Abstract
We report on two consanguineous sibs affected with severe intellectual disability and autistic features due to a homozygous missense variant of GRIN1. Massive parallel sequencing was performed using a gene panel including 450 genes related to intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders. We found a homozygous missense variation of GRIN1 (c.679G>C; p.(Asp227His)) in the two affected sibs, which was inherited from both unaffected heterozygous parents. Heterozygous variants of GRIN1, encoding the GluN1 subunit of the NMDA receptor, have been reported in patients with neurodevelopmental disorders including epileptic encephalopathy, severe intellectual disability, and movement disorders. The p.(Asp227His) variant is located in the same aminoterminal protein domain as the recently published p.(Arg217Trp), which was found at the homozygous state in two patients with a similar phenotype of severe intellectual disability and autistic features but without epilepsy. In silico predictions were consistent with a deleterious effect. The present findings further expand the clinical spectrum of GRIN1 variants and support the existence of hypomorphic variants causing severe neurodevelopmental impairment with autosomal recessive inheritance.
Introduction
GRIN1 (MIM *138249) encodes the GluN1 subunit of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors, members of the glutamate receptor channel superfamily, which are heteromeric protein complexes with multiple subunits arranged to form a ligand-gated ion channel. These subunits have a key role in the plasticity of synapses, which underlies memory and learning.1
De novo heterozygous variants of GRIN1 were first identified by targeted Sanger sequencing in two patients with intellectual disability (ID) with or without epilepsy (MIM #614254).2 Recent advances in next-generation sequencing have shown that GRIN1 de novo heterozygous variants represent a recurrent cause of epileptic encephalopathy with early onset.3, 4 A recent paper provided a better delineation of the GRIN1 phenotypic spectrum that includes severe ID with absent speech, muscular hypotonia, hyperkinetic movements, oculogyric crises, hand stereotypies, cortical blindness, and epilepsy.5 This article also reported for the first time two homozygous GRIN1 variants in families with severe neurodevelopmental phenotypes.
In the present paper we report a second family including two affected sibs with a homozygous missense variant, thus expanding the phenotype–genotype correlations related to GRIN1 variants.
Patients and methods
Patients
The patients were born to first-cousin parents from Morocco (Figure 1a). Parents provided informed signed consent for genetic studies on blood samples from them and their children.
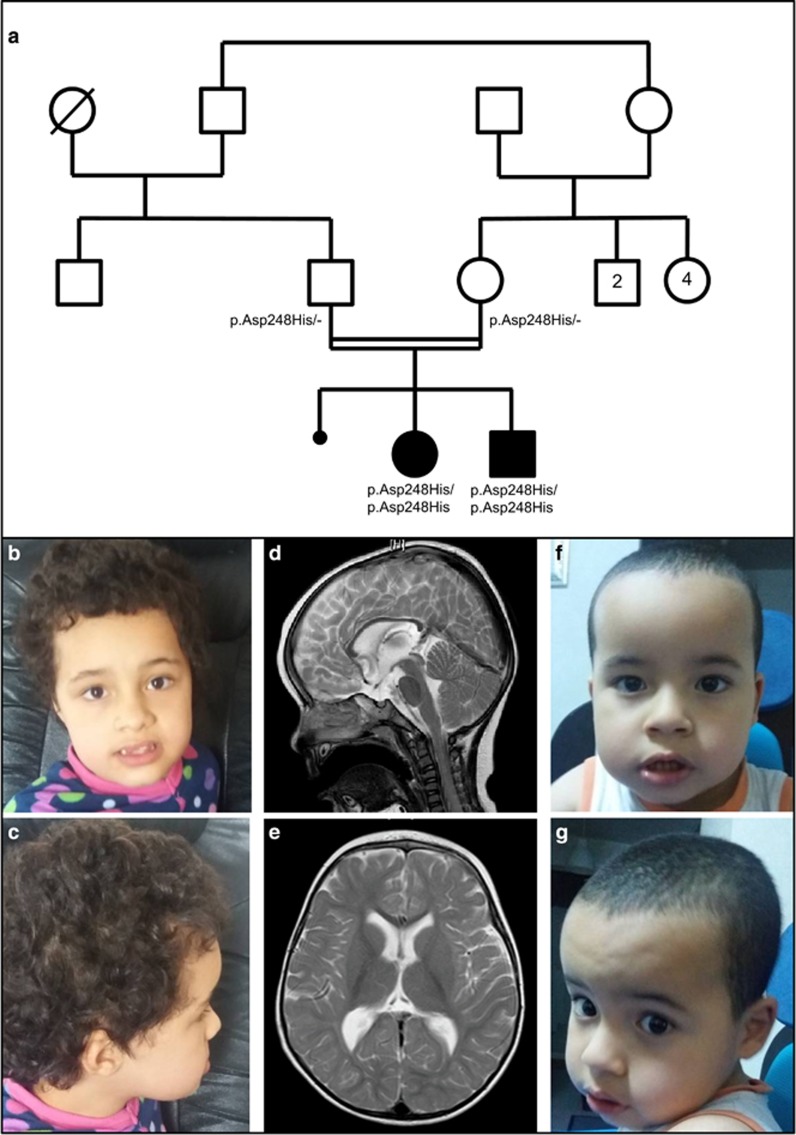
Figure 1.
(a) Pedigree of the family – normal allele. (b–e) Patient 1. Facial features at 7 years and 8 months of age (b and c) showing frontal bossing and mild midface hypoplasia. Brain MRI (T2-weighed images; (d): sagittal; (e): axial), performed at 18 months of age, showed no specific abnormalities: note mild brain atrophy and thin corpus callosum. (f and g) Patient 2 (at 3 years and 9 months of age) showing mild frontal bossing and no specific dysmorphic facial features.
Gene panel
Massive parallel sequencing was performed in patient 1 with a gene panel including 450 genes related to monogenic forms of ID and autistic spectrum disorders (gene list is available upon request). After sonication (Covaris, Woburn, MA, USA), library preparation was performed with Agilent SureSelectXT following manufacturer's recommendations (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). 2x75bp paired-end sequencing was performed on a NextSeq500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Genomic alignment against the hg19/GRCh37 assembly and variant calling were, respectively, done with BWA-MEM v.0.7.12 and GATK HaplotypeCaller v.3.4 (Broad Institute, Boston, MA, USA). Mean depth of coverage was 320 × with 98.5% of the target bases above 40 ×. Only highly confident variants were kept for analysis (total depth >9; alternative allele depth >4; no strand bias; mosaicism >10%). Rare variants were considered as having a frequency <1% in public databases (ExAC, EVS, and 1000G). Sanger sequencing was used to confirm variations that would possibly affect protein function.
Clinical description
The first pregnancy of the couple ended in a miscarriage.
Patient 1
This girl was the first sib born at term after an uneventful pregnancy; delivery was normal. At birth, weight was 3470 g (50th centile), length was 50.5 cm (50th centile), and occipital frontal circumference (OFC) was 33.5 cm (10–25th centile). Hypotonia, developmental delay, and strabismus were noted since the first months of life.
At the age of 23 months, she started sitting unsupported. Clinical examination showed frontal bossing, mild midface hypoplasia (Figures 1b and c), global hypotonia with normal reflexes, and poor eye contact. Standing with support was achieved at the age of 3.5 years. EEG was normal at 16 months.
At the age of 5.5 years, OFC was 50 cm (25–50th centile), height was 104.5 cm (25th centile), and weight was 17 kg (25th centile). Global hypotonia, involuntary stereotypic movements, poor eye contact and social interactions, normal reflexes, and loose joints were noted. Speech was absent. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), performed at 18 months of age, showed mild cerebral atrophy and thin corpus callosum (Figures 1d and e). Brain magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) was normal. Auditory evoked potential, fundus oculi examination, electroretinogram, and electromyography were normal. Heart and abdominal ultrasounds scans (USS) were normal. Genetic and metabolic assessment was normal, including standard karyotype, array-CGH; MECP2 screening by sequencing and MLPA (multiple ligation probe amplification); methylation analysis for Prader–Willi syndrome, search of homozygous SMN1 deletion by QMPSF (quantitative multiplex PCR of short fluorescent fragments) for spinal muscular atrophy, Southern blot for Steinert's disease and Fragile X syndrome; liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for plasma and urine amino acids, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for urine organic acids and plasma very-long-chain fatty acids; screening for congenital disorders of glycosylation (Western blot). Blood levels of lactate, pyruvate (enzymatic spectrophotometry), and creatine kinase (CK; measured according to the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry) were also normal.
Patient 2
This boy was the second sib, born at 36 weeks of gestation after uneventful pregnancy and delivery. At birth, weight was 2550 g (25th centile), length was 47 cm (25–50th centile), and OFC was 32 cm (10–25th centile). Developmental delay and hypotonia were noted. At the age of 18 months, clinical examination showed frontal bossing (Figures 1f and g) and left transverse palmar crease. He could not sit unsupported and had hypotonia and stereotypic movements (he used to look frequently at his hands and feet).
At the age of 3 years, OFC was 50 cm (50th centile), height was 95.5 cm (50th centile), and weight was 14.8 kg (75th centile). He was able to sit with support, but not to stand. Hypotonia, normal reflexes, and hand stereotypic movements were noted. Eye contact was present. No seizures were reported. Speech was absent. Brain MRI and MRS, heart and abdominal USS were normal. CK plasma level was normal as were ammonia, LC-MS/MS for plasma amino acids, GC-MS for plasma very-long-chain fatty acids and urine organic acids. Urine mucopolysaccharides (electrophoresis), oligosaccharides (thin-layer chromatography), sialic acid (MS/MS), urinary screening for adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency (analysis of succinyl-AICA riboside by thin-layer chromatography) and plasma and urinary screening for creatine metabolism deficiencies (MS/MS) were normal.
Results
Fourteen rare variants were identified including only one homozygous missense transversion of GRIN1 in both siblings (hg19 chr9:g.140051128G>C). According to the longest isoform (NM_001185090.1) the nomenclature of this variant is c.742G>C and the expected protein change is (NP_001172019.1) p.(Asp248His). In this paper, however, we will rather use the NM_007327.3 isoform to allow comparison with previous reports (NM_007327.3 c.679G>C and NP_015566 p.Asp227His). It was not previously reported (PubMed, HGMD) and was absent from public databases of control individuals (Exome Variant Server, 1000 genomes and ExAC) in patients. In silico prediction tools for pathogenicity were in favor of a deleterious effect (Grantham=81, SIFT=1, and Polyphen-2=1). Sanger sequencing confirmed the homozygous variant in both affected siblings and showed that both unaffected parents were heterozygous carriers (Figure 1a). The variant was submitted to the specific GRIN1 LOVD database (variant ID 0000129232).
Discussion
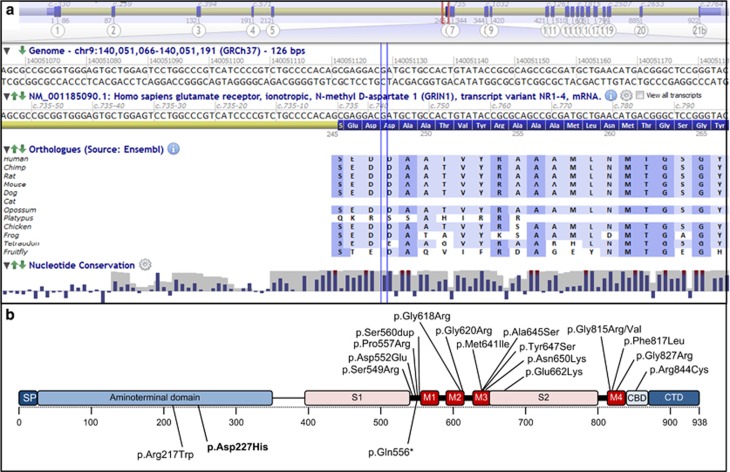
The c.679G>C GRIN1 transversion was the only homozygous rare variant found in the two affected children and at the heterozygous state in the parents, who were healthy. The variant affects a rather conserved asparagine residue in the Zn2+ binding site, located within the aminoterminal domain of the gene and is predicted to be deleterious by SIFT and Polyphen-2 (Figure 2a). Our patients have phenotypic similarities with two other sibs recently reported, who had a different homozygous missense variant c.649C>T (p.(Arg217Trp)), located nearby within the aminoterminal domain of GRIN1 (Figure 2b).5 Patients from the two families share psychomotor delay, hypotonia, and profound ID, as well as autistic features such as hand stereotypies (Table 1). Interestingly, they did not experience seizures, which is in strong contrast with patients carrying de novo heterozygous missense variants, who frequently had early onset drug-resistant epilepsy (70%, n=16/23). In contrast to the two homozygous missense variants, those heterozygous variants cluster in and around the transmembrane domains, which is highly conserved among different species. In vitro functional experiments showed that most de novo heterozygous variants lead to a dominant negative effect, whereas the c.649C>T variant showed impaired activation due to tonic inhibition of GRIN1Arg217Trp-GRIN2A receptors.5
Figure 2.
(a) Local protein sequence alignments among several GRIN1 orthologs. Vertical blue lines indicate Asp248. (b) Distribution of the different variants reported in patients along the protein structure. Heterozygous missense variants are displayed on the upper part, whereas the three variants reported at the homozygous state are shown on the lower part. The variant reported in the present study is in bold. The reference cDNA and protein sequences used for numbering are NM_007327.3 and NP_015566.1, respectively. Modified from Lemke et al.5 CBD, calmodulin-binding domain; CTD, C-terminal domain; M1-4, transmembrane domains; S1-2, ligand binding sites; SP, signal peptide.
Table 1. Clinical data of the patients with a homozygous GRIN1 mutation from the present study and from Lemke et al. 5 .
| Present family | Family 1 [5] | Family 2 [5] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant | c.679G>C p.(Asp227His) | c.679G>C p.(Asp227His) | c.742C>T p.(Arg217Trp) | c.649C>T p.(Arg217Trp) | c.1666C>T p.(Gln556*) | c.1666C>T p.(Gln556*) | c.1666C>T p.(Gln556*) |
| Sex | F | M | M | M | M | F | F |
| Age at inclusion | 5.5y | 3y | 13.5y | 12y | † 5mo | † 12d | † 5d |
| Seizure onset | No seizures | No seizures | No seizures | No seizures | 1st d | 1st d | 1st d |
| Seizure type at onset | None | None | None | None | Myoclonic, clonic with desaturation, continuous | Clonic, continuous | Clonic, continuous |
| Seizure outcome | None | None | None | None | Deceased from status epilepticus | Deceased due to ongoing seizures and desaturation | Deceased due to ongoing seizures |
| EEG at onset | Normal | ND | 6 months of age: spikes during sleep | 10 months: diffuse spikes and waves during sleep | Burst suppression | Burst suppression | Burst suppression |
| Development | Severe ID. No language or walking | Severe ID. No language or walking | Severe ID. No language or walking | Severe ID. No language or walking | No development until death | † 12d | † 5d |
| Behavior | Autistic, stereotypic movements of the midline. | Autistic, stereotypic movements of the midline | Autistic agitated, hyperventilation, outbursts of laughing, stereotypic movements of the midline. Self-injury | Autistic, stereotypic movements of the midline. Agitated | — | — | — |
| Neurological examination | Hypotonia | Hypotonia | Axial hypotonia, tetraspastic, distal amyotrophy, dystonic features of knees and ankles | Axial hypotonia, tetraspastic distal amyotrophy | Hypotonia at birth, later hypertonia | Hypertonia, opisthotonic posturing | No formal exam due to continuous convulsions |
| Vision | Normal ERG | ND | Macular atrophy at ERG with normal visually evoked potential | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Additional features | Frontal bossing, mild midface hypoplasia | Frontal bossing, left transverse palmar crease | Constipation | Constipation, gynecomastia, macroglossia, sleep disturbances | Hyperlaxity thumbs, gap between first and second toe | — | — |
| Brain MRI | Mild atrophy, thin corpus callosum (18 m) | Normal (1y) | Normal (at 6 m) | Normal (at 10 m) | 1 s month: possible punctiform hemorrhage in thalami | TFE (no MRI): two small periventricular cysts | Post-mortem MRI: microcephaly, delayed formation of sulci and delayed myelinisation |
Abbreviations: d, day; EEG, electro encephalogram; ERG, electroretinogram, F, female; ID, intellectual deficiency; M, male; mo, month; ND, not done; TFE, transfontanellar echography; y, years.The reference cDNA and protein sequences used for numbering are NM_007327.3 and NP_015566.1, respectively. †Age at death.
In addition, another family was reported, including three sibs affected with neonatal epileptic encephalopathy with intractable seizures leading to death between 5 days and 5 months. The affected sibs had a homozygous truncating variant of GRIN1 c.1666C>T (p.(Gln556*)), which was found at the heterozygous state in the unaffected parents. This suggests that heterozygous truncating variants of GRIN1 apparently do not result in a neurological phenotype.
Variants in the Zn2+ binding domain appear to be rare in genes encoding NMDAR subunits. The heterozygous missense variant p.(Ala243Val) in GRIN2A has been shown to significantly reduce high-affinity Zn2+ inhibition, mediating a gain-of-function.6 For the c.679G>C variant, which is located in GRIN1 in a position similar to p.(Ala243Val) in GRIN2A, we could rather expect a loss-of-function mechanism. Functional studies, however, would be useful to answer this question.
The fact that the phenotypic expression of deleterious variants in a given gene may be related to different modes of transmission has been reported for several genes. LMNA is probably the most famous example. This gene is associated with about 15 different diseases including Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1B and Huntchinson–Gilford progeria that mostly follow an autosomal-dominant mode of inheritance, and Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 2B1 that is an autosomal recessive disorder.7 In the field of epilepsy, such a situation has also been observed for several genes. Some variants in POLG are found in families with autosomal-dominant progressive external ophtalmoplegia, whereas other variants cause a range of autosomal-recessive conditions including Alpers syndrome, mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy, or sensory ataxic neuropathy, dysarthria, and ophtalmoparesis syndrome.8 Recently, some missense variants of RELN have been shown to cause autosomal-dominant lateral temporal epilepsy, whereas other variants were previously found in patients affected with autosomal-recessive lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia.9, 10 Homozygous or biallelic variants have not been reported so far for genes encoding other subunits of NMDA receptors, such as GRIN2A and GRIN2B, whose heterozygous variants cause various ranges of neurodevelopmental disorders with epilepsy.11, 12, 13, 14
The present family together with previous reports suggests that heterozygous variants located in the aminoterminal domain may have a hypomorphic effect, whereas heterozygous variants located in the transmembrane region may rather lead to a gain-of-function.
In conclusion, the c.679G>C (p.Asp227His) transversion is likely to be a hypomorphic variant, which is pathogenic at the homozygous state, whereas the functionality of one normal allele is sufficient to avoid clinical expression in heterozygous carriers.
Acknowledgments
We thank the NGS platform of Lyon University Hospital and the bioinformaticians (Claire Bardel and Pierre Antoine Rollat-Farnier), as well as Raphaelle Lamy for technical assistance.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Paoletti P, Bellone C, Zhou Q: NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2013; 14: 383–400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan FF, Gauthier J, Araki Y et al: Excess of de novo deleterious mutations in genes associated with glutamatergic systems in nonsyndromic intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 306–316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen AS, Berkovic SF, Cossette P et al: De novo mutations in epileptic encephalopathies. Nature 2013; 501: 217–221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohba C, Shiina M, Tohyama J et al: GRIN1 mutations cause encephalopathy with infantile-onset epilepsy, and hyperkinetic and stereotyped movement disorders. Epilepsia 2015; 56: 841–848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke J, Geider K, Helbig KL et al: Delineating the GRIN1 phenotypic spectrum–a distinct genetic NMDA receptor encephalopathy. Neurology 2016; 86: 2171–2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endele S, Rosenberger G, Geider K et al: Mutations in GRIN2A and GRIN2B encoding regulatory subunits of NMDA receptors cause variable neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 1021–1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand AT, Chikhaoui K, Yaou RB, Bonne G: Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in laminopathies. Biochem Soc Trans 2011; 39: 1687–1692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf JD, Copeland WC: Mitochondrial DNA replication and disease: insights from DNA polymerase γ mutations. Cell Mol Life Sci 2011; 68: 219–233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo E, Fanciulli M, Serioli E et al: Heterozygous reelin mutations cause autosomal-dominant lateral temporal epilepsy. Am J Hum Genet 2015; 96: 992–1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong SE, Shugart YY, Huang DT et al: Autosomal recessive lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia is associated with human RELN mutations. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 93–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesca G, Rudolf G, Bruneau N et al: GRIN2A mutations in acquired epileptic aphasia and related childhood focal epilepsies and encephalopathies with speech and language dysfunction. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 1061–1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke JR, Lal D, Reinthaler EM et al: Mutations in GRIN2A cause idiopathic focal epilepsy with rolandic spikes. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 1067–10672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvill GL, Regan BM, Yendle SC et al: GRIN2A mutations cause epilepsy-aphasia spectrum disorders. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 1073–1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke JR, Hendrickx R, Geider K et al: GRIN2B mutations in West syndrome and intellectual disability with focal epilepsy. Ann Neurol 2014; 75: 147–154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]