Abstract
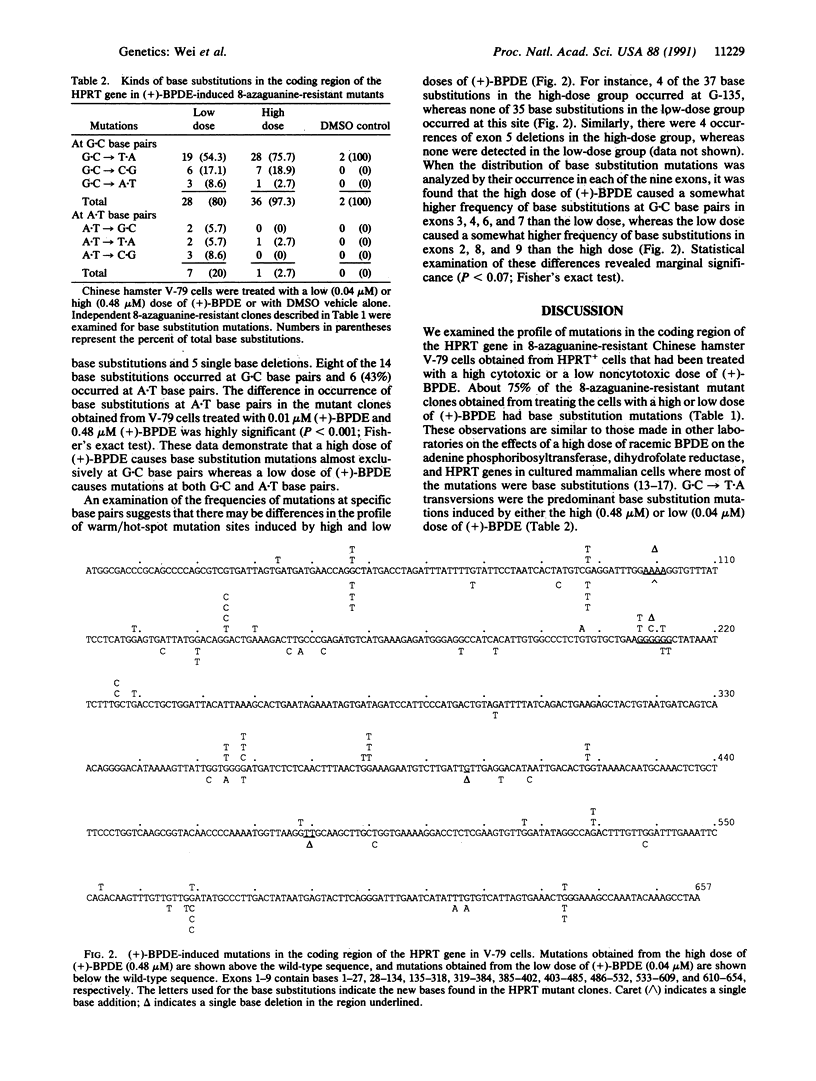
Mutations in the coding region of the hypoxanthine (guanine) phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) gene of Chinese hamster V-79 cells were examined after exposure of the cells to a high cytotoxic dose (0.48 microM; 35% survival) and a low noncytotoxic dose (0.04 microM; 100% survival) of the ultimate carcinogen (+)-7R,8S-dihydroxy-9S,10R-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene [(+)-BPDE]. Independent 8-azaguanine-resistant colonies were isolated and cDNAs were prepared by reverse transcription. The coding region of the cDNA of the HPRT gene was amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and sequenced. An examination of the DNA base sequence changes induced by different doses of (+)-BPDE demonstrated that the high dose of (+)-BPDE caused base substitution mutations almost exclusively at G.C base pairs whereas the low dose of (+)-BPDE caused mutations at both G.C and A.T base pairs. Thus, use of a low dose of (+)-BPDE allowed the detection of mutations (at A.T base pairs) that were not readily observed with a high dose of (+)-BPDE. The data also suggest that the low dose of (+)-BPDE may have caused a different profile of base substitutions at G.C base pairs and exon deletions than the high dose. The results indicate dose-dependent differences in the profile of mutations for an ultimate carcinogen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buening M. K., Wislocki P. G., Levin W., Yagi H., Thakker D. R., Akagi H., Koreeda M., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Tumorigenicity of the optical enantiomers of the diastereomeric benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-diol-9,10-epoxides in newborn mice: exceptional activity of (+)-7beta,8alpha-dihydroxy-9alpha,10alpha-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5358–5361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Grunberger D. DNA base changes in benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-induced dihydrofolate reductase mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jan;11(1):189–192. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.1.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Effect of excision repair by diploid human fibroblasts on the kinds and locations of mutations induced by (+/-)-7 beta,8 alpha-dihydroxy-9 alpha,10 alpha-epoxy-7,8,9,10- tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene in the coding region of the HPRT gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8680–8684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Lack of a cell cycle-dependent strand bias for mutations induced in the HPRT gene by (+/-)-7 beta,8 alpha-dihydroxy-9 alpha,10 alpha-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo(a)pyrene in excision repair-deficient human cells. Cancer Res. 1991 May 15;51(10):2587–2592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Hilton B. D., Roman J. M., Dipple A. DNA adducts from carcinogenic and noncarcinogenic enantiomers of benzo[a]pyrene dihydrodiol epoxide. Chem Res Toxicol. 1989 Sep-Oct;2(5):334–340. doi: 10.1021/tx00011a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koreeda M., Moore P. D., Wislocki P. G., Levin W., Yagi H., Jerina D. M. Binding of benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-diol-9,10-epoxides to DNA, RNA, and protein of mouse skin occurs with high stereoselectivity. Science. 1978 Feb 17;199(4330):778–781. doi: 10.1126/science.622566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Endogenous carcinogenesis: molecular oncology into the twenty-first century--presidential address. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 15;49(20):5489–5496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur M., Glickman B. W. Sequence specificity of mutations induced by benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide at endogenous aprt gene in CHO cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Jul;14(4):393–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01534647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan T., Straub K. Double-stranded DNA steroselectively binds benzo(a)pyrene diol epoxides. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):410–412. doi: 10.1038/277410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne M. R., Harvey R. G., Brookes P. The reaction of trans-7,8-dihydroxy-anti-9,10-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo(a)pyrene with DNA involves attack at the N7-position of guanine moieties. Chem Biol Interact. 1978 Jan;20(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(78)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaga T. J., Bracken W. J., Gleason G., Levin W., Yagi H., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Marked differences in the skin tumor-initiating activities of the optical enantiomers of the diastereomeric benzo(a)pyrene 7,8-diol-9,10-epoxides. Cancer Res. 1979 Jan;39(1):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Chang R. L., Levin W., Yagi H., Thakker D. R., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Differences in mutagenicity of the optical enantiomers of the diastereomeric benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-diol-9,10-epoxides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1389–1396. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Goode R. L., Chang R. L., Levin W., Conney A. H., Yagi H., Dansette P. M., Jerina D. M. Mutagenic and cytotoxic activity of benzol[a]pyrene 4,5-, 7,8-, and 9,10-oxides and the six corresponding phenols. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3176–3180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi H., Akagi H., Thakker D. R., Mah H. D., Koreeda M., Jerina D. M. Absolute sterochemistry of the highly mutagenic 7,8-diol 9,10-epoxides derived from the potent carcinogen trans-7,8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzol[a]pyrene. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Mar 30;99(7):2358–2359. doi: 10.1021/ja00449a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. L., Chen R. H., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Kinds and location of mutations induced by (+/-)-7 beta,8 alpha-dihydroxy-9 alpha,10 alpha-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene in the coding region of the hypoxanthine (guanine) phosphoribosyltransferase gene in diploid human fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jan;12(1):71–75. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. L., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Amplification and direct nucleotide sequencing of cDNA from the lysate of low numbers of diploid human cells. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. L., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Kinds of mutations formed when a shuttle vector containing adducts of (+/-)-7 beta, 8 alpha-dihydroxy-9 alpha, 10 alpha-epoxy-7,8,9, 10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene replicates in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3787–3791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. L., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Kinds of mutations formed when a shuttle vector containing adducts of benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide replicates in COS7 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1267–1270. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



