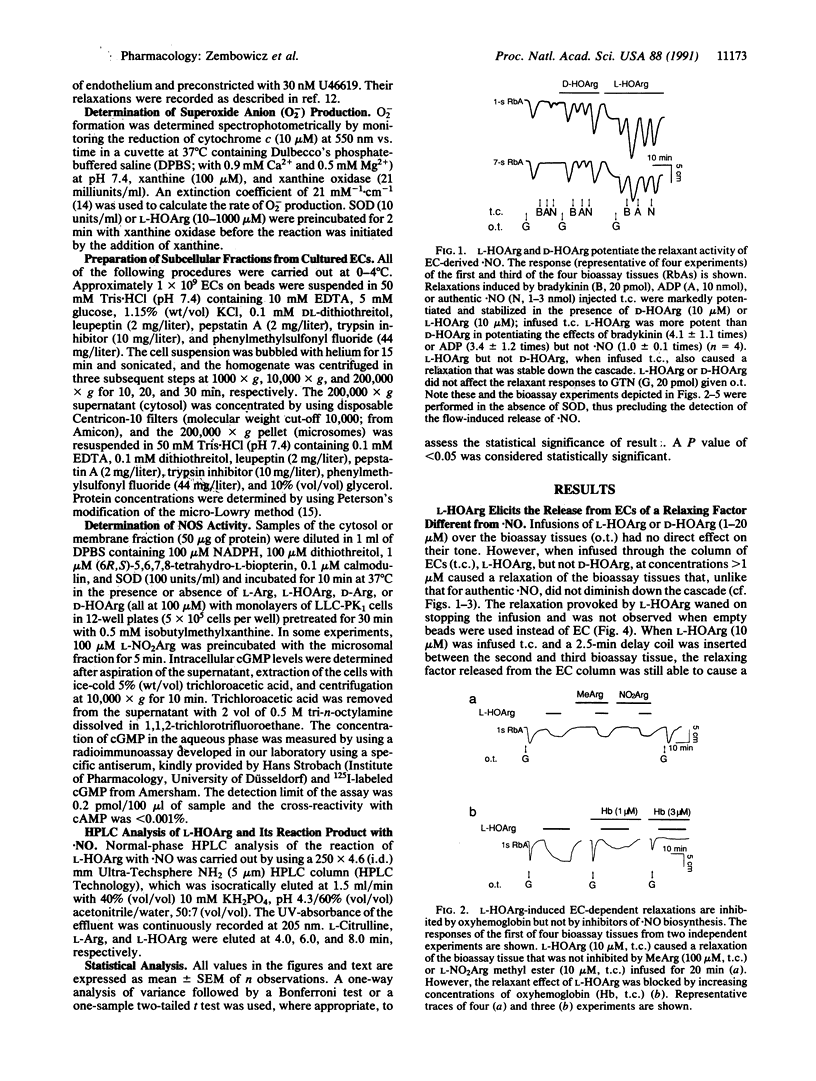
Abstract
The hypothesis was investigated that NG-hydroxy-L-arginine (L-HOArg) is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nitric oxide (.NO) from L-arginine (L-Arg) by the constitutive .NO synthase (NOS) present in endothelial cells (ECs). When infused through a column of bovine aortic ECs on beads, either L-HOArg or D-HOArg (1-10 microM) substantially potentiated relaxations of the bioassay tissues to .NO released from the cells by ADP or bradykinin, and this effect was abolished by coinfusions of NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NO2Arg) methyl ester (10 microM) or NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-MeArg; 30 microM). Both L-HOArg and D-HOArg, irrespective of the presence of ECs, also potentiated relaxations induced by authentic .NO, but not glyceryl trinitrate. This was due to a rapid chemical reaction of either isomer with .NO, resulting in the formation of a potent and more stable vasodilator. When infusions of L-HOArg (3 microM) were consequently made in the presence of D-HOArg (10 microM), the L-isomer no longer had any effect on relaxations induced by authentic .NO, but significantly increased the stimulated release of .NO from the column of ECs. The conclusion that L-HOArg is a substrate for the constitutive NOS in cultured ECs was strongly supported by the L-NO2Arg-sensitive conversion of L-HOArg, but not D-HOArg, to .NO by NOS preparations from these cells. Interestingly, cultured ECs produced from L-HOArg (greater than or equal to 3 microM), but not D-HOArg, a stable vasodilator, the effects of which were inhibited by oxyhemoglobin (0.3-3 microM). However, the formation of this substance was not prevented by L-NO2Arg methyl ester (10 microM) or L-MeArg (10-100 microM), suggesting an enzymatic pathway different from NOS.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Calmodulin-dependent endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase activity is present in the particulate and cytosolic fractions of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1788–1792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Moncada S., Palmer R. M. Bioassay of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) from porcine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):685–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Superoxide anion is involved in the breakdown of endothelium-derived vascular relaxing factor. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):454–456. doi: 10.1038/320454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Lückhoff A., Mülsch A., Kohler J., Bessler W., Busse R. Induction and activity of NO synthase in bone-marrow-derived macrophages are independent of Ca2+. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):351–356. doi: 10.1042/bj2700351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Sessa W. C., Harris H. J., Anggård E. E., Vane J. R. The metabolism of L-arginine and its significance for the biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: cultured endothelial cells recycle L-citrulline to L-arginine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8612–8616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Gilker C., Griffith O. W., Matthews D. E., Stuehr D. J. L-citrulline production from L-arginine by macrophage nitric oxide synthase. The ureido oxygen derives from dioxygen. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13442–13445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. A., Hecker M., Vane J. R. The generation of L-arginine in endothelial cells is linked to the release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 6;176(2):253–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90541-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Hibbs J. B., Jr Role of nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90079-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Cellek S., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Dexamethasone prevents the induction by endotoxin of a nitric oxide synthase and the associated effects on vascular tone: an insight into endotoxin shock. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 14;173(2):541–547. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Bredt D. S. Nitric oxide as a neuronal messenger. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90526-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Griffith O. W., Feldman P. L., Wiseman J. N omega-hydroxy-L-arginine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6259–6263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Anggård E. E., Botting R. M. Regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):27–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace G. C., Gulati P., Fukuto J. M. N omega-hydroxy-L-arginine: a novel arginine analog capable of causing vasorelaxation in bovine intrapulmonary artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):528–534. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90957-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Gryglewski R. J., Warner T. D., Vane J. R. Receptor-mediated release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and prostacyclin from bovine aortic endothelial cells is coupled. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


