Abstract
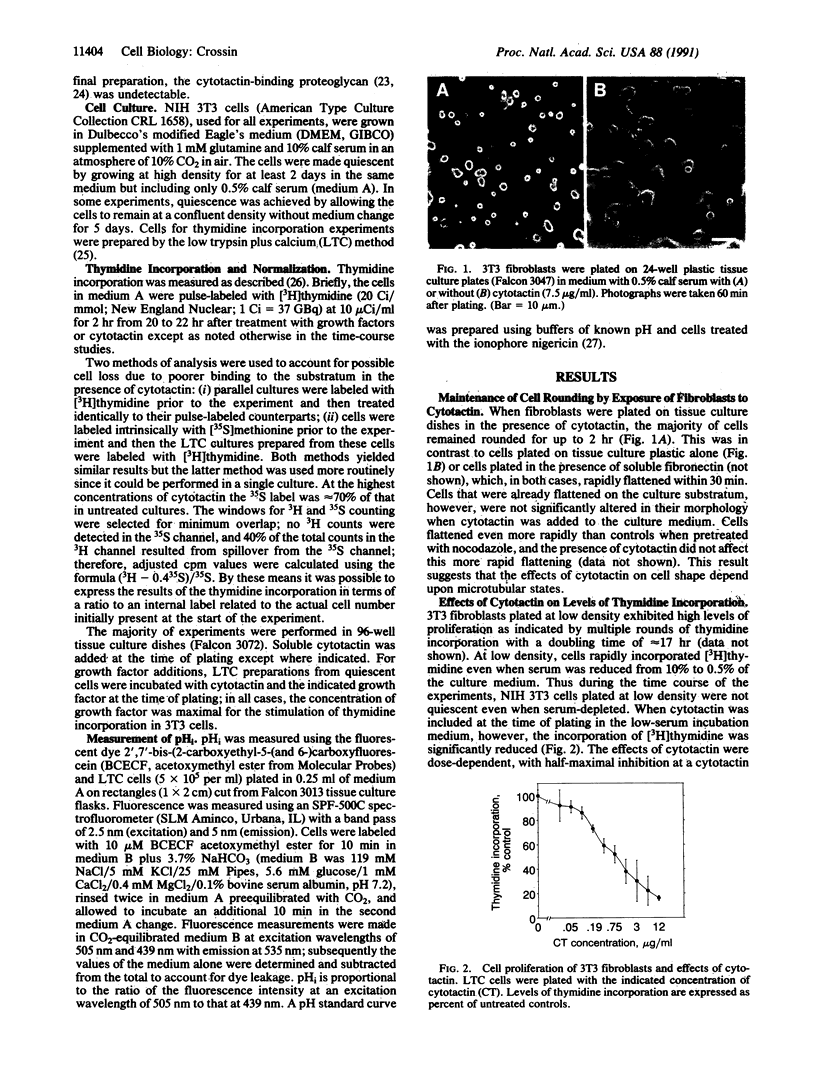
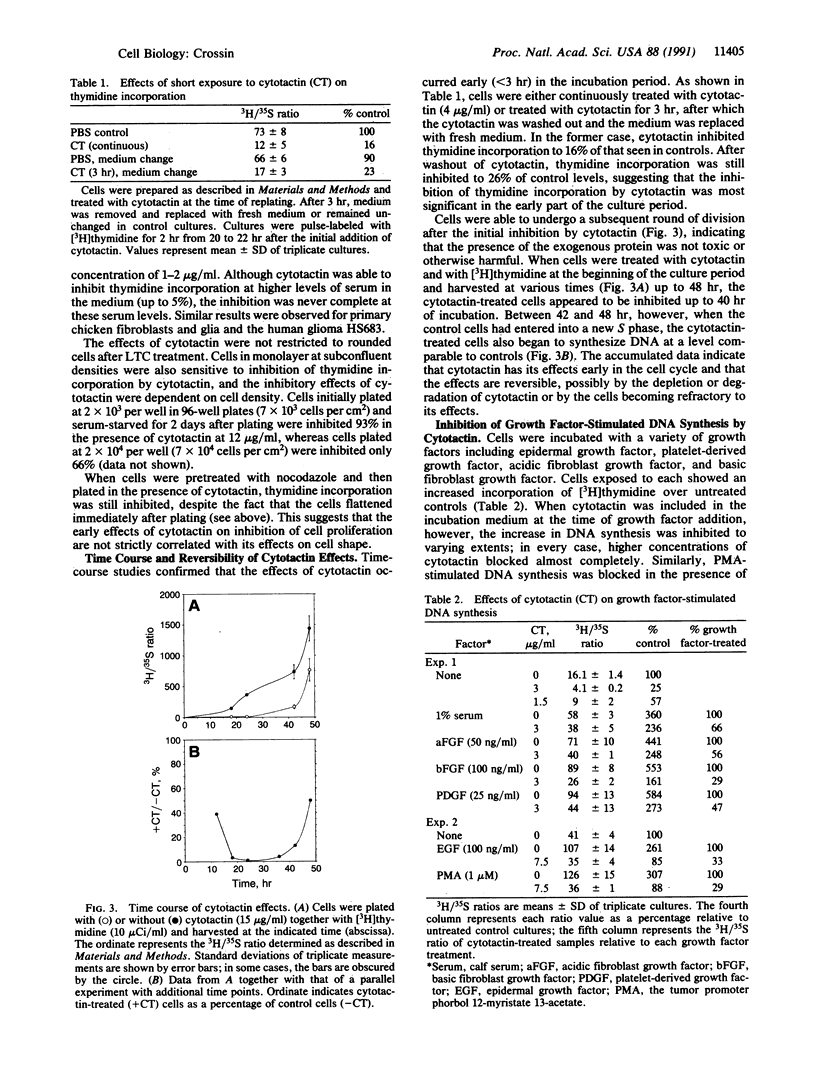
Cytotactin is an extracellular matrix protein that is dynamically and transiently expressed in a place-dependent fashion during development by glial cells, fibroblasts, and several other cell types. In the present study, the effects of cytotactin on cell proliferation were examined in fibroblastic cells in culture. NIH 3T3 mouse cells plated on tissue culture substrata in the presence of soluble cytotactin remained rounded for longer periods than untreated control cells, similar to their response to cytotactin-coated substrates. These rounding effects could be prevented by pretreatment of the cells with nocodazole, a microtubule-disrupting agent. Cytotactin inhibited the proliferation of fibroblasts in culture in a dose- and time-dependent manner, and this inhibition occurred even after nocodazole treatment. In addition, the presence of cytotactin inhibited proliferation stimulated by growth factors or tumor promoter. These effects on cell growth were accompanied by an early inhibition of the intracellular alkalinization that normally occurs upon mitogenic stimulation by a number of growth-promoting agents. Together these observations suggest that cytotactin is an endogenous cell surface modulatory protein and provide a possible mechanism whereby cytotactin may contribute to pattern formation during development, regeneration, tumorigenesis, and wound healing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash J. F., Vogt P. K., Singer S. J. Reversion from transformed to normal phenotype by inhibition of protein synthesis in rat kidney cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3603–3607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubin J. E., Carlsen S. A., Ling V. Colchicine permeation is required for inhibition of concanavalin A capping in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4516–4520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon M. A., Ruoslahti E. Tenascin mediates cell attachment through an RGD-dependent receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):1149–1155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenbury R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Distinct calcium-independent and calcium-dependent adhesion systems of chicken embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):387–391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Kalla P., Pearson C. A., Beck K., Chiquet M. Tenascin interferes with fibronectin action. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Mackie E. J., Pearson C. A., Sakakura T. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein involved in tissue interactions during fetal development and oncogenesis. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosson P., de Curtis I., Pouysségur J., Griffiths G., Davoust J. Low cytoplasmic pH inhibits endocytosis and transport from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):377–387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Carney D. H. Evidence that microtubule depolymerization early in the cell cycle is sufficient to initiate DNA synthesis. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Hoffman S., Grumet M., Thiery J. P., Edelman G. M. Site-restricted expression of cytotactin during development of the chicken embryo. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1917–1930. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Hoffman S., Tan S. S., Edelman G. M. Cytotactin and its proteoglycan ligand mark structural and functional boundaries in somatosensory cortex of the early postnatal mouse. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Prieto A. L., Hoffman S., Jones F. S., Friedlander D. R. Expression of adhesion molecules and the establishment of boundaries during embryonic and neural development. Exp Neurol. 1990 Jul;109(1):6–18. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(05)80004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I. Temperature-sensitive changes in surface modulating assemblies of fibroblasts transformed by mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2047–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epperlein H. H., Halfter W., Tucker R. P. The distribution of fibronectin and tenascin along migratory pathways of the neural crest in the trunk of amphibian embryos. Development. 1988 Aug;103(4):743–756. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., Bourdon M. A. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein prominent in specialized embryonic tissues and tumors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:71–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faissner A., Kruse J. J1/tenascin is a repulsive substrate for central nervous system neurons. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander D. R., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Functional mapping of cytotactin: proteolytic fragments active in cell-substrate adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2329–2340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk S. E., Sage E. H. The Ca2(+)-binding glycoprotein SPARC modulates cell cycle progression in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2648–2652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter W., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Tucker R. P. The effect of tenascin and embryonic basal lamina on the behavior and morphology of neural crest cells in vitro. Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;132(1):14–25. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Molecular forms, binding functions, and developmental expression patterns of cytotactin and cytotactin-binding proteoglycan, an interactive pair of extracellular matrix molecules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):519–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. A proteoglycan with HNK-1 antigenic determinants is a neuron-associated ligand for cytotactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Prusty D., Frangioni J. V., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lechene C., Schwartz M. A. Control of intracellular pH and growth by fibronectin in capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1803–1811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Crossin K. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Identification and characterization of the promoter for the cytotactin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochter A., Vaughan L., Kaplony A., Prochiantz A., Schachner M., Faissner A. J1/tenascin in substrate-bound and soluble form displays contrary effects on neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1159–1171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. J., Tucker R. P., Halfter W., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Epperlein H. H. The distribution of tenascin coincides with pathways of neural crest cell migration. Development. 1988 Jan;102(1):237–250. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.1.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis L. B., Rozovskaja I. A., Cragoe E. Intracellular pH and cell adhesion to solid substrate. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):449–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., D'Eustachio P., Edelman G. M. Role of surface modulating assemblies in growth control of normal and transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):666–670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H. Effects of growth factors on intracellular pH regulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:363–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parton R. G., Dotti C. G., Bacallao R., Kurtz I., Simons K., Prydz K. pH-induced microtubule-dependent redistribution of late endosomes in neuronal and epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):261–274. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto A. L., Jones F. S., Cunningham B. A., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Localization during development of alternatively spliced forms of cytotactin mRNA by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):685–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. F., Shi D. L., Chiquet M., Boucaut J. C. Exogenous tenascin inhibits mesodermal cell migration during amphibian gastrulation. Dev Biol. 1990 Feb;137(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90256-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Counillon L., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiporter, glycoprotein of 110 kD. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.2154036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Kimura H. Substratum-growth factor collaborations are required for the mitogenic activities of activin and FGF on embryonal carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):841–846. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Both G., Lechene C. Effect of cell spreading on cytoplasmic pH in normal and transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4525–4529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lechene C. P. pH regulation in spread cells and round cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1327–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Lechene C., Ingber D. E. Insoluble fibronectin activates the Na/H antiporter by clustering and immobilizing integrin alpha 5 beta 1, independent of cell shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7849–7853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Crossin K. L., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Asymmetric expression in somites of cytotactin and its proteoglycan ligand is correlated with neural crest cell distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7977–7981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrle B., Chiquet M. Tenascin is accumulated along developing peripheral nerves and allows neurite outgrowth in vitro. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):401–415. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. The effects of concanavalin A on the mobility of lymphocyte surface receptors. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Sep;81(1):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



