Abstract
To investigate tolerance to extrathymic self molecules, we produced two groups of transgenic mice: one expressed the major histocompatibility complex molecule H-2Kb in pancreatic beta cells, and the other expressed rearranged T-cell receptor genes encoding an anti-H-2Kb receptor. The transgenic T-cell receptor genes were shown to confer the correct specificity and to be expressed appropriately. T cells bearing this receptor were activated by H-2Kb in vitro and in vivo, and they underwent negative selection in mice expressing H-2Kb in the thymus. To determine the fate and function of these anti-H-2Kb T cells in mice expressing H-2Kb exclusively in the periphery, the two groups of transgenic mice were mated to produce double transgenic offspring. In these, transgene-expressing T cells were present in both thymus and periphery. Persisting T cells had not down-regulated either their antigen-specific receptors or their CD8 molecules. Despite the persistence of large numbers of potentially reactive T cells, the mice were tolerant of H-2Kb in that they could not reject H-2Kb-bearing skin grafts, although they did reject third-party grafts. The results show that peripheral T-cell tolerance, unlike that imposed in the thymus, does not involve deletion of T cells. The existence of T cells bearing receptors specific for self components raises the possibility that aberrant activation of such cells may lead to the development of autoimmune disease.
Full text
PDF
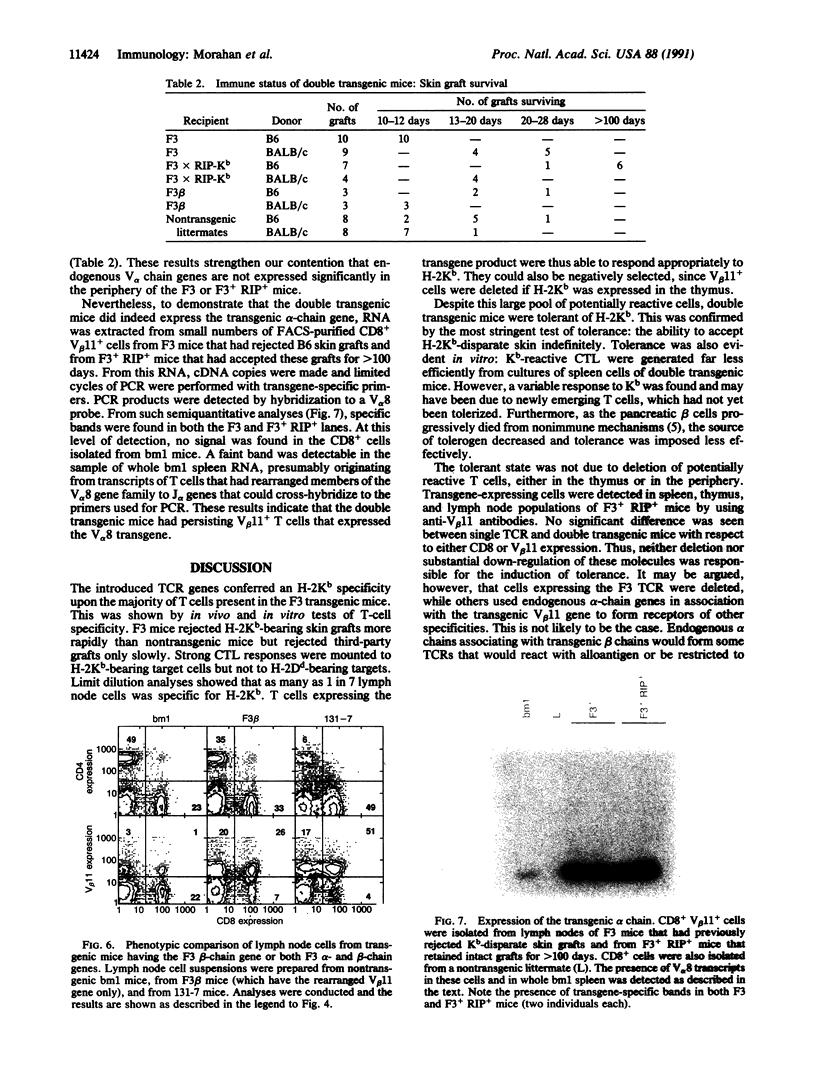

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J., Campbell I. L., Morahan G., Mandel T. E., Harrison L. C., Miller J. F. Diabetes in transgenic mice resulting from over-expression of class I histocompatibility molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):529–533. doi: 10.1038/333529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blüthmann H., Kisielow P., Uematsu Y., Malissen M., Krimpenfort P., Berns A., von Boehmer H., Steinmetz M. T-cell-specific deletion of T-cell receptor transgenes allows functional rearrangement of endogenous alpha- and beta-genes. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):156–159. doi: 10.1038/334156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou H. S., Behlke M. A., Godambe S. A., Russell J. H., Brooks C. G., Loh D. Y. T cell receptor genes in an alloreactive CTL clone: implications for rearrangement and germline diversity of variable gene segments. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2149–2155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Roehm N., Marrack P. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90568-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisielow P., Blüthmann H., Staerz U. D., Steinmetz M., von Boehmer H. Tolerance in T-cell-receptor transgenic mice involves deletion of nonmature CD4+8+ thymocytes. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):742–746. doi: 10.1038/333742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo D., Burkly L. C., Widera G., Cowing C., Flavell R. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Diabetes and tolerance in transgenic mice expressing class II MHC molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Morahan G., Allison J. Extrathymic acquisition of tolerance by T lymphocytes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 2):807–813. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Daitch L., Rath S., Selsing E. Tissue-specific expression of allogeneic class II MHC molecules induces neither tissue rejection nor clonal inactivation of alloreactive T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan G., Allison J., Miller J. F. Tolerance of class I histocompatibility antigens expressed extrathymically. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):622–624. doi: 10.1038/339622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan G., Brennan F. E., Bhathal P. S., Allison J., Cox K. O., Miller J. F. Expression in transgenic mice of class I histocompatibility antigens controlled by the metallothionein promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. M., Weaver C. T., Elish M., Allen P. M., Loh D. Y. Peripheral tolerance to allogeneic class II histocompatibility antigens expressed in transgenic mice: evidence against a clonal-deletion mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10034–10038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi P. S., Oehen S., Buerki K., Pircher H., Ohashi C. T., Odermatt B., Malissen B., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Ablation of "tolerance" and induction of diabetes by virus infection in viral antigen transgenic mice. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90164-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pircher H., Mak T. W., Lang R., Ballhausen W., Rüedi E., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M., Bürki K. T cell tolerance to Mlsa encoded antigens in T cell receptor V beta 8.1 chain transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):719–727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Meleedy-Rey P., McCulley D. E., Sha W. C., Nelson C. A., Loh D. Y. Evidence for CD8-independent T cell maturation in transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3318–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Liggitt D., Pitts S. L., Hansen S. E., Stewart T. A. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90414-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönrich G., Kalinke U., Momburg F., Malissen M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Malissen B., Hämmerling G. J., Arnold B. Down-regulation of T cell receptors on self-reactive T cells as a novel mechanism for extrathymic tolerance induction. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90163-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha W. C., Nelson C. A., Newberry R. D., Kranz D. M., Russell J. H., Loh D. Y. Positive and negative selection of an antigen receptor on T cells in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):73–76. doi: 10.1038/336073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha W. C., Nelson C. A., Newberry R. D., Kranz D. M., Russell J. H., Loh D. Y. Selective expression of an antigen receptor on CD8-bearing T lymphocytes in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):271–274. doi: 10.1038/335271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonari K. A rat antibody against a structure functionally related to the mouse T-cell receptor/T3 complex. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(6):455–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00355379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonari K., Lovering E. T-cell receptor-specific monoclonal antibodies against a V beta 11-positive mouse T-cell clone. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(6):445–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00355377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. L., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Amplification and direct nucleotide sequencing of cDNA from the lysate of low numbers of diploid human cells. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H. Developmental biology of T cells in T cell-receptor transgenic mice. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:531–556. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]