Abstract
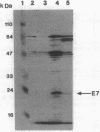
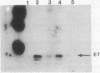
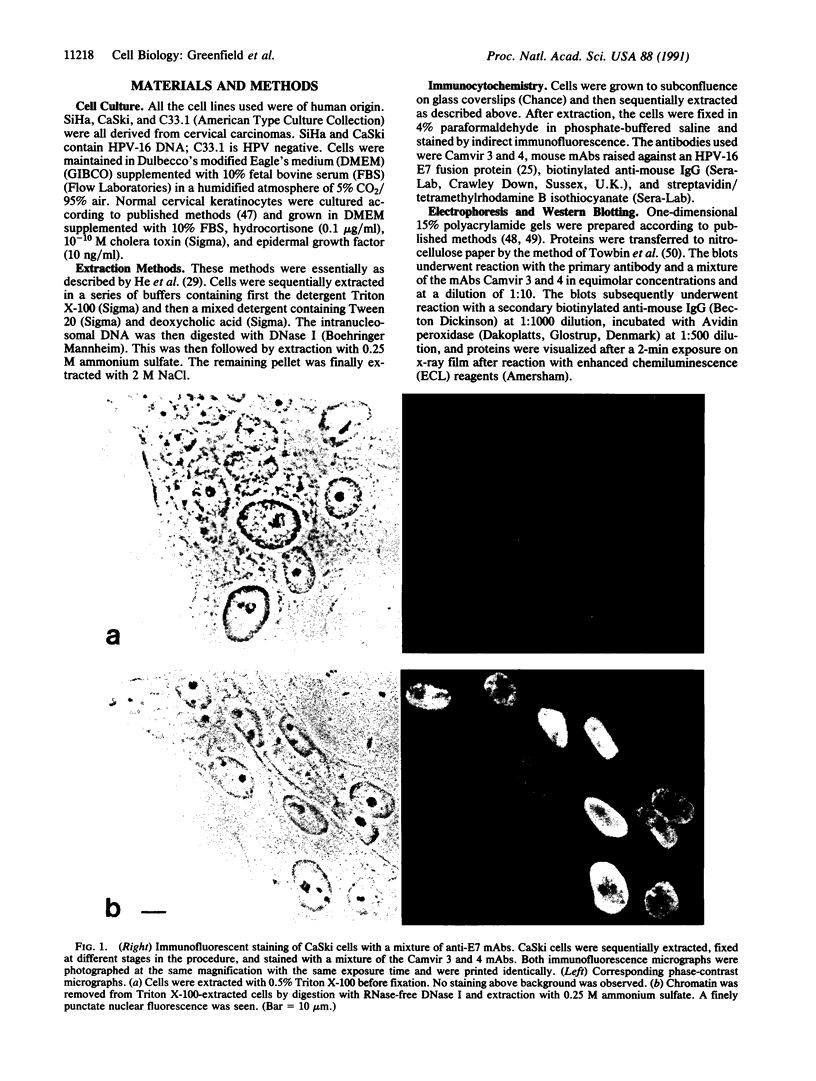
The cellular localization of the human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 E7 gene product in the cell lines CaSki and SiHa has been determined by both biochemical and immunocytochemical methods. These measurements show E7 to be localized in the cell nucleus, specifically with the nonchromatin nuclear structure or nuclear matrix. This localization of E7 required an unambiguous fractionation of the nuclear constituents. This was achieved by using a gentle sequential fractionation procedure to prepare the scaffold consisting of the nuclear matrix and intermediate filaments (NM-IF). Chromatin was cleaved with nuclease and the resulting nucleosomes eluted with 0.25 M ammonium sulfate. Immunostaining of cells after this extraction procedure with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to E7 revealed a fine grained, punctate nuclear fluorescence in CaSki and SiHa, which was absent in normal cervical keratinocytes and the HPV-negative cell line C33.1. Western blots of cell fractions with these mAbs showed that E7 was localized in the NM-IF fraction in SiHa and CaSki but was not detected in HPV-negative cells. A second protein of slightly higher mobility is identified by these antisera in HPV-16-containing cells. The data suggest that the previous inability to directly visualize E7 by immunocytology is due to the masking of epitopes by cellular components and not to low levels of protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of HPV-18 are sufficient for inducing two-stage in vitro transformation of human keratinocytes. Oncogene. 1989 Dec;4(12):1529–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrack E. R., Coffey D. S. The specific binding of estrogens and androgens to the nuclear matrix of sex hormone responsive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7265–7275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrack E. R. The nuclear matrix of the prostate contains acceptor sites for androgen receptors. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):430–432. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Abulafia R., Aloni Y. SV40 virions and viral RNA metabolism are associated with cellular substructures. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1225–1231. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Nuclear protein matrix: association with newly synthesized DNA. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):291–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1145202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capco D. G., Wan K. M., Penman S. The nuclear matrix: three-dimensional architecture and protein composition. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):847–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90446-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee P. K., Flint S. J. Partition of E1A proteins between soluble and structural fractions of adenovirus-infected and -transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1018–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1018-1026.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen A. P., Reid R., Campion M., Lörincz A. T. Analysis of the physical state of different human papillomavirus DNAs in intraepithelial and invasive cervical neoplasm. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):606–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.606-612.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Fey E. G., Penman S., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Progressive changes in the protein composition of the nuclear matrix during rat osteoblast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4605–4609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey E. G., Penman S. Nuclear matrix proteins reflect cell type of origin in cultured human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):121–125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. G., Girardi F., Pfister H. Human papillomavirus DNA in normal, metaplastic, preneoplastic and neoplastic epithelia of the cervix uteri. Int J Cancer. 1988 Jan 15;41(1):41–45. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwo S., Bryan J. Immuno-identification of Ca2+-induced conformational changes in human gelsolin and brevin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):227–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Zanma S., Watanabe S., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Two immunodominant regions of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein are masked in the nuclei of monkey COS-1 cells. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):723–731. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90613-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Characterization of primary human keratinocytes transformed by human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1917-1924.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCready S. J., Godwin J., Mason D. W., Brazell I. A., Cook P. R. DNA is replicated at the nuclear cage. J Cell Sci. 1980 Dec;46:365–386. doi: 10.1242/jcs.46.1.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Okamoto T., Reuter P., Ugarkovic D., Schröder H. C. Functional characterization of Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Evidence that Tat links viral RNAs to nuclear matrix. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3803–3808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Wenger R., Reuter P., Renneisen K., Schröder H. C. Association of Tat protein and viral mRNA with nuclear matrix from HIV-1-infected H9 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 7;1008(2):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(80)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Werness B. A., Dyson N., Phelps W. C., Harlow E., Howley P. M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4099–4105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson J. A., Krochmalnic G., Wan K. M., Penman S. Chromatin architecture and nuclear RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro G., Morgan D., Defendi V. Differential effects of human papillomavirus type 6, 16, and 18 DNAs on immortalization and transformation of human cervical epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):563–567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. C., Caussy D., Brinton L. A., Brenes M. M., Montalvan P., Gomez B., de Britton R. C., Morice E., Gaitan E., de Lao S. L. Case-control study of human papillomaviruses and cervical cancer in Latin America. Int J Cancer. 1987 Oct 15;40(4):450–454. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie P. S., Bruchovsky N., Cheng H. Isolation of 3 S androgen receptors from salt-resistant fractions and nuclear matrices of prostatic nuclei after mild trypsin digestion. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7623–7630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Hearing P., Anderson C. W., Reich N., Levine A. J. Identification and characterization of an immunologically conserved adenovirus early region 11,000 Mr protein and its association with the nuclear matrix. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):565–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90389-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Watanabe S., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein expressed in Escherichia coli and monkey COS-1 cells: immunofluorescence detection of the nuclear E7 protein. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmbeck R., Deppert W. Nuclear subcompartmentalization of simian virus 40 large T antigen: evidence for in vivo regulation of biochemical activities. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2308–2316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2308-2316.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvey L. A., Tindle R. W., Geysen H. M., Haller C. J., Smith J. A., Frazer I. H. Identification of B-epitopes in the human papillomavirus 18 E7 open reading frame protein. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3105–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen R. C., Means A. R., Clark J. H. Estrogen modulation of nuclear matrix-associated steroid hormone binding. Endocrinology. 1984 Sep;115(3):1197–1202. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-3-1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Boyle W. J., Keith D. E., Press M. F., Golde D. W., Souza L. M. Subnuclear localization of the trans-activating protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):680–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.680-686.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley M. A., Parkinson E. K. Growth requirements of human cervical epithelial cells in culture. Int J Cancer. 1979 Oct 15;24(4):407–414. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Pim D., Murray A., Osborn K., Banks L., Crawford L. Comparison of the in vitro transforming activities of human papillomavirus types. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1815–1820. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuurman N., Van Driel R., De Jong L., Meijne A. M., Van Renswoude J. The protein composition of the nuclear matrix of murine P19 embryonal carcinoma cells is differentiation-stage dependent. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Feb;180(2):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindle R. W., Smith J. A., Geysen H. M., Selvey L. A., Frazer I. H. Identification of B epitopes in human papillomavirus type 16 E7 open reading frame protein. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommasino M., Contorni M., Scarlato V., Bugnoli M., Maundrell K., Cavalieri F. Synthesis, phosphorylation, and nuclear localization of human papillomavirus E7 protein in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Gene. 1990 Sep 14;93(2):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90234-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A., Lowy D. R. The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 encodes a transforming gene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Wilson R. C., Efstratiadis A. Autonomous splicing and complementation of in vivo-assembled spliceosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):765–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Wilson R. C., Efstratiadis A. Autonomous splicing and complementation of in vivo-assembled spliceosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):765–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]