Abstract
Background
CHIP, the protein encoded by STUB1, is a central component of cellular protein homeostasis and interacts with several key proteins involved in the pathogenesis of manifold neurodegenerative diseases. This gives rise to the hypothesis that mutations in STUB1 might cause a far more multisystemic neurodegenerative phenotype than the previously reported cerebellar ataxia syndrome.
Methods
Whole exome sequencing data-sets from n = 87 index subjects of two ataxia cohorts were screened for individuals with STUB1 mutations. In-depth phenotyping by clinical evaluation and neuroimaging was performed in mutation carriers.
Results
We identified four novel STUB1 mutations in three affected subjects from two index families (frequency 2/87 = 2.3%). All three subjects presented with a severe multisystemic phenotype including severe dementia, spastic tetraparesis, epilepsy, and autonomic dysfunction in addition to cerebellar ataxia, plus hypogonadism in one index patient. Diffusion tensor imaging revealed degeneration of manifold supra- and infratentorial tracts.
Conclusions
Our findings provide clinical and imaging support for the notion that CHIP is a crucial converging point of manifold neurodegenerative processes, corresponding with its universal biological function in neurodegeneration. Further, our data reveal the second STUB1 family with ataxia plus hypogonadism reported so far, demonstrating that Gordon Holmes syndrome is indeed a recurrent manifestation of STUB1. However, it does not present in isolation, but as part of a broad multisystemic neurodegenerative process. This supports the notion that STUB1 disease should be conceptualized not by historical or clinical syndromic names, but as a variable multisystemic disease defined by disturbed function of the underlying STUB1 gene, which translates into a multidimensional gradual spectrum of variably associated clinical signs and symptoms.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0580-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Neurodegeneration, Neurodegenerative disease, CHIP, Gordon Holmes syndrome, Ataxia, Recessive ataxia, Spastic ataxia, Early onset ataxia, Dementia, Early-onset dementia, Hypogonadism, Magnetic resonance imaging
Background
Mutations in STUB1, the gene encoding the protein CHIP (C-terminus of HSC70-interacting Protein), were recently identified as a cause of autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia (ARCA) in several families [1–5]. Most of the reported individuals with STUB1 mutations had a relatively circumscribed phenotype, mainly consisting of an ataxia syndrome with involvement of only one or two additional neurologic systems. For example, in one index patient hypogonadotropic hypogonadism was identified concomitant to ataxia, leading to the notion that STUB1 is a cause of Gordon Holmes syndrome [5, 6]. Yet it remains unclear whether hypogonadism is a systematic part of the phenotypic spectrum of STUB1 and not just a coincidental finding in a single family [5].
The current notion of STUB1 as causing a relatively circumscribed ‘ataxia plus phenotype’ is remarkable, since CHIP, the protein encoded by STUB1, is a key component of general cellular protein homeostasis [7, 8] and interacts with several proteins involved in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative diseases and system degenerations, including Tau, α-Synuclein, Parkin2, LRRK2, Ataxin1, Ataxin3, and ATCAY (for references and overview, see Figure Additional file 1). Accordingly, it is to be expected that in patients with STUB1 mutations, disruption of CHIP function might lead to far more extensive neurodegeneration than the previously reported cerebellar ataxia syndrome. Specifically, given the central role of CHIP in protein homeostasis and its interactions with many neurodegenerative proteins, we hypothesized that mutant STUB1 should lead to damage of almost all brain systems.
Here we report the clinical, genetic and imaging findings from three novel STUB1 patients and four novel STUB1 mutations. We demonstrate that mutant STUB1 leads to severe multisystemic neurodegeneration affecting almost all brain tracts and, correspondingly, presenting with a broad multisystemic phenotype including severe dementia, spastic tetraparesis, epilepsy, and autonomic dysfunction in addition to cerebellar ataxia. These clinical and imaging findings correspond with the broad protein interactome of CHIP with other neurodegenerative disease proteins. Moreover, our data provide the first confirmation from an independent family showing that hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is indeed a recurrent part of the phenotypic spectrum of STUB1 mutations, rendering them an important cause of Gordon Holmes syndrome; yet not in isolation, but as part of a broad multisystemic neurodegenerative process. This indicates that STUB1 disease should not be conceptualized by distinct syndromic names, but as a variable multisystemic disease defined by disturbed function of the underlying STUB1 gene, which translates into a multidimensional gradual spectrum of variably associated signs and symptoms.
Methods
Genetic sequencing
Whole exome sequencing (WES) data-sets from n = 87 index subjects of two ataxia cohorts (n = 35 from Tuebingen, Germany; exomes generated from 2014 and 2015; and n = 52 from Antwerp, Belgium exomes generated from 2012 until 2015) were screened for individuals with biallelic STUB1 mutations. Cohorts comprised subjects with early-onset degenerative ataxia compatible with autosomal inheritance (i.e. progressive ataxia with onset <40 years with ataxia in no more than one generation), negative for trinucleotide repeat expansions causing Friedreich’s ataxia and spinocerebellar ataxia type 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, and 17. WES was performed using the SureSelect Human All Exon 50 Mb kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) for in-solution enrichment and the Hiseq2000 instrument (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) as described before [9]. All data were then annotated and imported into the GENESIS (gem.app) platform, a web-based tool for next generation sequencing data analysis (http://thegenesisprojectfoundation.org/) [10, 11]. Variants were filtered for (i) non-synonymous homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in STUB1 that were (ii) absent or extremely rare (minor allele frequency <0.5%) in the public databases dbSNP137, NHLBI ESP6500, 1000Genomes project, and ExAc (60706 exomes; Exome Aggregation Consortium; Cambridge, MA http://exac.broadinstitute.org) as well as in GENESIS (<11 heterozygous or homozygous alleles in 5996 subjects in the GENESIS database), and showed an at least (iii) moderate conservation (PhastCons score [100 vertebrate genomes] >0.5 AND phyloP [100 vertebrate genomes] >1.5) and (iv) moderate genotype quality (quality filter [QUAL] >35 and genotype quality GQ > 50).
The data collection was approved by the Ethics Committees of the University Hospital Antwerp and the University Hospital Tuebingen (598/2011BO1).
In-depth phenotyping
All STUB1 subjects were examined by an experienced neurologist (Tuebingen patients: M.S.; Antwerp patients: J.B.) according to a standardized clinical assessment protocol covering all neurological systems, including scales to capture cognition, spasticity, ataxia, and overall handicap (Spinocerebellar degeneration functional score [SDFS]). This SDFS evaluates the disability stage from 0 to 7 (0: no functional handicap; 1: no functional handicap but signs at examination; 2: mild, able to run, walking unlimited; 3: moderate, unable to run, limited walking without help; 4: severe, walking with one stick; 5: walking with two sticks; 6: unable to walk, requiring wheelchair; 7: confined to the bed) [12].
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
In addition to clinical routine cerebral imaging, performed in all STUB1 subjects, detailed diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was performed on a 3 Tesla scanner (Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with a 32 channel head coil in one STUB1 subject. DTI data was acquired with 64 diffusion directions (b = 1000 s/mm2) and one b0 image with an isotropic resolution of 2 mm and coverage of the whole head. The patient and nine age and gender matched healthy controls (mean age 32.9 years, range 27–38 years) were examined at the same scanner with the same DTI protocol. Data were processed with Tract-Based Spatial Statistics (TBSS) [13]. TBSS projects all subjects’ fractional anisotropy (FA) data onto a mean FA tract skeleton which represents the centres of all tracts common to the group. Usually, such maps are analysed voxel-wise for significant differences between groups. However, given the group size of n = 1 for the patient, a voxel-wise comparison would lead to many misleading false positive and false negative results. Therefore, we here compared the FA of whole tracts defined by the 48 labelled white matter tracts of the ICBM-DTI-81 atlas [14] provided in FSL (FMRIB Sofware Library, available at http://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/fslwiki/) between the patient and the control group. All labels that covered at least 600 voxels of the skeleton were evaluated with a t-test for significant between-group differences between the healthy control group and the STUB1 patient. To correct for multiple comparison the Bonferroni method was used and the significance level was set at α < 0.0011.
For methods of the western blot analysis, see Additional file 2. For methods of the CHIP protein-protein-network analysis, see Additional file 1.
Results
Genetic findings
WES revealed four STUB1 mutations (one nonsense, three missense), all of them not previously linked to human disease, in subjects from two different index families (2/87 = 2.3% frequency in total cohort) from Central Europe (family 1: German origin; family 2 Belgian origin). Subject II.1 of family 1 carried the variant c.355C > T in Exon 2, which is predicted to result in a stop codon at position 119 (p.Arg119*), most probably leading to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay due to the premature stop codon. The second variant, c.880A > T in Exon 7, leads to an amino acid exchange from isoleucine to phenylalanine at position 294 (p.Ile294Phe) (Fig. 1a), affecting the highly conserved U-Box domain of the protein (Fig. 1b). Subjects II.1 and II.4 of family two carried the STUB1 missense variants, c.433A > C in Exon 3, p.Lys145Gln, located outside the tetratricopeptide repeat sequence and the U-Box domain (Fig. 1b); and c.728C > T in Exon 6, p.Pro243Leu (Fig. 1a) which affects the U-Box domain of the protein. All four variants were absent or very rare in in the Exome Variant Server (EVS) and in-house databases (Table 1).
Fig. 1.
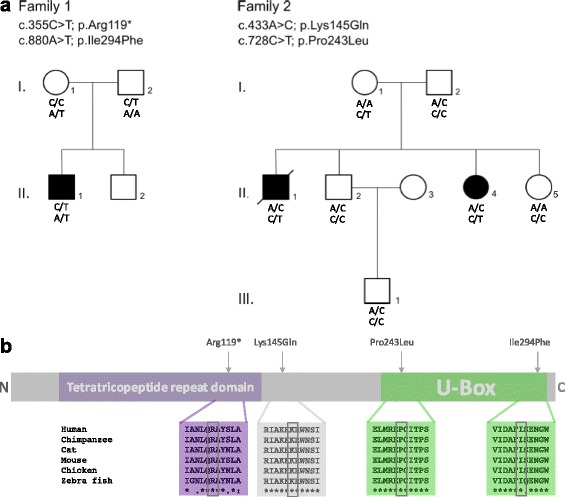
Pedigrees of STUB1 families and domain location of the four novel STUB1 mutations. a Compound heterozygous STUB1 mutations and pedigrees of the two reported families. In family 1, one affected individual (II.1) carried the compound heterozygeous mutations p.Arg119* and p.Ile294Phe. In family 2, two affected siblings (II.1 and II.4) both carried the mutations p.Lys145Gln and p.Pro243Leu. b Schematic representation of CHIP, the protein encoded by STUB1, with the highly conserved N-terminal tetratricopeptide repeat and C-terminal U-box domain. Of the four novel mutations, two are located in the U-Box domain (p.Pro243Leu and p.Ile294Phe), one in between the conserved domains (Lys145Gln) and one is predicted to locate to the tetratricopeptide repeat domain (p.Arg119*), which, however, most probably leads to nonsense-mediated decay on RNA level
Table 1.
Summary of the novel STUB1 mutations
| Sybject | Family 1, II.1 | Family 2, II.1 + II.4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype | Dementia, upper motor neuron damage, hypogonadism, ataxia, epilepsy | Dementia, upper motor neuron damage, epilepsy, ataxia | ||
| Genomic position | Chr16:732457 | Chr16:731347 | Chr16:731512 | Chr16:732223 |
| cDNA change | c.880A > T | c.355C > T | c.433A > C | c.728C > T |
| Protein change | p.Ile294Phe | p.Arg119* | p.Lys145Gln | p.Pro243Leu |
| GVS Function | missense | nonsense | missense | missense |
| PhyloP 100 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 7.07 | 5.85 |
| PolyPhen2 (div) | probably damaging | NA | possibly damaging | probably damaging |
| SIFT | D | NA | D | D |
| Mutation Taster | D | D | D | D |
| ExAc/EVS/1000G | 0 | 0 | 0.001/0.001/0.001 | 0/NA/NA |
| GENESIS allele counts | 1 | 1 | 6 (het) | 1 |
Overview of the mutations including phenotypic features, rating by the mutation prediction softwares PhyloP, PolyPhen2, SIFT, and Mutation Taster and a summary of the allele frequency in the databases ExAc/EVS/1000G MAF and GENESIS. Legend: NA not applicable. ExAc Exome Aggregation Consortium, EVS Exome Variant Server, 1000G MAF 1000 Genomes minor allele frequency, het heterozygous, GVS Genome Variant Server
All three missense mutations were predicted to be damaging by at least three different in silico prediction tools (Table 1). All mutations were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Biallelic localization of the respective STUB1 variants in trans was confirmed in both families by testing for a heterozygous state of the respective variant in the parents. In line with the fact that affected patients of both STUB1 families carried at least one missense STUB1 variant (rather than two truncating variants), no truncation of the CHIP protein was observed (Additional file 2).
Clinical findings
A summarized overview of clinical symptoms in all three affected subjects is provided in Table 2 (for detailed case vignettes, see Additional file 3). Subject II.1, family 1, presented with slightly delayed early motor development, generalized tonic-clonic seizures (years 1–2 of life) and undescended testes (surgery at age 7). He did not show ataxia symptoms until age 12. Also subject II. 4 of family 2 did not present with ataxia as initial symptom, but with cataracts requiring surgery at the age of 11. Ataxia did not start before age 20. Only in subject II.1, STUB1 disease started with ataxia as initial symptom (age 12 years), followed by spasticity starting at the age of 20 and cognitive deficits starting at 23 years. All three subjects developed severe dementia with predominantly frontal-executive dysfunction and progressive loss of language in the first three decades of life, leading to mutism in 2/3 cases before the age of 40. Likewise, all three subjects developed severe pyramidal tract damage to arms and legs, including incapacitating tetraspasticity. Extrapyramidal hyperkinetic movement disorders included choreo-athetotic movements in 2/3 subjects and dystonia in 1/3 subjects. Gait disturbances were quickly progressive in all three subjects, leading to wheelchair-dependency 6, 9, and 15 years after respective onset of gait difficulties. All three subjects developed severe dysphagia, starting between age 20 to age 35, and necessitating gastric tube feeding in both subjects from family 2 at the age of 36 and 43, respectively. This severe multisystemic neurodegenerative disease led to complete care dependency in all three subjects before aged 40, and premature death at the age of 40 in one of them.
Table 2.
Summary of clinical, imaging, and laboratory data of the STUB1 patients
| Family | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Subject | II.1 | II.1 | II.4 |
| STUB1 mutation | c.355C > T p.Arg119* + c.880A > T p.Il294Phe | c. 433A > C p.Lys145Gln + c.728C > T p.Pro243Leu | c.433A > C p.Lys145Gln + c.728C > T p.Pro243Leu |
| Gender | M | M | F |
| Age at last investigation | 34y | 35y (patient died aged 40) | 45y |
| First symptom, age of onset | epilepsy, 2y | ataxia, age 12y | cataract surgery left eye, 11y |
| Ataxia, age of onset | 12y | 12y | 20y |
| Tendon reflexes | increased in UE/LE | increased in UE/LE | increased in UE/LE |
| Spacticity | +++ in UE and LE | + in UE and LE | + in UE and LE |
| Babinski’s sign | + bilateral | + bilateral | + bilateral |
| Ankle clonus | - | + bilateral | + bilateral |
| Urge incontinence | + | + | + (40y) |
| Parkinsonism | hypomimia | - | - |
| Hyperkinetic movements (dystonia/athetosis) | focal dystonia upper limb | intermittend ballistic athetotic movements | intermittend ballistic athetotic movements |
| Epilepsy | GTCS in early childhood | GTCS (onset 35y) | GTCS? (onset 42y) |
| Muscle atrophy | distal UE/LE, possibly secondary to disuse | generalized UE/LE atrophy secondary to disuse | distal UE/LE, possibly secondary to disuse |
| Sense of vibration | cannot be tested reliability due to dementia | cannot be tested reliability due to dementia | cannot be tested reliability due to dementia |
| Cognitive impainment | severe | severe, mutism, PEG at 36y | severe, mutism, PEG at 43y |
| Neuropsychology | not testable anymore due to too severe cognitive deficits | not testable anymore; TIQ 85 (WAIS) at 32y | not testable anymore; MMSE 29/30 at 24y, work as secretary in early 20ies |
| SDFS | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| SARA | 36 | 40 | 40 |
| SPRS | 36 | 34 | 40 |
| Nerve conduction studies | sural and tibial nerve normal | sural and tibial nerve normal | sural and tibial nerve normal |
| Motor evoked potentials | n/a | normal | normal (SSEP’s and BAEP also normal) |
| Cerebral imaging | cerebellar, mesencephalic and parieto-occipital cortical atrophy | cerebellar atrophy | severe cerebellar atrophy, vermis and hemispheric, brainstem normal (33y) |
| Hypogonadism | + | secondary sex characteristics present | secondary sex characteristics present |
| Hormones | Testosteron 5,2 nmol/I; LH 0,8 IU/I; FSH 0,8 IU/I | normal (36y) | n/a |
| Testicular volume (sonography) | right testicle: 4.2 ml left testicle: 3.9 ml | n/a | not applicable |
Legend: M male, F female, y years, n/a not applicable, UE upper extremity, LE lower extremity, GTCS generalized tonic-clonic seizure, TIQ total intelligence quotient, WAIS Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, MMSE Mini Mental State Examination, SDFS Spinocerebellar Degeneration Functional Score. This score was used to evaluate the disability stage from 1 to 7 (0: no functional handicap; 1: no functional handicap but signs at examination; 2: mild, able to run, walking unlimited; 3: moderate, unable to run, limited walking without help; 4: severe, walking with one stick; 5: walking with two sticks; 6: unable to walk, requiring wheelchair; 7: confined to the bed). SARA, Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia, reaching from 0 to 40, with higher scores indicating more severe ataxia [17]; scores <3 points are considered unspecific. SPRS, Spastic Paraplegia Rating Scale, reaching from 0 to 52, with higher scores indicating more severe spastic paraplegia [18] (please note, however, that several items of the SPRS scale increase also with more severe ataxia); SSEP, somatosensory evoked potential; BAEP, brainstem auditory evoked potentials; LH, luteinizing hormone; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone
Neuroimaging
Routine imaging (cerebral magnetic resonance imaging [cMRI] in two subjects, cerebral computer tomography [cCT] in one subject) showed cerebellar atrophy in all three subjects and, in addition, mesencephalic and parieto-occipital cortical atrophy in subject II.1, family 1. To reveal the atrophy pattern of different neural tracts in more detail, diffusion tension imaging (DTI) imaging was performed in subject II.1. It showed a widespread atrophy and globally reduced fractional anisotropy (FA) of literally all brain fiber tracts, from the corticospinal tract via the corona radiata to the superior, middle and inferior cerebellar peduncle (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
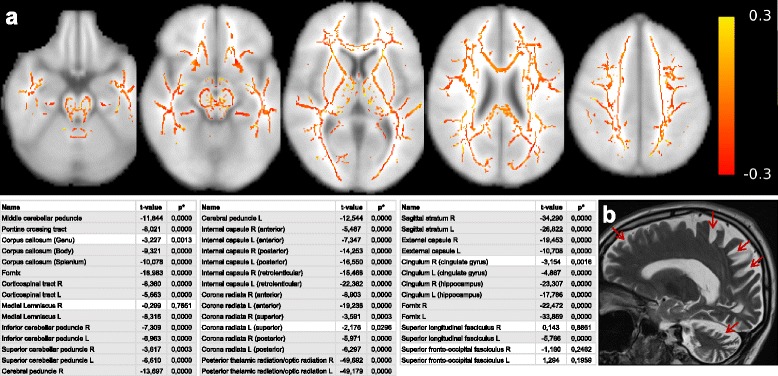
MR imaging features of an individual with STUB1/CHIP mutation. a Top: illustration of the FA differences between patient II.1, family 1 versus the healthy control group, overlaid onto a standard brain available in FSL. The mean FA skeleton was calculated voxelwise over all 9 control subjects, and then subtracted from the FA skeleton of the STUB1 patient. Red color encodes a negative difference, i.e. a decreased FA in the STUB1 subject compared to the mean FA of the controls. Yellow color encodes an increased FA in the STUB1 subject compared to the mean FA of the controls. Individual FA can theoretically range from 0 to 1, in vivo FA usually ranges between 0.05 in GM and 0.9 in large WM tracts. Over the whole skeleton negative values are much more common, in line with the statistical evaluation of whole fiber tracts: Bottom: corresponding list of all brain tracts, and the results of a t-test of the voxels of each tract comparing the STUB1 subject with the healthy control group. Tracts with gray background are statistically significant. b Sagittal T2 MRI showing marked cerebellar degeneration and global cerebral atrophy with an emphasis on the parietal and occipital lobes in subject II.1 of family 1 (arrows). FA, fractional anisotropy; FSL, FMRIB Sofware Library; GM, gray matter; WM, white matter
Discussion
Our findings on four novel mutations in three novel STUB1 subjects extend the genetic spectrum of STUB1, corroborating earlier findings that STUB1 mutations both inside and outside of the tetratricopeptide repeat and U-Box domain of CHIP can lead to neurodegenerative disease [1]. The approximate frequency estimate of 2.3% confirms our previous data from an independent early-onset ataxia cohort that STUB1 is a recurrent, but overall rare cause of early-onset ataxia (previous frequency estimate: 1.8%; [1]).
More importantly, however, our findings provide evidence for a severe multisystemic neurodegenerative disease, corresponding with the universal protein function of CHIP in neurodegeneration (see Figs. 2, 3, and Figure Additional file 1). Specifically, in line with the universal biological role of CHIP as a crucial converging point of multiple pathways important for neuronal homeostasis (Additional file 1), the disease phenotype is not limited to an ataxia syndrome with minor involvement of one or two additional systems, but rather involves almost all brain tracts (Figs. 3 and 2). This is evidenced clinically by the fact that ataxia is only one feature of a broad multisystemic phenotype which includes severe dementia advancing to mutism, epilepsy, profound pyramidal tract damage including tetraspasticity, and extrapyramidal hyperkinetic movement disorders. In fact, ataxia was not even the first feature in the evolution of the disease in two out of the three affected subjects.
Fig. 3.
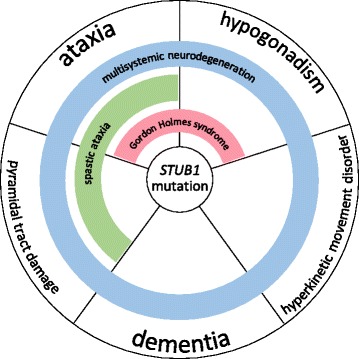
The unfolding phenotypic spectrum of STUB1 disease. The clinical spectrum of STUB1 mutations unfolds along five different neurological key features: ataxia, pyramidal tract damage, dementia, hypogonadism, and hyperkinetic movement disorders. Accordingly, each or several of these key features might be missing in single individuals with STUB1 disease. Moreover, it illustrates that STUB1 causes ataxia and hypogonadism (=Gordon Holmes syndrome) not in isolation, but as part of a continuous spectrum of STUB1-associated disease features. These features can be variably combined in STUB1-disease clusters, e.g. ataxia and hypogonadism (red bar ≙ Shi et al. [5]), ataxia with pyramidal tract damage (spastic ataxia; green bar ≙ Synofzik et al. [1]), or ataxia plus hypogonadism, pyramidal tract damage, dementia and hyperkinetic movement disorders, i.e. encompassing all STUB1 disease features (blue bar ≙ current report)
The notion of aberrant CHIP function leading not only to ataxia syndromes, but to a broad neurodegeneration, is further evidenced by DTI imaging. In line with the clinical findings, DTI demonstrates neurodegeneration of almost all brain fiber tracts, from the corticospinal tract via the corona radiata to the cerebellar peduncles. Taken together, our findings of widespread neurodegeneration affecting manifold brain systems provide clinical and imaging evidence that CHIP seems to be an important protein for cell survival in various neuronal cell types.
Finally, our data provide the first confirmation from an independent family showing that hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is indeed part of the phenotypic cluster of STUB1 mutations. So far, only one STUB1 family has been reported to include also hypogonadism as part of the clinical phenotype [5]. Our description of a second, independent case from a different ethnic background now confirms hypogonadism as part of the disease spectrum. It adds further support of STUB1 as one important cause of Gordon Holmes syndrome [6], which shows a substantial genetic heterogeneity as it can also be caused by mutations in e.g. PNPLA6 [9]. Importantly, we demonstrate here that STUB1 causes the Gordon Holmes syndrome (early onset ataxia plus hypogonadism) not in isolation, but rather as part of a broad multisystemic neurodegenerative process (see Fig. 3). It thus resembles also other genes which cause Gordon Holmes syndrome as part of a multisystemic disease spectrum, e.g. PNPLA6 [9].
Correspondingly, in line with the reclassifications of other neurodegenerative diseases [15, 16], we suggest viewing STUB1-associated disease not in terms of syndromic names (e.g. “ataxia-dementia-hypogonadotropism syndrome” or “Gordon Holmes syndrome”); rather, it should be conceptualized as a fluid, complex, multisystemic neurodegenerative disease affecting various regions and/or systems of the nervous system (cerebellar, extrapyramidal, pyramidal, cortical, endocrine) defined by disturbed STUB1 function that translates phenotypically into a multidimensional gradual spectrum of variably associated signs and symptoms (Fig. 3).
Conclusion
Our findings provide clinical and imaging support for the notion that CHIP is a crucial converging point of widespread multisystemic neurodegenerative processes, thus corresponding with its universal biological function in neuronal homeostasis. Further, we show that Gordon Holmes syndrome presents as part of this widespread, variable multisystemic neurodegenerative process.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project and its ongoing studies which produced and provided exome variant calls for comparison.
Funding
M.S. was supported by the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung. This work was furthermore supported from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the ERA-NET Cofund action N° 643578. It was supported by the BMBF (01GM1607 to M.S.), under the frame of the E-Rare-3 network PREPARE. Moreover, it received support from the Association Belge contre les Maladies Neuromusculaire (ABMM) and the EU FP7/2007-2013 under grant agreement number 2012-305121 (NEUROMICS). J.B. is supported by a Senior Clinical Researcher mandate of the Research Fund - Flanders (FWO). Publication of this article was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Open Access Publishing Fund of University of Tübingen.
Availability of data and materials
Please contact author for data requests.
Authors’ contributions
SNH: acquisition of data, preparation of figures, drafting and revision of the manuscript; TD acquisition of data, revision of the manuscript; BB: acquisition of data, preparation of figures, revision of the manuscript; KS: acquisition of data, revision of the manuscript; SZ: acquisition of data, revision of the manuscript; SR: acquisition of data, preparation of figures, revision of the manuscript; LS: revision of the manuscript; RS: acquisition of data, revision of the manuscript; PDJ: acquisition of data, revision of the manuscript; JB: acquisition of data, revision of the manuscript; MS: acquisition of data, conceptualization of the study, revision and finalization of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
S.N.H., T.D., B.B., K.S., S.Z., S.R., L.S., R.S., P.D.J., and J.B. have nothing to disclose. M.S. received speaker’s honoraria and research support from Actelion Pharmaceuticals, unrelated to the current project and manuscript. B.B. received travel funding by Bayer Vital, unrelated to the current project and manuscript.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from every patient/legal guardian.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The data collection was approved by the Ethics Committees of the University Hospital Antwerp and the University Hospital Tuebingen (598/2011BO1). Written informed consent was obtained from every patient/legal guardian.
Abbreviations
- ARCA
Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia
- ATCAY
Ataxia, cerebellar, Cayman type
- BAEP
Brainstem auditory evoked potentials
- CHIP
C-terminus of HSC70-interacting Protein
- CT
Computer tomography
- DTI
Diffusion tensor imaging
- EVS
Exome Variant Server
- ExAc
Exome Aggregation Consortium
- F
Female
- FA
Fractional anisotropy
- FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- GM
Gray matter
- GTCS
Generalized tonic-clonic seizure
- GVS
Genome variant server
- LE
Lower extremity
- LH
Luteinizing hormone
- M
Male
- MAF
Minor allele frequency
- MMSE
Mini Mental State Examination
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- SARA
Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia
- SDFS
Spinocerebellar Degeneration Functional Score
- SPRS
Spastic Paraplegia Rating Scale
- SSEP
Somatosensory evoked potential
- STUB1
STIP1 homology and U-box containing protein 1
- TBSS
Tract-based spatial statistics
- TIQ
Total intelligence quotient
- UE
Upper extremity
- WAIS
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
- WES
Whole exome sequencing
- WM
White matter
Additional files
Protein network analysis. (DOCX 1176 kb)
Western blots of CHIP in mutation carriers. (DOCX 241 kb)
Case vignettes. Detailed medical history and clinical examination data of the three STUB1 patients. (DOCX 14 kb)
Contributor Information
Stefanie Nicole Hayer, Email: stefanie.hayer@med.uni-tuebingen.de.
Tine Deconinck, Email: tine.deconinck@molgen.vib-ua.be.
Benjamin Bender, Email: benjamin.bender@med.uni-tuebingen.de.
Katrien Smets, Email: katriensmets@yahoo.com.
Stephan Züchner, Email: SZuchner@med.miami.edu.
Selina Reich, Email: selina.reich@uni-tuebingen.de.
Ludger Schöls, Email: ludger.schoels@uni-tuebingen.de.
Rebecca Schüle, Email: rebecca.schuele-freyer@med.uni-tuebingen.de.
Peter De Jonghe, Email: peter.dejonghe@molgen.vib-ua.be.
Jonathan Baets, Email: jonathan.baets@molgen.vib-ua.be.
Matthis Synofzik, Phone: +49-7071-2982060, Email: matthis.synofzik@uni-tuebingen.de.
References
- 1.Synofzik M, Schüle R, Schulze M, Gburek-Augustat J, Schweizer R, Schirmacher A, Krägeloh-Mann I, Gonzalez M, Young P, Züchner S, Schöls L, Bauer P. Phenotype and frequency of STUB1 mutations: next-generation screenings in Caucasian ataxia and spastic paraplegia cohorts. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:57. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-9-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shi Y, Wang J, Li J-D, Ren H, Guan W, He M, Yan W, Zhou Y, Hu Z, Zhang J, Xiao J, Su Z, Dai M, Wang J, Jiang H, Guo J, Zhou Y, Zhang F, Li N, Du J, Xu Q, Hu Y, Pan Q, Shen L, Wang G, Xia K, Zhang Z, Tang B. Identification of CHIP as a novel causative gene for autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia. PLoS One. 2013;8:e81884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bettencourt C, de Yébenes JG, López-Sendón JL, Shomroni O, Zhang X, Qian S-B, Bakker IMC, Heetveld S, Ros R, Quintáns B, Sobrido M-J, Bevova MR, Jain S, Bugiani M, Heutink P, Rizzu P. Clinical and Neuropathological Features of Spastic Ataxia in a Spanish Family with Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations in STUB1. Cerebellum. 2015;14:378–81. doi: 10.1007/s12311-014-0643-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Heimdal K, Sanchez-Guixé M, Aukrust I, Bollerslev J, Bruland O, Jablonski GE, Erichsen AK, Gude E, Koht JA, Erdal S, Fiskerstrand T, Haukanes BI, Boman H, Bjørkhaug L, Tallaksen CME, Knappskog PM, Johansson S. STUB1 mutations in autosomal recessive ataxias - evidence for mutation-specific clinical heterogeneity. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:146. doi: 10.1186/s13023-014-0146-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shi C-H, Schisler JC, Rubel CE, Tan S, Song B, McDonough H, Xu L, Portbury AL, Mao C-Y, True C, Wang R-H, Wang Q-Z, Sun S-L, Seminara SB, Patterson C, Xu Y-M. Ataxia and hypogonadism caused by the loss of ubiquitin ligase activity of the U box protein CHIP. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:1013–24. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Holmes G. A form of familial degeneration of the cerebellum. Brain. 1907;30:466–89. doi: 10.1093/brain/30.4.466. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Edkins AL. CHIP: a co-chaperone for degradation by the proteasome. Subcell Biochem. 2015;78:219–42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-11731-7_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Murata S, Chiba T, Tanaka K. CHIP: a quality-control E3 ligase collaborating with molecular chaperones. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35:572–8. doi: 10.1016/S1357-2725(02)00394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Synofzik M, Gonzalez MA, Lourenco CM, Coutelier M, Haack TB, Rebelo A, Hannequin D, Strom TM, Prokisch H, Kernstock C, Durr A, Schöls L, Lima-Martínez MM, Farooq A, Schüle R, Stevanin G, Marques W, Züchner S. PNPLA6 mutations cause Boucher-Neuhauser and Gordon Holmes syndromes as part of a broad neurodegenerative spectrum. Brain. 2014;137(Pt 1):69–77. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gonzalez M, Falk MJ, Gai X, Postrel R, Schüle R, Zuchner S. Innovative Genomic Collaboration Using the GENESIS (GEM.app) Platform. Hum Mutat. 2015;36:950–6. doi: 10.1002/humu.22836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gonzalez MA, Lebrigio RFA, Van Booven D, Ulloa RH, Powell E, Speziani F, Tekin M, Schüle R, Züchner S. GEnomes Management Application (GEM.app): A New Software Tool for Large-Scale Collaborative Genome Analysis. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:842–6. doi: 10.1002/humu.22305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Anheim M, Monga B, Fleury M, Charles P, Barbot C, Salih M, Delaunoy JP, Fritsch M, Arning L, Synofzik M, Schöls L, Sequeiros J, Goizet C, Marelli C, Le Ber I, Koht J, Gazulla J, De Bleecker J, Mukhtar M, Drouot N, Ali-Pacha L, Benhassine T, Chbicheb M, M’Zahem A, Hamri A, Chabrol B, Pouget J, Murphy R, Watanabe M, Coutinho P, et al. Ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 2: Clinical, biological and genotype/phenotype correlation study of a cohort of 90 patients. Brain. 2009;132:2688–98. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM, Behrens TEJ. Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage. 2006;31:1487–505. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mori S, Wakana S, van Zijl PCM, Nagae-Poetscher LM. MRI Atlas of Human White Matter. 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Synofzik M, Gasser T. Moving beyond syndromic classifications in neurodegenerative disease: the example of PLA2G6. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2017;4:8–11. doi:10.1002/mdc3.12441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Synofzik M, Schüle R. Overcoming the divide between ataxias and spastic paraplegias:shared phenotypes, genes and pathways. Mov Disord. 2017: accepted for publication [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Schmitz-Hübsch T, du Montcel ST, Baliko L, Berciano J, Boesch S, Depondt C, Giunti P, Globas C, Infante J, Kang J-S, Kremer B, Mariotti C, Melegh B, Pandolfo M, Rakowicz M, Ribai P, Rola R, Schöls L, Szymanski S, van de Warrenburg BP, Dürr A, Klockgether T, Fancellu R. Scale for the assessment and rating of ataxia: development of a new clinical scale. Neurology. 2006;66:1717–20. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000219042.60538.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schüle R, Holland-Letz T, Klimpe S, Kassubek J, Klopstock T, Mall V, Otto S, Winner B, Schöls L. The Spastic Paraplegia Rating Scale (SPRS): a reliable and valid measure of disease severity. Neurology. 2006;67:430–4. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000228242.53336.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Please contact author for data requests.


