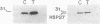Abstract
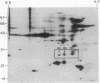
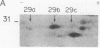
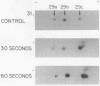
Thrombin plays a critical role in platelet activation, hemostasis, and thrombosis. Cellular activation by thrombin leads to the phosphorylation of multiple proteins, most of which are unidentified. We have characterized several 29-kDa proteins that are rapidly phosphorylated following exposure of intact human platelets to thrombin. A murine monoclonal antibody raised to an unidentified estrogen receptor-related 29-kDa protein selectively recognized these proteins as well as a more basic, unphosphorylated 27-kDa protein. Cellular activation by thrombin led to a marked shift in the proportion of protein from the 27-kDa unphosphorylated form to the 29-kDa phosphoprotein species. Using this antibody, we isolated and sequenced a human cDNA clone encoding a protein that was identical to the mammalian 27-kDa heat shock protein (HSP27), a protein of uncertain function that is known to be phosphorylated to several forms and to be transcriptionally induced by estrogen. The 29-kDa proteins were confirmed to be phosphorylated forms of HSP27 by immunoprecipitation studies. Thus, the "estrogen receptor-related protein" is HSP27, and the three major 29-kDa proteins phosphorylated in thrombin-activated platelets are forms of HSP27. These data suggest a role for HSP27 in the signal transduction events of platelet activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Hajj H., Edwards D. P., Bjercke R. J., McGuire W. L. Detection of a Mr 24,000 estrogen-regulated protein in human breast cancer by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1983 Sep;43(9):4297–4301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Suhan J. P., Welch W. J. Dynamic changes in the structure and intracellular locale of the mammalian low-molecular-weight heat shock protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5059–5071. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P. Tumor necrosis factor induces the rapid phosphorylation of the mammalian heat shock protein hsp28. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1276–1280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Welch W. J. Characterization and purification of the small 28,000-dalton mammalian heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15359–15369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Nairn A. C., Kuo J. F. Protein kinases 1988: a current perspective. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2957–2969. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.14.2972578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Pouyssegur J. Thrombin-induced protein phosphorylation in resting platelets and fibroblasts: evidence for common post-receptor molecular events. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):1034–1044. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91404-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffer A. I., King R. J. Characterization of p29, an estrogen-receptor associated tumor marker. J Steroid Biochem. 1988 Nov;31(5):745–750. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(88)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffer A. I., Lewis K. M., Brockas A. J., King R. J. Monoclonal antibodies against a component related to soluble estrogen receptor. Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;45(8):3686–3693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbon J. M., Issandou M., Tournier J. F., Bayard F. The respective 27 kDa and 28 kDa protein kinase C substrates in vascular endothelial and MCF-7 cells are most probably heat shock proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demolle D., Lecomte M., Boeynaems J. M. Pattern of protein phosphorylation in aortic endothelial cells. Modulation by adenine nucleotides and bradykinin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18459–18465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. P., Adams D. J., McGuire W. L. Estradiol stimulates synthesis of a major intracellular protein in a human breast cancer cell line (MCF-7). Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1981;1(3):209–223. doi: 10.1007/BF01806261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidt J. F., Allison P., Noble S., Ashton J., Golino P., McNatt J., Buja L. M., Willerson J. T. Thrombin is an important mediator of platelet aggregation in stenosed canine coronary arteries with endothelial injury. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):18–27. doi: 10.1172/JCI114138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Thrombin stimulates the activities of multiple previously unidentified protein kinases in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20723–20729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuqua S. A., Blum-Salingaros M., McGuire W. L. Induction of the estrogen-regulated "24K" protein by heat shock. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 1;49(15):4126–4129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaestel M., Schröder W., Benndorf R., Lippmann C., Buchner K., Hucho F., Erdmann V. A., Bielka H. Identification of the phosphorylation sites of the murine small heat shock protein hsp25. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14721–14724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Zeheb R., Yang A. Y., Rafferty U. M., Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L., Dano K., Lebo R. V., Gelehrter T. D. cDNA cloning of human plasminogen activator-inhibitor from endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1673–1680. doi: 10.1172/JCI112761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J. R., Coffer A. I., King R. J. Immunoaffinity purification and characterisation of p29--an estrogen receptor related protein. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 30;37(4):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(90)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey E., Brandon S. E., Potter R., Stein G., Stein J., Weber L. A. Sequence and organization of genes encoding the human 27 kDa heat shock protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4127–4145. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., Welch W. J., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor increase phosphorylation of the small heat shock protein. Effects in fibroblasts, Hep G2 and U937 cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 4;258(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81671-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Shuman J., Sette M., Przybyla A. Phosphorylation pattern of a 25 Kdalton stress protein from rat myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):682–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91651-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Finley J. R., Coffer A. I., Millis R. R., Rubens R. D. Characterization and biological relevance of a 29-kDa, oestrogen receptor-related protein. J Steroid Biochem. 1987;27(1-3):471–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)90342-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Fröhli E., Steiger R. H., Schäfer R., Aoyama A. Alpha B-crystallin is a small heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3652–3656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Schafer A. I. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1181–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Zavoico G. B., Schafer A. I. Control of platelet protein kinase C activation by cyclic AMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 8;970(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Santell L. Thrombin- and histamine-induced signal transduction in human endothelial cells. Stimulation and agonist-dependent desensitization of protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):174–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludány A., Kellermayer M. Protein synthesis in human platelets. Clin Biochem. 1988 Apr;21(2):107–110. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(88)80097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced protein phosphorylation in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):924–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn M. E., O'Neill S., George D., Loscalzo J. Inhibition of fibrinogen binding to human platelets by S-nitroso-N-acetylcysteine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19028–19034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Percy C., Young R. A. Gene isolation by screening lambda gt11 libraries with antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:458–469. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. A., Jefferson A. B., Bejeck B. E., Brugge J. S., Deuel T. F., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-stimulated immunoprecipitation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9396–9400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. Interaction of hsp90 with steroid receptors: organizing some diverse observations and presenting the newest concepts. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Nov 12;74(1):C69–C76. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90198-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12111–12114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Meizel S. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in human sperm stimulated with follicular fluid or progesterone is dependent upon Ca2+ influx. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):539–546. doi: 10.1042/bj2640539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J. Phorbol ester, calcium ionophore, or serum added to quiescent rat embryo fibroblast cells all result in the elevated phosphorylation of two 28,000-dalton mammalian stress proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3058–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicki A. N., Walz A., Gerber-Huber S. N., Wenger R. H., Vornhagen R., Clemetson K. J. Isolation and characterization of human blood platelet mRNA and construction of a cDNA library in lambda gt11. Confirmation of the platelet derivation by identification of GPIb coding mRNA and cloning of a GPIb coding cDNA insert. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Jun 30;61(3):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]