Fig. 4.
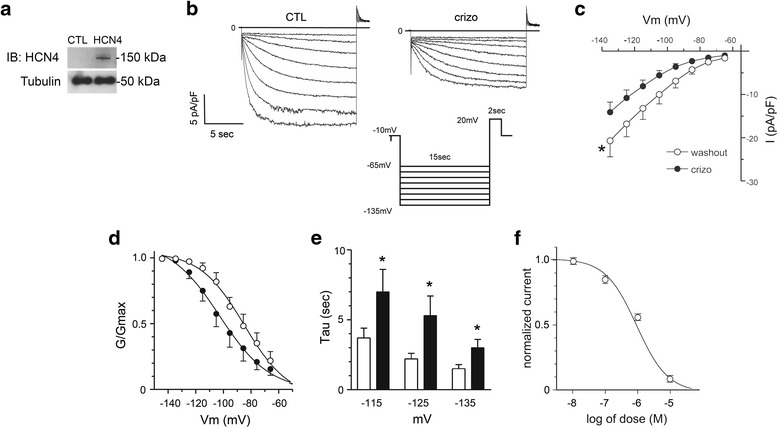
Crizotinib inhibits HCN4 channel activity. a Protein lysates from non-transfected control HEK-293 cells (CTL) and HEK-293 cells with stable expression of human HCN4 (HCN4) were subjected to sequential immunoblotting (IB) for HCN4 and then tubulin, as indicated. The whole cell patch-clamp technique was then used to assess HCN4 channel activity in HEK-293 cells with stable expression of human HCN4. b Representative traces of IHCN4 recorded in HCN4-expressing HEK-293 cells before (CTL) and during perfusion with crizotinib (crizo,1 μmol/L). IHCN4 was elicited by 15 s test pulses from a holding potential of -10 mV to test potentials ranging from −65 to -135 mV (in 10 mV increments) and then back to +20 mV for 2 s to test tail current, followed by return to holding potential (inset). c, Current–voltage (I-V) relationship for IHCN4 with crizotinib perfusion (crizo, filled circles) and after washout (open circles) (n = 9 per group). Current shown was normalized to membrane capacitance (pA/pF). A significant reduction in HCN4 current density was noted with crizotinib exposure at test potentials from −65 mv to −135 mV (p < 0.05, washout vs. crizotinib treated I-V curves by two-way ANOVA). d Effect of crizotinib on the voltage dependence of HCN4 activation. Activation curves were generated for IHCN4 with crizotinib perfusion (crizo, filled circles) and after washout (open circles). Crizotinib shifted the activation curve to the left towards more hyperpolarized potentials and shifted the average activation midpoint (V0.5) (V0.5 = −84 ± 2 vs. -102 ± 2 mV, washout vs. crizo, p < 0.05). e Average time constants (Tau) of HCN4 channel activation are plotted against test potentials with crizotinib perfusion (filled bars) and after washout (open bars) (n = 11 for each group). Crizotinib resulted in slower HCN4 channel activation at test potentials ≥ −115 mV (*, washout vs. crizo, p < 0.05). f IHCN4 (normalized to untreated controls) was measured at increasing crizotinib concentrations (0–10 μmol/L) in HCN4-expressing HEK-293 cells. A smooth curve was obtained by fitting the data with the Hill equation. Half-maximal inhibition concentration (IC50) was 1.4 ± 0.3 μmol/L (n = 4–18 at each concentration)
