physically defined phospholipid vesicles and diacylglycerols. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10819–10825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. The HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line: proliferation, differentiation, and cellular oncogene expression. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Kishimoto A., Aihara H., Yasuda I., Mikawa K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C during differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line, HL-60. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80698-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutter D., Caldwell A. B., Morin M. J. Dissociation of protein kinase C activation from phorbol ester-induced maturation of HL-60 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5979–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin M. J., Kreutter D., Rasmussen H., Sartorelli A. C. Disparate effects of activators of protein kinase C on HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11758–11763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura H., Ase K., Sekiguchi K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y., Nakano Y., Satoh T. Stereospecificity of diacylglycerol for stimulus-response coupling in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):1143–1151. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90754-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R., Young N. The stereospecific activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):818–823. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura S., Ase K., Berry N., Kikkawa U., McCaffrey P. G., Minowada J., Nishizuka Y. Expression of protein kinase C subspecies in human leukemia-lymphoma cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81369-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- William F., Wagner F., Karin M., Kraft A. S. Multiple doses of diacylglycerol and calcium ionophore are necessary to activate AP-1 enhancer activity and induce markers of macrophage differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18166–18171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Gotoh H., Aizu E., Kato R. Failure of 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol to mimic the cell-differentiating action of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate in HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14230–14234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


