Abstract
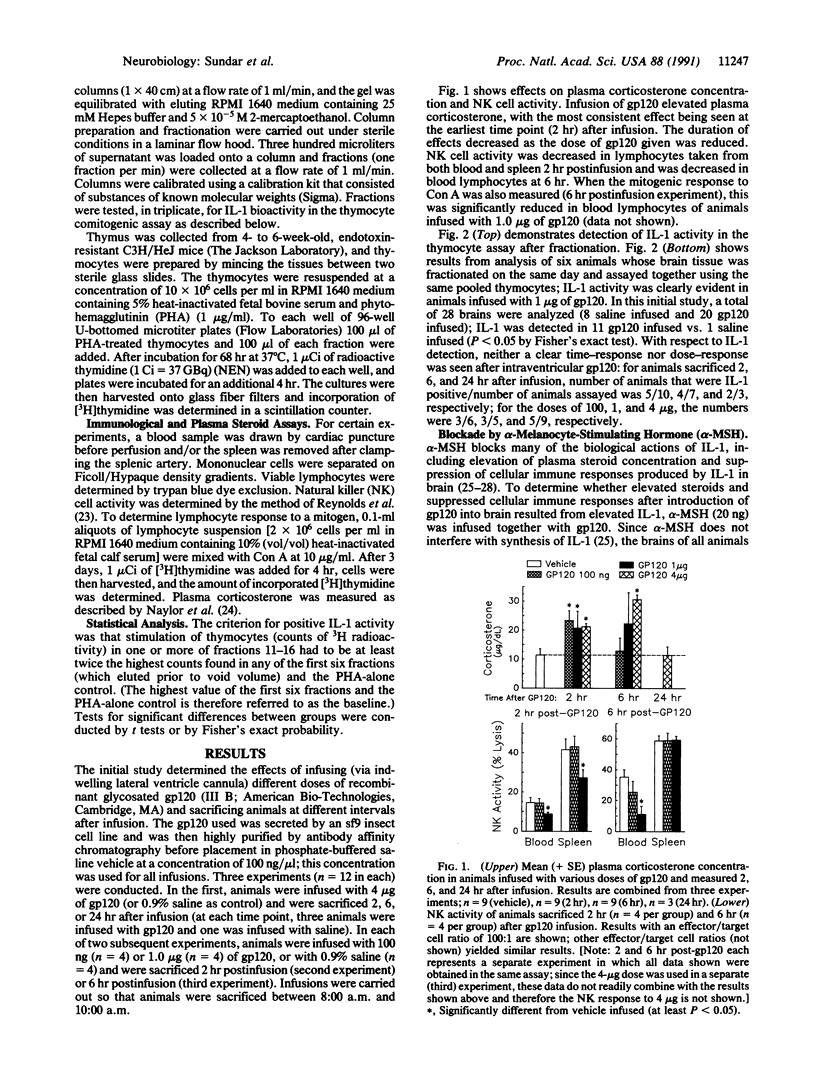
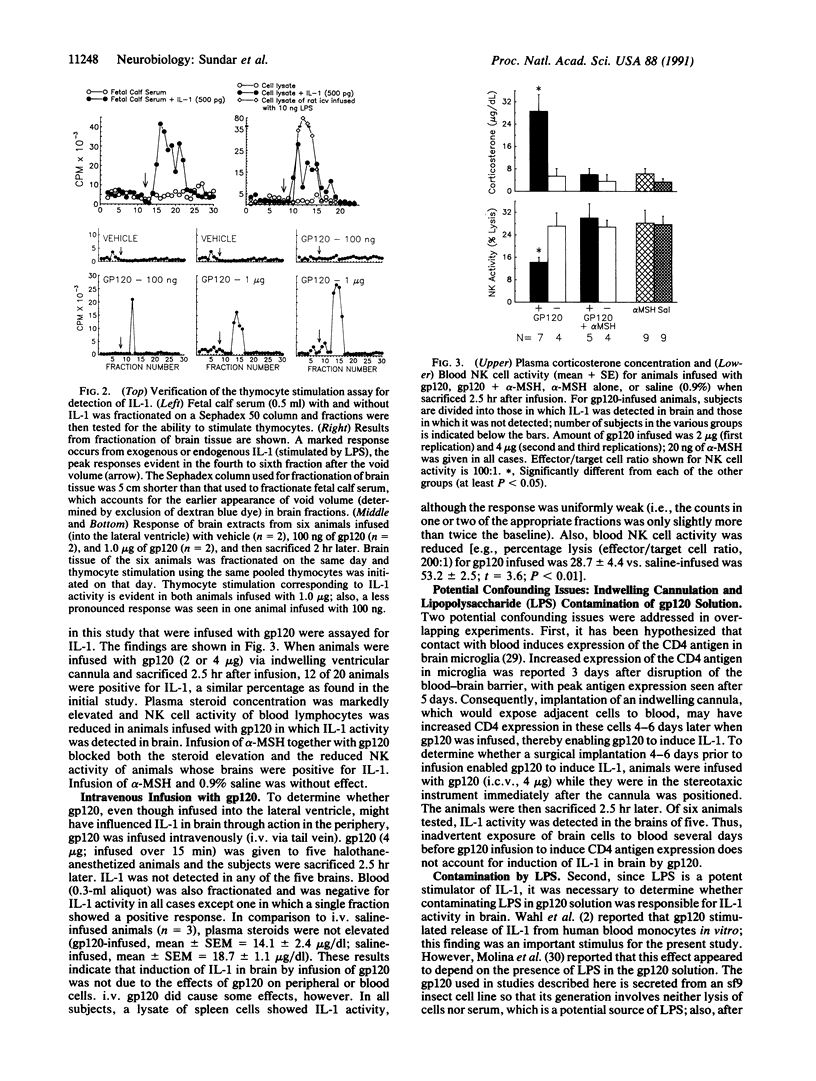
Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) infusion of glycosylated recombinant gp120, the envelope protein of human immunodeficiency virus, in various doses (100 ng to 4 micrograms) resulted in detection of interleukin 1 (IL-1) activity in a high percentage (61%; 33 of 54) of rat brains, whereas IL-1 was very rarely detected in brains of animals infused with several control substances (4%; 1 of 28). To detect IL-1, clarified glial lysate of diencephalon plus brainstem was subjected to gel exclusion chromatography and fractions were assessed for thymocyte stimulation. IL-1 was seen 2, 6, and 24 hr postinfusion. i.c.v. gp120 also produced known effects of IL-1 in brain, elevating steroid concentration in plasma and decreasing cellular immune responses [natural killer (NK) cell activity and mitogenic response to Con A] of blood and splenic lymphocytes. When gp120 was infused together with alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (20 ng), which blocks many biological actions of IL-1, gp120 no longer elevated steroids or decreased NK cell activity. After intravenous gp120, IL-1 was not found in brain or plasma, indicating that stimulation of IL-1 in brain by i.c.v. gp120 was not due to gp120 affecting infiltrating cells from blood or to elevated circulating IL-1. That induction of IL-1 in brain might have resulted from lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the gp120 solution was ruled out by studies showing that (i) heating of the infusion solution, which does not affect the capacity of LPS to induce IL-1, eliminated the ability of gp120 infusion to induce brain IL-1, and (ii) gp120 induced IL-1 in brains of LPS-resistant C3H/HeJ mice. Injection of gp120 directly into the hippocampus stimulated IL-1 more readily than i.c.v. infusion. Thymocyte stimulation produced by active fractions of gp120-infused brains was blocked by monoclonal antibody to IL-1 receptors. These findings indicate that elevation of IL-1 in brain can result from infection with human immunodeficiency virus and may be responsible for certain abnormalities (e.g., elevated activity of pituitary-adrenal axis) seen in AIDS patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ban E., Milon G., Prudhomme N., Fillion G., Haour F. Receptors for interleukin-1 (alpha and beta) in mouse brain: mapping and neuronal localization in hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1991;43(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90412-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernton E. W., Beach J. E., Holaday J. W., Smallridge R. C., Fein H. G. Release of multiple hormones by a direct action of interleukin-1 on pituitary cells. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):519–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2821620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besedovsky H., del Rey A., Sorkin E., Dinarello C. A. Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.3014662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., Saper C. B. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3258444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R., Li Z., Vriend C. Y., Nirula R., Janz L., Falk J., Nance D. M., Dyck D. G., Greenberg A. H. Suppression of splenic macrophage interleukin-1 secretion following intracerebroventricular injection of interleukin-1 beta: evidence for pituitary-adrenal and sympathetic control. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jan;132(1):84–93. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90008-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Dinarello C. A. Increased plasma interleukin-1 activity in women after ovulation. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.3871966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tatro J. B., Reichlin S., Dinarello C. A. Alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone inhibits immunostimulatory and inflammatory actions of interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2232–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daynes R. A., Robertson B. A., Cho B. H., Burnham D. K., Newton R. Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone exhibits target cell selectivity in its capacity to affect interleukin 1-inducible responses in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kloet E. R., Ratka A., Reul J. M., Sutanto W., Van Eekelen J. A. Corticosteroid receptor types in brain: regulation and putative function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;512:351–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb24973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Mier J. W., Bernheim H. A., LoPreste G., Lynn D. L., Love R. N., Webb A. C., Auron P. E., Reuben R. C. Multiple biological activities of human recombinant interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1734–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI112495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Kilian P. L., Ruff M. R., Hill J. M., Pert C. B. Visualization and characterization of interleukin 1 receptors in brain. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):459–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Grob P. J. Astrocyte-derived interleukin-1-like factors. Lymphokine Res. 1984;3(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Weber E., Dayer J. M. Synthesis of interleukin 1/endogenous pyrogen in the brain of endotoxin-treated mice: a step in fever induction? J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1696–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo P., Frei K., Rordorf C., Lazdins J., Tavolato B., Fontana A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the central nervous system: an evaluation of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jul;23(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Baker T. J., Shih L. C., Lachman L. B. Interleukin 1 of the central nervous system is produced by ameboid microglia. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):594–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 stimulation of astroglial proliferation after brain injury. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3872478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Walter J., Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M., Chedid L. Sleep-promoting effects of endogenous pyrogen (interleukin-1). Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):R994–R999. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.6.R994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B. S., Weiss J. M., Schwartz L. S. Selective retention of corticosterone by limbic structures in rat brain. Nature. 1968 Nov 30;220(5170):911–912. doi: 10.1038/220911a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Koyanagi Y., Chen I. S. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha can be induced from mononuclear phagocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 binding to the CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4404–4408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4404-4408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina J. M., Scadden D. T., Amirault C., Woon A., Vannier E., Dinarello C. A., Groopman J. E. Human immunodeficiency virus does not induce interleukin-1, interleukin-6, or tumor necrosis factor in mononuclear cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2901–2906. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2901-2906.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. T., Richards D. B., Lipton J. M. Antipyretic potency of centrally administered alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone. Science. 1983 Jul 8;221(4606):192–193. doi: 10.1126/science.6602381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor M. R., Krishnan K. R., Manepalli A. N., Ritchie J. C., Jr, Wilson W. H., Carroll B. J. Circadian rhythm of adrenergic regulation of adrenocorticotropin and cortisol secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Aug;67(2):404–406. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-2-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. W. Organic mental disorders caused by HIV: update on early diagnosis and treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1990 Jun;147(6):696–710. doi: 10.1176/ajp.147.6.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Gordon S. Modulation of CD4 antigen on macrophages and microglia in rat brain. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1138–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R. M. A mechanism for glucocorticoid toxicity in the hippocampus: increased neuronal vulnerability to metabolic insults. J Neurosci. 1985 May;5(5):1228–1232. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-05-01228.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R., Rivier C., Yamamoto G., Plotsky P., Vale W. Interleukin-1 stimulates the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.2821621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundar S. K., Becker K. J., Cierpial M. A., Carpenter M. D., Rankin L. A., Fleener S. L., Ritchie J. C., Simson P. E., Weiss J. M. Intracerebroventricular infusion of interleukin 1 rapidly decreases peripheral cellular immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6398–6402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundar S. K., Cierpial M. A., Kilts C., Ritchie J. C., Weiss J. M. Brain IL-1-induced immunosuppression occurs through activation of both pituitary-adrenal axis and sympathetic nervous system by corticotropin-releasing factor. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3701–3706. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03701.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tracey D. E., Mitchell W. M., De Souza E. B. Interleukin-1 receptors in mouse brain: characterization and neuronal localization. Endocrinology. 1990 Dec;127(6):3070–3078. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-6-3070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler I., Borbély A. A., Schwyzer M., Fontana A. Interleukin-1 derived from astrocytes enhances slow wave activity in sleep EEG of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 3;104(1-2):191–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verges B., Chavanet P., Desgres J., Vaillant G., Waldner A., Brun J. M., Putelat R. Adrenal function in HIV infected patients. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Nov;121(5):633–637. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1210633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Corcoran M. L., Pyle S. W., Arthur L. O., Harel-Bellan A., Farrar W. L. Human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein (gp120) induction of monocyte arachidonic acid metabolites and interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):621–625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. M., Simson P. G., Hoffman L. J., Ambrose M. J., Cooper S., Webster A. Infusion of adrenergic receptor agonists and antagonists into the locus coeruleus and ventricular system of the brain. Effects on swim-motivated and spontaneous motor activity. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Apr;25(4):367–384. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. M., Sundar S. K., Cierpial M. A., Ritchie J. C. Effects of interleukin-1 infused into brain are antagonized by alpha-MSH in a dose-dependent manner. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 3;192(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



